Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Concept Maps
Enviado por
Norsaniah IsmailDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Concept Maps
Enviado por
Norsaniah IsmailDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
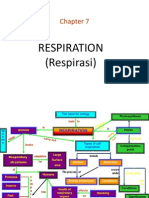
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 1 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
1
at
carbon dioxide diffuses
oxygen diffuses
oxygen
combines
with
Structure
Human Respiratory
System
consists of
involves
movement
of
Oxygen
Transport
Blood
capillaries
Parts
Nasal cavity
Trachea
Bronchi and
bronchioles
Lungs
Ribs
Diaphragm
Intercostal
muscles
Respiratory
system
diseases
Bronchitis
Emphysema
Lung cancer
Asthma
Breathing
Inhalation
Nicotine
Haze
Tar
Diaphragm Ribs
Haemoglobin
Exhalation
Gaseous
exchange
Provide large
surface area
Thin wall
Many blood
capillaries
Cigarette
smoke
Factory
smoke
Vehicle
exhaust
Sulphur
dioxide
Carbon
monoxide
Alveoli
to form
decomposes to
release
diffuses
into
characteristics for efficient
gaseous exchange
Moist wall
Haemoglobin
Oxyhaemoglobin
Cells
Oxygen
carbon
dioxide
diffuses
such
as
contains
contains
contains
cause
Importance of a
Healthy Respiratory System
Harmful
substances
RESPIRATION
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 2 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
2
consists of
types
types
consists of
called
called
types
Humans
Heart Blood
vessels
Artery
Vein
Capillary
Plasma
A
Blood
cells
Red
blood
cell
TRANSPORT SYSTEM
Blood circulatory
system
Universal donor
Universal recipient
B O AB
White
blood
cell
Platelet
Blood Blood groups
consists of
occurs
mainly
through
rate affected by
size controlled
by
such as
Xylem Phloem
Carries synthesised
food substances
from leaves to all
parts of the plant
Carries water
and dissolved
minerals from
roots to leaves
Transpiration
lncreases with
temperature
Increases with
light intensity
Increases with
air movement
Decreases with
humidity
Two guard
cells
Stoma
Factors
Plants
lose water
through
Plant vascular system
Temperature Light intensity Air movement Humidity
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 3 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
3
consists of
consists of
made up of
EXCRETION
Excretory system
Kidneys
(one pair)
Excretory
products
Water
Mineral salts
Urea (small
amount)
Humans
Skin
Excretory
products
Carbon
dioxide
Water
Latex
Tannin
Resin
Gum
Volatile oils
Quinine
Nicotine
Cocaine
Excretory
products
Water
Urea
Mineral salts
Lungs
Plants
Cortex
Ureters
(one pair)
Urinary
bladder
Urethra
Oxygen Water Carbon
dioxide
Pelvis
Medulla
Urinary system
methods of excretion
excretory products
examples
excretory products
Diffusion out
of stomata
Depositing in plant
parts and shedding of
parts in some cases
Complex waste
products
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 4 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
4
carried out by
divided into
have
called called
contains
consists of
leads to
process of
transfer to stigma
produces
REPRODUCTION
Humans
Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction
Male reproductive
system
Female reproductive
system
Male reproductive
part
Female
reproductive part
Sperm
Zygote
Embryo
Baby
Ovum
produces produces
to form
Fertilisation
Flower
Filament
Stamen
Anther
Sepals
contains
produces
Stigma
Style
Ovary
Ovule
development of
Seed
Testa
(seed coat)
consists
of
Fruit
consists
of
Cotyledon
Radicle
Plumule
Suitable
temperature
Air
Water
Pollination
Foetus
Pistil
Male gamete Female gamete
Pollen
Other parts
types
carried out
by most
Vegetative
reproduction
Budding
Binary
fission
Spore
formation
Regeneration
Embryo
Petals
Fertilisation
Conditions
for
germination
Flowering plants
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 5 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
5
GROWTH
defined as
measured using
age
divided into
boys girls
Increase in size and
change in shape and
function of an organism
Comparison between
boys and girls
Human Growth Pattern
Human growth curve
Height
Slow Most rapid Rapid Negative
Weight
Childhood Infancy Adulthood Adolescence Old age
growth
rate
growth
rate
growth
rate
growth
rate
Girls faster
than boys
17 years 18 years
Boys faster
than girls
growth
rate
growth
rate
growth
rate
growth
rate
12 14
years
0 11
years
About the
same
Minimal or
zero
Age at
which
growth
stops
14 18
years
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 6 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
6
Examples
Gold
Silver
Platinum
Graphite
Sulphur
exist as
LAND AND ITS RESOURCES
Elements Compounds Wood Fossil fuels
Natural gas Coal
Examples
Oxides
Sulphides
Carbonates
Silicates Uses
Fuel
Synthetic
materials
Solvent
Metal oxide Metal sulphide
Petroleum
fractions
Uses
Glass
Ceramics
Electronic
chips
Optical
fibres
Examples
Clay
Feldspar
Asbestos
Mica
Jade
Uses
Cement
Tiles
Drying agent
Reduce soil acidity
Examples
Marble
Limestone
Coral
Shells
Egg shells
Examples
Sand
Quartz
Silicon
Oxygen
Silicon
Oxygen
Metals
Metals
Oxygen Sulphur
Non-metals
reacts with metal reacts with metal
Petroleum
Silicates
Silica
include
examples
divided into
contains
such as
heat
add a
little
water
add more water
contain
contain
fractional
distillation
Silicon
compounds
Calcium
compounds
Calcium hydroxide
solution (limewater)
contains
reacts with acid
Salt + water +
carbon dioxide
Calcium
Carbon
Oxygen
Calcium
carbonate
Calcium
oxide
(quicklime)
Calcium
hydroxide
(slaked lime)
Minerals Natural Fuel Resources
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 7 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
7
Static electrical charges Current Magnets
Voltage
Resistance
Electromagnet
Direction of current
Ohms law
Rubbing
certain
substances
together
Like charges
repel each
other
Unlike charges
attract each
other
Positive
charges
Negative
charges
Series
circuit
Parallel
circuit
Magnetic
field
Magnetic field
lines
Closer together
when magnetic
field is
stronger
From north
pole to south
pole
Current flowing
through conductor
Magnetic field
around conductor
Temporary
magnet
V
R =
I
types of
electric
circuits
electrical
quantities
is the
study of
Electrostatics Electricity Magnetism
Electromagnetism
produced
by
flow to
produce
relationship
known as
properties
principle
used in produces
have
can be
represented by
distance
between
lines
direction
direction
depends on
is a
poles depend on
types
ELECTRICITY
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 8 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
8
Diesel
Nuclear
Brown Blue
Hydroelectric
Power station
Transformer station
Switch zone
National Grid Network
Main substation
Step-up Step-down
Branch substations
Mains fuse Electric meter
P = VI
Energy use = Power Time
To prevent current that is too large from flowing in a circuit Fuse
Fuse
3-Pin plug
Socket
To carry current leakage to the earth Earth wire
Thermal
Gas turbine
Mains
switch
Circuit
breaker
Green and
yellow stripes
Live
wire
Neutral
wire
Electrical
appliance
Power
circuit
Earth
wire
Lighting
circuit
Cost of Electrical Energy Usage
Fuse and Earth Wire
Transformers
G
E
N
E
R
A
T
I
O
N
O
F
E
L
E
C
T
R
I
C
I
T
Y
Types of
Generators
Home Wiring
System
Electricity
Transmission
and Distribution
System
used in
contain
live wire
formulae for calculations
function
function
neutral wire
2 types
contains
colour colour colour
for fixing to
connected to
Consumer unit
earth
wire
has
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 9 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
9
Atmosphere
Corona Photosphere
Temperature
Colour
Elliptical Irregular
Milky Way
Brightness Nebula Galaxy
Chromosphere
Prominence
Solar flare
Sunspot
Climate Aurora Satellites
Core
Heat
Size Red giant
Light
Red Blue
White dwarf Supernova
Supergiant
Nuclear
reactions
Neutron
star
Black
hole
Communications
systems
Phenomena
occurring on Suns
surface
Sun Stars
is made up of
location of consists of
produce
determines
coolest hottest
large star super-large star
includes
classified by
include
formed
in death of
a star
millions or billions
form a
classified by
shape into
has effects on Earth
such as
STARS AND GALAXIES
Spiral
small and
medium-sized
stars
large and
super-large
stars
Arah Pendidikan Sdn Bhd 10 Concept Maps Science Form 3
Chapter
10
Rocket
Telescope Space probe Space station
Space shuttle Satellite
Weather Defence
Forestry
Geology
Agriculture
Satellite
Communications Navigation
Scientists, astronomers
and their contributions
technology
related to space
involving
used in
applied in
the field of
SPACE EXPLORATION
Developments in the
Field of Astronomy
Applications of
Technology Related
to Space
Disaster
management
Remote sensing
Developments in
Space Exploration
Você também pode gostar
- GCSE Biology Revision GuideDocumento113 páginasGCSE Biology Revision GuideFair Pisuttisarun50% (2)
- How To Make HeroinDocumento2 páginasHow To Make HeroinRay Binda67% (3)
- The Respiratory System ReviewerDocumento6 páginasThe Respiratory System ReviewerJP LozadaAinda não há avaliações
- Ap Bio Practice Exam Section IDocumento6 páginasAp Bio Practice Exam Section INaama GoutiAinda não há avaliações
- CSEC Biology 2014 RevisionDocumento44 páginasCSEC Biology 2014 RevisionNabeel Uddin89% (9)
- Poison MushroomsDocumento24 páginasPoison MushroomsDarkMattata100% (4)
- An Introduction To LichensDocumento17 páginasAn Introduction To LichensStu CrawfordAinda não há avaliações
- OCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision NotesDocumento4 páginasOCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision Notes24wrightphilip100% (1)
- Poetry Form 1Documento88 páginasPoetry Form 1Norsaniah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ScienceDocumento10 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To Sciencenaza977583% (18)
- IGCSE Biology Revision Workbook - Gas Exchange and TransportDocumento34 páginasIGCSE Biology Revision Workbook - Gas Exchange and TransportSameer Ala'i100% (2)
- Botanica - An English-Spanish Glossary of TerminologyDocumento63 páginasBotanica - An English-Spanish Glossary of Terminologymrmister001Ainda não há avaliações
- LESSON PLAN: Science-Living and Non Living ThingsDocumento24 páginasLESSON PLAN: Science-Living and Non Living Thingsapi-310311516Ainda não há avaliações
- SBA1B Ans eDocumento33 páginasSBA1B Ans eChan Sin YeeAinda não há avaliações
- Burgess Flower Book For Children 1923Documento478 páginasBurgess Flower Book For Children 1923homeschoolspeewah100% (3)
- Potato, A Global History by Andrew F. SmithDocumento144 páginasPotato, A Global History by Andrew F. SmithSubhranil Biswas0% (1)
- Sustainable Shale Oil and Gas: Analytical Chemistry, Geochemistry, and Biochemistry MethodsNo EverandSustainable Shale Oil and Gas: Analytical Chemistry, Geochemistry, and Biochemistry MethodsAinda não há avaliações
- Physiological Ecology of Forest Production: Principles, Processes and ModelsNo EverandPhysiological Ecology of Forest Production: Principles, Processes and ModelsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Sustainable Energy Technologies for Seawater DesalinationNo EverandSustainable Energy Technologies for Seawater DesalinationAinda não há avaliações
- LAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human BodyDocumento8 páginasLAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human Bodyley leynAinda não há avaliações
- Particulates Matter: Impact, Measurement, and Remediation of Airborne PollutantsNo EverandParticulates Matter: Impact, Measurement, and Remediation of Airborne PollutantsAinda não há avaliações
- Bio2 90462 GasexchangeDocumento2 páginasBio2 90462 Gasexchangeapi-298466880Ainda não há avaliações
- Summary Form 3Documento26 páginasSummary Form 3Prakkash RajanAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Key WordsDocumento16 páginasBiology Key WordsMadavi JayakodyAinda não há avaliações
- F211 Revision ChecklistDocumento2 páginasF211 Revision ChecklistJoseph WheatlandAinda não há avaliações
- GCSE Biology Summary Volume One - Life Processes and Green PlantsDocumento11 páginasGCSE Biology Summary Volume One - Life Processes and Green PlantsNurul HidayahmyAinda não há avaliações
- Plant CellDocumento4 páginasPlant Cellemdadul2009Ainda não há avaliações
- Air Pollution Calculations: Quantifying Pollutant Formation, Transport, Transformation, Fate and RisksNo EverandAir Pollution Calculations: Quantifying Pollutant Formation, Transport, Transformation, Fate and RisksAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Exchange in Animals: We Will Be Studying The Diversity of Adaptations For This Process in Four Animal GroupsDocumento42 páginasGas Exchange in Animals: We Will Be Studying The Diversity of Adaptations For This Process in Four Animal GroupsMiss IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- List of Scientific Laws and TheoriesDocumento45 páginasList of Scientific Laws and TheoriesraviAinda não há avaliações
- Diffusion BiologyDocumento2 páginasDiffusion BiologyrubeenelbashaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Presentation CH 2Documento56 páginasAnatomy Presentation CH 2api-155864611Ainda não há avaliações
- Ocr Biology Unit f221 Revision Notes 1231102726226412 1Documento14 páginasOcr Biology Unit f221 Revision Notes 1231102726226412 1Liam GalvinAinda não há avaliações
- Life'S Transport, Exchange and Defense System: - Respiratory System - Circulatory System - Immune SystemDocumento47 páginasLife'S Transport, Exchange and Defense System: - Respiratory System - Circulatory System - Immune Systemcale suarez0% (1)
- 2 RespirationDocumento86 páginas2 RespirationAkwa ManAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Form 5Documento16 páginasBiology Form 5alibinahmad88Ainda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Spring Final Review 2023Documento2 páginasAnatomy Spring Final Review 2023lucas?Ainda não há avaliações
- CED-424 (C) Environmetal Impact AssesmentDocumento17 páginasCED-424 (C) Environmetal Impact AssesmentAastha SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Traductorado Material Orientador NivelDocumento15 páginasTraductorado Material Orientador NivelEnglish O'clock OnlineAinda não há avaliações
- Transport ExchangeDocumento17 páginasTransport ExchangeMikzy MercadoAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Project - Rate of Evaporation (PR & TG)Documento17 páginasChemistry Project - Rate of Evaporation (PR & TG)Anay Datta100% (1)
- Agr122 109Documento9 páginasAgr122 109pandalyna100% (1)
- Air Microbiology 2nd YrDocumento47 páginasAir Microbiology 2nd YrBlueSagaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Notes WeeblyDocumento31 páginasChapter 3 Notes Weeblyapi-292796192Ainda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Hydrogen Production and Utilization in Fuel Cell SystemsNo EverandFundamentals of Hydrogen Production and Utilization in Fuel Cell SystemsAinda não há avaliações
- B4 and B5 Model AnswersDocumento23 páginasB4 and B5 Model AnswersJonathan ManningAinda não há avaliações
- Biology NotesDocumento12 páginasBiology NotesDarrell Ibrahim NaryamaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Preliminary Study NotesDocumento23 páginasBiology Preliminary Study NotesNabiha SyedaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology GuideDocumento14 páginasPlant Anatomy and Physiology GuideorangeviewAinda não há avaliações
- PSLE Science Mass Lecture Series: Key ConceptsDocumento46 páginasPSLE Science Mass Lecture Series: Key ConceptsMax LeeAinda não há avaliações
- BOTANY 105 (1st Le Notes)Documento14 páginasBOTANY 105 (1st Le Notes)Anonymous RbkgTBn1K3Ainda não há avaliações
- RespirationDocumento68 páginasRespirationNorhidayah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- 4 QNDocumento1 página4 QNNur Fitrahtul Adilah Mohd Firdaus NelsonAinda não há avaliações
- The Global Carbon Cycle and Climate Change: Scaling Ecological Energetics from Organism to the BiosphereNo EverandThe Global Carbon Cycle and Climate Change: Scaling Ecological Energetics from Organism to the BiosphereAinda não há avaliações
- STD 8 ScienceDocumento60 páginasSTD 8 Scienceemmanuelbanda2021Ainda não há avaliações
- Cell Structure FunctionDocumento42 páginasCell Structure Functionsvk_chatterjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Week 3 - Ch. 28 + 29: Chapter 28: Phylogenies and The History of LifeDocumento10 páginasWeek 3 - Ch. 28 + 29: Chapter 28: Phylogenies and The History of LifeHarris ChoeAinda não há avaliações
- Elsc Exam 2nd QuarterDocumento4 páginasElsc Exam 2nd QuarterRhelee Mae DagantaAinda não há avaliações
- Bio NotesDocumento18 páginasBio Notes185839Ainda não há avaliações
- Year 8 Science CambridgeDocumento6 páginasYear 8 Science CambridgeRebecca TunAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrient Transport in PlantsDocumento31 páginasNutrient Transport in PlantsFidaAinda não há avaliações
- Celina Nassar D: Biology Department Biology Worksheet 7 - Second Semester Name: SectionDocumento37 páginasCelina Nassar D: Biology Department Biology Worksheet 7 - Second Semester Name: SectionCelina NassarAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling of Microscale Transport in Biological ProcessesNo EverandModeling of Microscale Transport in Biological ProcessesSid M. BeckerAinda não há avaliações
- Transport: Factor That Effected The of Substances The Circulatory SystemDocumento24 páginasTransport: Factor That Effected The of Substances The Circulatory Systemliming8112Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1Documento20 páginasLecture 1ALL ABOUT PAGEANTARYAinda não há avaliações
- Transport Xylem and Phloem 2015 PDFDocumento46 páginasTransport Xylem and Phloem 2015 PDFjuanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento6 páginasChapter 1Norsaniah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Modul Mikroorganisma Dan Kesannya Kepada ManusiaDocumento16 páginasModul Mikroorganisma Dan Kesannya Kepada ManusiaNorliyana Ali100% (5)
- Students Matching F 5Documento10 páginasStudents Matching F 5faezahsapixAinda não há avaliações
- Essay ExerciseDocumento2 páginasEssay ExerciseNorsaniah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- I Am What I AmDocumento4 páginasI Am What I AmNorsaniah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- The Pencil by Ali MajoodDocumento7 páginasThe Pencil by Ali MajoodNorsaniah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Summary ExercisesDocumento2 páginasSummary ExercisesNorsaniah Ismail100% (1)
- Characteristics of The Classes of VertebratesDocumento1 páginaCharacteristics of The Classes of VertebratesNorsaniah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- The World Through Our SensesDocumento18 páginasThe World Through Our SensesHannanNashruddinAinda não há avaliações
- Notes - Flower StructureDocumento2 páginasNotes - Flower Structureapi-238421605Ainda não há avaliações
- Antimicrobial Activity of Flowers of Ixora Pavetta AndrDocumento3 páginasAntimicrobial Activity of Flowers of Ixora Pavetta AndrxiuhtlaltzinAinda não há avaliações
- Biology AssignmentDocumento2 páginasBiology AssignmentKidus WendesenAinda não há avaliações
- Biology 9 Icse Sample Paper 5 PDFDocumento7 páginasBiology 9 Icse Sample Paper 5 PDFAnubrata SarkarAinda não há avaliações
- Reproduction in Plants - Revision QuestionsDocumento2 páginasReproduction in Plants - Revision Questionsradhika fomraAinda não há avaliações
- P6 Science SA2 2017 Nanyang Exam PapersDocumento52 páginasP6 Science SA2 2017 Nanyang Exam PapersKui LiuAinda não há avaliações
- Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research Werer Research Center Crop Research Process Horticultural Crop Research DivisionDocumento53 páginasEthiopian Institute of Agricultural Research Werer Research Center Crop Research Process Horticultural Crop Research DivisionYitagesAinda não há avaliações
- Reading TOEFL Exercise 3Documento10 páginasReading TOEFL Exercise 3Chan Dra0% (1)
- Eenadu - Pratibha: Eamcet Grand Test (Medical)Documento49 páginasEenadu - Pratibha: Eamcet Grand Test (Medical)shanthi_miminaAinda não há avaliações
- Report Individu-Eleonora Yuanita Intan BudyastutiDocumento15 páginasReport Individu-Eleonora Yuanita Intan BudyastutiEleonora IntanAinda não há avaliações
- Ampalaya Production GuideDocumento10 páginasAmpalaya Production Guideapo_mallariAinda não há avaliações
- Study On Results Obtained by Different Researchers On in Vitro Propagation of Herbaceous PeonyDocumento8 páginasStudy On Results Obtained by Different Researchers On in Vitro Propagation of Herbaceous PeonyCazan Nicolae GeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- Tissues: Biology Le.6Documento41 páginasTissues: Biology Le.69B 36 Raghuram VedantamAinda não há avaliações
- COMMON NAME: Hibisus, Shoe Flower BOTANICAL NAME: Hibiscus RosaDocumento2 páginasCOMMON NAME: Hibisus, Shoe Flower BOTANICAL NAME: Hibiscus Rosasagar shahAinda não há avaliações
- Cell - Unit of Life Notes+ EXEDocumento95 páginasCell - Unit of Life Notes+ EXEheena lakhwaniAinda não há avaliações
- Seedless Vascular Plants: Pteridophyta (Lycophyta and Monilophyta)Documento110 páginasSeedless Vascular Plants: Pteridophyta (Lycophyta and Monilophyta)Maharani Putri ChaniaAinda não há avaliações
- The Uncanny Nepenthes: Recent EpisodesDocumento26 páginasThe Uncanny Nepenthes: Recent EpisodesMark Ronald Samijon ManseguiaoAinda não há avaliações
- Torrent Downloaded FromDocumento48 páginasTorrent Downloaded FromshilparabAinda não há avaliações
- Botany MidtermDocumento4 páginasBotany MidtermMatthew PerryAinda não há avaliações
- Jib 115 Plant Diversity T1b 31 January 2019, Thursday, 12-1 PM Chapter 4-TissuesDocumento43 páginasJib 115 Plant Diversity T1b 31 January 2019, Thursday, 12-1 PM Chapter 4-TissuesAction PotentialAinda não há avaliações
- BE - Fresh Press - 5.4.12Documento2 páginasBE - Fresh Press - 5.4.12Saeyoung ChoAinda não há avaliações