Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
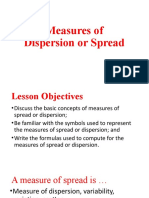
Descriptive Statistics
Enviado por
MissMumtazDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Descriptive Statistics
Enviado por
MissMumtazDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Analysing data using descriptive statistics
How to calculate it To calculate this, you add up all numbers and divide by number of numbers Advantages it makes use of all the numbers in the data set, and so is a sensitive measure. Disadvantages
Mean = the average
Measures of central tendency
(what the relationship is of the values with the central point)
Mode = the most common number
Median = central value
This is calculated by putting similar scores together, and counting which one occurs the most frequently This is calculated by arranging scores in order and finding the mid point The range is the a measure of the spread of a set of scores, shown by the difference between the highest value and the lowest This is the measure of the spread of data around the mean. The higher the value the more variation in your scores.
it can be used with nominal (categorical) data, and that it provides information about frequency
it is affected by extreme scores (high or low) and can misrepresent the numbers as a result It can only be used with certain types of data (eg. ratio or interval data, with a zero) the data may have several modes (bimodal = 2 modes)
it is not affected by extreme scores it can be used with ordinal data
A disadvantage is that it is not as sensitive as the mean, as not all values are reflected
its easy to calculate, and shows extreme values
Range Measures of dispersio n
(how dispersed or spread out the data are)
it is affected by extreme values, and does not take into account the number of observations in the data set; it does not give info on whether the scores are clustered around the mean or spread out it is more complicated to calculate than the range it may hide some characteristics of the data
Standar d deviatio n
it gives a more precise and sensitive measure of dispersion than the range, as all values are taken into account
Você também pode gostar
- 2 - Descriptive StatisticsDocumento29 páginas2 - Descriptive StatisticsVishal ShivhareAinda não há avaliações
- Descriptive Statistics Explained: Measures of Central Tendency, Spread and ShapeDocumento34 páginasDescriptive Statistics Explained: Measures of Central Tendency, Spread and ShapeNAVANEETHAinda não há avaliações
- Measures Central Tendency GuideDocumento6 páginasMeasures Central Tendency GuideBrentt WilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- Unit IVDocumento80 páginasUnit IVneelabhronanda02Ainda não há avaliações
- Measures of Dispersion ExplainedDocumento17 páginasMeasures of Dispersion ExplainedReshmaAinda não há avaliações
- Descriptive Statistics SummaryDocumento37 páginasDescriptive Statistics SummaryFahad MushtaqAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 Repaired)Documento8 páginasUnit 1 Repaired)mussaiyibAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3.5. Basic Statistics For TeachersDocumento19 páginasLesson 3.5. Basic Statistics For TeachersAngie De La CruzAinda não há avaliações
- PLANNING DATA ANALYSIS USING STATISTICSDocumento27 páginasPLANNING DATA ANALYSIS USING STATISTICSJayson Jayjamzkie RepolidoAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 7-9 Measure of Central TendencyDocumento58 páginasLecture 7-9 Measure of Central TendencyAbdullah Munir NourozAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Modelling: Statistical MeasuresDocumento6 páginasFinancial Modelling: Statistical MeasuresManfredi SopraniAinda não há avaliações
- Maam Teslyn ReportDocumento38 páginasMaam Teslyn ReportCJ Marco TumarongAinda não há avaliações
- Biostatistics: Khadeeja PKDocumento27 páginasBiostatistics: Khadeeja PKArif Khan Abdul Karim0% (1)
- Gaaan 1Documento26 páginasGaaan 1Ayesha ChAinda não há avaliações
- Calculating Standard Deviation and Interpreting Error BarsDocumento1 páginaCalculating Standard Deviation and Interpreting Error BarsNatasha Kit.Ainda não há avaliações
- Basics for Understanding Statistics in 40 CharactersDocumento8 páginasBasics for Understanding Statistics in 40 CharacterssamAinda não há avaliações
- StatisticsDocumento33 páginasStatisticsAnonymous J5sNuoIy100% (2)
- Mean Median, ModeDocumento15 páginasMean Median, Mode21010324029Ainda não há avaliações
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocumento30 páginasStatistics For Data ScienceArminSayadiAinda não há avaliações
- Week One: Introduction To Quantitative Methods MBA 2013Documento49 páginasWeek One: Introduction To Quantitative Methods MBA 2013Hardik NaikAinda não há avaliações
- Module 3 Descriptive Statistics FinalDocumento15 páginasModule 3 Descriptive Statistics FinalJordine Umayam100% (1)
- Statistics and Computer: Tools For Analyzing of Assessment DataDocumento10 páginasStatistics and Computer: Tools For Analyzing of Assessment DataLoger Kent BernabeAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Data AnalysisDocumento27 páginasQuantitative Data AnalysisHaneef Mohamed100% (1)
- Measures of Location - MIDocumento12 páginasMeasures of Location - MISaudulla Jameel JameelAinda não há avaliações
- Descriptive and Inferential Stats in 40 CharactersDocumento18 páginasDescriptive and Inferential Stats in 40 CharactersShyam MaariAinda não há avaliações
- Unit .......Documento45 páginasUnit .......Rajan shahAinda não há avaliações
- Unit IiDocumento25 páginasUnit IiAlessandra Kate ParboAinda não há avaliações
- Math4E Week 7 - Lecture 6Documento19 páginasMath4E Week 7 - Lecture 6John Cris Lustria PüblicoAinda não há avaliações
- Merits and DemeritsDocumento10 páginasMerits and DemeritsRamesh SafareAinda não há avaliações
- Summary Statistics and Visualization Techniques To ExploreDocumento30 páginasSummary Statistics and Visualization Techniques To ExploreMarshil ShibuAinda não há avaliações
- MeasuresDocumento8 páginasMeasureswhitekaisuAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Summarising Data - Averages and DispersionDocumento22 páginasUnit 3 Summarising Data - Averages and DispersionjemimaAinda não há avaliações
- Project 10 (StatisticsDocumento14 páginasProject 10 (StatisticsArkin DuttaAinda não há avaliações
- Week 4 Statistics Recap MAKING MEANING OF MEASUREMENTS & RAW TEST SCORESDocumento39 páginasWeek 4 Statistics Recap MAKING MEANING OF MEASUREMENTS & RAW TEST SCORESFlevian OgonjiAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 15Documento7 páginasTutorial 15Yeong Zi YingAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics basics introDocumento5 páginasStatistics basics introAryan SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- RSU - Statistics - Lecture 3 - Final - myRSUDocumento34 páginasRSU - Statistics - Lecture 3 - Final - myRSUirina.mozajevaAinda não há avaliações
- Measures of Central TendencyDocumento3 páginasMeasures of Central TendencystatiksAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Weighted Average?Documento12 páginasWhat Is A Weighted Average?SachinAinda não há avaliações
- Measures of Central TendencyDocumento22 páginasMeasures of Central TendencyDenisho Dee86% (7)
- Statistical Machine LearningDocumento12 páginasStatistical Machine LearningDeva Hema100% (1)
- Chapter Six For StudentsDocumento56 páginasChapter Six For StudentsBeky AbrahamAinda não há avaliações
- StatDocumento44 páginasStatLoreth Aurea OjastroAinda não há avaliações
- FXGFHGJHKJLKDocumento19 páginasFXGFHGJHKJLKbethAinda não há avaliações
- Biostatistics MeasuresDocumento45 páginasBiostatistics MeasuresHarshitha LokeshAinda não há avaliações
- Analyzing The DataDocumento54 páginasAnalyzing The DataMagnolia KhineAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocumento27 páginasStatistics For Data ScienceDr. Sanjay GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Measures of Spread-2023Documento25 páginasMeasures of Spread-2023AmielRayyanB.Badrudin 309Ainda não há avaliações
- Using Assessment Data to Measure Student PerformanceDocumento6 páginasUsing Assessment Data to Measure Student PerformanceJessa Mae CantilloAinda não há avaliações
- ClassX DS Teacher PresentationDocumento45 páginasClassX DS Teacher PresentationYtber SoftAinda não há avaliações
- Data AnalysisDocumento55 páginasData AnalysisSwati PowarAinda não há avaliações
- Research StatisticsDocumento2 páginasResearch StatisticsAaron Paul SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics Document Title Under 40 CharactersDocumento9 páginasStatistics Document Title Under 40 CharactersTejashwi KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment of Learning Ii: Dr. Louie D. Asuncion InstructorDocumento73 páginasAssessment of Learning Ii: Dr. Louie D. Asuncion Instructorjoy panganibanAinda não há avaliações
- Measures of Dispersion EditDocumento8 páginasMeasures of Dispersion EditShimaa KashefAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Data AnalysisDocumento31 páginasQuantitative Data Analysisakoeljames8543Ainda não há avaliações
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocumento93 páginasStatistics For Data ScienceCesar LobatoAinda não há avaliações
- Measure of Central TendencyDocumento24 páginasMeasure of Central Tendencymariell quitorianoAinda não há avaliações
- Descriptive StatisticsDocumento19 páginasDescriptive StatisticsAnnRubyAlcaideBlandoAinda não há avaliações
- Overview Of Bayesian Approach To Statistical Methods: SoftwareNo EverandOverview Of Bayesian Approach To Statistical Methods: SoftwareAinda não há avaliações
- PSYA4 - Term GuidanceDocumento73 páginasPSYA4 - Term GuidanceMissMumtazAinda não há avaliações
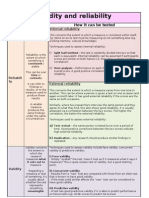
- Validity and ReliabilityDocumento2 páginasValidity and ReliabilityMissMumtazAinda não há avaliações
- As RevisionDocumento25 páginasAs RevisionMissMumtazAinda não há avaliações
- Self-Assessment Sheet: Specification What It Is E.G. Advantage Disadvantage Overall MarkDocumento3 páginasSelf-Assessment Sheet: Specification What It Is E.G. Advantage Disadvantage Overall MarkMissMumtazAinda não há avaliações
- Key TermsDocumento8 páginasKey TermsMissMumtazAinda não há avaliações
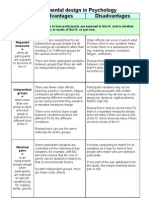
- Experimental DesignsDocumento2 páginasExperimental DesignsMissMumtazAinda não há avaliações