Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Augusta Ada King
Enviado por
mansoorahmed86Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Augusta Ada King
Enviado por
mansoorahmed86Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
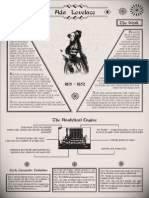
Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace (10 December 1815 27 November 1852), born Augusta Ada Byron and
d now commonly known as Ada Lovelace, was an English mathematician and writer chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's early mechanical general-purpose computer, the analytical engine. Her notes on the engine include what is recognised as the first algorithm intended to be processed by a machine; thanks to this, she is sometimes considered the world's first computer [1][2] programmer. Ada was the only legitimate child of the poet Lord Byron (with Anne Isabella Milbanke, 11th Baroness Wentworth). She had no relationship with her father, who died when she was nine. As a young adult, she took an interest in mathematics, and in particular Babbage's work on the analytical engine. Between 1842 and 1843, she translated an article by Italian mathematician Luigi Menabrea on the engine, which she supplemented with a set of notes of her own. These notes contain what is considered the first computer program that is, an algorithm encoded for processing by a machine. Ada's notes are important in the early history of computers. She also foresaw the capability of computers to go beyond mere calculating or number-crunching while others, including Babbage himself, focused only on these capabilities.
First computer program
In 1842 Charles Babbage was invited to give a seminar at the University of Turin about his analytical engine. Luigi Menabrea, a young Italian engineer, and future prime minister of Italy, wrote up Babbage's lecture in French, and this transcript was subsequently published in the Bibliothque Universelle de Genve in October 1842
Você também pode gostar
- Isaac AsimovDocumento2 páginasIsaac Asimovmansoorahmed860% (1)
- Computer Programming - History of Computer ProgrammingDocumento2 páginasComputer Programming - History of Computer ProgrammingJoniel MartinAinda não há avaliações
- Ada Lovelace: The First Computer Programmer: QuestionsDocumento1 páginaAda Lovelace: The First Computer Programmer: Questions711debbie100% (1)
- Ada LovelaceDocumento1 páginaAda Lovelacevalgreen.caAinda não há avaliações
- The First Computer ProgrammerDocumento2 páginasThe First Computer ProgrammerSara Margarita EsparzaAinda não há avaliações
- Ada Lovelace - Reading Comprehension + AnswersDocumento1 páginaAda Lovelace - Reading Comprehension + AnswersDanielaElenaGuraliucAinda não há avaliações
- Charles BabbageDocumento2 páginasCharles Babbageamritpal5699Ainda não há avaliações
- The First Computer Programmer Daniela Mathison CI 28022913 - 307Q1Documento3 páginasThe First Computer Programmer Daniela Mathison CI 28022913 - 307Q1Daniela MathisonAinda não há avaliações
- The First Computer Programmer Daniela Mathison CI 28022913 - 307Q1Documento3 páginasThe First Computer Programmer Daniela Mathison CI 28022913 - 307Q1Daniela MathisonAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Inventors and Contributors: Arboleda National High SchoolDocumento6 páginasComputer Inventors and Contributors: Arboleda National High SchoolErlinda Cabanilla TadeoAinda não há avaliações
- The Greatest Mathematician of The Past 100 YearsDocumento2 páginasThe Greatest Mathematician of The Past 100 YearsZaina JatoiAinda não há avaliações
- A Woman Who Invented App and Technology - English PresentationDocumento6 páginasA Woman Who Invented App and Technology - English PresentationAdam AlifAinda não há avaliações
- TextDocumento1 páginaTextNaniAinda não há avaliações
- Who Was Ada Lovelace PDFDocumento1 páginaWho Was Ada Lovelace PDFcbamba479Ainda não há avaliações
- V.F - Muhammed Ismail Thouheed: Name: Reg No.: TopicDocumento3 páginasV.F - Muhammed Ismail Thouheed: Name: Reg No.: TopicV.F.MUHAMMED ISMAIL THOUHEEDAinda não há avaliações
- History of ComputerDocumento5 páginasHistory of Computerhariramjoshi74Ainda não há avaliações
- First Computer Programmer From 1800sDocumento1 páginaFirst Computer Programmer From 1800sNihar R. PandeAinda não há avaliações
- Meeting11 BEAP.2021Documento1 páginaMeeting11 BEAP.2021David ArdiantoAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento1 páginaUntitledsavitri raokAinda não há avaliações
- STEMDocumento1 páginaSTEMGellért KirályAinda não há avaliações
- Ada Lovelace 1.doxDocumento3 páginasAda Lovelace 1.doxrufino aparisAinda não há avaliações
- Charles BabbageDocumento8 páginasCharles Babbagealexmarko992Ainda não há avaliações
- DocumentoDocumento5 páginasDocumentoLuciAinda não há avaliações
- Famous Women - Ada LovelaceDocumento8 páginasFamous Women - Ada Lovelaceadinau_2100% (1)
- The First Mechanical Computer, Created by In, Doesn't Really Resemble What Most Would Consider A Computer TodayDocumento1 páginaThe First Mechanical Computer, Created by In, Doesn't Really Resemble What Most Would Consider A Computer TodayMursleen KianiAinda não há avaliações
- Charles BabbageDocumento1 páginaCharles BabbageAngelica Mae CornejoAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Scientist (Computer Lessons SY 2015-2016) Scientist Name/Origin Birth/Death ContributionsDocumento7 páginasComputer Scientist (Computer Lessons SY 2015-2016) Scientist Name/Origin Birth/Death ContributionsRandy Alejaga RosalesAinda não há avaliações
- Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace Stage 6 Comp - Reading Comprehension 1Documento3 páginasCharles Babbage and Ada Lovelace Stage 6 Comp - Reading Comprehension 1Eddie ZhouAinda não há avaliações
- Charles Babbage - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocumento3 páginasCharles Babbage - Britannica Online EncyclopediaAdi SuratmanAinda não há avaliações
- Ada Lovelace Infographic (For Children)Documento1 páginaAda Lovelace Infographic (For Children)cristina0dscAinda não há avaliações
- Ada Lovelace: "The First Computer Programmer"Documento1 páginaAda Lovelace: "The First Computer Programmer"cristina0dscAinda não há avaliações
- Calculator-: A - He Was Born In, - His Father's Name Was Etienne.. Pascal Was Completely Educated by His FatherDocumento3 páginasCalculator-: A - He Was Born In, - His Father's Name Was Etienne.. Pascal Was Completely Educated by His FatherSahal T YousephAinda não há avaliações
- History of ComputerDocumento12 páginasHistory of Computersg3bestAinda não há avaliações
- Ada Lovelace Answer KeyDocumento1 páginaAda Lovelace Answer KeyTony AppsAinda não há avaliações
- First Presentation of My LifeDocumento28 páginasFirst Presentation of My LifeKapil AryalAinda não há avaliações
- Anji - Web1Documento3 páginasAnji - Web1Yugandhara RaoAinda não há avaliações
- BornDocumento3 páginasBornkalaikavindAinda não há avaliações
- Computer ResearchDocumento6 páginasComputer Researchapi-291529918Ainda não há avaliações
- Charles BabbageDocumento1 páginaCharles BabbagediabroblancoAinda não há avaliações
- Done by - Sayan .T. Youseph Roll No - 19 Vii - B KVNO-2Documento10 páginasDone by - Sayan .T. Youseph Roll No - 19 Vii - B KVNO-2Sahal T YousephAinda não há avaliações
- Ada Lovelace BiographyDocumento2 páginasAda Lovelace BiographyAAMCAinda não há avaliações
- From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento8 páginasFrom Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediasindhusmAinda não há avaliações
- Charles BabbageDocumento12 páginasCharles BabbageRex CulpableAinda não há avaliações
- LAD - Communicative Test (Reading and Writing)Documento2 páginasLAD - Communicative Test (Reading and Writing)Nor Rahma SukowatiAinda não há avaliações
- Evolution of Computers BCA @NDDocumento8 páginasEvolution of Computers BCA @NDRAVI KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Actividad 1.1Documento4 páginasActividad 1.1Edinsson Alberto López LópezAinda não há avaliações
- Ge Elect 2 1Documento9 páginasGe Elect 2 1QUIJANO, FLORI-AN P.Ainda não há avaliações
- Timeline Sample TextDocumento3 páginasTimeline Sample TextMary Antoinette FranciscoAinda não há avaliações
- History of ComputerDocumento7 páginasHistory of ComputerRoselle TanAinda não há avaliações
- ICT and COMPUTER EDUC.Documento16 páginasICT and COMPUTER EDUC.jhohanna talaAinda não há avaliações
- Unidad3 Tarea02Documento1 páginaUnidad3 Tarea02Aliesky RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Week 1 Reviewer Intro ComputingDocumento2 páginasWeek 1 Reviewer Intro ComputingHannyAinda não há avaliações
- History of ComputerDocumento10 páginasHistory of ComputerPRANSHU KATIYARAinda não há avaliações
- Comp 101 ReviewerDocumento17 páginasComp 101 Reviewerxbautista124Ainda não há avaliações
- Ada Byron and Her Contributions To Early Computer Science PSSOH 2018Documento4 páginasAda Byron and Her Contributions To Early Computer Science PSSOH 2018Titilayo Deborah CadmusAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Histor-WPS OfficeDocumento55 páginasComputer Histor-WPS OfficeRayl Quiza ColardoAinda não há avaliações
- Charles BabbageDocumento3 páginasCharles BabbageNayeemur RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Charles BabbageDocumento9 páginasCharles Babbagekristen_cullen123Ainda não há avaliações
- Ada Lovelace Infographic (For Adults)Documento1 páginaAda Lovelace Infographic (For Adults)cristina0dscAinda não há avaliações
- The Mechanical AgeDocumento4 páginasThe Mechanical AgenoelAinda não há avaliações
- Using Roadmap in Web Dynpro ABAP PDFDocumento23 páginasUsing Roadmap in Web Dynpro ABAP PDFAgustin PighinAinda não há avaliações
- Thomas Alva EdisonDocumento2 páginasThomas Alva Edisonmansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- SAPscript Control CommandsDocumento2 páginasSAPscript Control CommandsJoy DeyAinda não há avaliações
- Working With Tabstrip WDADocumento19 páginasWorking With Tabstrip WDAmcsrAinda não há avaliações
- John Von NeumannDocumento2 páginasJohn Von Neumannmansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- Jack St. Clair: Awards and HonorDocumento1 páginaJack St. Clair: Awards and Honormansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- Charles Babbage Was Born in London DecDocumento1 páginaCharles Babbage Was Born in London Decmansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- George Boole: AnalysisDocumento2 páginasGeorge Boole: Analysismansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- Fear of FeedbackDocumento2 páginasFear of Feedbackmansoorahmed86100% (1)
- SP Imran Ahmed KhanDocumento6 páginasSP Imran Ahmed Khanmansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- Yahya Shoaib - SAP Consultant - AuDocumento3 páginasYahya Shoaib - SAP Consultant - Aumansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- SheikhAsadullahMahrab NewDocumento2 páginasSheikhAsadullahMahrab Newmansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- Daniyal Final CVDocumento3 páginasDaniyal Final CVmansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- ABAP Performance and Best Practices A Bible V1 0Documento77 páginasABAP Performance and Best Practices A Bible V1 0Harshal Joshi100% (1)
- Talent Pool ApplicationDocumento1 páginaTalent Pool Applicationmansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações
- Search TechniquesDocumento5 páginasSearch Techniqueslojo123Ainda não há avaliações
- Code Optimization Techniques - Tips and TricksDocumento11 páginasCode Optimization Techniques - Tips and Tricksmansoorahmed86Ainda não há avaliações