Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
What Causes Cystic Fibrosis1
Enviado por
RSarkawyDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
What Causes Cystic Fibrosis1
Enviado por
RSarkawyDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
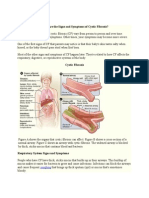
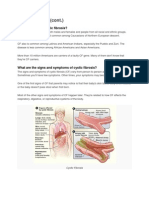
What causes cystic fibrosis?
A mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulatory protein
What does the CFTR protein do?
It helps control the viscosity (or stickiness) of mucus that lines the epithelial cells of the airways, digestive and reproductive systems
mucus
cilia
epithelial cell
If the mucus in airways is
too sticky: the cilia cannot beat and remove the mucus, which then clogs up airways
too runny: the mucus can flood the airways
When there is excess water in the mucus
Water is drawn out of the mucus and it thickens
ClNa+
H2O
mucus
apical membrane
5 CFTR channel closed
Na+ channel open
basal membrane
pump
H2O
4
3 Cl-
Na+
H2O
tissue fluid
When there is too little water in the mucus
Water is drawn out of the mucus and it becomes less sticky
Na+ 3
apical membrane
Na+
2
Cl-
mucus
4
Na+ channel closed
CFTR channel open
1 Cl-
H2O
H2O
5
The CFTR somehow blocks the sodium channels
basal membrane
pump
Na+
H2O
tissue fluid
With cystic fibrosis
The mucus becomes very thick and sticky
Cl2
apical membrane
Na+
H2O 3
mucus
X
Na+ channel open
CFTR nonfunctional
Water drawn out by osmosis H2O
basal membrane
The CFTR protein cannot block the sodium channels so they are always open
Cl-
H2O
tissue fluid
How cystic fibrosis affects the lungs
Sticky mucus builds up in the airways, reducing flow of air into alveoli. Lungs gradually fill up with mucus, making them less effective for gas exchange.
Symptoms: Severe coughing - to remove excess mucus. Breathlessness - shortage of oxygen increases tiredness and lack of energy Infections - as bacteria are trapped in mucus
How does cystic fibrosis affect the reproductive systems?
Men Women
Sperm duct is blocked During the menstrual and prevents cycle the levels of movement of sperm mucus vary. Women with CF have thick levels of mucus which can block the cervix so sperm cannot reach them.
Can lack the sperm ducts
How cystic fibrosis affects the digestive system:
Thick, sticky mucus blocks the pancreatic duct preventing enzymes from reaching the duodenum.
Food is not digested and absorbed sufferers fail to put on body mass and suffer malnutrition.
Trapped digestive enzymes damage the pancreatic cells affecting cells producing insulin resulting in diabetes.
Você também pode gostar
- Cystic Fibrosis PDFDocumento22 páginasCystic Fibrosis PDFAbdelrahman AlshatnawiAinda não há avaliações
- T2 Cystic FibrosisDocumento3 páginasT2 Cystic FibrosisErnest SiaoAinda não há avaliações
- Ward Class On Cystic FibrosisDocumento58 páginasWard Class On Cystic FibrosisJannen CasasAinda não há avaliações
- In-depth study of genetic disease cystic fibrosisDocumento2 páginasIn-depth study of genetic disease cystic fibrosisIllharm Sherrif100% (2)
- Cystic Fibrosis PathophysiologyDocumento5 páginasCystic Fibrosis PathophysiologyKim Enrico JumarangAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento3 páginasCystic FibrosisYousra Al-DabhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento32 páginasCystic FibrosisSrm Genetics100% (1)
- Biochemistry Presentation.Documento3 páginasBiochemistry Presentation.MIMIbako67Ainda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento26 páginasCystic FibrosisEliza ButtAinda não há avaliações
- Cysticfibrosis 150401114224 Conversion Gate01Documento29 páginasCysticfibrosis 150401114224 Conversion Gate01Marwan SweityAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Cystic FibrosisDocumento5 páginasAnatomy of Cystic FibrosislazylawatudentAinda não há avaliações
- E Maternal Adaptations To PregnancyDocumento27 páginasE Maternal Adaptations To PregnancyGeraldine PatayanAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Cystic FibrosisDocumento15 páginasWhat Is Cystic FibrosisSarika YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Lower Respiratory Tract Disorder 2Documento12 páginasLower Respiratory Tract Disorder 2RON PEARL ANGELIE CADORNAAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento26 páginasCystic FibrosisSajjal JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic Fibrosis: Zoe Drullard and Avril GuillermoDocumento18 páginasCystic Fibrosis: Zoe Drullard and Avril Guillermozoe drullardAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento9 páginasCystic Fibrosisapi-432406854Ainda não há avaliações
- Case Study: Cystic Fibrosis: Manalo, Joanne Erica S. BS Respiratory TherapyDocumento20 páginasCase Study: Cystic Fibrosis: Manalo, Joanne Erica S. BS Respiratory TherapyJohn Carlo ConsultaAinda não há avaliações
- Nature of DiseaseDocumento14 páginasNature of DiseaseLambo Ignacio Queen Quin100% (1)
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento29 páginasCystic FibrosisAviva TutejaAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento9 páginasCystic FibrosiszarasarAinda não há avaliações
- Gallbladder HydropsDocumento6 páginasGallbladder HydropsSaifulAnamAinda não há avaliações
- (2023 - 10 - 23) Sci Cystic FibrosisDocumento37 páginas(2023 - 10 - 23) Sci Cystic FibrosisjesslynaureliaAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic Fibrosis Signs and Symptoms ExplainedDocumento3 páginasCystic Fibrosis Signs and Symptoms ExplainedsakthiprimeAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento3 páginasCystic FibrosissakthiprimeAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic Fibrosis Affects Lungs and DigestionDocumento2 páginasCystic Fibrosis Affects Lungs and DigestionYanyan Umpar PologAinda não há avaliações
- Trachea and Lung Anatomy FunctionsDocumento14 páginasTrachea and Lung Anatomy Functionssamia islamAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Systems in Cystic Fibrosis PatientsDocumento24 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Systems in Cystic Fibrosis PatientsKyle WindsorAinda não há avaliações
- CatheterizationDocumento14 páginasCatheterizationV_RNAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Elimination: Four Major Parts of Urinary SystemDocumento17 páginasUrinary Elimination: Four Major Parts of Urinary SystemMabes100% (2)
- Vpatho Module 2Documento73 páginasVpatho Module 2Lib PalmaresAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento23 páginasCystic Fibrosisclarytah0% (1)
- Presentation of Cystic FibrosisDocumento16 páginasPresentation of Cystic Fibrosisanon-662103100% (3)
- CYSTIC FIBROSIS Explanation EndDocumento3 páginasCYSTIC FIBROSIS Explanation EndRenee Dwi Permata MessakaraengAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento71 páginasCystic Fibrosishumera0% (1)
- Cystic Fibrosis TextDocumento9 páginasCystic Fibrosis Textzoe drullardAinda não há avaliações
- L8 - Digestion and Absorption - 6th AugDocumento45 páginasL8 - Digestion and Absorption - 6th AugSupritam KunduAinda não há avaliações
- 1.3.7 Cystic Fibrosis: Chapter 3 Cystic Fibrosis HBIO1 - The Body and Its Diseases AQA AS Human BiologyDocumento22 páginas1.3.7 Cystic Fibrosis: Chapter 3 Cystic Fibrosis HBIO1 - The Body and Its Diseases AQA AS Human BiologyMaha NaserAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento15 páginasCystic FibrosisRupesh M DasAinda não há avaliações
- Pemicu 1 Blok GiDocumento35 páginasPemicu 1 Blok GiMudita DewiAinda não há avaliações
- Pat Hop Harm OlogyDocumento1 páginaPat Hop Harm OlogyNoel BaluAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento2 páginasCystic FibrosismilaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of The Renal System For Pharmacy 2023Documento86 páginasPathophysiology of The Renal System For Pharmacy 2023Marlene NiyomuhozaAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic Fibrosis PDFDocumento4 páginasCystic Fibrosis PDFMostafa MahmoudAinda não há avaliações
- C Ystic Fibrosis (CF) : Learning Issues For Tutorial 2 Cheryl Tompkins, Group 6Documento3 páginasC Ystic Fibrosis (CF) : Learning Issues For Tutorial 2 Cheryl Tompkins, Group 6k2m1b6ksAinda não há avaliações
- Peptic UlcersDocumento4 páginasPeptic UlcersAkash JoeAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System and NutritionDocumento6 páginasDigestive System and NutritionAthena HuynhAinda não há avaliações
- Urinary Elimination: Kidneys, Bladder and Urine FormationDocumento14 páginasUrinary Elimination: Kidneys, Bladder and Urine FormationMina RacadioAinda não há avaliações
- Thomson - The Excretory SystemDocumento24 páginasThomson - The Excretory Systemapi-263178717Ainda não há avaliações
- Urinary System-Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento20 páginasUrinary System-Anatomy and PhysiologyFlo Neri BerondoAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic Fibrosis (Cont.)Documento3 páginasCystic Fibrosis (Cont.)Rellette Shane DangdangAinda não há avaliações
- Normal PhysiologyDocumento49 páginasNormal PhysiologyDakshayini MbAinda não há avaliações
- CholeraDocumento10 páginasCholeraapi-309893409Ainda não há avaliações
- Midterm Review 2009-10 2007Documento12 páginasMidterm Review 2009-10 2007TaylorAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic Fibrosis With Case StudyDocumento27 páginasCystic Fibrosis With Case StudyAviva Tuteja100% (1)
- Askep Tuberculosis (TBC) Paru: Bab I PendahuluanDocumento21 páginasAskep Tuberculosis (TBC) Paru: Bab I Pendahuluanayu maryeniAinda não há avaliações
- Biology: Chapter 6: NutrientDocumento6 páginasBiology: Chapter 6: NutrientNorashikin AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Cystic FibrosisDocumento28 páginasCystic FibrosisJon BoAinda não há avaliações
- CR Project On Cystic FibrosisDocumento3 páginasCR Project On Cystic FibrosisMorgan PeggAinda não há avaliações
- Cataracts: What Are They?Documento3 páginasCataracts: What Are They?RSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Mechanics Help BookletDocumento88 páginasPhysics Mechanics Help Bookletdj7597100% (1)
- DiseasesDocumento21 páginasDiseasesRSarkawy100% (1)
- TelomereDocumento38 páginasTelomereRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- 7096 IAL June 2014 Timetable - WEB v2Documento11 páginas7096 IAL June 2014 Timetable - WEB v2Nithoo NishAinda não há avaliações
- Complete Advanced Level Mathematics - Pure MathematicsDocumento512 páginasComplete Advanced Level Mathematics - Pure MathematicsRSarkawy86% (14)
- The Tenses in English GrammarDocumento6 páginasThe Tenses in English GrammarRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Matter Help BookletDocumento18 páginasPhysics Matter Help Bookletdj7597Ainda não há avaliações
- Cell AgingDocumento19 páginasCell AgingRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Advice Letters PDFDocumento5 páginasAdvice Letters PDFRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- 6PH01 01 Pef 20130815Documento66 páginas6PH01 01 Pef 20130815RSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Nuclear Physics A Level RevisionDocumento32 páginasNuclear Physics A Level Revisionsupniggas80% (5)
- June 2012 OLs Grade ThresholdsDocumento30 páginasJune 2012 OLs Grade ThresholdsRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Edexcel As BiologyDocumento1 páginaEdexcel As BiologyRSarkawy100% (1)
- Freindly Letters - Descriptive PDFDocumento11 páginasFreindly Letters - Descriptive PDFRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Biology RevisionDocumento3 páginasBiology RevisionMiguel HoffmannAinda não há avaliações
- Society and Sex RolesDocumento5 páginasSociety and Sex RolesRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Form Design 1 & 2Documento1 páginaForm Design 1 & 2RSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2Documento14 páginasUnit 2RSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Edexcel GCE Biology - AS Unit 3: Heart Rate / BPMDocumento1 páginaEdexcel GCE Biology - AS Unit 3: Heart Rate / BPMRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- 4BI0 1B Que 20130109Documento28 páginas4BI0 1B Que 20130109Sharif MahmudAinda não há avaliações
- 8BI01 GCE08 Biology Rep 20090813 US021143 Unit 3Documento12 páginas8BI01 GCE08 Biology Rep 20090813 US021143 Unit 3nourhanjAinda não há avaliações
- GCSE Business NotesDocumento43 páginasGCSE Business NotesGadgetshop Station33% (3)
- Edexcel Topic 2 Energy ChangesDocumento4 páginasEdexcel Topic 2 Energy ChangesSan SiddzAinda não há avaliações
- Behaviour in AnimalsDocumento14 páginasBehaviour in AnimalsRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- Answers On Next PageDocumento5 páginasAnswers On Next PageRSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- CH 5 Test Yourself Q & ADocumento1 páginaCH 5 Test Yourself Q & ARSarkawyAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Business Studies Revision GuideDocumento12 páginasIGCSE Business Studies Revision GuideRSarkawy50% (4)
- CH 23 Notes P2Documento1 páginaCH 23 Notes P2RSarkawyAinda não há avaliações