Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Discussin and Conclusion Geotechnical Falling Head
Enviado por
Azizi YahyaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Discussin and Conclusion Geotechnical Falling Head
Enviado por
Azizi YahyaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Discussion :
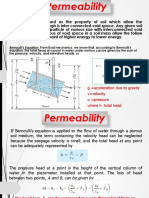
The passage of water through porous material is called seepage. A material with continuous voids is called a permeable material. Hence permeability is a property of a porous material which permits passage of fluids through inter connecting conditions. Hence permeability is defined as the rate of flow of water under laminar conditions through a unit cross-sectional area perpendicular to the direction of flow through a porous medium under unit hydraulic gradient and under standard temperature conditions. The principle behind the test is Darcys law for laminar flow. The rate of discharge is proportional to (i x A)
q= kiA
We calculate permeability of the soil by using the following equation :
Where: K = coefficient of permeability at temperature T, cm/sec. L = length of specimen in centimeters t = time for discharge in seconds Q = volume of discharge in cm3 (assume 1 mL = 1 cm3) A = cross-sectional area of h = hydraulic head difference across length L, in cm of water;
During test there should be no volume change in the soil, there should be no compressible air present in the voids of soil i.e. soil should be completely saturated. The flow should be laminar and in a steady state condition. Coefficient of permeability is used to assess drainage characteristics of soil, to predict rate of settlement founded on soil bed.
Conclusion :
The Coefficient of permeability for 5th minutes = 0.1774 cm/s Coefficient of permeability for 6th minutes = 0.2007 cm/s
Você também pode gostar
- 3.0 Determination of Liquid Limit Using The Cone PenetrometerDocumento10 páginas3.0 Determination of Liquid Limit Using The Cone PenetrometerasAinda não há avaliações
- Sand ReplacementDocumento4 páginasSand ReplacementHidayah MuzaimilAinda não há avaliações
- LAB 8 - Compaction - LEVEL 2 - AINUR NASUHA BINTI MOHAMMAD RODZI-2019892466Documento8 páginasLAB 8 - Compaction - LEVEL 2 - AINUR NASUHA BINTI MOHAMMAD RODZI-2019892466Ainur NasuhaAinda não há avaliações
- LAB 1 - PARTICLE DENSITY & MOISTURE CONTENT (Level 1)Documento6 páginasLAB 1 - PARTICLE DENSITY & MOISTURE CONTENT (Level 1)Muhd MuqhreyAinda não há avaliações
- Aggregate Impact ValueDocumento8 páginasAggregate Impact ValueAnis Nurfarahanim Abdul HalimAinda não há avaliações
- Falling Head PermeabilityDocumento13 páginasFalling Head PermeabilitySitiAinda não há avaliações
- Dry Sieve AnalysisDocumento9 páginasDry Sieve AnalysisHamierul Mohamad0% (1)
- Report Lab 2b Fault Bedding Lab 2bDocumento9 páginasReport Lab 2b Fault Bedding Lab 2bfuad haziqAinda não há avaliações
- ConclusionDocumento1 páginaConclusionmacs_smac100% (3)
- Soil Compaction LabDocumento7 páginasSoil Compaction LabShiva Jake Ramberan100% (1)
- Aggregate Crushing Value Test Lab ReportDocumento2 páginasAggregate Crushing Value Test Lab ReportComr A Y ZarginaAinda não há avaliações
- Sieve AnalysisDocumento7 páginasSieve AnalysisTinaaTiny100% (1)
- Lab 3: Atterberg Limits CE 340Documento8 páginasLab 3: Atterberg Limits CE 340satyam agarwal100% (1)
- Atterburg Limits Lab Report (Lab Report 1)Documento18 páginasAtterburg Limits Lab Report (Lab Report 1)ahsannasha67% (3)
- Lab Sheet - Atterberg LimitsDocumento6 páginasLab Sheet - Atterberg LimitsLuqman YusofAinda não há avaliações
- Falling Heat Permeability TestDocumento10 páginasFalling Heat Permeability TestAiryn UyienAinda não há avaliações
- Shear Box TestDocumento13 páginasShear Box TestNoor100% (1)
- Unconfined Compression TestDocumento6 páginasUnconfined Compression TestBahaaAbdalkareemAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Atterberg LimitDocumento7 páginasLab Atterberg LimitAnip EsanAinda não há avaliações
- UU Test ReportDocumento4 páginasUU Test ReportSharunieRavikumar33% (3)
- Lab Report Vicat TestDocumento2 páginasLab Report Vicat TestmanAinda não há avaliações
- Full Report HighwayDocumento19 páginasFull Report HighwayShahrel Bin Salleh100% (1)
- DiscussionDocumento4 páginasDiscussionOchini ChandrasenaAinda não há avaliações
- Consolidation TestDocumento4 páginasConsolidation TestrbhavishAinda não há avaliações
- Falling Head Permeability Lab TestDocumento6 páginasFalling Head Permeability Lab TestHamierul MohamadAinda não há avaliações
- Highway Report 2Documento30 páginasHighway Report 2Kerol Kerol Kerol100% (1)
- Standard Proctor Compaction TestDocumento3 páginasStandard Proctor Compaction TestSami Sami80% (5)
- Atterberg Limit: Liquid and Plastic Limit ReportDocumento6 páginasAtterberg Limit: Liquid and Plastic Limit ReportAbigail Lorico100% (2)
- Lab 6 - Unconfined Compression TestDocumento3 páginasLab 6 - Unconfined Compression Testdixn__0% (4)
- Lab Plastic LimitDocumento17 páginasLab Plastic LimitnurulselangorAinda não há avaliações
- Outflow MeterDocumento5 páginasOutflow MeterFirash ImranAinda não há avaliações
- Consolidation TestDocumento8 páginasConsolidation TestCasper da MagnificientAinda não há avaliações
- Plastic LimitDocumento9 páginasPlastic LimitPoovan Rajaratnam100% (1)
- Open Channel Flow Report LabDocumento16 páginasOpen Channel Flow Report LabShauQi Lutfi60% (5)
- Hydrometer PaperDocumento7 páginasHydrometer PaperdexAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulic Chapter3Documento78 páginasHydraulic Chapter3faraeiin570% (1)
- Standard Proctor Compaction TestDocumento7 páginasStandard Proctor Compaction TestGnabBang75% (4)
- Lab Soil UctDocumento3 páginasLab Soil UctSyed Zulfaizzuan AljufriAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 2 - Basic HydrologyDocumento18 páginasExperiment 2 - Basic HydrologyEiyra Nadia50% (2)
- Transport OpenEnded Lab UpdatedDocumento6 páginasTransport OpenEnded Lab UpdatedHwee YeeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 1 - Particle Density TestDocumento6 páginasLab 1 - Particle Density Testeijal1179% (14)
- 4) Hydrometer Analysis TestDocumento4 páginas4) Hydrometer Analysis TestPn Ekanayaka100% (4)
- Sieve AnalysisDocumento8 páginasSieve Analysisr6Yamaha100% (5)
- Compaction ReportDocumento6 páginasCompaction ReportharinderAinda não há avaliações
- Sand Replacement MethodDocumento8 páginasSand Replacement MethodMudin DinAinda não há avaliações
- Test Title Core CutterDocumento8 páginasTest Title Core Cutteraniem_beeAinda não há avaliações
- Constant Head Permeability TestDocumento6 páginasConstant Head Permeability TestSalih MohayaddinAinda não há avaliações
- Geomatics Lab Report 1Documento20 páginasGeomatics Lab Report 1szeweiAinda não há avaliações
- Dry Sieve ReportDocumento11 páginasDry Sieve ReportNoor Shahirah Md Ruba'i93% (15)
- Lab Manual 3.2 - LEVEL 1 - Determination of Hydraulic Parameters in Uniform Flow For Open Channels.Documento4 páginasLab Manual 3.2 - LEVEL 1 - Determination of Hydraulic Parameters in Uniform Flow For Open Channels.Muhamad IzzanAinda não há avaliações
- Consolidation TestDocumento2 páginasConsolidation TestTenzinKesang100% (1)
- 2) Linear Shrinkage TestDocumento4 páginas2) Linear Shrinkage TestPn Ekanayaka75% (4)
- Falling Head Permeability TestDocumento8 páginasFalling Head Permeability Testdwivediashish2100% (2)
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985No EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Ainda não há avaliações
- Bernoulli's Equation: From Fluid Mechanics, We Know That, According To Bernoulli'sDocumento40 páginasBernoulli's Equation: From Fluid Mechanics, We Know That, According To Bernoulli'sJami Ahmed100% (1)
- G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadDocumento23 páginasG Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadMinhaz Khan100% (1)
- Lesson 8Documento16 páginasLesson 8Joash SalamancaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento13 páginasChapter 6Ma. Niña Michelle ElicAinda não há avaliações
- Permeability: G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadDocumento22 páginasPermeability: G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadSabiha sultanaAinda não há avaliações
- CE 411 AssignmentDocumento2 páginasCE 411 Assignmentibrahimaabdullahi0508Ainda não há avaliações
- Chiller SystemDocumento1 páginaChiller SystemAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Solic Mechanic Apr2009 Past Year PDFDocumento23 páginasSolic Mechanic Apr2009 Past Year PDFAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Chiller SystemDocumento1 páginaChiller SystemAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Chiller SystemDocumento1 páginaChiller SystemAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Disscusion Survey TraverseDocumento2 páginasDisscusion Survey TraverseAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Chiller SystemDocumento1 páginaChiller SystemAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- ELS LevellingDocumento21 páginasELS LevellingHironmoy DashAinda não há avaliações
- ColliMatiOn Error On SurveyingDocumento1 páginaColliMatiOn Error On SurveyingAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Levelling Result EditedDocumento3 páginasLevelling Result EditedAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- TAcheoasdsd Asddas DsadsDocumento1 páginaTAcheoasdsd Asddas DsadsAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Orthographic ProjectionDocumento44 páginasOrthographic ProjectionAzizi YahyaAinda não há avaliações