Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Skin Anatomy
Enviado por
YayaswaraDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Skin Anatomy
Enviado por
YayaswaraDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The skin is an ever-changing organ that contains many specialized cells and structures.
The skin functions as a protective barrier that interfaces with a sometimes-hostile environment. It is also very involved in maintaining the proper temperature for the body to function well. It gathers sensory information from the environment, and plays an active role in the immune system protecting us from disease. Understanding how the skin can function in these many ways starts with understanding the structure of the 3 layers of skin - the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. Epidermis The epidermis is the outer layer of skin. The thickness of the epidermis varies in different types of skin. It is the thinnest on the eyelids at .05 mm and the thickest on the palms and soles at 1.5 mm. The epidermis contains 5 layers. From bottom to top the layers are named:
stratum basale stratum spinosum stratum granulosum stratum licidum stratum corneum
The bottom layer, the stratum basale, has cells that are shaped like columns. In this layer the cells divide and push already formed cells into higher layers. As the cells move into the higher layers, they flatten and eventually die. The top layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum, is made of dead, flat skin cells that shed about every 2 weeks.
Illustration of maturation of epidermis cells
Specialized Epidermal Cells There are three types of specialized cells in the epidermis.
The melanocyte produces pigment (melanin) The Langerhans' cell is the frontline defense of the immune system in the skin The Merkel's cell's function is not clearly known
Dermis The dermis also varies in thickness depending on the location of the skin. It is .3 mm on the eyelid and 3.0 mm on the back. The dermis is composed of three types of tissue that are present throughout - not in layers. The types of tissue are:
collagen elastic tissue reticular fibers
Layers of the Dermis The two layers of the dermis are the papillary and reticular layers.
The upper, papillary layer, contains a thin arrangement of collagen fibers. The lower, reticular layer, is thicker and made of thick collagen fibers that are arranged parallel to the surface of the skin.
Specialized Dermal Cells The dermis contains many specialized cells and structures.
The hair follicles are situated here with the erector pili muscle that attaches to each follicle. Sebaceous (oil) glands and apocrine (scent) glands are associated with the follicle. This layer also contains eccrine (sweat) glands, but they are not associated with hair follicles. Blood vessels and nerves course through this layer. The nerves transmit sensations of pain, itch, and temperature. There are also specialized nerve cells called Meissner's and Vater-Pacini corpuscles that transmit the sensations of touch and pressure.
Subcutaneous Tissue The subcutaneous tissue is a layer of fat and connective tissue that houses larger blood vessels and nerves. This layer is important is the regulation of temperature of the skin itself and the body. The size of this layer varies throughout the body and from person to person. The skin is a complicated structure with many functions. If any of the structures in the skin are not working properly, a rash or abnormal sensation is the result. The whole specialty of dermatology is devoted to understanding the skin, what can go wrong, and what to do if something does go wrong.
Kulit adalah organ yang selalu berubah yang mengandung sel-sel khusus banyak dan struktur. Fungsi kulit sebagai pelindung yang interface dengan lingkungan kadang-bermusuhan. Hal ini juga sangat terlibat dalam mempertahankan suhu yang tepat bagi tubuh untuk berfungsi dengan baik. Hal mengumpulkan informasi sensorik dari lingkungan, dan memainkan peran aktif dalam sistem kekebalan tubuh melindungi kita dari penyakit. Memahami bagaimana kulit dapat berfungsi dalam banyak cara dimulai dengan memahami struktur 3 lapisan kulit - epidermis, dermis, dan jaringan subkutan. Kulit ari Epidermis adalah lapisan luar kulit. Ketebalan epidermis bervariasi dalam berbagai jenis kulit. Ini adalah yang tertipis di kelopak mata pada 05 mm dan tebal di telapak tangan dan telapak kaki sebesar 1,5 mm. Epidermis mengandung 5 lapisan. Dari bawah ke atas lapisan yang bernama: stratum basale stratum spinosum stratum granulosum stratum licidum stratum korneum Lapisan bawah, basale strata, memiliki sel-sel yang berbentuk seperti kolom. Dalam lapisan ini sel-sel membelah dan dorong sudah terbentuk sel ke lapisan yang lebih tinggi. Sebagai sel bergerak ke dalam lapisan yang lebih tinggi, mereka merata dan akhirnya mati. Lapisan atas epidermis, stratum korneum, terbuat dari mati, sel-sel kulit yang datar yang menumpahkan setiap 2 minggu. Ilustrasi pematangan sel epidermis Khusus epidermal Sel Ada tiga jenis sel khusus dalam epidermis. Para melanosit memproduksi pigmen (melanin) Sel Langerhans 'adalah pertahanan garis depan dari sistem kekebalan pada kulit Fungsi sel Merkel itu tidak diketahui dengan jelas Dermis Dermis juga bervariasi dalam ketebalan tergantung pada lokasi kulit. Ini adalah .3 mm pada kelopak mata dan 3,0 mm di bagian belakang. Dermis terdiri dari tiga jenis jaringan yang ada di seluruh - tidak dalam lapisan. Jenis-jenis jaringan adalah: kolagen elastis jaringan
reticular serat Lapisan dermis yang Dua lapisan dermis adalah lapisan papiler dan retikuler. Lapisan, atas papiler, berisi pengaturan tipis dari serat kolagen. Lapisan, rendah retikuler, lebih tebal dan terbuat dari serat kolagen tebal yang disusun sejajar dengan permukaan kulit. Khusus Dermal Sel Dermis mengandung sel-sel khusus banyak dan struktur. Folikel rambut yang terletak di sini dengan otot pili erector yang melekat pada masing-masing folikel. Sebaceous (minyak) dan kelenjar (aroma) apokrin kelenjar yang terkait dengan folikel. Lapisan ini juga mengandung eccrine (keringat) kelenjar, tetapi mereka tidak terkait dengan folikel rambut. Pembuluh darah dan saraf saja melalui lapisan ini. Saraf mengirimkan sensasi rasa sakit, gatal, dan suhu. Ada juga sel-sel saraf khusus yang disebut Meissner ini dan Vater-Pacini korpuskel yang mengirimkan sensasi sentuhan dan tekanan. Subkutan Tissue Jaringan subkutan adalah lapisan jaringan lemak dan ikat yang rumah pembuluh darah besar dan saraf. Lapisan ini penting adalah pengaturan suhu kulit itu sendiri dan tubuh. Ukuran lapisan ini bervariasi di seluruh tubuh dan dari orang ke orang. Kulit adalah struktur rumit dengan banyak fungsi. Jika salah satu struktur di kulit tidak bekerja dengan benar, sensasi ruam atau abnormal adalah hasilnya. Keistimewaan seluruh dermatologi dikhususkan untuk memahami kulit, apa yang bisa salah, dan apa yang harus dilakukan jika ada sesuatu yang salah.
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Cut-And-Assemble Paper Skin Model: Background InformationDocumento4 páginasCut-And-Assemble Paper Skin Model: Background Informationnao_gataAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Sensory ConsiderationsDocumento20 páginasSensory Considerationsmujtaba malikAinda não há avaliações
- Human Ear Worksheet PDFDocumento3 páginasHuman Ear Worksheet PDFRamisaAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Jan Nicole Salimbangon - NERVOUS SYSTEM PDFDocumento31 páginasJan Nicole Salimbangon - NERVOUS SYSTEM PDFJan Nicole SalimbangonAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Sciences in Ophthalmology - 9788184486087-EmailDocumento446 páginasBasic Sciences in Ophthalmology - 9788184486087-EmailwulanfarichahAinda não há avaliações
- Camel IntegumentDocumento4 páginasCamel IntegumentDarkCupid Mynhero100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- PNS and Special SensesDocumento12 páginasPNS and Special SensesChristine Joanne CelendroAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Eye andDocumento86 páginasAssessment and Management of Patients With Eye andEsmareldah Henry SirueAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
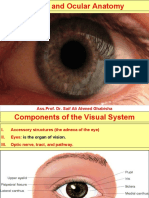
- Ass - Prof. Dr. Saif Ali Ahmed GhabishaDocumento103 páginasAss - Prof. Dr. Saif Ali Ahmed Ghabishaalina nguynAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Bullous Pemphigoid Vs Epydermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: Diagnosis and How To DifferentiateDocumento12 páginasBullous Pemphigoid Vs Epydermolysis Bullosa Acquisita: Diagnosis and How To DifferentiateIrene Irene100% (1)
- The Quick Guide To OCT Mastery - Vol. 1 - PreviewDocumento12 páginasThe Quick Guide To OCT Mastery - Vol. 1 - PreviewANDREW OMAKAAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Family Case AnalysisDocumento194 páginasFamily Case AnalysisDianneAinda não há avaliações
- EGurukul - SquintDocumento21 páginasEGurukul - SquintOscar Daniel MendezAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Cataract InformationDocumento25 páginasCataract Informationvasanth_1515Ainda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Postinflamatory Hyperpigmentation: Pembimbing: Dr. Retno Mustikaningsih, Sp. KK Oleh: Muhammad Fadhil SiregarDocumento19 páginasPostinflamatory Hyperpigmentation: Pembimbing: Dr. Retno Mustikaningsih, Sp. KK Oleh: Muhammad Fadhil Siregarking adjucasAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocumento33 páginasThe Human Eye and The Colourful WorldHarshit GoelAinda não há avaliações
- Mine? ? ??Documento16 páginasMine? ? ??Samskruthi ChallaAinda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary of Our Senses PDFDocumento3 páginasVocabulary of Our Senses PDFDavid EcheverriaAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- NCM IO3 Eye ExaminationDocumento50 páginasNCM IO3 Eye ExaminationNicole NipasAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Anatomy Topography of The EyeDocumento46 páginasAnatomy Topography of The Eyeikayapmd100% (1)
- Nasal Analysis and Anatomy: Anthropometric Proportional Assessment in Asians-Aesthetic Balance From Forehead To Chin, Part IDocumento7 páginasNasal Analysis and Anatomy: Anthropometric Proportional Assessment in Asians-Aesthetic Balance From Forehead To Chin, Part IAngga PutraAinda não há avaliações
- Four Major Divisions of Auditory System - AnatomyDocumento9 páginasFour Major Divisions of Auditory System - AnatomyJoshuaAinda não há avaliações
- Neuro Osce Cheat Sheet LolsDocumento1 páginaNeuro Osce Cheat Sheet LolsDjan Kurvie ValencerinaAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Structure of SkinDocumento19 páginasStructure of SkinFiqi Lampard100% (1)
- Keratitis and Corneal Ulcers in Patients Visiting at Hospital Dr.H.Abdoel Moeloek Lampung Province in 2013-2014Documento10 páginasKeratitis and Corneal Ulcers in Patients Visiting at Hospital Dr.H.Abdoel Moeloek Lampung Province in 2013-2014Alif OktaviaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of The Ear TMN NewDocumento26 páginasAnatomy of The Ear TMN NewMerriAinda não há avaliações
- Otitis Media - CSDocumento14 páginasOtitis Media - CSMASII100% (3)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Part I. Multiple Choice: Direction: Read Each Question Carefully. Choose The Letter of The CorrectDocumento3 páginasPart I. Multiple Choice: Direction: Read Each Question Carefully. Choose The Letter of The CorrectHanna Grace Honrade100% (1)
- P.A. 1Documento6 páginasP.A. 1SamSarah BongolanAinda não há avaliações
- 8 KandleDocumento7 páginas8 KandleKezia KurniaAinda não há avaliações