Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Simple Colloid Goitre
Enviado por
A. Pathak50%(2)50% acharam este documento útil (2 votos)
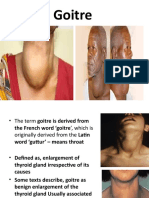
4K visualizações7 páginasGoitre is defined as thyroid enlargement caused by compensatory hyperplasia and hypertrophy of follicular epithelium. Goitre reflects impaired synthesis of thyroid hormone, most often due to dietary deficiency of iodine.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PPT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoGoitre is defined as thyroid enlargement caused by compensatory hyperplasia and hypertrophy of follicular epithelium. Goitre reflects impaired synthesis of thyroid hormone, most often due to dietary deficiency of iodine.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT ou leia online no Scribd
50%(2)50% acharam este documento útil (2 votos)
4K visualizações7 páginasSimple Colloid Goitre
Enviado por
A. PathakGoitre is defined as thyroid enlargement caused by compensatory hyperplasia and hypertrophy of follicular epithelium. Goitre reflects impaired synthesis of thyroid hormone, most often due to dietary deficiency of iodine.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 7
Simple Colloid Goitre
• Goitre is defined as thyroid
enlargement caused by
compensatory hyperplasia and
hypertrophy of follicular epithelial
response to Thyroid hormone
deficiency.
Etiopathogenesis
• Two morphological forms of
goitre are distinguished,
–Simple or colloid goitre.
–Nodular goitre.
• The presence of goitre reflects
impaired synthesis of thyroid hormone,
most often due to dietary deficiency of
iodine. Impairment of thyroid hormone
synthesis leads to a compensatory rise
in serum TSH level which in turn
causes hypertrophy and hyperplasia of
thyroid follicular cells, which ultimately
causes gross enlargement of thyroid.
Gross Appearance
• In colloid goitre the enlargement of
thyroid gland is moderate,
symmetric and diffuse.
• Cut surface is gelatinous and
translucent brown. Secondary
changes such as fibrosis,
haemorrhage, cystic degeneration
and calcification are common in
late presentations
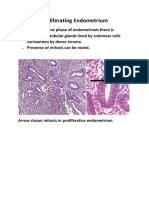
Microscopic appearance
• The follicular epithelium shows 2
stages,Hyperplastic stage (early
stage).Involution stage (late stage).
• Hyperplastic stage: It is the early stage
and is characterised by tall columnar
follicular epithelium showing papillary
infoldings and formation of small new
follicles
• Involution stage: Generally follows
hyperplastic stage after variable period of
time. This stage is characterised by small to
large follicles distended by colloid and lined
by flat follicular epithelium. Few follicles may
show microscopic papillae formation. Areas
of haemorhage may be seen at places.
Fibrous scarring with foci of calcification may
also be seen.
Flat epithelium
Colloid
Você também pode gostar
- AnaemiaDocumento70 páginasAnaemiaapi-3822841Ainda não há avaliações
- 2014 - Lecture - Pathology of The Small and Large IntestineDocumento12 páginas2014 - Lecture - Pathology of The Small and Large IntestinesammysandsongAinda não há avaliações
- AnaemiaDocumento4 páginasAnaemiaHarinash RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple MyelomaDocumento46 páginasMultiple MyelomaHula Hulahulag100% (1)
- Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar StateDocumento17 páginasHyperglycemic Hyperosmolar StateAqila Mumtaz50% (2)
- Renal Tubular Acidosis SlideshareDocumento31 páginasRenal Tubular Acidosis Slidesharehector100% (1)
- Bullous PemphigoidDocumento21 páginasBullous PemphigoidChe Ainil ZainodinAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacotherapy of Urinary Tract InfectionDocumento75 páginasPharmacotherapy of Urinary Tract InfectionMariana CreciunAinda não há avaliações
- GoiterDocumento42 páginasGoiterWw WwAinda não há avaliações
- GoiterDocumento33 páginasGoiterAmit Maniar0% (1)
- GoitreDocumento20 páginasGoitreSuma100% (1)
- Endocrine PathologyDocumento157 páginasEndocrine Pathologynoto susantoAinda não há avaliações
- NONTOXIC GOITER NarationDocumento2 páginasNONTOXIC GOITER NarationJam JamaAinda não há avaliações
- PDF]Jan-Febc 2010 - Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers jaypeebrothers.com/pdf/cataloginmonths/jan-feb2010.pdf by S Bhat - 2010 A unique book on clinical methods in surgery along with interactive DVD-ROM ... and clinical approach to each and individual surgical cases .... including a brief outline on prognosis. • Provides in-depth ..... Susmita Bhattacharya. Epidemiology. mbbs books - Scribd https://www.scribd.com/doc/239765747/mbbs-books Sep 15, 2014 - mbbs books - Download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text ... BHATTACHARYA SHORT CASES IN SURGERY 5TH 2002 200.00 BOOKS1 - Scribd https://www.scribd.com/doc/99385577/BOOKS1 Jul 7, 2012 - BOOKS1 - Ebook download as PDF File (.pdf), Text file (.txt) or read book ... LAWRENCE W. SHORT CASES IN SURGERY / BHATTACHARYA, ... Medical Books - mbbs exam questions for second third and ... hafeesh.blogspot.com/2009/12/medical-books.html Dec 25, 2009 - GUPTE SHORT TEXTBOOK OF MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 8TH 2002 .... BHATTACHARYA SHORT CASESDocumento3 páginasPDF]Jan-Febc 2010 - Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers jaypeebrothers.com/pdf/cataloginmonths/jan-feb2010.pdf by S Bhat - 2010 A unique book on clinical methods in surgery along with interactive DVD-ROM ... and clinical approach to each and individual surgical cases .... including a brief outline on prognosis. • Provides in-depth ..... Susmita Bhattacharya. Epidemiology. mbbs books - Scribd https://www.scribd.com/doc/239765747/mbbs-books Sep 15, 2014 - mbbs books - Download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text ... BHATTACHARYA SHORT CASES IN SURGERY 5TH 2002 200.00 BOOKS1 - Scribd https://www.scribd.com/doc/99385577/BOOKS1 Jul 7, 2012 - BOOKS1 - Ebook download as PDF File (.pdf), Text file (.txt) or read book ... LAWRENCE W. SHORT CASES IN SURGERY / BHATTACHARYA, ... Medical Books - mbbs exam questions for second third and ... hafeesh.blogspot.com/2009/12/medical-books.html Dec 25, 2009 - GUPTE SHORT TEXTBOOK OF MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 8TH 2002 .... BHATTACHARYA SHORT CASESSaiSuryaTeja0% (1)
- Blood Cell MorphologyDocumento41 páginasBlood Cell MorphologykinausmanAinda não há avaliações
- Granulomatous Inflammation ThyroidDocumento55 páginasGranulomatous Inflammation ThyroidKamlesh PrajapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah Patologi Gangguan Metabolisme 2017Documento89 páginasKuliah Patologi Gangguan Metabolisme 2017Oman SetiyantoAinda não há avaliações
- Ug Practical SlideDocumento18 páginasUg Practical SlideKAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 MLTDocumento24 páginasLecture 2 MLTAbood dot netAinda não há avaliações
- Degenerative ChangesDocumento45 páginasDegenerative ChangesAbhishek JhaAinda não há avaliações
- 4 I Morpho - Reversible Cell InjuryDocumento21 páginas4 I Morpho - Reversible Cell InjuryKartikey MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Atrophy, Metaplasia, Cloudy Swelling 13.6.2014 CDocumento21 páginasAtrophy, Metaplasia, Cloudy Swelling 13.6.2014 CPradeepAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid and Parathyroid PathologyDocumento68 páginasThyroid and Parathyroid PathologygregAinda não há avaliações
- Premalignant Lesions & ConditionsDocumento76 páginasPremalignant Lesions & ConditionsAman KankariaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathology of The Thyroid Gland: Prof. Dipak Shah Department of Pathology UWI, MonaDocumento44 páginasPathology of The Thyroid Gland: Prof. Dipak Shah Department of Pathology UWI, MonaadeprieAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid GlandDocumento4 páginasThyroid GlandLea MonzerAinda não há avaliações
- Endemic GoiterDocumento4 páginasEndemic GoiterAishaAinda não há avaliações
- L1 Hypo, Hyperthyroidism and Hashimoto ThyroiditisDocumento12 páginasL1 Hypo, Hyperthyroidism and Hashimoto ThyroiditisSivaAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Neoplastic Disorders: Lymphoid SystemDocumento36 páginasNon-Neoplastic Disorders: Lymphoid SystemMutiana Muspita JeliAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Vstup Do Patologii DystrofiiDocumento18 páginas1 Vstup Do Patologii DystrofiiPraveen NayakAinda não há avaliações
- ADAPTATIONSDocumento32 páginasADAPTATIONSMahalakshmi PalanisamiAinda não há avaliações
- THYROID GLAND Final (Autosaved)Documento81 páginasTHYROID GLAND Final (Autosaved)ABUBEKER BESHIRAinda não há avaliações
- I. Intracellular Accumulations of Lipids Fatty ChangeDocumento5 páginasI. Intracellular Accumulations of Lipids Fatty ChangeIsak ShatikaAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Criteria and NomenclatureDocumento17 páginasDiagnostic Criteria and NomenclatureRavishankar NagarajanAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Swelling and Overload of Glycogen, Protein and Cholesterol in CellDocumento20 páginasCellular Swelling and Overload of Glycogen, Protein and Cholesterol in CellMohan ChoudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Block 4 Quiz+ Lab Exam ReviewDocumento47 páginasBlock 4 Quiz+ Lab Exam ReviewMira ThakkarAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Thyroid GlandDocumento40 páginas7 Thyroid GlandNipun ShamikaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 - Intra and Extra-Cellular Accumulation RevisedDocumento54 páginas1 - Intra and Extra-Cellular Accumulation Revisedaimi BatrisyiaAinda não há avaliações
- Pigmentation DisordersDocumento32 páginasPigmentation DisordersElijah MogoaAinda não há avaliações
- Benign Thyroid DiseasesDocumento138 páginasBenign Thyroid DiseasesAliAinda não há avaliações
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC)Documento19 páginasVernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC)api-3742497Ainda não há avaliações
- Pathology Seminar Review (Semester 1)Documento26 páginasPathology Seminar Review (Semester 1)Lin AdutAinda não há avaliações
- NNYGDocumento13 páginasNNYGrose OAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Injury & Cellular Adaptations: Dr. Vigneshwara N Junior Resident, ImchDocumento113 páginasCell Injury & Cellular Adaptations: Dr. Vigneshwara N Junior Resident, ImchAjmal RockzzAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Injury: Ii PharmdDocumento51 páginasCell Injury: Ii PharmdBharath GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- Tuberculous LymphadenitisDocumento16 páginasTuberculous LymphadenitisA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Leukocytes: - GranulocytesDocumento38 páginasLeukocytes: - GranulocytesCurrencyAinda não há avaliações
- Epithelial Tissue - Clinical Correlations and Glandular EpitheliumDocumento14 páginasEpithelial Tissue - Clinical Correlations and Glandular EpitheliumWynlor AbarcaAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid EnlargementDocumento6 páginasThyroid Enlargementthev0206Ainda não há avaliações
- Thyroid GlandDocumento59 páginasThyroid Glandbessan alfqeatAinda não há avaliações
- University of Gondar Cmhs Departement of OptometryDocumento47 páginasUniversity of Gondar Cmhs Departement of Optometryhaymanot aynalemAinda não há avaliações
- Synopsis: Gestational Trophoblastic DiseasesDocumento74 páginasSynopsis: Gestational Trophoblastic DiseasesJeena RajAinda não há avaliações
- Soft Tissue PicDocumento132 páginasSoft Tissue PicDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands: Hurthle CellsDocumento25 páginasThyroid & Parathyroid Glands: Hurthle CellschristianAinda não há avaliações
- Multinodular Goiter: Dr.V.V.Subrahmanyam Professor of Surgery Narayana Medical College & HospitalDocumento34 páginasMultinodular Goiter: Dr.V.V.Subrahmanyam Professor of Surgery Narayana Medical College & HospitalPraveen Chandra GanjiAinda não há avaliações
- Intracellular Accumulations:: Substances That May Be Harmless or Cause Varied Degrees of Cell InjuryDocumento6 páginasIntracellular Accumulations:: Substances That May Be Harmless or Cause Varied Degrees of Cell InjuryyuvanAinda não há avaliações
- Gestational Trophoblastic Diseases FinalDocumento71 páginasGestational Trophoblastic Diseases FinalJeena RajAinda não há avaliações
- Alcoholic HepatitisDocumento28 páginasAlcoholic HepatitisWaqar AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation GametogenesisDocumento33 páginasPresentation GametogenesisAndy ZempaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Injury: Third Grade 312 Theory Dr. Batool SalimDocumento17 páginasCell Injury: Third Grade 312 Theory Dr. Batool SalimAli AzizAinda não há avaliações
- Bacterial ToxinsDocumento25 páginasBacterial ToxinsA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocumento66 páginasHypersensitivity ReactionsA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Physiochemical and Microbial Quality of Boiled MilkDocumento6 páginasPhysiochemical and Microbial Quality of Boiled MilkA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Biodiversity and Concentration of Airborne Fungi of Suburban Weekly Market Associated EnvironmentDocumento8 páginasBiodiversity and Concentration of Airborne Fungi of Suburban Weekly Market Associated EnvironmentA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Extramural Aero-Bacteriological Quality of Hospital EnvironmentDocumento8 páginasExtramural Aero-Bacteriological Quality of Hospital EnvironmentA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- InfectionDocumento72 páginasInfectionA. Pathak100% (1)
- Assessment of Air-Borne Bacteria of Urban Grain-Market AreaDocumento10 páginasAssessment of Air-Borne Bacteria of Urban Grain-Market AreaA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Giant Cell Tumor or OsteoclastomaDocumento6 páginasGiant Cell Tumor or OsteoclastomaA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Sant Chetana Ka MatrupravahDocumento60 páginasSant Chetana Ka MatrupravahA. Pathak100% (1)
- Primary ImmunodeficiencyDocumento140 páginasPrimary ImmunodeficiencyA. Pathak100% (1)
- Pleomorphic Adenoma of Parotid GlandDocumento14 páginasPleomorphic Adenoma of Parotid GlandA. Pathak100% (1)
- Coins by Dr. H.D. PathakDocumento17 páginasCoins by Dr. H.D. PathakA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Revabhutis Coin by Dr. H. D. PathakDocumento15 páginasRevabhutis Coin by Dr. H. D. PathakA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Fibroadenoma of BreastDocumento7 páginasFibroadenoma of BreastA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- LipomaDocumento11 páginasLipomaA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Adenocarcinoma of BreastDocumento7 páginasAdenocarcinoma of BreastA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Tuberculous LymphadenitisDocumento16 páginasTuberculous LymphadenitisA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Auto ImmunityDocumento44 páginasAuto ImmunityA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocumento12 páginasSquamous Cell CarcinomaA. Pathak0% (1)
- Immune SystemDocumento145 páginasImmune SystemA. Pathak100% (9)
- MeningitisDocumento65 páginasMeningitisA. Pathak100% (7)
- Adhering To The Surface of HostDocumento50 páginasAdhering To The Surface of HostA. Pathak100% (1)
- Rare Coins From UJJAINDocumento18 páginasRare Coins From UJJAINA. Pathak100% (1)
- Acute AppendicitisDocumento8 páginasAcute AppendicitisA. PathakAinda não há avaliações
- Adenomatous PolypDocumento11 páginasAdenomatous PolypA. PathakAinda não há avaliações











![PDF]Jan-Febc 2010 - Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers jaypeebrothers.com/pdf/cataloginmonths/jan-feb2010.pdf by S Bhat - 2010 A unique book on clinical methods in surgery along with interactive DVD-ROM ... and clinical approach to each and individual surgical cases .... including a brief outline on prognosis. • Provides in-depth ..... Susmita Bhattacharya. Epidemiology. mbbs books - Scribd https://www.scribd.com/doc/239765747/mbbs-books Sep 15, 2014 - mbbs books - Download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text ... BHATTACHARYA SHORT CASES IN SURGERY 5TH 2002 200.00 BOOKS1 - Scribd https://www.scribd.com/doc/99385577/BOOKS1 Jul 7, 2012 - BOOKS1 - Ebook download as PDF File (.pdf), Text file (.txt) or read book ... LAWRENCE W. SHORT CASES IN SURGERY / BHATTACHARYA, ... Medical Books - mbbs exam questions for second third and ... hafeesh.blogspot.com/2009/12/medical-books.html Dec 25, 2009 - GUPTE SHORT TEXTBOOK OF MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 8TH 2002 .... BHATTACHARYA SHORT CASES](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/270707806/149x198/154b6610c1/1605034206?v=1)