Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Temporary Vision Loss in One Eye May Signal Impending Stroke
Enviado por
Bryan De HopeDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Temporary Vision Loss in One Eye May Signal Impending Stroke
Enviado por
Bryan De HopeDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Amaurosis fugax
Alternative Names
Transient monocular blindness
Definition of Amaurosis fugax
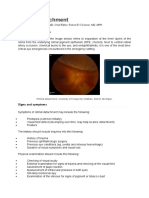
Amaurosis fugax is loss of vision in one eye due to a temporary lack of blood flow to the retina. It may be a sign of an impending stroke.
Causes, incidence, and risk factors
Amaurosis fugax is a symptom of carotid artery disease. It occurs when a piece of plaque in a carotid artery breaks off and travels to the retinal artery in the eye. The carotid arteries provide the main blood supply to the brain. They are located on each side of your neck under the jaw.
Symptoms
Symptoms include the sudden loss of vision in one eye. This usually only lasts seconds but may last several minutes. Some patients describe the loss of vision as a gray or black shade coming down over their eye.
Signs and tests
Tests include a complete eye and neurological exam. In some cases, an eye exam will reveal a bright spot where the clot is blocking the retinal artery. A carotid ultrasound or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) scan should be done to evaluate a blockage in the carotid artery.
Treatment
Treatment of amaurosis fugax depends on the severity of the blockage in the carotid artery. The goal of treatment is to prevent a stroke.
Expectations (prognosis)
Amaurosis fugax itself usually does not result in permanent disability. However, it means you have atherosclerosis and an increased risk for stroke.
Review
Daniel Kantor, MD, Medical Director of Neurologique, Ponte Vedra, FL and President of the Florida Society of Neurology (FSN). Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc. 10/4/2010
Você também pode gostar
- Causes and Symptoms of Amaurosis FugaxDocumento12 páginasCauses and Symptoms of Amaurosis FugaxSubashini G DeviAinda não há avaliações
- Bagheri 2015Documento15 páginasBagheri 2015Juliana Valentina CedeñoAinda não há avaliações
- Neurovascular DisordersDocumento42 páginasNeurovascular DisordersAlexandra Nedelcoff-GhiranlieffAinda não há avaliações
- Amaurosis FugaxDocumento11 páginasAmaurosis FugaxRexArtem100% (1)
- Neurovascular Conditions: Stroke and Transient Ischemic AttackDocumento7 páginasNeurovascular Conditions: Stroke and Transient Ischemic AttackGinAinda não há avaliações
- Neurovascular Conditions Treated at PennDocumento7 páginasNeurovascular Conditions Treated at PennFatrawati BahuaAinda não há avaliações
- Optic Neuritis: Demyelinating Disorders: Multiple Sclerosis (MS)Documento4 páginasOptic Neuritis: Demyelinating Disorders: Multiple Sclerosis (MS)Najibah YaAinda não há avaliações
- Retinal DetachmentDocumento10 páginasRetinal DetachmentSilpi HamidiyahAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebral AneurysmsDocumento45 páginasCerebral AneurysmsJerinAinda não há avaliações
- Retinal vein occlusion patient informationDocumento5 páginasRetinal vein occlusion patient informationRana PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Retinal Disorder Case StudyDocumento6 páginasRetinal Disorder Case StudyGabbii CincoAinda não há avaliações
- Note DRDocumento2 páginasNote DRZuhair Al-JaffalAinda não há avaliações
- Age-Related Macular Disease: Fitriani Umi Hasanah 201820401011121 Pembimbing: Dr. Fatin Hamamah, SP.MDocumento28 páginasAge-Related Macular Disease: Fitriani Umi Hasanah 201820401011121 Pembimbing: Dr. Fatin Hamamah, SP.MKim NayoungAinda não há avaliações
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion and Branch Retinal Vein OcclusionDocumento5 páginasCentral Retinal Vein Occlusion and Branch Retinal Vein OcclusionPOPPYAinda não há avaliações
- Literatur MataDocumento46 páginasLiteratur MataBoeng BektiAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Kasper Notes 2020 OphthalmologyDocumento33 páginas12 Kasper Notes 2020 OphthalmologyMohamed Rikarz Ahamed RikarzAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetic Eye Disease ExplainedDocumento35 páginasDiabetic Eye Disease Explainedruwan555Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is A Brain AVMDocumento5 páginasWhat Is A Brain AVMCj UritaAinda não há avaliações
- What is diabetic retinopathy and its stagesDocumento6 páginasWhat is diabetic retinopathy and its stagesArvindan SubramaniamAinda não há avaliações
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocumento3 páginasSubarachnoid Hemorrhagetenaj_purpleAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Brain AVM?: Symptoms and Bleeding Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento5 páginasWhat Is A Brain AVM?: Symptoms and Bleeding Diagnosis and Treatmentrita mulyanaAinda não há avaliações
- 4 RetinaDocumento59 páginas4 RetinaLala Komala Sari HakimAinda não há avaliações
- What Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? Symptoms, Types, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento4 páginasWhat Is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)? Symptoms, Types, Diagnosis and TreatmentRafika MonalisaAinda não há avaliações
- (Printing) Pass Medicine Notes - OphthalmologyDocumento22 páginas(Printing) Pass Medicine Notes - OphthalmologyJoanne HoAinda não há avaliações
- Sensory Impairment in Older AdultsDocumento22 páginasSensory Impairment in Older AdultsBethany CrusantAinda não há avaliações
- Optic AtrophyDocumento6 páginasOptic Atrophyrutuparna383Ainda não há avaliações
- Buta Mendadak / Acute Vision Loss: Dr. R. Handoko Pratomo, SPMDocumento33 páginasButa Mendadak / Acute Vision Loss: Dr. R. Handoko Pratomo, SPMSesria NasutionAinda não há avaliações
- Manage Neovascular GlaucomaDocumento13 páginasManage Neovascular GlaucomadennisadityaAinda não há avaliações
- Retinal Detachment Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento6 páginasRetinal Detachment Diagnosis and TreatmentDeasy Arindi PutriAinda não há avaliações
- EURETINA. Management of - Retinal Vein Occlusion.Documento40 páginasEURETINA. Management of - Retinal Vein Occlusion.Javier Infantes MolinaAinda não há avaliações
- Coats Disease GuideDocumento6 páginasCoats Disease GuideAnggie Imaniah SitompulAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryDocumento10 páginasCerebral Aneurysms: Aneurysms Posterior Circulation Basilar Artery Vertebral Arteries Posterior Communicating ArteryRani SujithAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Deep Learning Techniques For Prediction of Eye Diseases: A Systematic ReviewDocumento34 páginasAnalysis of Deep Learning Techniques For Prediction of Eye Diseases: A Systematic ReviewAkAnKsHa BaLiAinda não há avaliações
- 4 RetinaDocumento59 páginas4 RetinajanechaterineAinda não há avaliações
- Ahmed 2010Documento11 páginasAhmed 2010Karamjot SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Glaukoma UnilateralDocumento11 páginasGlaukoma UnilateralrenyAinda não há avaliações
- Ophthalmology - Passmedicine 2012 - 62013146Documento18 páginasOphthalmology - Passmedicine 2012 - 62013146abuahmed&janaAinda não há avaliações
- Central Retinal Artery Occlusion GuideDocumento16 páginasCentral Retinal Artery Occlusion GuidermurtiaAinda não há avaliações
- Abducens Nerve Palsy - AAODocumento6 páginasAbducens Nerve Palsy - AAOnurcahayaantikaAinda não há avaliações
- Ocular Ischemic Syndrome Survey OphthalmologyDocumento33 páginasOcular Ischemic Syndrome Survey OphthalmologyamaiacAinda não há avaliações
- Vision Loss PreventionDocumento22 páginasVision Loss Preventionmadara ëAinda não há avaliações
- Journal Article 20 334 PDFDocumento7 páginasJournal Article 20 334 PDFAnuj KodnaniAinda não há avaliações
- Vitreous Hemorrhage: Major ReviewDocumento4 páginasVitreous Hemorrhage: Major Reviewmutya yulindaAinda não há avaliações
- Case Based Ophthalmology GuideDocumento12 páginasCase Based Ophthalmology GuideGradestack100% (2)
- Bahan HimefaDocumento15 páginasBahan HimefaLili DelpianiAinda não há avaliações
- Age Related Macular DegenerationDocumento60 páginasAge Related Macular DegenerationputrifitriacahyaniAinda não há avaliações
- RvoDocumento43 páginasRvoOrchlon LkAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVMDocumento7 páginasCerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVMCj UritaAinda não há avaliações
- Vitreous HemorrhageDocumento7 páginasVitreous HemorrhageindahAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Age-Related Macular Degeneration?Documento2 páginasWhat Is Age-Related Macular Degeneration?Santosh Sharma VaranasiAinda não há avaliações
- Biousse 2017Documento7 páginasBiousse 2017elmon patadunganAinda não há avaliações
- Retinal DetachmentDocumento14 páginasRetinal DetachmentPui_Yee_Siow_6303Ainda não há avaliações
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage - Stroke (CVA) - Merck Manual Home Edition2Documento8 páginasSubarachnoid Hemorrhage - Stroke (CVA) - Merck Manual Home Edition2Noval LiadyAinda não há avaliações
- Proiect Nerv OpticDocumento7 páginasProiect Nerv Opticiuliabucur92Ainda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology of Arteriovenous Accesses for HemodialysisNo EverandDiagnostic and Interventional Radiology of Arteriovenous Accesses for HemodialysisAinda não há avaliações
- Neurology Equations Made Simple: Differential Diagnosis and NeuroemergenciesNo EverandNeurology Equations Made Simple: Differential Diagnosis and NeuroemergenciesAinda não há avaliações
- Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Current Treatment ConceptsNo EverandAge-Related Macular Degeneration: Current Treatment ConceptsW.E. AlbertiAinda não há avaliações
- Retinal and Choroidal Vascular Diseases of the EyeNo EverandRetinal and Choroidal Vascular Diseases of the EyeJay ChhablaniAinda não há avaliações
- Anti-Fungal Activity of Capsicum Frutescence and Zingiber Officinale Against Key Post-Harvest Pathogens in CitrusDocumento6 páginasAnti-Fungal Activity of Capsicum Frutescence and Zingiber Officinale Against Key Post-Harvest Pathogens in CitrusBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Story of My LifeDocumento3 páginasStory of My LifeBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Razer Cortex Diagnostics ReportDocumento8 páginasRazer Cortex Diagnostics ReportBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Me 1Documento7 páginasMe 1Bryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Follow UpDocumento2 páginasFollow UpBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- 4919 13766 1 PBDocumento4 páginas4919 13766 1 PBBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Situasi Kamar GueDocumento1 páginaSituasi Kamar GueBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Add On MozillaDocumento1 páginaAdd On MozillaBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Sri An A 0202Documento12 páginasSri An A 0202SelviAinda não há avaliações
- Situasi Kamar GueDocumento1 páginaSituasi Kamar GueBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Add On MozillaDocumento1 páginaAdd On MozillaBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Sudden Visual Loss Clinical PresentationDocumento8 páginasSudden Visual Loss Clinical PresentationBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- DissertationDocumento136 páginasDissertationBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Application PDFDocumento2 páginasApplication PDFBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Kistral Guide ArtileryDocumento5 páginasKistral Guide ArtileryBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- GINA Pocket2013 May15Documento0 páginaGINA Pocket2013 May15David BarzalloAinda não há avaliações
- LirikDocumento29 páginasLirikBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- 86 Normal Low Tension GlaucomaDocumento4 páginas86 Normal Low Tension GlaucomaBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Industry Interventions For Addressing MSD in NZ Meat ProcessingDocumento49 páginasIndustry Interventions For Addressing MSD in NZ Meat ProcessingBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Sprains and Strains FFDocumento4 páginasSprains and Strains FFBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- MUSCULOSKELETAL Sprains Strains Dislocations - NarraDocumento4 páginasMUSCULOSKELETAL Sprains Strains Dislocations - NarraBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Guia Muscul en Angles.v1355478068 2Documento25 páginasGuia Muscul en Angles.v1355478068 2Bryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Working Armour Control of Sprains Train Injuries 20251Documento30 páginasWorking Armour Control of Sprains Train Injuries 20251Bryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Scabies - NarraDocumento2 páginasScabies - NarraBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Sprains and Strains FFDocumento4 páginasSprains and Strains FFBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Scabies - NarraDocumento2 páginasScabies - NarraBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- MUSCULOSKELETAL Sprains Strains Dislocations - NarraDocumento4 páginasMUSCULOSKELETAL Sprains Strains Dislocations - NarraBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- 4919 13766 1 PBDocumento4 páginas4919 13766 1 PBBryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações
- Guia Muscul en Angles.v1355478068 2Documento25 páginasGuia Muscul en Angles.v1355478068 2Bryan De HopeAinda não há avaliações