Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
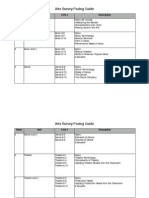
Math Pacing Guide
Enviado por
api-237679273Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Math Pacing Guide
Enviado por
api-237679273Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Mathematics Pacing Guide
Week 1 Unit Unit 1: Operations and Expressions COS # 6-EE1 6-EE2 6-EE3 6-EE4 6-EE6 6-NS4
Description
Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents. Write, read, and evaluate expressions in which letters stand for numbers. Apply the properties of operations to generate equivalent expressions. Identify when two expressions are equivalent (i.e., when the two expressions name the same number regardless of which value is substituted into them). Use variables to represent numbers, and write expressions when solving a realworld or mathematical problem; understand that a variable can represent an unknown number or, depending on the purpose at hand, any number in a specified set. Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Use the distributive property to express a sum of two whole numbers 1-100 with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no common factor. Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi-digit decimals using the standard algorithm for each operation.
Unit 2: Decimal Operations
6-NS2 6-NS3
Unit 4: Multiplying and 6-NS1 Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to Dividing Fractions
represent the problem.
Unit 5: Ratios, Rates, 6-RP1 Understand the concept of a ratio, and use ratio language to describe a ratio and Percents 6-RP2 relationship between two quantities. 6-RP3 Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b 0,
and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship. Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations.
Mathematics Pacing Guide
Week 5 Unit Unit 6: Units of Measure COS # Description
Understand that a set of data collected to answer a statistical question has a distribution which can be described by its center, spread, and overall shape. Recognize that a measure of center for a numerical data set summarizes all of its values with a single number, while a measure of variation describes how its values vary with a single number. Display numerical data in plots on a number line, including dot plots, histograms, and box plots.
6-SP5 Summarize numerical data sets in relation to their context.
Unit 7: Collect, 6-SP2 Organize, and Analyze 6-SP3 Data 6-SP4 6 Unit 8: Probability Unit 9: Integers
6-SP1 Recognize a statistical question as one that anticipates variability in the data related to the 6-NS5 6-NS6 6-NS7
Unit 10: Algebra: Equations and Functions
6-EE5 6-EE7 6-EE8 6-EE9 6-NS8
question and accounts for it in the answers. Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/ below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates. Understand ordering and absolute value of rational numbers. Understand solving an equation or inequality as a process of answering a question: which values from a specied set, if any, make the equation or inequality true? Use substitution to determine whether a given number in a specied set makes an equation or inequality true. Solve real-world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations of the form x + p = q and px = q for cases in which p, q, and x are all nonnegative rational numbers. Write an inequality of the form x > c or x < c to represent a constraint or condition in a realworld or mathematical problem. Recognize that inequalities of the form x > c or x < c have infinitely many solutions; represent solutions of such inequalities on number line diagrams. Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another; write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate.
Mathematics Pacing Guide
Week 8 Unit Unit 11: Geometric Figures COS # Description 6-G1 Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; 6-G3
apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. Draw polygons in the coordinate plane given coordinates for the vertices; use coordinates to nd the length of a side joining points with the same rst coordinate or the same second coordinate. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. Represent three-dimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles and triangles, and use the nets to find the surface area of these figures. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.
Unit 12: Perimeter and 6-G4 Area
Unit 13: Surface Area 6-G2 Find the volume of a right rectangular prism with fractional edge lengths by and Volume packing it with unit cubes of the appropriate unit fraction edge lengths, and show that the volume is the same as would be found by multiplying the edge lengths of the prism. Apply the formulas V = lwh and V = Bh to find volumes of right rectangular prisms with fractional edge lengths in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- FUll List Test Bank and Solution Manual 2020-2021 (Student Saver Team) - Best Copy 20001Documento222 páginasFUll List Test Bank and Solution Manual 2020-2021 (Student Saver Team) - Best Copy 20001Adam Kramer0% (3)
- Pre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)Documento2 páginasPre Test TOS Grade 8 Math (2016-17)Sherelyn Salanda AlcantaraAinda não há avaliações
- Example of A Student ScheduleDocumento1 páginaExample of A Student Scheduleapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Faculty and StaffDocumento2 páginasFaculty and Staffapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Mock School TechDocumento3 páginasMock School Techapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Lunch MenuDocumento6 páginasLunch Menuapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Beginning Band Pacing GuideDocumento3 páginasBeginning Band Pacing Guideapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Teacher ScheduleDocumento3 páginasTeacher Scheduleapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Arts Survey Pacing GuideDocumento3 páginasArts Survey Pacing Guideapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Science Pacing GuideDocumento3 páginasScience Pacing Guideapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Reading Pacing GuideDocumento2 páginasReading Pacing Guideapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Language Arts Pacing GuideDocumento4 páginasLanguage Arts Pacing Guideapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Physical Education Pacing GuideDocumento2 páginasPhysical Education Pacing Guideapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Social Science Pacing GuideDocumento3 páginasSocial Science Pacing Guideapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Report Card ScheduleDocumento1 páginaReport Card Scheduleapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Edu 4471 Activity Calendar Mock SchoolDocumento2 páginasEdu 4471 Activity Calendar Mock Schoolapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- R B Wiregrass Middle School Bell ScheduleDocumento1 páginaR B Wiregrass Middle School Bell Scheduleapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Year Long School CalendarDocumento1 páginaYear Long School Calendarapi-237679273Ainda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Paper For Class-X 2010Documento8 páginasMathematics Paper For Class-X 2010Apex Institute100% (2)
- Universiti: Pendidikan Sultan LorisDocumento4 páginasUniversiti: Pendidikan Sultan LorisChimChim UrkAinda não há avaliações
- Differential Equation NotesDocumento211 páginasDifferential Equation NotesRafael Almeida100% (1)
- Uem Sol To Exerc ContentsDocumento5 páginasUem Sol To Exerc Contents9Ak CHANNELAinda não há avaliações
- MA1002Documento1 páginaMA1002Cherry CharanAinda não há avaliações
- The Essentials of Finite Element Modeling and Adaptive RefinementDocumento29 páginasThe Essentials of Finite Element Modeling and Adaptive RefinementMomentum PressAinda não há avaliações
- Past Year 4 Paper 1Documento9 páginasPast Year 4 Paper 1syieraAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment I Maths I 1Documento3 páginasAssignment I Maths I 1yasharmasterAinda não há avaliações
- FmseDocumento5 páginasFmseJacky Boy Endencio AtienzaAinda não há avaliações
- Amch1: Mathematics Iii: 1. Partial Differentiation and Partial Differential EquationDocumento2 páginasAmch1: Mathematics Iii: 1. Partial Differentiation and Partial Differential EquationAnonymous 70lCzDJv100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Higher Order EquationsDocumento8 páginasChapter 5 Higher Order EquationsMehmet Akif KözAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Equation in One VariableDocumento22 páginasLinear Equation in One VariablethinkiitAinda não há avaliações
- MTE119 - Solutions Hw3Documento12 páginasMTE119 - Solutions Hw3Monojit KonarAinda não há avaliações
- 04 - Structural Engineering and Construction ManagementDocumento45 páginas04 - Structural Engineering and Construction ManagementCandace Buckner0% (1)
- M2 Unit 1Documento56 páginasM2 Unit 1Hitwardhan DhadwalAinda não há avaliações
- Free Body DiagramDocumento10 páginasFree Body Diagramjames arajaAinda não há avaliações
- Acceleration Analysis of 3-RPS Parallel Manipulators by Means of Screw TheoryDocumento17 páginasAcceleration Analysis of 3-RPS Parallel Manipulators by Means of Screw TheoryIvan AvramovAinda não há avaliações
- Topic1 2to1 4Documento35 páginasTopic1 2to1 4Sesha Sai KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Programme Scheulde-Ncams-2022Documento16 páginasProgramme Scheulde-Ncams-2022Sanket TikareAinda não há avaliações
- Mark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 B1Documento10 páginasMark Scheme: Q Scheme Marks Aos Pearson Progression Step and Progress Descriptor 1 B1Nasser ElmanzalawyAinda não há avaliações
- LP Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring 2022-2023Documento3 páginasLP Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring 2022-2023John Richie GohetiaAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Algebra Lesson 3 1Documento23 páginasPre Algebra Lesson 3 1412137Ainda não há avaliações
- A Rei B 4a Lesson Solving Completing SquareDocumento2 páginasA Rei B 4a Lesson Solving Completing SquareHaimen BuisanAinda não há avaliações
- Modelica03 AdvancedTutorialDocumento34 páginasModelica03 AdvancedTutorialWuberestAinda não há avaliações
- HIGH STANDARDS IN MATH ADMA P2-UnlockedDocumento125 páginasHIGH STANDARDS IN MATH ADMA P2-UnlockedChikuta Shingalili100% (1)
- Capability Curves PDFDocumento10 páginasCapability Curves PDFRidho IrzamzamAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Brochure BStat (2016)Documento36 páginasRevised Brochure BStat (2016)ManishKumarAinda não há avaliações