Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Me2304 - Engineering Metrology and Measurements Question Bank For Regulation 2008
Enviado por
Ashok Kumar RajendranTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Me2304 - Engineering Metrology and Measurements Question Bank For Regulation 2008
Enviado por
Ashok Kumar RajendranDireitos autorais:
R.M.
K COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
RSM NAGAR, PUDUVOYAL-601206
ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONS
ME2308 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS
III B.E., V Sem., ME Jun13 Nov13
UNIT I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT Part A 1.1) What is metrology? 1.2) What is the need for measurement? 1.4) What is reliability of measurement? 1.6) Define the term sensitivity 1.7) Define sensitivity. 1.8) What is the relationship between sensitivity and the range? 1.9) Explain the term calibration. 1.10) What is meant by calibration of a measuring instrument? 1.11) Give the difference between accuracy and precision. 1.12) Define the term 'Sensitivity' f an instrument. 1.13) What do you mean by sensitivity of a measuring instrument? 1.14) Define the term precision. [AU, May / June 2007, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2007] 1.16) Define Readability. 1.17) Distinguish between repeatability and reproducibility 1.18) What is inaccuracy?
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK 1
1.3) What are the basic components of a measuring system? 1.5) Distinguish between 'Line Standard' and 'End Standard'.
[AU, Nov / Dec 2008, May / June 2007] [AU, April / May 2008, Nov / Dec 2005]
1.15) What is repeatability? Distinguish between reproducibility and repeatability. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012]
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
1.19) What is bias? 1.20) What are the types of error are measurements? 1.21) What are the causes by sources of errors in measurement? 1.22) What is loading error? 1.23) What is dynamic error? 1.24) What is cosine error? 1.25) Write short note on "Systematic errors". 1.26) Define systematic errors and discuss the causes of these errors. [AU, Nov / Dec 2005, 2006] 1.27) Define "Repeatability." [AU, April / May 2011] 1.28) What is the relation between accuracy, repeatability and systematic error? 1.29) What is the relation between total static error of a measuring system and linearity error, reading error, characteristic error and environmental error? 1.30) Define random errors. 1.31) Distinguish between relative error and random error. 1.32) Differentiate between dimensional and form tolerances 1.33) Define interchangeability. Part B 1.34) Describe the various elements and its functions of generalized measurement systems. [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] 1.35) Draw the block diagram of a generalized measurement system and explain the various stages with an example. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010, 2012] 1.36) Explain briefly the classification of various measuring methods. [AU, May / Jun 2012] 1.37) Enumerate the desirable characteristics of precision measuring instruments. [AU, Nov / Dec 2008, May / Jun 2012] 1.38) What are the Principles of high precision measurements? [AU, April / May 2008] [AU, April / May 2011] 1.40) State the requirements for an instrument to measure accurately. [AU, April / May 2011] 1.41) Distinguish between accuracy and precision. [AU, May / Jun 2012]
2
[AU, May / June 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2008]
[AU, April / May 2011]
[AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] [AU, May / Jun 2013] [AU, May / Jun 2013]
1.39) Explain in detail the basic elements of the accuracy of measuring system.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
1.42) Distinguish between 'Precision' and 'Accuracy' with suitable examples. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 1.43) Explain the difference between precision and accuracy with suitable sketches of graphs. 1.44) Define accuracy. Explain how the accuracy of an instrument can be specified. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] 1.45) Explain the classification of various measuring methods. 1.46) How are end standards derived from line standards? Explain. 1.47) Write detailed notes on units and standards. calibration. describe the term traceability in connection with standards. 1.50) Explain the following terms with suitable examples: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (i) Readability Repeatability Calibration and Dynamic response. [AU, May / June 2007, Nov / Dec 2012] Sensitivity [AU, Nov / Dec 2008] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2013] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007, 2008]
1.48) Explain the purpose of calibrating the instrument and discuss the primary and secondary 1.49) Explain the need of standards of measurements in the modem industrial system and
1.51) Write detailed notes on : (ii) Calibration (iii) Precision (iv) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 1.53) Write notes on: (i) (ii) Calibration Interchangeability Interchangeability
1.52) Explain the following terms in precision measurements: Accuracy Sensitivity Repeatability Interchangeability
[AU, May / Jun 2012]
[AU, May / Jun 2012]
3
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
1.54) Explain the term 'interchangeability'.
[AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007, May / June 2009]
1.55) Describe the different types of errors and how they can be eliminated. 1.56) Describe in detail the various types of errors that may arise in measurements. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] 1.57) Describe in detail systematic errors. [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2008] 1.59) Briefly discuss on the characteristics of systematic errors and random errors. [AU, April / May 2008] 1.60) Describe Systematic errors and Random errors. Discuss the means adopted to minimize these errors. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 1.61) What are the various possible sources of errors in precision measurement? Distinguish between systematic and random errors. How are random errors analyzed? [AU, May / Jun 2012] 1.62) Explain the sources of errors in precision measurement with suitable illustrations. [AU, May / Jun 2013] 1.63) What is meant by combined sine and cosine error? Explain with sketches. 1.64) Describe the application of least square principle for assessing the deviation of errors relative to some particular datum. 1.65) Briefly explain the various types of input signal. 1.66) What are the requirements of an Inspection tool? [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, April / May 2011] [AU, April / May 2011] 1.68) What is the necessity of accurate measurement? Bring out the importance of interchangeability 1.58) Define Systematic errors and explain the causes of these errors with suitable examples.
1.67) Discuss on geometric and dimensional tolerancing with suitable examples.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
UNIT II LINEAR AND ANGULAR MEASUREMENT Part A 2.1) What are the techniques to the followed in using the engineer's steel rule? Explain with sketches. 2.2) What is the importance of calipers in measurements? 2.3) Name the different types of calipers. 2.4) Give the advantages of digital vernier caliper. 2.5) What is meant by dial calipers? 2.6) What is wringing of slip gauges? 2.7) What is meant by wringing of slip gauges? boxes. 2.9) Indicate the various grades of slip gauges. 2.10) What are the materials used in the manufacture of slip gauges? measurements made? [AU, Nov / Dec 2008] 2.11) What will happen if the gauge blocks are just simply placed over one another and [AU, Nov / Dec 2007, 2012] 2.12) A 10.00 mm job is measured with an instrument and the following readings were obtained 10.02, 9.97, 10.03, 9.96 and 9.98 mms. What is the error of the instrument? 2.13) Mention the purpose of Goneometric heads in Tool makers microscope. [AU, May / Jun 2012] 2.14) State the Principle of interferometry. 2.15) What is a surface plate? 2.16) What are the 3 vital types of surface plates? What are the precautions to be taken in using the surface plates? 2.17) Compare and contrast the characteristics of C.I. and granite surface plates. 2.18) What are straight edges? 2.19) Describe the working principle of a spirit level in the measurement of minute angular variations. 2.20) What are limit gauges? [AU, April / May 2005, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 2.8) Indicate the various sizes of slip gauges made available in normal set and special set [AU, April / May 2008]
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
2.21) What Taylors principle is as applied to the design of limit gauges? [AU, May / June 2007] 2.22) What are optical flats? 2.23) What is a comparator? 2.24) Narrate the need for comparators. 2.25) What are the different types of comparators? 2.26) What are the advantages of mechanical comparator? 2.28) List the advantages of electrical type comparators. comparators. 2.30) What are the advantages and disadvantages of mechanical comparators and optical comparators? 2.31) What are the merits of mechanical comparators? 2.32) State any two uses of optical comparators. 2.33) What are the uses of accurate measurement of angles? 2.34) Name any two instruments used for measurement of tapers. 2.35) What is the use of a sine centre? 2.36) What is a sine bar? 2.37) Differentiate between sine bar and sine center. 2.38) Define sine centre in sine bar [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, April / May 2005] [AU, May / Jun 2013] [AU, April / May 2008] [AU, April / May 2011] 2.40) State any two limitations of sine bar. [AU, Nov / Dec 2008] [AU, May / June 2007] 2.42) A 200 mm sine bar is to be set to an angle of 320 5 6. Find the height of the gauge block required using any appropriate set of gauge blocks. required using any appropriate set of gauge blocks. [AU, Nov / Dec 2007, 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012]
6
[AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2013] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, May / June 2007]
2.27) Briefly discuss the merits and demerits of electrical and pneumatic comparators. 2.29) Briefly discuss the vital requirements of comparators. Also mention the uses of
[AU, April / May 2011] [AU, May / June 2007]
2.39) State the essential requirements of accuracy in the construction of a sine bar.
2.41) State the essential requirements for accuracy in the construction of a sine bar.
2.43) A 250 mm sine bar is to be set to an angle of 35"5'6. Find the height of the gauge blocks
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
2.44) Why is the Autocollimator in mechanical instrument? Part B
[AU, April /May 2007]
2.45) Explain with neat sketches, suitable methods of measuring or checking the following: (i) (ii) Diameter of a small hole up to 3mm diameter Diameter of hole up to 50mm diameter
(iii) Diameter of hole greater than 50mm [AU, Nov / Dec 2008, May / Jun 2012] 2.46) A vernier scale consists of 25 divisions on 12 mm spacing and the main scale has 24 Divisions on 12 mm. What is the least count? Screw gauge, dial gauge - in tabular form. 2.48) What do you understand by the term cosine error? 2.49) Describe the 4 balls method of bore-diameter measurement using a vernier height gauge or depth gauge. 2.50) How is a vernier height gauge specified? Describe briefly the constructional requirements of the different parts of a vernier height gauge. micrometer. 2.52) Explain the following with neat sketches (i) Differential screw micrometer (ii) Micrometer depth gauge (iii) Thread micrometer caliper 2.53) Explain the following with neat sketches (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Differential screw micrometer Thread Micrometer Blade type micrometer Micrometer thread Gauge [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006]
7
[AU, Nov / Dec 2008] [AU, Nov / Dec 2008]
2.47) Compare and contrast the relative merits and demerits of vernier calipers. Micrometer
[AU, Nov / Dec 2007]
2.51) With a neat diagram, explain the construction and working principle of a depth
[AU, April / May 2008, Nov / Dec 2012]
2.54) What are slip gauges? How are they manufactured? 2.55) Discuss the characteristics and applications of slip gauges.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
2.56) Explain the precautionary measures are shall follow at various stages of using slip gauges. 2.57) Explain the process of Wringing in slip gauges. number of slip gauges for making a required dimension? measurement. of making surface plates from those materials? 2.61) List out the slips to be wrung together to produce an overall dimension of 92.357 mm using 2 protective slips of 2.500 mm size. 2.62) The limits of size for a hole are 25.033 mm and 25 mm. The limits of size for a shaft are 24.980 mm and 24.959 mm. Design the plug gauge and gap gauge to check the fit. [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] 2.63) Describe the different types of go and no-go plug gauges and snap gauges with sketches. 2.64) Why are spherically ended rods used instead of plug gauges for checking very large holes? 2.65) What are the marking usually engraved upon the plug gauges? 2.66) Describe the different types of plain ring-gauges used for checking the shaft diameter with sketches. 2.67) Design the plug and ring gauges to monitor the production of shaft and hole pair of specification 50H7 d8 (Dimension is in mm) [AU, May / June 2007] 2.68) Shafts of 75 + 0.02 mm diameter are to be checked with the help of a GO - NOT GO snap gauges. Design the gauge, sketch it and show its GO size and NO GO size dimensions. Assume normal wear allowance and gauge maker's tolerance 2.69) What is Taylor's principle of gauge design? 2.70) Describe a method of determining an absolute length of dip gauges using interferometer. [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] 2.71) Briefly explain the magnification principles used in mechanical comparators with simple sketches.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
[AU, May / June 2007] [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, May / Jun 2012]
2.58) What are the accuracy requirements of slip gauges? Why is it required to use minimum 2.59) Explain the precautionary measures to be taken at various stages of using slip gauges for 2.60) Can surface plates be made from materials other then cast iron? What are the advantages
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
2.72) Describe the Flatness testing method by using Interferometry Applied. [AU, April / May 2011] 2.73) What are the fundamental requirements of comparators? 2.74) How does a comparator differ from a measuring instrument? [AU, April / May 2011] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2013] 2.76) Explain the working method of mechanical optical comparator with a sketch. [AU, April / May 2011] 2.77) Explain the operation of a mechanical comparator. [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2008] 2.79) Explain how a pneumatic comparator works and briefly enumerate the advantages of differential pneumatic comparator. giving its advantages and applications. [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2005] [AU, May / June 2007] 2.82) Explain the working of electrical comparators (LVDT) with a sketch. 2.83) Describe the functioning of an electronic comparator. 2.84) Explain, with a sketch the construction and working of Solex Pneumatic Comparator. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 2.85) Explain the working of free floor air-gauges (pneumatic comparator gauges) with suitable sketches. 2.86) Explain, with neat sketch, the construction and working of a Tool Maker's Microscope. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 2.87) Explain the working principles of Tool Makers Microscope with neat sketch. Also list out its applications. [AU, May / Jun 2013] 2.88) Explain the working principle of an auto collimator for making very accurate measurement of extremely small angular tilts and give its applications. 2.80) Explain with a neat sketch, the construction and operation of a pneumatic comparator, 2.81) Explain with a schematic sketch the working principle of solex pneumatic comparators. 2.78) Explain the working principle of optical comparators with sketches.
2.75) What is a comparator? Discuss the different types of comparators and its applications.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
2.89) Describe the method of checking the squareness of machined surfaces using an autocollimator. 2.90) Describe the working principle of small bore-measurement by a pivoted system and autocollimator. 2.91) The straightness of the straight edge was measured using an autocollimator and the following readings were obtained. Accuracy of the instrument is 1 sec= 0.5. Compute the straightness error 5 10', 5 20', 4 52', 4 58', and 5 26'. 2.92) What are the special uses of micro alignment telescope? Describe its constructional features with sketches. 2.93) Explain mathematically why sine bars are not suitable for measuring angles above 45. [AU, May / Jun 2012] 2.94) With a neat sketch, explain the use of sine bar for measuring the angle of a taper plug gauge. [AU, Nov / Dec 2005] [AU, May / June 2007] 2.96) What is the constructional difference between an auto collimator and an angle dekkor? 2.97) Describe the working of an angle dekkor and mention its special advantages. [AU, April / May 2008] 2.98) Describe the principle and working of an Angle Dekkor. State its applications. [AU, May / Jun 2012] 2.99) What is the principle of Angle Dekkor? How it is used for the measurement of angles? [AU, May / June 2007, Nov / Dec 2010] 2.100) Discuss the working principle of Angle Dekkor with a sketch. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] 2.101) Explain the working principle of angle dekkor. How is the job of angle 43 24' 12" checked 2.102) Explain the working principle of Angle Dekkor with a neat sketch. Also write the applications of Angle Dekkor. 2.103) Describe the various components of Bevel protractor. application.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
2.95) Explain why bars are not suitable for measuring angles above 45 degrees.
[AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012]
2.104) Describe the different types of bevel protractors with sketches and mention their special
10
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
2.105) Sketch and explain the function of optical bevel protractor with Vernier. [AU, April / May 2011] 2.106) Explain the construction and uses of an optical bevel protractor. [AU, Nov / Dec 2005, 2008, April / May 2008]
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
11
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
12
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
UNIT III FORM MEASUREMENT Part A 3.1) Define screw thread. 3.2) Define pitch of a thread. 3.3) Define lead of a thread. 3.4) Define effective diameter of thread. 3.5) Define helik angle of a screw thread. 3.6) What is pitch diameter? 3.7) What is drunken thread? sketches. 3.9) What is the best wire size? 3.10) What is meant by 'Best size wire' in screw thread measurement? [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 3.11) How is Taylor's principle applied to screw thread gauges? 3.12) What is progressive error in screw threads? [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2012] 3.14) What is floating carriage micrometer? plug gauge by rollers, slip gauges and micrometer. 3.16) Define gear tooth thickness. 3.17) Name the various methods of checking gear tooth thickness 3.18) State the methods used for checking gear tooth profile. 3.19) Define the term 'constant chord' of a gear. 3.20) What is constant chord of a gear? 3.21) What are the 2 vital types of gear tooth profiles? 3.22) Define involutes gear tooth profile. 3.23) Define cycloidal gear tooth profile. 3.24) Define base circle of a gear. 3.25) Define pitch circle of a gear.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
[AU, Nov/ Dec 2008]
[AU, May / June 2007]
3.8) What is the consequence of pitch errors in male and female threads? Explain with suitable
3.13) List the reasons for the occurrence of progressive pitch errors in screw threads. [AU, May / Jun 2013] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, Nov / Dec 2008] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, May / Jun 2012]
3.15) State the precautions that must be taken in the method of measuring diameters of a taper
13
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
3.26) Define module of a gear. 3.27) What is diameter pitch? 3.28) What is circular pitch? What is the relation between diameter pitch and circular pitch? 3.29) What is line of action? What is pressure angle? 3.30) What is helix angle of a gear? 3.31) Define lead angle 3.32) What is backlash? 3.33) What are the sources of errors in manufacturing gears? 3.34) What is kinematics error of gear relation? 3.35) What is tooth to tooth composite error - single flank? 3.36) What is total composite error - single flank? 3.37) What is tooth to tooth composite error-double flank? 3.38) What is total composite error-double flank? 3.39) What is tooth thickness error? 3.40) What is cyclic error? 3.41) What is periodic error? 3.42) What is gear run out? 3.43) What is radial run out? 3.44) Name the Roundness measuring devices. 3.45) Name the methods used to measure roundness. 3.46) List the causes of out of roundness of shafts. [AU, April / May 2008, Nov / Dec 2012] 3.47) What is eccentricity? 3.48) What is undulation? 3.49) What is tooth alignment error? 3.50) Define straightness of a line. 3.51) How is the accuracy of a straight-edge specified? 3.52) Differentiate between straightness and flatness 3.53) What are the 3 vital types of errors of circularity? 3.54) What are the causes of out of circularity of machined parts?
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
[AU, May / June 2008]
[AU, Nov / Dec 2006, 2012] [AU, April / May 2011] [AU, May / Jun 2012]
[AU, May / June 2007] [AU, May / Jun 2013]
14
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
3.55) Define the error of circularity. 3.56) What are the corrections applied in the measurement of effective diameter by the method of wires? 3.57) What is the importance of surface finish? 3.58) What are the Lays in surface measurements? 3.59) What is roughness? What is waviness? 3.60) Define concentricity. 3.61) What is meant by Reproducing Method? [AU, April / May 2011] [AU, Nov / Dec 2005] Part - B 3.63) How is the minor diameter of internal threads measured? Show with sketches 3.64) Explain the 2 wire method of measuring the effective diameter of a screw thread with sketches. with sketches. 3.66) Derive the formula for measuring the effective diameter of a screw thread by three-wire method. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 3.67) What do you mean by major, minor and effective diameter of a thread? 3.68) Describe a bench micrometer. Explain how it is used for measuring the diameter of the screw thread. [AU, May / June 2007] 3.69) It is desired to measure the (a) effective diameter of a 32 x 3.5 mm pitch metric plug screw gauge. For this purpose, the following readings (average values) were noted. Micrometer reading over standard cylinder of 30.500 mm and wires of 2.000 mm diameter as 13.3768 mm. Micrometer reading over gauge and wires is 12.248 mm. (b) Calculate the effective diameter considering the rake and compression correction, assuming a measuring force of 2.5 newtons. 3.70) What is meant by best size mm in screw thread measurement?
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
[AU, Nov / Dec 2007] [AU, May / June 2007]
3.62) Name the various stylus probe instruments used for surface finish measurement.
[AU, May / June 2007]
3.65) Explain the 3 wire method of accurately measuring the effective diameter of screw thread
15
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
3.71) Derive an expression for the best size wire with a sketch. 3.72) Derive an expression for estimation of best size wise. diameter by the method of wires. Discuss in detail. 3.75) Discuss the various types of screw pitch errors.
[AU, Nov / Dec 2006, 2012] [AU, Nov/ Dec 2008] [AU, May / Jun 2012]
3.73) Derive an expression for the best size wire applied in the measurement of effective 3.74) How is the pitch of the screw thread measured by using the tool makers microscope? [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] 3.77) Describe the working of a gear tooth caliper with a sketch. 3.78) Describe a gear tooth vernier caliper and show how it is used for checking gears. [AU, May / Jun 2012] 3.79) Describe the instrument gear tooth vernier caliper. Calculate the gear tooth caliper settings to measure the chordal tooth thickness of a gear of 45 teeth having a module of 4. [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] 3.80) With the help of a neat sketch, describe the construction and working of a profilometer [AU, Nov / Dec 2005] 3.81) How will you check the thread form and angle using the principle of optical projection? [AU, April / May 2005] 3.82) Explain the principle of measuring gear tooth thickness by Base tangent method. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 3.83) Explain the base tangent method of measuring the gear tooth thickness. [AU, May / Jun 2012] 3.84) Explain how gear tooth thickness and base tangent length is measured using vernier gear tooth caliper and flange micrometer. [AU, May / Jun 2013] [AU, Nov / Dec 2005] 3.86) Describe the chordal thickness method using gear tooth vernier caliper. [AU, May /Jun 2007] 3.85) Describe the constant chord method of gear tooth thickness measurement.
3.76) Describe a method of inspecting the involute profile of a spur gear tooth.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
16
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
3.87) Briefly explain any one method of measuring the gear tooth thickness. [AU, April / May 2008] 3.88) Explain the following tooth thickness measurement. (i) (ii) Constant Chord method Chordal Thickness method [AU, May / Jun 2013] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012]
3.89) Explain the working principles of Gleason gear testing machine with neat sketch. Also list out its applications. module of the gear? 3.90) The outer diameter of a gear is 110 mm and the number of teeth is 20. What is the 3.91) Explain the principle of measuring gear tooth thickness by base target method. What is the span length over 5 teeth of gear having 45 teeth, module 4 mm, and pressure angle 20? 3.92) Explain the working of Gear rolling Test method with a neat sketch. [AU, April / May 2011] 3.93) With the help of a neat sketch explain the principle of operation of Rolling gear tester. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] 3.94) Explain with a sketch the principle of operation of a rolling gear tester [AU, Nov / Dec 2006, 2008] 3.95) Explain kinematic accuracy in gear rotation 3.96) List the various Types of errors in gears. [AU, April / May 2008] [AU, April / May 2011]
3.97) What are the elements of gears which are checked for accuracy? [AU, May / Jun 2012] 3.98) With a neat sketch, describe the construction and working of a profilometer. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 3.99) Describe the procedure of straightness checking using an auto-collimator with suitable diagrams and tabulation. 3.100) Briefly explain the visual inspection methods of surface roughness. [AU, May / Jun 2012] 3.101) Describe any one method of testing flatness of a surface plate [AU, Nov / Dec 2005, 2008] 3.102) Describe a method used to check the flatness of a surface plate. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012]
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
17
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
3.103) Describe how the straightness of a surface is assessed in workshops. [AU, May / Jun 2012] 3.104) Explain the use of an optical flat to test the flatness of measuring surfaces. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 3.105) Explain with a neat diagram the measurement of straightness using autocollimator. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] 3.106) Describe the procedure of flatness checking using an auto-collimator. 3.107) Explain the method of checking the straightness of a component using either an autocollimator or a spirit level. sketch. [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, April / May 2008, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, April/May 2005] 3.108) Briefly explain the step by step procedure for determining the flatness of a surface with 3.109) Explain the working principle of an auto collimator of roundness with suitable sketches. 3.111) Describe briefly the principles of a roundness testing machine. [AU, May / June 2007] 3.112) Explain the functions of Tomlinson surface meter. measurement. [AU, April / May 2011] 3.113) Explain with a neat sketch the working of Talysurf instrument for surface finish [AU, April / May 2005, May / June 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] [AU, May / June 2007] 3.116) Define Ra, Rt, Rz and tp% with respect to surface roughness. [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] 3.117) Discuss the merits and demerits of various roughness parameters RMS, CLA and RZ [AU, Nov / Dec 2008, 2012] 3.118) Describe in detail the method of checking roundness by using a roundness measuring machine. State its advantages. [AU, April / May2005] [AU, May / June 2008] 3.119) Write notes on the types of irregularities of a circular part and mention its causes. 3.114) How is the straightness of a straight edge measured?
3.110) Explain the 4 types of reference circles internationally used in the measurement of out
3.115) Explain one method of assessing the straightness of a straight-edge.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
18
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
3.120) The radius of an arc was measured by allowing a 20mm diameter roller to and fro on it and the time for 25 oscillations was found to be 56.25 sec. determine the radius of the arc. [AU, May / June 2007] 3.121) What is the difference between primary texture and secondary texture? Describe an instrument that may be used to obtain a graphical record of primary texture. [AU, May / Jun 2012] 3.122) Write short note an: (i) Secondary Texture [AU, April / May 2011] (ii) Primary Texture.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
19
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
UNIT IV LASER AND ADVANCES IN METROLOGY Part A 4.1) What are the special advantages of using a laser beam in the precision instruments? 4.2) What is the property of laser Radiation? 4.3) What are the characteristic of laser? 4.4) State any two advantages of LASER in interferometry. 4.5) What is the advantage of using laser beam in interferometry? 4.6) Write the application of Laser Interferometry. 4.7) What is the use of beam-splitters? 4.8) What is a laser micrometer? 4.9) List the applications of laser in measurement. 4.10) What do you mean by alignment test on machine tools? 4.11) Define axial slip of a machine tool. 4.12) What do you understand by scanning laser gauges? 4.13) What are the advantages of laser interferometer? 4.14) State the advantages of laser interferometer. 4.15) What is the advantage of using laser beam in interferometry? [AU, Nov / Dec 2005] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, Nov / Dec 2005] [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, April / May 2005] 4.17) What are the advantages of using laser equipment for alignment tests on machine tools? [AU, April / May 2005] 4.18) What are cube corners? State its purpose metrology function? 4.20) Distinguish between co - ordinate and conventional metrology. 4.21) Mention the vital advantages of using computers in metrology. 4.22) Name the four common types of CMM construction 4.24) Name the modes of operation in C.M.M. 4.25) Mention any four types of CMM. [AU, April/May 2005, 2008] [AU, April / May 2011] [AU, Nov / Dec 2005]
20
[AU, April / May 2011] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006]
4.16) List out the different methods of dimensional measurements using laser.
[AU, May / June 2007]
4.19) What means are incorporated in an engineering microscope to make it suitable for
4.23) State any two characteristics of CMM. [AU, May / Jun 2012]
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
4.26) Name the types of accuracy specifications used for CMM [AU, Nov / Dec 2008, 2012, May / Jun 2012] 4.27) What are the applications of co-ordinate measuring machines? 4.28) State the applications of CMM in reverse engineering. 4.29) What is a CNC CMM? 4.30) What are the advantages of CMM? 4.31) Give the advantages of coordinate measuring machines. CMM? 4.33) List any four possible causes of errors in CMM [AU, April / May 2007, Nov / Dec 2012] 4.34) What is spherical co-ordinate measuring machine? 4.35) Define machine vision. 4.36) State any two applications of machine vision system 4.37) List the equipments needed for computer aided inspection. 4.38) List any four applications of computer aided inspection. Part B 4.39) Define straightness. Describe any one method of measuring straightness of a surface. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 4.40) What are the special characteristics of laser beam? Compare and contrast the ordinary light with a laser beam. 4.41) Discuss the different types of laser light sources. 4.42) Discuss briefly on the types and uses of LASER light sources [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007, 2012] [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, April / May 2011] 4.44) What is a laser telemetric system? Explain the working of a laser telemetric system with sketches. 4.45) Explain the construction and working of a laser Telemetric system with a neat sketch. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, May / Jun 2013] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, May / Jun 2013]
4.32) How is numerical error correction accomplished during the measuring process of a
4.43) What is the various laser techniques used to measures the dimensions? And explain it.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
21
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
4.46) With a neat sketch, explain the working of an AC laser interferometer. [AU, Nov / Dec 2005, 2006] 4.47) With a neat sketch explain the working of laser interferometer. 4.48) Describe the principle and working of a laser interferometer. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2012] 4.50) Explain how the displacements are measured using laser interferometer. [AU, Nov / Dec 2005] 4.51) Explain how to use laser interferometer to predict machine tool accuracies. [AU, May / Jun 2013] 4.52) How the flatness of a cast iron plate is checked using LASER interferometer? Explain with the help of a block diagram. [AU, May / June 2007] 4.53) Describe the working of a dual-frequency laser interferometer with a schematic diagram. 4.54) Describe the working principle of a dual frequency laser interferometer and state its application. [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, May / Jun 2012] 4.56) Describe the construction and working of a laser micrometer. [AU, Nov / Dec 2006, 2012] 4.57) Discuss the testing of machine tools using interferometer machine tool. [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] 4.58) Explain the various geometrical tests that are to be done to get a better accuracy in the 4.59) Describe the working principle of scanning laser gauge with a schematic diagram. 4.60) Describe the working of laser triangulation sensors - with a diagram. 4.61) Explain the working of two-frequency laser interferometer with a diagram. 4.62) Explain the working of laser scanning gauge. What are the special advantages? 4.63) Briefly describe the 4 different types of CMMs with simple sketches. 4.64) Describe the important features of CMM's. 4.65) Describe the construction and operation of a co-ordinate measuring machine. [AU, April / May 2005, Nov / Dec 2010]
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
4.49) Describe the applications of Laser interferometer in machine tool metrology
4.55) Explain the working principle of a dual frequency laser interferometer with a neat sketch.
22
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
4.66) With the help of sketches explain the construction and operation of any two types of CMM. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2013] 4.68) Explain the construction and working of various bridge type Co-ordinate Measuring Machines. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, April / May 2008] 4.70) What are the major aspects that need consideration in evaluating the performance of a CMM? [AU, May / June 2007] 4.71) Briefly describe the 4 different types of computer controlled CMM, with simple sketches. 4.72) Explain the functioning of trigger type probe system used in CMM with simple sketches. [AU, May / June 2007] 4.73) Explain the construction details of column type CMMs [AU, May / June 2007] [AU, April / May 2011] 4.75) Explain the procedure to be used in measurement of various dimensions of a typical component using a bridge type CMM. [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2012] 4.77) What are the advantages of bridge type CMMs? [AU, May / June 2007] 4.78) What are the possible squareness deviations of Y-carriage of a CMM? Indicate by a sketch with a suitable diagram; briefly describe the effects of systematic deviation of Ycarriage. 4.79) Describe the steps involved in measurement in CMM for a typical component. [AU, Nov / Dec 2006, 2008] 4.80) State the advantages of CMM. 4.81) Briefly describe the various aspects of machine vision systems. 4.82) Discuss the need of computers in inspection. [AU, April / May 2005, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 4.76) Explain the constructional and working details of horizontal arm CMM. 4.74) What are the various types of C.M.M and explain any two types with neat sketch. 4.69) Briefly explain the calibration of three co-ordinate measuring machine with sketch. 4.67) Discuss the need, types and constructional features of Coordinate measuring Machine.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
23
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
4.83) What is meant by computer aided inspection? State its importance [AU, May / Jun 2012] 4.84) Explain in detail the operation of a machine vision system. [AU, April / May 2005, May / June 2007] 4.85) Discuss the use of computers in the fields of metrology. 4.86) Discuss the merits of computer aided inspection. [AU, April / May 2008] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012]
4.87) Describe the use of LASERS as a means of alignment testing. [AU, May / June 2007]
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
24
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
UNIT V MEASUREMENT OF POWER, FLOW, AND TEMPERATURE RELATED PROPERTIES Part A 5.1) Differentiate between primary and secondary transducers. 5.2) Define force 5.3) Define Power 5.4) Differentiate between force and torque 5.5) What are load cells? 5.6) What is the difference between weight and mass? 5.7) State any two principles of force measurement. 5.8) List out the devices used to measure force 5.9) List any two methods used to measure power. 5.10) Define torque. 5.11) Name any four torque measuring devices. 5.12) List any two methods employed for measuring torque 5.13) Name any four methods employed for measuring torque. 5.15) Why is flow measurement important? 5.16) What are secondary or rate meters? 5.17) On what basic principle does an orifice meter work? 5.18) List out the advantages and limitations of a venturimeter. 5.19) What are the requirements of the Bourdon pressure gauge? 5.20) What are the applications of a pitot tube? 5.21) Name the instrument used for low pressure measurements 5.22) What is a pyrometer? 5.23) List three areas where temperature measurement is important. 5.24) Define temperature 5.25) Give the classification of temperature measuring instruments. 5.26) What is the working principle of bimetallic thermometer? [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, May / Jun 2013] [AU, April / May 2008] AU, April / May 2011] [AU, Nov / Dec 2008] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, May / Jun 2012]
5.14) What are the advantages and applications of an electrical torsion meter?
5.27) List five properties a material should have to be an element of a bimetallic strip.
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
25
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
5.28) List any four major disadvantages of using bimetallic strips for temperature measurements. 5.29) What is a pressure thermometer? 5.30) What are the merits of liquid metal Thermometer? 5.31) Define the principles of electrical resistance thermistor. 5.32) What are the limitations of a thermistor? 5.33) What is a thermocouple? 5.34) What is the working principle of a thermocouple? 5.35) State the principle of thermocouples. 5.36) What are the common materials used for thermocouples? 5.37) Give the composition and useful temperature range of any one commercial thermocouple 5.38) What is the purpose of connecting thermocouples in parallel? 5.39) List the three laws of thermocouples. 5.40) State the basic principle of a thermocouple. 5.41) Explain how a pendulum scale works 5.42) How is a proving ring used to measure force? Part B 5.43) Explain the method of measuring force using a strain gauge load cell. 5.44) Explain with the help of a neat sketch a method used for force measurement using elastic force measurement [AU, Nov / Dec 2008] 5.45) Explain the method of measuring force using a hydraulic load cell. 5.46) Explain the method of measuring force using a pneumatic load cell. 5.47) Explain the construction and working of a pneumatic force meter AU, May / Jun 2012] 5.48) Explain the method of measuring torque using a mechanical dynamometer. 5.49) List the various methods of measuring torque. Explain with a neat sketch the straingauge torsion meter. 5.50) Explain briefly any one method of torque measurement. [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012]
26
[AU, May / June 2007, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, April / May 2011] [AU, May / Jun 2013]
[AU, Nov / Dec 2006, 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2012]
[AU, Nov / Dec 2006]
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
5.51) Explain the different types of torque measurement techniques with example. [AU, May / Jun 2013] 5.52) Briefly explain a torque meter. [AU, April / May 2008] 5.53) Explain the principle of operation of a hydraulic dynamometer. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 5.54) Explain the working principle of Hydraulic dynamometer with sketch. [AU, April / May 2011] 5.55) Explain about hydraulic dynamometers. 5.56) Explain the working principle of a stroboscope. 5.57) Explain about electrical dynamometers. 5.58) How to measure the power by using rope brake dynamometer? Explain with a neat diagram 5.59) Name the Types of flow instruments. 5.60) Explain the construction and working of an orifice meter. 5.61) Describe a method of orifice flow measurement using a suitable instrument. [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] 5.62) Describe any power measurement equipment. 5.63) Describe any two types of flow measurement equipment. 5.64) Explain the construction and working of a Venturimeter. [AU, Nov / Dec 2007, 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2007] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] 5.66) Explain the working of a rotameter with a neat sketch. 5.67) Explain the construction and working of a Rotometer. [AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] [AU, May / Jun 2012] 5.69) Describe the working of a rotameter. 5.70) State Rotameters applications. 5.71) Explain the construction and working of a pitot tube 5.72) Explain how to use the pitot tube for flow measurements? 5.73) Describe any one method used to measure very high pressure 5.74) Write short notes on any TWO instruments from the following:
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
[AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, April / May 2011]
5.65) Explain the principle of operation of Bourdon tube pressure gauge.
5.68) Describe the construction and working of a rotameter. State its advantages.
[AU, May / June 2007] [AU, April / May 2008] [AU, Nov / Dec 2008]
27
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
(i) (ii) (iii) (i) (ii)
Radiation pyrometer Rota meter Hot wire Anemometer with constant temp. Venturimeter Rotameter [AU, April / May 2011] [AU, May / Jun 2012]
5.75) Write short notes on the following:
5.76) Explain how cup and vane type anemometers are used to measure air movement. 5.77) Explain the working of bimetallic strip type temperature measurement system. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] 5.78) With a neat sketch explain how bimetallic strips are used for temperature measurements. [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] 5.79) Explain how a thermocouple is used to measure temperature. 5.80) What are thermo couples? State its applications. 5.81) List and explain the three laws of thermocouples. 5.82) List out different types of thermocouples and the materials used. State and explain the laws governing thermocouples and explain the temperature measuring techniques with thermo couples. 5.84) Describe about thermistors. 5.85) Explain about pressure thermometers. thermister. thermistor. [AU, Nov / Dec 2006] [AU, Nov / Dec 2008] [AU, May / Jun 2012] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012] 5.89) Explain the working principle of an electrical resistance thermometer. [AU, May / June 2007] 5.90) List the advantages of temperature measurement by using the resistance thermometer. [AU, Nov / Dec 2006]
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
[AU, May / June 2007]
[AU, April / May 2008]
5.83) Explain the working of a bimetallic strip type temperature measurement system.
5.86) Explain the method of measuring temperature of body using electrical resistance 5.87) What is a thermistor? Explain with a neat sketch the construction and working of a 5.88) Explain the working and purpose of electrical resistance thermisters.
28
R.M.K COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH / AQ / R2008/ ME2308 / V / MECH / JUNE 2013 NOV 2013
5.91) Using a sketch, explain the working of an optical pyrometer. 5.92) Describe any two types of Row measurement equipment. 5.93) Describe the following temperature measuring instruments (i) Thermocouple (ii) Pyrometer.
[AU, Nov / Dec 2010] [AU, Nov / Dec 2012]
[AU, May / Jun 2012, 2013]
ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION BANK by ASHOK KUMAR.R (AP / Mech)
29
Você também pode gostar
- Interchangeability and Selective AssemblyDocumento20 páginasInterchangeability and Selective Assemblyaneesh19in100% (1)
- NC3010 - Workshop Practice L2 Nov QP 2019Documento5 páginasNC3010 - Workshop Practice L2 Nov QP 2019Ipfi Thanks50% (2)
- Defeating An Old Adversary Cement Kiln BallsDocumento5 páginasDefeating An Old Adversary Cement Kiln BallsManish KumarAinda não há avaliações
- A Winning Formula: Debrief For The Asda Case (Chapter 14, Shaping Implementation Strategies) The Asda CaseDocumento6 páginasA Winning Formula: Debrief For The Asda Case (Chapter 14, Shaping Implementation Strategies) The Asda CaseSpend ThriftAinda não há avaliações
- EC2 406006 001 EFE 0121 - Controgen Generator Excitation System Description - Rev - ADocumento29 páginasEC2 406006 001 EFE 0121 - Controgen Generator Excitation System Description - Rev - AAnonymous bSpP1m8j0n50% (2)
- Powerpoint Presentation R.A 7877 - Anti Sexual Harassment ActDocumento14 páginasPowerpoint Presentation R.A 7877 - Anti Sexual Harassment ActApple100% (1)
- SQL Datetime Conversion - String Date Convert Formats - SQLUSA PDFDocumento13 páginasSQL Datetime Conversion - String Date Convert Formats - SQLUSA PDFRaul E CardozoAinda não há avaliações
- Unit II Curves & SurfacesDocumento57 páginasUnit II Curves & Surfacesvishwajeet patilAinda não há avaliações
- ME83691-Computer Aided Design and ManufacturingDocumento15 páginasME83691-Computer Aided Design and Manufacturingraman thiru55Ainda não há avaliações
- Assigment 1 - SWIPEDocumento2 páginasAssigment 1 - SWIPEMr-Mk MughalAinda não há avaliações
- WS03 Machining CNC - Lathe - Process SheetDocumento2 páginasWS03 Machining CNC - Lathe - Process Sheetsherif115040 BueAinda não há avaliações
- CAM Lab Manual 2019 PDFDocumento54 páginasCAM Lab Manual 2019 PDFJay JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Dyna 1750 Manual ModifiedDocumento336 páginasDyna 1750 Manual ModifiedckooipgAinda não há avaliações
- Anna University Exam Paper Theory of Metal Cutting: Production EngineeringDocumento3 páginasAnna University Exam Paper Theory of Metal Cutting: Production EngineeringAkash Kumar DevAinda não há avaliações
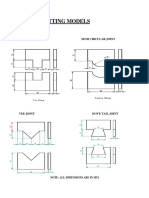
- Fitting Models: Semi Circular JointDocumento2 páginasFitting Models: Semi Circular Jointsubba reddyAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Iii Visual RealismDocumento59 páginasUnit Iii Visual RealismJabin JoeAinda não há avaliações
- Question Paper Tool DesignDocumento1 páginaQuestion Paper Tool DesignVishwas Shetty100% (1)
- Simulation Lab ManualDocumento60 páginasSimulation Lab Manualvensesfrank100% (1)
- CAD Lab ManualDocumento89 páginasCAD Lab ManualDhamotharan S100% (1)
- Assignment Questions: Unit I Subjective QuestionsDocumento2 páginasAssignment Questions: Unit I Subjective QuestionsKalai ArasanAinda não há avaliações
- CNC Machine Lab Report and Process PlannDocumento5 páginasCNC Machine Lab Report and Process PlannMuhammad JahanzaibAinda não há avaliações
- Ce 8381som Lab ManualDocumento31 páginasCe 8381som Lab ManualAERO JPR50% (2)
- Production Technology Question PaperDocumento3 páginasProduction Technology Question PaperChirag100% (2)
- CC7007-Metrology and Non Destructive TestingDocumento15 páginasCC7007-Metrology and Non Destructive Testingamk3745Ainda não há avaliações
- Tool Makers Microscope PPT - Siddhant SinghDocumento15 páginasTool Makers Microscope PPT - Siddhant SinghSiddhant Singh100% (1)
- Chapter 3 METROLOGY - IntroductionDocumento14 páginasChapter 3 METROLOGY - IntroductionMadhu pspkAinda não há avaliações
- Manufacturing Processes Iiprof A B Chattopadhyay Prof A K Chattopadhyay PDFDocumento618 páginasManufacturing Processes Iiprof A B Chattopadhyay Prof A K Chattopadhyay PDFp KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank 3D PrintingDocumento2 páginasQuestion Bank 3D PrintingSujit Mule100% (1)
- Jig and Fix Model QPDocumento4 páginasJig and Fix Model QPDharmaraj ParamasivamAinda não há avaliações
- V2 ECU For AMT TurbinesDocumento26 páginasV2 ECU For AMT TurbinesAmin Anjom100% (1)
- CD 5291 Computer Aided Tools For ManufactiringDocumento2 páginasCD 5291 Computer Aided Tools For ManufactiringGnaneswaran Narayanan63% (8)
- Press Tool TechDocumento48 páginasPress Tool Technikhil sidAinda não há avaliações
- 500 Mechanical Sy MP-I Smart QuestionsDocumento23 páginas500 Mechanical Sy MP-I Smart QuestionsGeorge CamachoAinda não há avaliações
- Metrology ICS Lab Manual A.y-2018-19Documento93 páginasMetrology ICS Lab Manual A.y-2018-19chandrarao chAinda não há avaliações
- Final PPT For Minor Project 2021-22Documento19 páginasFinal PPT For Minor Project 2021-22Dashanand RavanAinda não há avaliações
- 15me835 PLCM Module 2Documento17 páginas15me835 PLCM Module 2prashanth prabhuAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank - All UnitsDocumento11 páginasQuestion Bank - All UnitsParamasivam Veerappan100% (1)
- NC2270 - Workshop Practice L2 Nov QP 2010Documento5 páginasNC2270 - Workshop Practice L2 Nov QP 2010Ipfi Thanks100% (1)
- CNC TURNING MachineDocumento14 páginasCNC TURNING MachineFaiz AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Straightness Flatness Roundness CylindricityDocumento7 páginasStraightness Flatness Roundness CylindricityChristopher Plume De ChineAinda não há avaliações
- ME2309 CAD CAM Lab Manual PDFDocumento39 páginasME2309 CAD CAM Lab Manual PDFAnonymous bj8F8c100% (1)
- Tool Design 2 MarksDocumento85 páginasTool Design 2 MarksKesava PrasadAinda não há avaliações
- Sathyabama Question PaperDocumento3 páginasSathyabama Question PaperamiestudentAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 & 5 ME8691 Computer Aided Design and ManufacturingDocumento26 páginasUnit 4 & 5 ME8691 Computer Aided Design and ManufacturingMECHGOKUL KRISHNA KAinda não há avaliações
- GTDMC ReportDocumento11 páginasGTDMC ReportOwais AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 6 - Face Milling On CNC MachineDocumento5 páginasLab 6 - Face Milling On CNC MachineHaris NaveedAinda não há avaliações
- Unit IV Assembly of Parts PDFDocumento16 páginasUnit IV Assembly of Parts PDFSudhakarAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Material - SyllabusDocumento2 páginasMechanics of Material - SyllabusRahul PatilAinda não há avaliações
- ME2029 DJF 2 Marks +16 Mark QuestionsDocumento15 páginasME2029 DJF 2 Marks +16 Mark QuestionssureshkumarAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Control of Manufacturing Systems Y KorenDocumento9 páginasComputer Control of Manufacturing Systems Y Korenbhagat1030% (1)
- Assignment Question Set On Modern Manufacturing ProcessDocumento1 páginaAssignment Question Set On Modern Manufacturing ProcessSagar KhanAinda não há avaliações
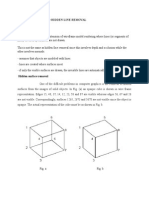
- Hidden Surface RemovalDocumento8 páginasHidden Surface RemovalAshok KumarAinda não há avaliações
- 15ME202 Manufacturing Technology: Unit - 5 Machine ToolsDocumento68 páginas15ME202 Manufacturing Technology: Unit - 5 Machine ToolsMouriya0% (1)
- Chapter 03 - Transducers and Their ResponseDocumento42 páginasChapter 03 - Transducers and Their ResponsehlkjjkAinda não há avaliações
- CNC Turning CentreDocumento10 páginasCNC Turning CentreArun100% (1)
- Powerinspect Manual CmmsDocumento2 páginasPowerinspect Manual CmmsFelipe Cordeiro100% (1)
- Design of Form ToolsDocumento2 páginasDesign of Form ToolsSunny GaekwadAinda não há avaliações
- Shape Function GeneratioDocumento34 páginasShape Function Generatiodtr17Ainda não há avaliações
- Dies and Its TypesDocumento2 páginasDies and Its TypesRajat AhujaAinda não há avaliações
- Autocad Lab ManualDocumento84 páginasAutocad Lab ManualRaghu RamAinda não há avaliações
- Fea Question With Class Notes and Formula BookDocumento375 páginasFea Question With Class Notes and Formula BookAshok Kumar Rajendran96% (117)
- 485 Ass1 Exampes PDFDocumento375 páginas485 Ass1 Exampes PDFfgh fghfghfAinda não há avaliações
- Fea Question With Class Notes and Formula BookDocumento375 páginasFea Question With Class Notes and Formula BookSudhakar Uppalapati50% (2)
- Assignment Booklet Me2353 Finite Element Analysis Dec 2013 May 2014Documento85 páginasAssignment Booklet Me2353 Finite Element Analysis Dec 2013 May 2014Ashok Kumar Rajendran100% (9)
- Multiple Choice Questions: Faculty of Degree Engineering-083 Department of Mechanical Engineering - 19Documento25 páginasMultiple Choice Questions: Faculty of Degree Engineering-083 Department of Mechanical Engineering - 19Ashok Kumar RajendranAinda não há avaliações
- Ce8394 FMM Unit Test IDocumento1 páginaCe8394 FMM Unit Test IAshok Kumar RajendranAinda não há avaliações
- Ce6451 - Fluid Mechanics and Machinery NotesDocumento466 páginasCe6451 - Fluid Mechanics and Machinery NotesAshok Kumar Rajendran94% (16)
- Design Procedure For Design of Machine ElementsDocumento101 páginasDesign Procedure For Design of Machine ElementsAshok Kumar Rajendran83% (12)
- Fluid Mechancis and Machinery Question Bank For 2013 RegulationDocumento90 páginasFluid Mechancis and Machinery Question Bank For 2013 RegulationAshok Kumar Rajendran100% (9)
- Me2401 - Mechatronics Question Bank For Regulation 2008Documento42 páginasMe2401 - Mechatronics Question Bank For Regulation 2008Ashok Kumar Rajendran100% (7)
- Fea Question With Class Notes and Formula BookDocumento375 páginasFea Question With Class Notes and Formula BookAshok Kumar Rajendran96% (117)
- Assignment Booklet Me2353 Finite Element Analysis Dec 2013 May 2014Documento85 páginasAssignment Booklet Me2353 Finite Element Analysis Dec 2013 May 2014Ashok Kumar Rajendran100% (9)
- Mechatronics Notes For Regulation 2008Documento99 páginasMechatronics Notes For Regulation 2008Ashok Kumar Rajendran100% (7)
- Ashok Ahp NotesDocumento42 páginasAshok Ahp NotesAshok Kumar Rajendran0% (1)
- VP Construction Real Estate Development in NY NJ Resume Edward CondolonDocumento4 páginasVP Construction Real Estate Development in NY NJ Resume Edward CondolonEdwardCondolonAinda não há avaliações
- Business Testimony 3Documento14 páginasBusiness Testimony 3Sapan BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Petitioner's Response To Show CauseDocumento95 páginasPetitioner's Response To Show CauseNeil GillespieAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Flyback Transformers and Filter Inductor by Lioyd H.dixon, Jr. Slup076Documento11 páginasDesign of Flyback Transformers and Filter Inductor by Lioyd H.dixon, Jr. Slup076Burlacu AndreiAinda não há avaliações
- Danh Sach Khach Hang VIP Diamond PlazaDocumento9 páginasDanh Sach Khach Hang VIP Diamond PlazaHiệu chuẩn Hiệu chuẩnAinda não há avaliações
- The Finley ReportDocumento46 páginasThe Finley ReportToronto StarAinda não há avaliações
- Sacmi Vol 2 Inglese - II EdizioneDocumento416 páginasSacmi Vol 2 Inglese - II Edizionecuibaprau100% (21)
- UBITX V6 MainDocumento15 páginasUBITX V6 MainEngaf ProcurementAinda não há avaliações
- Hardware Architecture For Nanorobot Application in Cancer TherapyDocumento7 páginasHardware Architecture For Nanorobot Application in Cancer TherapyCynthia CarolineAinda não há avaliações
- DT2 (80 82)Documento18 páginasDT2 (80 82)Anonymous jbeHFUAinda não há avaliações
- Possession: I. A. Definition and Concept Civil Code Art. 523-530 CasesDocumento7 páginasPossession: I. A. Definition and Concept Civil Code Art. 523-530 CasesPierrePrincipeAinda não há avaliações
- Caso Kola RealDocumento17 páginasCaso Kola RealEvelyn Dayhanna Escobar PalomequeAinda não há avaliações
- Practical GAD (1-32) Roll No.20IF227Documento97 páginasPractical GAD (1-32) Roll No.20IF22720IF135 Anant PatilAinda não há avaliações
- NIELIT Scientist B' Recruitment 2016 - Computer Science - GeeksforGeeksDocumento15 páginasNIELIT Scientist B' Recruitment 2016 - Computer Science - GeeksforGeeksChristopher HerringAinda não há avaliações
- Majalah Remaja Islam Drise #09 by Majalah Drise - Issuu PDFDocumento1 páginaMajalah Remaja Islam Drise #09 by Majalah Drise - Issuu PDFBalqis Ar-Rubayyi' Binti HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Insurance Smart Sampoorna RakshaDocumento10 páginasInsurance Smart Sampoorna RakshaRISHAB CHETRIAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Data Sheet: Fumaric AcidDocumento9 páginasSafety Data Sheet: Fumaric AcidStephen StantonAinda não há avaliações
- ABB Price Book 524Documento1 páginaABB Price Book 524EliasAinda não há avaliações
- Lec # 26 NustDocumento18 páginasLec # 26 NustFor CheggAinda não há avaliações
- QuizDocumento11 páginasQuizDanica RamosAinda não há avaliações
- PHP IntroductionDocumento113 páginasPHP Introductionds0909@gmailAinda não há avaliações
- Quantity DiscountDocumento22 páginasQuantity Discountkevin royAinda não há avaliações
- Toa Valix Vol 1Documento451 páginasToa Valix Vol 1Joseph Andrei BunadoAinda não há avaliações
- 7Documento101 páginas7Navindra JaggernauthAinda não há avaliações
- Nissan E-NV200 Combi UKDocumento31 páginasNissan E-NV200 Combi UKMioMaulenovoAinda não há avaliações