Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Family Assessment Example
Enviado por
im3in1Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Family Assessment Example
Enviado por
im3in1Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
A-62
A P P E N D I X H FAMILY ASSESSMENT TOOLS
H.3 Case Example of Family Assessment
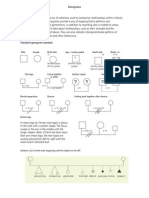
The Jeddi family is a real family in a real situation. They came to the attention of the nurse when the family was referred to the county home health agency for a baseline family assessment with their impending adoption of a 4-year-old boy from Russia. This upper middle class Caucasian family consists of Ben (age 51), Mare (age 43), and the son they will adopt, Alex (age 4). See Figure H-1 for the Jeddi family genogram and Figure H-2 for the Jeddi family ecomap. Ben and Mare have been married for 8 years. Ben has a PhD in chemical engineering and does consulting work. His business is located in the caretaker apartment located in the basement of their home. Mare has a PhD, is a pediatric nurse, and teaches at a private university. They are adopting a 4-year-old boy from Russia. Mare has a diagnosis of infertility after 2 years of trying to have a biologic child and extensive testing. The infertility issue was a signicant loss for both Ben and Mare. The couple considered in vitro fertilization. Mare decided against this approach because she felt the risks of failure of pregnancy and miscarriage were too great. Ben felt that this was Mares decision to make as it more directly involved her physical and mental health. He supported Mares decision to not pursue in vitro fertilization. Mare initiated the discussions about adoption. The decision to adopt a child was reached in May of this year after a year and a half of discussion and investigation. Initially, Ben was not equally committed to the concept of adoption and had a longer grieving process over their inability to have a child together than Mare. The issue of biologic heritage and the loss of blood lineage were more signicant to Ben. The signicant issue for Mare was the loss of being a parent and raising a child. The couple investigated several adoption agencies and attended potential adoptive parent classes a year and a half ago. At that time, Ben was not ready to make a commitment to adoption. The topic of adoption repeatedly was discussed by the couple over the course of the next year. In January 1994, the couple again seriously considered adoption. Mare investigated several adoption agencies again, as she was not satised with the one they selected the last time. A local adoption agency was found to be supportive and informative for them. The couple attended an information meeting. After much intense emotional discussion, the couple pursued more information about adoption with the support personnel from the agency. At the end of May, Ben and Mare decided they wanted to adopt a child and completed the application process. Both Ben and Mare feel this was an emotional time for them. After they made their decision to adopt, the next steps were to decide from which country they wanted to adopt a child, the childs age, and which child. They decided that, given their lifestyles and personalities, they wanted to adopt an older child between 3 and 5 years of age and not an infant. Ben wanted to adopt a son. Mare was not selective of the gender. Ben felt that the issue of race was important to him. He felt that he might have difculty bonding with a child of dark skin as his own family. Because of Bens immediate family origins from Finland, they decided to adopt a child from eastern Europe. Russia was selected because of its historical ties with Finland. Mare reviewed videotapes of 40 children and selected the top male children for them to select from. Mare is a pediatric nurse and was determined to be the one to make the decisions about health. After viewing the lms numerous times and reviewing a medical examination, Alex was the young child of choice. Ben and Mare made a formal petition to adopt Alex. The process has taken 6 months. They are currently waiting for the nal paperwork to arrive from the Russian government, which is expected in the next few days. They are in the midst of preparing their home for the arrival of Alex. They will both travel to Russia in 2 weeks to pick him up, complete the formal adoption process in Russia, and travel home together as a new family. They are nervous and excited about the adoption. They are concerned about how Alex will adjust to them and the move to America. They are concerned about how adopting a 4-year-old will change their lifestyle. The preparation of their home for the arrival of Alex has been time consuming. The arrangements for travel to Russia are being nalized. Ben had taken 2 years of Russian 20 years ago; both are currently taking individual language tutoring in Russian. Ben and Mare are currently working full-time. Mare plans to continue working full-time after they adopt Alex, but she does have a reduced workload for the next 4 months. They plan to have Alex attend full-time preschool. The initial assessment of the Jeddi family involved the use of two assessment approaches with their respective instruments, guidelines, a genogram, and an ecomap. A summary of the ndings from this assessment follows.
FAMILY SYSTEMS STRESSOR STRENGTH INVENTORY
The FS3I is presented, which focused on the Jeddi family stressors and strengths to create a plan of action. Ben and Mare were interviewed together in their home by the nurse. Each person completed the FS3I, which provided individual and composite scores. Figure H-1 presents a completed genogram. Figure H-2 shows the Jeddi family ecomap. Figures H-3 and H-4 provide the scoring for the quantitative summary of stressors and strengths. A
Copyright 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
A P P E N D I X H FAMILY ASSESSMENT TOOLS
Date Family name Jeddi family Completed by
A-63
72 years Resp. failure Generation 1
80 years Alzheimers Kyptosis Institutionalized
Overweight Hypertension Emphysema
62 years Lymphoma Sepsis
Generation 2 Ben (51) Engineer Overweight Hypertension High cholesterol Mare (43) Nurse Obese Infertility M 1986
Generation 3
@ 4 years of age Oct. 1994 Tom (4) 5% height and weight Speaks only Russian Orphan since 3 months
Figure H-1
Mother
Work
Social group Band
Friends
Friends
Ben (51) Tom (4)
Mare (43)
Sister
Adoption service in Arkansas Orphanage in Russia Local adoption service
Key Strong Tenuous Stressful Energy flow
Figure H-2 Copyright 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
A-64
A P P E N D I X H FAMILY ASSESSMENT TOOLS
qualitative summary (Figure H-5) presents a brief picture of the family stresses and strengths and served as the guide for the family care plan (Figure H-6). The general stressors of the family were the impending adoption of Alex, issues of family nutrition and dieting, and lowered self-image for both Ben and Mare. Mare was found to have a higher general stress level than Ben. She states that in addition to the above stressors she is concerned about: stress relative to housekeeping issues, an ongoing physical problem with her knee, and guilt for not accomplishing more than she presently is able. Ben noted that issues related to his mother, who has Alzheimers disease and lives in an assisted living center, causes him additional stress. The nurse rated their general and specic stressors higher than both Ben and Mare rated themselves. The specic stressor identied by Ben that is causing him the most stress is the impending adoption of Alex. He is concerned about time management with work and a new family member. The additional stress of his mothers care is requiring a lot of his time. She is well taken care of in an assisted living center, but he is concerned about her advancing dementia. At present he is actively involved in renting out his mothers home. The specic stressor identied by Mare was how she is going to manage food preparations and meal times after they adopt Alex. She stated that cooking and meal preparation are currently a big problem for her. Mare stated that Ben does not help with food preparation or clean up now. They both eat on different schedules. She is concerned about family dinners and feels this is an important time for them with Alex. Food preparation is not a new issue for them. She stated that she feels pressured and like a failure because she does not manage this aspect of their family life well now, before the addition of Alex. In the past the family has hired a cook which was a excellent solution for them. The have been without a cook for 2 years now after their previous cook moved out of state. The strengths of this family are many. They scored their individual strengths inventory almost identically, which demonstrates a similar perception of their family unit. Both Ben and Mare viewed their family and each other as experienced problem solvers. They have good, open communication between them and feel that the adoption of Alex has even brought them closer together. They recognized that much of their current stress is related to the unknown about Alex. They feel that once they meet Alex that they will be able to work together to solve their problems. The nurse concluded that this family has the strengths they need to adapt to their new family life cycle of a family with a preschooler. In looking at the ecomap, the family is found to be well supported by resources. They are responsive to information provided to them and ideas suggested by others for them to consider in their problem solving.
FRIEDMANS FAMILY ASSESSMENT FORM Identifying data
Ben and Mare Jeddi Portland, Maine Type of family: Nuclear Ethnic background: Ben comes from a Finnish background. Mare has no particular ethnic identity Religious: No afliation Social class: Upper middle class Leisure activities: Travel, gardening, music Occupations: Ben, consulting chemical engineer. Mare, pediatric nurse and university faculty
Developmental stage and history of family
The familys present developmental stage cannot be dened in the conventional family life cycle. Ben and Mare have been married for 8 years, so they do not t the categories for beginning families or families with children. However, they are in transition and, with the adoption of a 4-year-old boy, the family will t into the classical family life cycle stage of family with preschooler. Ben comes from a nuclear family of origin; however, his parents were divorced after 30 years of marriage. Mare comes from a nuclear family of origin.
Environmental data
The family live in an upper-middle-class urban neighborhood that is ethnically diverse. They are within close distance of schools, hospitals, re department, and shopping areas. The neighborhood is clean and relatively safe, as there have been a few burglaries in the neighborhood. Both attend the neighborhood community meetings. The family is centrally located only 8 blocks from freeways around town, 2 miles from downtown, and 5 blocks from a bus route. Ben works in the home, where the basement caretaker apartment has been converted into his ofce and laboratories. Mare works at the university, which is 4 miles away. She often rides her bike to work. Their home is a 75-year-old brick home that has four levels. It is situated on the edge of a hollow. The home is well kept but old. Both Ben and Mare enjoy their home and spend a lot of time there. They are slowing remodeling. The house is safe, but with the adoption of a 4-yearold boy, several safety factors need to be addressed. There is no medicine cabinet in the bathroom and medicines are easily within reach of a 4-year-old. The cleaning solutions are kept under the sinks in the kitchen and the bathroom. The patio above the garage does have a railing, but a 4year-old may be tempted to walk on it. A re plan needs to be made for the family because all of the bedrooms are on the top oor, which is three levels above the ground.
Text continued on p. A71
Copyright 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
A P P E N D I X H FAMILY ASSESSMENT TOOLS
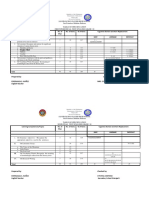
Family Systems Stressor-Strength Inventory (FS3I) Quantitative Summary Family Systems Stressors: General and Specific Family and Clinician Perception Scores Directions: Graph the scores from each family member inventory by placing an X at the appropriate location. (Use first name initial for each different entry and different color code for each family member.) Family Systems Stressors: General Scores for Wellness and Stability 5.0 4.8 4.6 4.4 4.2 4.0 3.8 3.6 3.4 3.2 3.0 2.8 2.6 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 PRIMARY SECONDARY TERTIARY Family Member Perception Score Clinician Perception Score Scores for Wellness and Stability 5.0 4.8 4.6 4.4 4.2 4.0 3.8 3.6 3.4 3.2 3.0 2.8 2.6 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 Prevention/Intervention Mode: Flexible Line Prevention/Intervention Mode: Normal Line Prevention/Intervention Mode: Resistance Lines 1.0 - 2.3 2.4 - 3.6 3.7 - 5.0 Family Systems Stressors: Specific Family Member Perception Score Clinician Perception Score
A-65
Breakdown of numerical scores for stressor penetration are suggested values
Copyright 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Figure H-3
A-66
A P P E N D I X H FAMILY ASSESSMENT TOOLS
Family Systems Stressor-Strength Inventory (FS3I) Quantitative Summary Family Systems Strengths Family and Clinician Perception Scores
Directions: Graph the scores from the inventory by placing an X at the appropriate location and connect with a line. (Use first name initial for each different entry and different color code for each family member.) Sum of Strengths Available for Prevention/ Intervention Mode 5.0 4.8 4.6 4.4 4.2 4.0 3.8 3.6 3.4 3.2 3.0 2.8 2.6 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 PRIMARY SECONDARY TERTIARY Prevention/Intervention Mode: Flexible Line Prevention/Intervention Mode: Normal Line Prevention/Intervention Mode: Resistance Lines 1.0 - 2.1 2.2 - 3.6 3.7 - 5.0 Family Systems Strengths Family Member Perception Score Clinician Perception Score
Breakdown of numerical scores for stressor penetration are suggested values
Copyright 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Figure H-4
A P P E N D I X H FAMILY ASSESSMENT TOOLS
A-67
Family Systems Stressor-Strength Inventory (FS3I) Qualitative Summary Family and Clinician Remarks Part I: Family Systems Stressors: General Summarize general stressors and remarks of family and clinician. Prioritize stressors according to importance to family members.
Part II: Family Systems Stressors: Specific A. Summarize specific stressor and remarks of family and clinician.
B. Summarize differences (if discrepancies exist) between how family members and clinician view effects of stressful situation on family.
C. Summarize overall family functioning.
.
D. Summarize overall significant physical health status for family members.
. . .
E. Summarize overall significant mental health status for family members.
Part III: Family Systems Strengths Summarize family systems strengths and family and clinician remarks that facilitate family health and stability.
Figure H-5 Copyright 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
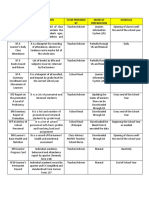
Family Systems and Stressor-Strength Inventory (FS3I) Family Care Plan* Prevention/Intervention Mode Primary, Secondary or Tertiary Prevention/Intervention Activities Outcomes Evaluation and Replanning
A-68
Diagnosis General and Specific Family System Stressors Prognosis Goals Family and Clinician Family Systems Strengths Supporting Family Care Plan
A P P E N D I X H FAMILY ASSESSMENT TOOLS
- -
Copyright 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
- -
*Prioritize the three most significant diagnoses
Figure H-6
A P P E N D I X H FAMILY ASSESSMENT TOOLS
A-69
Family structure
Communication is a strength of this family. There is an open relationship and communication pattern between Ben and Mare. Both are very verbal and expressive about their feelings, opinions, and needs. Because of this openness, they state that there is often conict and arguing between them. However, they feel that they are good at conict resolution. At times, however, the argument does get out of control and takes a personal attack format. When they realize this, usually Mare suggests that they take up the conversation at a later time when they can both approach the topic more calmly. They are not worried about arguing in front of their son. They feel that their open, honest communication will be helpful in raising their son. The decision making of the family is by consensus for important issues that affect the lives of both members. Otherwise, the decision-making style is accommodation. The power and decision making is more situational in that whoever has more experience with certain issues will inuence the decisions. For example, Mare is a nurse and has the referent power in health-related issues. Ben is a chemical engineer. He has referent power for concerns about xing things in the house or with cars. Both state that a strength of their family is that they are both known problem solvers. The role structure is typical relative to gender. Mare does the cooking, laundry, house cleaning, shopping, and kinship roles. Ben does the lawn mowing, carries out the garbage, and services the cars. Mare feels that she has more roles and expected behaviors of her than Ben does. They both work full-time outside the home. Both state they are concerned about role overload and time management issues with the adoption of their 4-year-old. Mare knows that she will be the primary caregiver but is not sure how much or in what way Ben will assist with these new role requirements. Ben is concerned about how much time the new child will demand and his ability to juggle all of these work responsibilities and family responsibilities. The family values are clear and shared by both Ben and Mare. The family values: education, open, honest communication, family, health, diversity, caring and compassion for others.
he has lived in an orphanage in Russia since the age of 3 months. They have investigated as much as possible about how other children adapt to their new situations. They plan to go to Russia to pick up their son, which will give them access to information about rules and rituals he is familiar with in the orphanage, and plan to institute them in their home. Socialization function Ben and Mare talk about the importance of parenting their son. They have openly discussed discipline to be used, which will be time-out. They plan to be involved in the child-rearing practices of their son. Their son will be in full-time preschool. They plan to be active in the education process of their son. Health care function The family has a primary care physician for Ben and Mare, but they have not selected a pediatrician for their son. Ben sees the physician regularly for management of hypertension and high cholesterol. Mare rarely sees the doctor. The have a medical report for their son. He appears to be in good health, except that he is below the fth percentile for height and weight. He is current on immunizations except hepatitis. They both have dental cleaning and examinations every 6 months. They value health, yet both are overweight. Mare is obese. A major concern for Mare is regular meal preparation for their son. At present, Ben and Mare do not eat together for dinner on a regular basis. In the past they have hired a cook to ensure that healthful meals were available, especially with Mare working full-time.
Family coping
The short-term stressors for this family are the imminent adoption of their 4-year-son from Russia in 3 weeks. They are concerned about his adaptation to his new environment, his ability to learn English, and how there lives will change with this adoption. Long-term stressors are not an issue at this time. The family has a large repertoire of successful coping strategies. They have a pattern of problem-solving issues to the best of their ability. They are seeking out information and garnering support from people and resources acceptable to them. They are a well-adjusted family unit. The family is open to education and information.
Family functions
Affective function Ben and Mare have a close, caring relationship and demonstrate a reciprocal emotional relationship. They are a close, cohesive family. They are excited about expanding their family with the adoption of Alex. They each state that the other is a major support person in their lives. The family has closed boundaries but does look to extended family members for needed support. They express concern about their sons adjustment to them as parents, because
Summary of assessments
In summary, both assessment approaches provided important information for the nurse and family to create a plan of action. There was some overlap of information, but the whole picture of the family was enhanced by merging data from both assessment tools.
Copyright 2008 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
Você também pode gostar
- Family Assessment PaperDocumento11 páginasFamily Assessment Paperjesse862005100% (7)
- Final Family Interview and Assessment PaperDocumento8 páginasFinal Family Interview and Assessment Paperapi-542033819100% (2)
- Family AssessmentDocumento7 páginasFamily Assessmentapi-267488377Ainda não há avaliações
- Freidman Family Assesment IdentifiedDocumento3 páginasFreidman Family Assesment IdentifiedDawn Targon50% (2)
- Family Assessment Form - For PrintingDocumento10 páginasFamily Assessment Form - For Printingapi-382970050% (2)
- Freidmean Assessment ModelDocumento21 páginasFreidmean Assessment Modelmdakbari100% (5)
- Family Assessment PaperDocumento11 páginasFamily Assessment Paperapi-24239430233% (3)
- Family Health NursingDocumento6 páginasFamily Health NursingDanna Bornilla RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- GenogramDocumento12 páginasGenogramMumtaz KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Family AssessmentDocumento13 páginasFamily Assessmentblast211140% (5)
- Omar's Family AssessmentDocumento10 páginasOmar's Family AssessmentfaizaAinda não há avaliações
- Family Assessment PaperDocumento16 páginasFamily Assessment Paperapi-231899545100% (1)
- Family Medicine Assessment ToolsDocumento60 páginasFamily Medicine Assessment ToolsDimple Kristine CruzatAinda não há avaliações
- Marcel Case StudyDocumento5 páginasMarcel Case StudyPrismatic Ray100% (1)
- Wolf Family Assessment and Treatment PlanDocumento9 páginasWolf Family Assessment and Treatment Planapi-487413988Ainda não há avaliações
- Reactive Attachment DisorderDocumento22 páginasReactive Attachment Disorderapi-355863009100% (1)
- EcomapDocumento1 páginaEcomapAngelica Cassandra VillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Family As A Unit of CareDocumento59 páginasFamily As A Unit of Careabstabs83% (6)
- Family Assessment Genogram EcomapDocumento8 páginasFamily Assessment Genogram Ecomapamal100% (1)
- Case ConferenceDocumento30 páginasCase Conferenceridazaheer29Ainda não há avaliações
- Genogram Symbols: A Guide to Relationship VisualizationDocumento8 páginasGenogram Symbols: A Guide to Relationship Visualizationchakshu sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Family Case StudyDocumento13 páginasFamily Case StudyKathleen Joy Costales MagtanongAinda não há avaliações
- Client Evaluation sw4997 Paper 2Documento12 páginasClient Evaluation sw4997 Paper 2api-242943882Ainda não há avaliações
- The Shirley Family AssessmentDocumento3 páginasThe Shirley Family AssessmentNicole Flores0% (1)
- SW 3020 Biopsychosocial Assessment-Final RevisedDocumento18 páginasSW 3020 Biopsychosocial Assessment-Final Revisedapi-286703035Ainda não há avaliações
- Family Health AssessmentDocumento3 páginasFamily Health Assessmentkashim123100% (1)
- Family AssessmentDocumento6 páginasFamily Assessmentapi-307439819Ainda não há avaliações
- Autism Case StudyDocumento19 páginasAutism Case Studyapi-275340609Ainda não há avaliações
- Family Case StudyDocumento10 páginasFamily Case StudyKryza CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- Autism Spectrum Disorder - A Case Study of MikeyDocumento25 páginasAutism Spectrum Disorder - A Case Study of MikeyMuhammad FadhilAinda não há avaliações
- Tools For Family AssessmentDocumento31 páginasTools For Family AssessmentRoy Acosta Gumban100% (11)
- Genogram Tool for Integrated Patient CareDocumento24 páginasGenogram Tool for Integrated Patient CareJaphet NwapiAinda não há avaliações
- Family Assessment and GenogramDocumento10 páginasFamily Assessment and GenogramSINJINI GHOSH 1837550Ainda não há avaliações
- Psychiatric Case StudyDocumento16 páginasPsychiatric Case Studyapi-402635887Ainda não há avaliações
- Ordinal Position in Family SystemDocumento67 páginasOrdinal Position in Family Systemvladbreana100% (1)
- Family AssessmentDocumento17 páginasFamily AssessmentJwllyn CC100% (1)
- Explaining GenogramsDocumento4 páginasExplaining GenogramsJonn Candace Yrad100% (2)
- Calgary Family Model SummaryDocumento2 páginasCalgary Family Model SummaryArianne VerzolaaaAinda não há avaliações
- The Adjustment of Nondisabled Adolescent Siblings of Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder in The HomeDocumento18 páginasThe Adjustment of Nondisabled Adolescent Siblings of Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder in The HomeAutism Society Philippines100% (4)
- Intake AssessmentDocumento2 páginasIntake Assessmentyourzxtruly0% (1)
- Family Health Assessment FormDocumento8 páginasFamily Health Assessment FormKevin Llorente50% (2)
- Genograms: Mapping Family RelationshipsDocumento2 páginasGenograms: Mapping Family RelationshipsPoetrie Princeez Sakoera100% (2)
- Tools in Family AssessmentDocumento3 páginasTools in Family AssessmentAnny Alvrz83% (6)
- Case Conceptualization 514Documento4 páginasCase Conceptualization 514Kyle RossAinda não há avaliações
- GenogramDocumento5 páginasGenogramapi-222460555100% (1)
- Zuchowski Assessment ReportDocumento7 páginasZuchowski Assessment Reportapi-532093342Ainda não há avaliações
- GenogramDocumento5 páginasGenogramAisya Yezid0% (1)
- Family Assessment ToolsDocumento29 páginasFamily Assessment ToolsMikha Tarigan100% (1)
- Sample Report 1Documento5 páginasSample Report 1jessefrank05100% (1)
- Case Presentation Format 3Documento1 páginaCase Presentation Format 3Priya Sharma Sabarad100% (3)
- Applying Neuman and Orem TheoriesDocumento3 páginasApplying Neuman and Orem TheoriesLin LanAinda não há avaliações
- Case ConceptualizationDocumento1 páginaCase Conceptualizationkiwifire520Ainda não há avaliações
- Rad Case Study Child-Based Research Review & ReflectionDocumento17 páginasRad Case Study Child-Based Research Review & Reflectionapi-282525755Ainda não há avaliações
- Friedman Family Assessment ModelDocumento3 páginasFriedman Family Assessment ModelJosh100% (7)
- Intake ReportDocumento3 páginasIntake ReportSarai67% (3)
- Cultural CompetenceDocumento14 páginasCultural Competenceapi-400251381100% (1)
- Running Head: Genogram and Ecomap: Brain 1Documento9 páginasRunning Head: Genogram and Ecomap: Brain 1Elizabeth FilmoreAinda não há avaliações
- Family Case StudyDocumento58 páginasFamily Case Studyrodcyruskent100% (1)
- Successful Children of Single Parents Stories To TellDocumento12 páginasSuccessful Children of Single Parents Stories To TellInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- w13 Final Family Interview and Assessment PaperDocumento9 páginasw13 Final Family Interview and Assessment Paperapi-709692563100% (1)
- AAP Bright Futures Periodicity ScheduleDocumento1 páginaAAP Bright Futures Periodicity Scheduleim3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- AAP Bright Futures Periodicity ScheduleDocumento1 páginaAAP Bright Futures Periodicity Scheduleim3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- FNP POS Concentration 9.19.12Documento1 páginaFNP POS Concentration 9.19.12im3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- CYDS Family Relationship Measure Scale DescriptionDocumento18 páginasCYDS Family Relationship Measure Scale Descriptionveridianaadam100% (3)
- Tablica Snellena Do DrukuDocumento5 páginasTablica Snellena Do DrukuTomasz GadzalskiAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative and Quantitative Research Comparison DB 1Documento3 páginasQualitative and Quantitative Research Comparison DB 1im3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- Charting Examples For Physical AssessmentDocumento16 páginasCharting Examples For Physical Assessmentim3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- Running Head: WHO AM I 1Documento2 páginasRunning Head: WHO AM I 1im3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- ConsumerismDocumento2 páginasConsumerismim3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- Good StewardDocumento2 páginasGood Stewardim3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- Impact and Penetration of Nursing ResearchDocumento3 páginasImpact and Penetration of Nursing Researchim3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- Impact and Penetration of Nursing ResearchDocumento3 páginasImpact and Penetration of Nursing Researchim3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- God and MediaDocumento1 páginaGod and Mediaim3in1Ainda não há avaliações
- La Biblia Del KarateDocumento293 páginasLa Biblia Del KarateAdrian Garcia100% (1)
- Australian Study Examines Touch Screen Tablet Impact on Emergent LiteracyDocumento14 páginasAustralian Study Examines Touch Screen Tablet Impact on Emergent Literacyvampirek91Ainda não há avaliações
- Mary Belle Montessori Faculty Meeting HighlightsDocumento3 páginasMary Belle Montessori Faculty Meeting HighlightsJep Jep PanghulanAinda não há avaliações
- Brunner JR V LyftDocumento28 páginasBrunner JR V LyftGMG EditorialAinda não há avaliações
- Religious TourismDocumento20 páginasReligious TourismShantanu Dubey50% (6)
- Salesforce The Path Toward EqualityDocumento18 páginasSalesforce The Path Toward Equalitylancekim21Ainda não há avaliações
- Metallurgical Accounting: AMIRA's P754 Code of Practice in ItsDocumento2 páginasMetallurgical Accounting: AMIRA's P754 Code of Practice in ItsEngineering Office Shahrak100% (1)
- Critical Journal Review Pendidikan Agama Kristen: Dosen PengampuDocumento11 páginasCritical Journal Review Pendidikan Agama Kristen: Dosen PengampuSteven Andrian LumbantobingAinda não há avaliações
- Integrated Product Development Process and Green Supply Chain ManagemenDocumento37 páginasIntegrated Product Development Process and Green Supply Chain ManagemenMuhammad Dzaky Alfajr DirantonaAinda não há avaliações
- TOSDocumento3 páginasTOSesperanza s. nunezAinda não há avaliações
- Personal Assignment: Muhammad Zaid SyahidDocumento3 páginasPersonal Assignment: Muhammad Zaid SyahidMuhammad Zaid SyahidAinda não há avaliações
- Errors Behind Asking Open-Ended Questions A StudyDocumento13 páginasErrors Behind Asking Open-Ended Questions A StudyAulia SafiraAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To International Trade Lesson 1Documento80 páginasIntroduction To International Trade Lesson 1Margaretta LiangAinda não há avaliações
- Stages of Team Development B. TuckmanDocumento3 páginasStages of Team Development B. Tuckmanlim999Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 1 TXE Is A Large Food Retailer. The Finance Director Is Worried As Last Year Profit Fell by 10%. I BlameDocumento8 páginas2 1 TXE Is A Large Food Retailer. The Finance Director Is Worried As Last Year Profit Fell by 10%. I BlameSabinaPlayzAinda não há avaliações
- Group Formation and Team Building: Tuckman's StagesDocumento46 páginasGroup Formation and Team Building: Tuckman's StagesAditya D TanwarAinda não há avaliações
- Reading Month NarrativeDocumento18 páginasReading Month NarrativeJMAR ALMAZANAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Session 4 - Writing Answer Key - GDocumento3 páginas4 Session 4 - Writing Answer Key - GVigitha RadhakrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- Recruitment Examination For The Post of Assistant Engineer (Civil) Under KMCDocumento1 páginaRecruitment Examination For The Post of Assistant Engineer (Civil) Under KMCRAHUL KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- 21-22 Annual Student Outcome Goal PlanDocumento2 páginas21-22 Annual Student Outcome Goal Planapi-56496735267% (3)
- CF 52 - Examples Sheet No Description UpdateDocumento25 páginasCF 52 - Examples Sheet No Description UpdatepassioncadetAinda não há avaliações
- Central Tuber Crops Research Institute JobDocumento2 páginasCentral Tuber Crops Research Institute JobKuldeep KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Final House Report - John Swallow InvestigationDocumento214 páginasFinal House Report - John Swallow InvestigationThe Salt Lake TribuneAinda não há avaliações
- Contract For Tutor Services For Website VersionDocumento5 páginasContract For Tutor Services For Website VersiongigiAinda não há avaliações
- Admit Card of B.Ed.Documento1 páginaAdmit Card of B.Ed.Taslim AnsariAinda não há avaliações
- Test English - Prepare For Your English ExamDocumento1 páginaTest English - Prepare For Your English ExamКузишин ВікторіяAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study JollibeeDocumento6 páginasCase Study JollibeeJonna Lynne88% (8)
- Title T-Shirts DesigningDocumento2 páginasTitle T-Shirts DesigningHumaira KhaniAinda não há avaliações
- School Forms Description To Be Prepared BY Mode of Preparation Schedule SF 1Documento2 páginasSchool Forms Description To Be Prepared BY Mode of Preparation Schedule SF 1ARTURO DE GUZMANAinda não há avaliações
- Cybercrime Act R.A 10175Documento11 páginasCybercrime Act R.A 10175Luis MasangkayAinda não há avaliações