Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Grammar Punctuation and Vocabulary 2014
Enviado por
api-226169467Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Grammar Punctuation and Vocabulary 2014
Enviado por
api-226169467Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
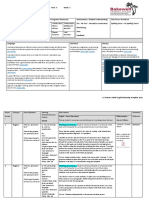
Shoal Bay Public School Grammar, Punctuation and Vocabulary
Kindergarten
ENe-9B demonstrates developing skills and knowledge in grammar, punctuation and vocabulary when responding to and composing texts begin to understand that grammar, punctuation and vocabulary are needed to achieve the purpose of the text show a growing awareness of words that enrich their vocabulary
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
EN3-6B uses knowledge of sentence structure, grammar, punctuation and vocabulary to respond to and compose clear and cohesive texts in different media and technologies understand that language is structured to create meaning according to audience, purpose and context understand that choices in grammar, punctuation and vocabulary contribute to the effectiveness of texts
EN1-9B uses basic grammatical features, EN2-9B uses effective and accurate sentence punctuation conventions and vocabulary structure, grammatical features, punctuation appropriate to the type of text when responding conventions and vocabulary relevant to the type to and composing texts of text when responding to and composing texts Students develop and apply contextual knowledge understand that ideas in texts can be understand that effective organisation of organised to enhance meaning using ideas in imaginative, informative and sentences and paragraphs persuasive texts enhances meaning understand that choice of vocabulary begin to understand that choice of impacts on the effectiveness of texts vocabulary adds to the effectiveness of text
Understand and apply knowledge of language forms and features recognise that texts are made up of words and groups of words that make meaning (ACELA1434) recognise that sentences are key units for expressing ideas (ACELA1435) identify statements, questions, commands and exclamations and their functions in texts experiment with adverbial phrases in structured and guided activities to indicate when, where and how actions occurred, eg last week, at home demonstrate an awareness of nouns, pronouns and conjunctions recognise simple pronoun references to maintain meaning understand that punctuation is a feature of written text different from letters; recognise how capital letters are used for names, and that capital letters and full stops signal the beginning and end of sentences (ACELA1432) identify features of sentence punctuation, eg question marks and exclamation marks, when reading and composing understand that paragraphs are used to organise ideas understand that simple connections can be made between ideas by using a compound sentence with two or more clauses usually linked by a coordinating conjunction(ACELA1467) explore differences in words that represent people, places and things (nouns, including pronouns), happenings and states (verbs), qualities (adjectives) and details such as when, where and how (adverbs) (ACELA1452) recognise that a preposition placed in front of a noun group can show where, when, eg 'on the box' (where), 'before my birthday' (when) recognise that time connectives sequence information in texts recognise that different types of punctuation, including full stops, question marks and exclamation marks, signal sentences that make statements, ask questions, express emotion or give commands (ACELA1449) recognise that capital letters signal proper nouns and commas are used to separate items in lists (ACELA1465) experiment with the use of quoted (direct) and reported (indirect) speech understand that paragraphs are a key organisational feature of written texts (ACELA1479) understand that a clause is a unit of grammar usually containing a subject and a verb and that these need to be in agreement (ACELA1481) understand how to elaborate on ideas in texts through the use of prepositional phrases understand how adverb groups/phrases and prepositional phrases work in different ways to provide circumstantial details about an activity (ACELA1495) understand that the meaning of sentences can be enriched through the use of noun groups/phrases and verb groups/phrases and prepositional phrases (ACELA1493) identify and use grammatical features, eg pronouns, conjunctions and connectives, to accurately link ideas and information understand that verbs represent different processes (doing, thinking, saying, and relating) and that these processes are anchored in time through tense(ACELA1482) experiment with punctuation to engage the reader and achieve purpose investigate how quoted (direct) and reported (indirect) speech work in different types of identify and explain how choices in language, for example modality, emphasis, repetition and metaphor, influence personal response to different texts (ACELT1615) understand the difference between main and subordinate clauses and that a complex sentence involves at least one subordinate clause (ACELA1507) experiment using a range of language features, eg connectives, topic sentences, active and passive voice and nominalisation understand how noun groups/phrases and adjective groups/phrases can be expanded in a variety of ways to provide a fuller description of the person, place, thing or idea (ACELA1508) understand how ideas can be expanded and sharpened through careful choice of verbs, elaborated tenses and a range of adverb groups/phrases (ACELA1523) show how ideas and points of view in texts are conveyed through the use of vocabulary, including idiomatic expressions, objective and subjective language, and that these can change according to context (ACELY1698) identify a variety of connectives in texts to indicate time, add information, clarify understanding, show cause and effect and
Shoal Bay Public School
text (ACELA1494) use apostrophes for contractions identify a variety of connectives in texts to indicate time, to add information and to clarify understanding indicate condition/concession use complex punctuation to engage the reader and achieve purpose understand how the grammatical category of possessives is signalled through apostrophes and how to use apostrophes with common and proper nouns(ACELA1506) understand the uses of commas to separate clauses (ACELA1521)
Understand and apply knowledge of vocabulary begin to build personal vocabulary know the meaning of commonly used words demonstrate an awareness that some words have multiple meanings
understand how texts are made cohesive through resources, for example word associations, synonyms, and antonyms(ACELA1464) recognise, discuss and use creative word play, eg alliteration and onomatopoeia
learn extended and technical vocabulary and ways of expressing opinion including modal verbs and adverbs (ACELA1484) experiment with vocabulary choices to engage the listener or reader
understand the use of vocabulary to express greater precision of meaning, and know that words can have different meanings in different contexts (ACELA1512) investigate how vocabulary choices, including evaluative language can express shades of meaning, feeling and opinion
compose effective sentences in writing using appropriate word order begin to use statements and questions with appropriate punctuation attempt to incorporate unfamiliar words in writing use a growing vocabulary to describe everyday events and experience
Respond to and compose texts begin to organise ideas into paragraphs compose a range of effective imaginative, when composing texts informative and persuasive texts using compose sentences effectively using basic language appropriate to purpose and grammatical features and punctuation audience conventions use grammatical features to create use subjectverb and nounpronoun complex sentences when composing texts agreement when composing texts and experiment with figurative language when responding to texts orally and in writing composing texts to engage an audience, eg demonstrate the use of more precise similes, metaphors, idioms and vocabulary to describe emotions and personification experiences when writing incorporate new vocabulary from a range of sources into students' own texts including vocabulary encountered in research (ACELA1498)
select some more challenging language features, literary devices (eg irony, humour) and grammatical features (eg modality) to engage and influence an audience experiment with different types of sentences, eg short sentences to build tension and complex sentences to add detail use topic sentences and appropriately organise main (independent) and subordinate (dependent) ideas to enhance coherence in written texts select appropriate language for a purpose, eg descriptive, persuasive, technical, evaluative, emotive and colloquial, when composing texts use grammatical features, eg pronouns, conjunctions and connectives, to accurately link ideas and information to ensure meaning when composing texts
Shoal Bay Public School Sequence of Grammar, Punctuation and Vocabulary
Term 1 Week
1
Kindergarten
sentence - one or more
clauses; a key unit for expressing ideas. A written sentence begins with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, question mark or exclamation mark.
Year 1
capital letters (JG unit 1)
start of sentences
Year 2
word families (JG unit 25)
words linked because they deal with the same topic
Year 3
dictionary use (JG unit 1)
Year 4
clause main a clause may
be a sentence on its own (main clause) or may be combined with a main clause to form a sentence
Year 5
topic sentence - a sentence that introduces the main idea or theme of a paragraph
Year 6
author voice - use of firstperson and third-person narration
capital letter - used for
names and to signal the beginning of a sentence
time
connectives
paragraphing (JG unit 25) begins with a topic sentence (introducing the idea) in factual texts
complex sentence an
independent (main) clause and a dependent (subordinate) clause linked by a subordinating conjunction . eg We all went outside when the sun came out. When the sun came out, we all went outside. clauses a complete message or thought expressed in words: a clause includes a verb
Clause verb
a clause includes a verb
words that sequence information in texts, eg first, next, finally
full stop - used to signal the
end of a sentence
word families - rhyming
speech marks (JG unit 3)
quoted (direct) speech eg, Kim said, I want to go home
clause noun a clause includes
a subject (noun or noun group that agrees with the verb in person and number), eg The children ran to the bus clause noun group a clause may include an object (additional noun or noun group, affected by the action), eg The children ran to the bus
noun - a naming word for a
person, place or thing
common nouns
(JG unit 6)
questions (JG unit 4) question mark -used to signal
the end of a question
paragraphs (JG unit 13)
noun group - a group of words built around a noun that describes or specifies the noun: may include adjectival phrases, eg the chair next to my desk
noun group - a group of words built around a noun that describes or specifies the noun: may include adjectival/ relative clauses, eg the chair that is next to my desk
proper nouns (JG unit 5) a
naming word for a person, place eg Mary, Sydney
commas in lists (JG unit 5)
paragraphs (JG unit 14)
plurals
adjective a word that describes a noun: classifying, eg native flower
statement - provides
information, eg I am leaving now
synonyms (JG unit 33) words
that have the same or similar meaning ,eg leave/depart
exclamation marks
(JG unit 6)
simple tense
eg Koalas eat leaves (present)
noun singular a naming word
for a person, place or thing: singular, eg girl
adjective a word that describes a noun: modal, eg possible answer
antonyms (JG unit 30)
words that have opposite meanings, eg hot/cold, arrive/leave
nounpronoun agreement
selection of the correct pronoun for the noun or noun group to which it refers, eg The girl ate her lunch
past tense
eg, She went home (past)
noun plural a naming word
for a person, place or thing: plural, eg girls
pronoun reference
determining the noun to which a pronoun refers, eg Koalas eat leaves. Koalas are not bears. They are
article - a or an
(JG unit 8)a, an, the placed before a noun to form part of a noun group; may refer to a specific person or thing (the), or a non-specific person or thing (a, an) plurals (JG unit 9)
proper nouns (JG unit 8)
direct speech
(JG unit 15 and 16) eg, I am going to leave, she said
noun collective a naming
word for a person, place or thing: collective eg crowd
pronoun - a word that stands instead of a noun: relative pronoun, eg who, that (for people) and which, that (for things)
elaborated tenses -multiple word tenses, eg We have been working for three hours
adjectives (JG unit 9)
describing, eg size, colour, shape round, beautiful, sunny) numbering,eg two
indirect speech
eg, She said that she was going to leave
noun groups
a group of words built around a noun that describes or specifies the noun
Shoal Bay Public School
Sequence of Grammar, Punctuation and Vocabulary
Term 2 Week 1 Kindergarten
capital letter - used for names and to signal the beginning of a sentence command tells us to do something, eg Close the door command tells us to do something, eg Close the door who/what/when/where words
Year 1
pronouns (JG unit 10) a word that stands instead of a noun: personal pronoun, eg I, me, it capital letter used for proper nouns
Year 2
plurals and es (JG unit 10)
Year 3
nouns singular and pluraleg girl, girls
Year 4
verbs relating a word that tells what is happening or what is: eg She is my teacher verb feeling a word that tells what is happening or what is eg I liked the movie
Year 5
main clause (independent clause) a clause that can stand alone as a complete sentence, though it may be joined with other clauses, eg The child came first.
Year 6
subordinate clause (dependent clause) a clause that cannot stand alone as a sentence
possessive adjective unit 11)
(JG
commas separates items in a list
homophones (JG unit 12)
homonyms words with the same sound and the same spelling,but a different meaning, eg bark (tree), bark (sound made by dog) homophones ( JG unit 29) words with the same sound but different spelling and meaning, eg fair, fare quotation marks used to signal dialogue, titles and quoted (direct) speech collective nouns (JG unit 33) eg crowd
verb possessing a word that tells what is happening or what is: eg He has a new car verb groups a group of words
built up around a verb: may include auxiliary (helping) verbs, eg She is sitting here may include two or more verbs, eg He huffed and puffed
word families -word webs (JG unit 33)
alphabetical order (JG units 1, 7, 13)
who/what/when/where words
action verbs (JG unit 14) describes doing or saying, eg run, shout
sentences, verbs (JG unit 14) clauses - a complete message or thought expressed in words: a clause includes at least one noun and one verb adverbs (JG unit 15) adverbial phrases contributes extra information about the main clause, eg how, when, where, why verb to be present (JG unit 16)
adjectives possessive a word that describes a noun: possessive, eg our
questions and question marks asks for an answer, eg Are you busy? pronouns (he, she, they) a word that stands instead of a noun, eg I, me, he, she conjunctions joining word, eg and, so, but
past tense verbs (JG unit 15)
clauses subject and object (JG unit 35)
adjectives comparative a word that describes a noun: comparative, eg bigger adverbs modality a word that tells something about a verb, adjective or another verb modality, eg possibly adverbs degree a word that tells something about a verb, adjective or another verb degree, eg very apostrophes used to signify a contraction
evaluative language words used to give a text a particular perspective(eg judgemental, critical ,emotional), to evoke a particular audience response, and to express shades of feeling, meaning or opinion, eg: emotive language nominalisation forming nouns from verbs (eg reaction from react or departure from depart)
evaluative language words used to give a text a particular perspective(eg judgemental, critical ,emotional), to evoke a particular audience response, and to express shades of feeling, meaning or opinion, eg modality (possibility, probability, obligation, conditionality)
present tense verbs (JG unit 26)
adjectives (JG unit 23)
nominalisation adjectives (eg length from long, eagerness from eager)
future tense verbs (JG unit 18)
regular past tense (JG unit 17)
contractions (JG unit 19)
clause structure revision statement, command, question
nouns
irregular past tense (JG unit 18)
syllables (JG unit 6 and 12)
Shoal Bay Public School
Sequence of Grammar, Punctuation and Vocabulary
Term 3 Week Kindergarten
adjectives a word that describes a noun
Year 1
compound sentences and conjunctions two
or more clauses usually linked by a coordinating conjunction ,eg The bell rang and Kim went home
Year 2
creative language features onomatopoeia, eg the wind whooshed - repetition proofreading sentences and paragraphing (JG Unit 20)
Year 3
subject of sentence (JG unit 25)
Year 4
noun a naming word for a person, place or thing: terms of address, eg Mr Jones
Year 5
apostrophe - used to signify possession
Year 6
comma - used to separate clauses
adjectives a word that describes a noun
nouns (JG unit 20)
object of a sentence (JG unit 26)
word origins the source and history of words (etymology), eg telephone (Greek), pedestrian (Latin), bungalow (Indian) preposition placed in front of a noun group to show time (when), place (where), manner (how) or causality (why), eg in front of, throughout, underneath prepositional phrase
units of meaning within a clause that begin with a preposition; indicate how, when, where or why, eg She ran into the garden, He is available from nine oclock
conjunctions joining word, eg and, so, but
adjectives - describing (JG units 21 and 22) describing, eg size, colour, shape (big, red, round, beautiful, sunny)
verb to be past and subject verb agreement (JG Unit 21) selection of a verb
form which matches the number of its subject (noun or noun group), eg They were at home; The cat is sitting still; The people are on the boat
subject and object pronouns (JG unit 27)
reference links links that keep track of the people, animals or objects throughout a text; usually nouns or pronouns, eg Mabel played netball on Saturday. She fell over and hurt her arm
creative language features emphasis, irony, humour
conjunctions joining word, eg and, so, but
adjectives - numbering numbering, eg two
expanding a sentence and compound sentences (JG Unit 22) two or more
clauses usually linked by a coordinating conjunction ,eg The bell rang and Kim went home
Adverb a word that tells
something about a verb, adjective or another verb, eg manner, place or time. Adverbs may show: modality, eg possibly, degree, eg very comments or opinions, eg luckily
pronoun a word that stands instead of a noun, eg I, me, he, she pronoun a word that stands instead of a noun, eg I, me, he, she
word families colours words linked because they deal with the same topic compound words (JG unit 24)
conjunctions and indirect speech (JG Unit 23) eg, Kim said that she wanted to go home plurals s and ies (JG Unit 24)
connectives words with link
paragraphs and sentences, eg on the other hand, however, furthermore, therefore, because, although
cohesive links eg, pronouns, conjunctions, connectives connectives words which link
paragraphs and sentences, eg on the other hand, however, furthermore, therefore, because, although
idiom eg Pull yourself together
Voice indicates who or what is performing an action; modified by changing the beginning focus of a clause :active voice the doer comes before the verb, eg Mark (doer) finished (verb) the work (done to)
7 8 9
exclamations and exclamation marks for emphasis, eg I won! exclamations and exclamation marks for emphasis, eg I won! clause structure revision statement, command, question, exclamation
antonyms and synonyms (JG Unit 30) action verbs (JG Unit 26) thinking verbs a word that tells what is happening or what is: eg wonder, imagine
abstract nouns eg happiness, surprise proofreading stories (JG Unit 26) prefixes (JG Unit 27) attached to the beginning of a base word to change the meaning, eg unhappy
collective nouns (JG unit 33) verb tense (JG unit 36)
complex and compound sentence personification eg The water licked at my feet nonsense words spoonerisms, neologisms, puns
Voice indicates who or what is performing an action; modified by changing the beginning focus of a clause- passive voice the receiver of the action is placed before the verb, eg The work (receiver) was finished (action) by Mark (doer)
possessive pronouns (JG unit 28)
Shoal Bay Public School
Sequence of Grammar, Punctuation and Vocabulary
Term 4 Week 1 Kindergarten
adverbial phrases (where) contributes extra information about the main clause adverbial phrases (when) contributes extra information about the main clause adverbial phrases (how) contributes extra information about the main clause conjunctions joining word, eg and, so, but quotation marks used to signal quoted (direct) speech quotation marks used to signal quoted (direct) speech pronoun a word that stands instead of a noun, eg I, me, he, she adjective/noun clause structure revision statement, command, question, exclamation
Year 1
adverbs (JG units 27 and 28)
Year 2
apostrophes (JG unit 28) used to signify a contraction
Year 3
metaphor eg She is an angel
Year 4
homonyms words with the same sound and the same spelling, but a different meaning, eg bark (tree), bark (sound made by dog) homophones words with the same sound but different spelling and meaning, eg fair, fare cohesive links
Year 5
verb group a group of words built up around a verb :may include a preposition or adverb, eg The plane took off
Year 6
verb group a group of words built up around a verb: may include modal verbs, eg It might be finished tomorrow
base words eg happy
contractions (JG unit 29) apostrophe for missing letter or letters
simile eg She sings like an angel
alliteration eg slippery, slithering snakes
prepositions (JG unit 30)
nonsense words nonsense words, spoonerisms, neologisms, puns
noun a naming word for a person, place or thing: technical, eg nucleus
verb group a group of words built up around a verb: may be complex verbs, eg The plane started to move
articles and adjectives eg the sunny day, a long and bumpy road speech marks (JG unit 32) question mark (JG units 34 and 35) exclamation mark
finding the meaning (JG unit 31) suffix ing (JG unit 32)
homophones (JG unit 30) personification eg The water licked at my feet irregular plurals (JG unit 24) contractions (JG unit 2419)
simile eg She sings like an angel metaphor eg She is an angel idiom eg Pull yourself together direct speech eg, I am going to leave, she said indirect speech eg, She said that she was going to leave quotation marks used to signal dialogue, titles and quoted (direct) speech elaborated tenses multiple word tenses,eg We have been working for three hours
suffixes er and est (JG unit 33) verbs action and thinking
7 8 9
nouns revision nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns (JG unit 36)
commas in speech (JG unit 35) parsing (JG unit 36)
proper nouns places (JG unit 10) proper adjectives (JG unit 11)
Você também pode gostar
- Ais Y2 English Scope and Sequence v9Documento4 páginasAis Y2 English Scope and Sequence v9api-263015735Ainda não há avaliações
- Speaking and Listening 1 Scope and Sequence 2014Documento5 páginasSpeaking and Listening 1 Scope and Sequence 2014api-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Yearly Overview Language Literature Literacy: Interpreting, Analysing, EvaluatingDocumento4 páginasYearly Overview Language Literature Literacy: Interpreting, Analysing, Evaluatingapi-278745102Ainda não há avaliações
- Reading and Viewing 2Documento6 páginasReading and Viewing 2api-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 3-6 EALD Progression by Mode WritngDocumento1 página2 3-6 EALD Progression by Mode WritngS TANCREDAinda não há avaliações
- Acara Scope and Sequence - Year 8 EnglishDocumento13 páginasAcara Scope and Sequence - Year 8 Englishapi-327852760Ainda não há avaliações
- Intermediate Levels BrochureDocumento2 páginasIntermediate Levels BrochureOni DanielleAinda não há avaliações
- AIS CuriculumDocumento4 páginasAIS CuriculumSukma eka putriAinda não há avaliações
- G6 English SyllabusDocumento6 páginasG6 English SyllabusEllen Grace Cepeda ManzanoAinda não há avaliações
- Task 3 Assessment 2Documento23 páginasTask 3 Assessment 2api-330154764Ainda não há avaliações
- Literacy Rotations - Sarah BianchiDocumento21 páginasLiteracy Rotations - Sarah Bianchiapi-317851832Ainda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Guide EnglishDocumento35 páginasCurriculum Guide EnglishAce Dela Cruz EnriquezAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar Unit Term 4Documento14 páginasGrammar Unit Term 4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- F-Educ4671-20s1-Sp1 91390975 1066268600 Holly Buttler - Integrated Literacy PlanDocumento9 páginasF-Educ4671-20s1-Sp1 91390975 1066268600 Holly Buttler - Integrated Literacy Planapi-425610696Ainda não há avaliações
- LessonsDocumento33 páginasLessonsapi-220617761Ainda não há avaliações
- Topic 2bDocumento65 páginasTopic 2bKritikaa De BritoAinda não há avaliações
- 2020 Curriculum Map English 1-2Documento6 páginas2020 Curriculum Map English 1-2Rachael HoneyAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Phonics WedDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan Phonics Wedapi-336176285Ainda não há avaliações
- Highlighted Framework PointsDocumento7 páginasHighlighted Framework Pointsprincess27SAinda não há avaliações
- Elementary Levels BrochureDocumento2 páginasElementary Levels BrochureOni DanielleAinda não há avaliações
- English Language Arts - Grade 8 Standards: Students Spend A Majority of Time Immersed in Quality Texts and TasksDocumento7 páginasEnglish Language Arts - Grade 8 Standards: Students Spend A Majority of Time Immersed in Quality Texts and Tasksapi-327134647Ainda não há avaliações
- Year 5 Curriculum OutlineA3Documento5 páginasYear 5 Curriculum OutlineA3StAugustinesSchoolAinda não há avaliações
- s2 The Lost Thing English UnitDocumento19 páginass2 The Lost Thing English Unitapi-233094051Ainda não há avaliações
- Eal D Students ContentDocumento2 páginasEal D Students Contentapi-317064960Ainda não há avaliações
- Ela 2nd Quarter Revised-New 1-Use This OneDocumento10 páginasEla 2nd Quarter Revised-New 1-Use This Oneapi-267962355Ainda não há avaliações
- Stage 2 Literacy Unit JOURNEYSDocumento11 páginasStage 2 Literacy Unit JOURNEYSS TANCRED100% (2)
- Website Content Des and ElabDocumento3 páginasWebsite Content Des and Elabapi-264952803Ainda não há avaliações
- Gold Rush LetterDocumento19 páginasGold Rush Letterapi-253614149Ainda não há avaliações
- RMT Grade 4 Learning OutcomesDocumento4 páginasRMT Grade 4 Learning Outcomesapi-307152920Ainda não há avaliações
- Finals HandoutsDocumento5 páginasFinals Handoutscecille ramirezAinda não há avaliações
- Expressing and Developing Ideas Interacting With Others Responding To LiteratureDocumento10 páginasExpressing and Developing Ideas Interacting With Others Responding To Literatureapi-558855172Ainda não há avaliações
- Hero Intro Gramma R Survival Pack Persuasi Ve Essay Peak Study Hero Narrativ e Socratic Seminar Term GradeDocumento2 páginasHero Intro Gramma R Survival Pack Persuasi Ve Essay Peak Study Hero Narrativ e Socratic Seminar Term Gradeapi-307036001Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 3-6 EALD Progression by Mode Reading ViewingDocumento1 página6 3-6 EALD Progression by Mode Reading ViewingS TANCRED100% (1)
- Year 2 English Portfolio SatisfactoryDocumento0 páginaYear 2 English Portfolio SatisfactoryernsteinsAinda não há avaliações
- Scope and Sequence EnglishDocumento12 páginasScope and Sequence Englishapi-265440308Ainda não há avaliações
- Y2 Grammar T 2Documento2 páginasY2 Grammar T 2api-208000806Ainda não há avaliações
- Diff Assignment 2Documento11 páginasDiff Assignment 2api-478112286Ainda não há avaliações
- RMT Grade 2 Learning OutcomesDocumento5 páginasRMT Grade 2 Learning Outcomesapi-307152920Ainda não há avaliações
- English: Assignment One Modelled Writing Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasEnglish: Assignment One Modelled Writing Lesson Planapi-357571395Ainda não há avaliações
- Content For Year 5 - Learning Area Content DescriptionsDocumento4 páginasContent For Year 5 - Learning Area Content Descriptionsapi-298473661Ainda não há avaliações
- Scheme of Work English Stage 8.v1Documento32 páginasScheme of Work English Stage 8.v1Sue Adames de Velasco100% (7)
- Secondary Course (English-202) : CurriculumDocumento7 páginasSecondary Course (English-202) : CurriculumSrinivas MantryAinda não há avaliações
- Lbs 400 English ReflectionDocumento2 páginasLbs 400 English Reflectionapi-281334959Ainda não há avaliações
- KG Language Learning OutcomesDocumento4 páginasKG Language Learning Outcomesapi-293281365Ainda não há avaliações
- English K To 12 Curriculum Guide - Grades 1 To 3, 7 To 10Documento35 páginasEnglish K To 12 Curriculum Guide - Grades 1 To 3, 7 To 10Jeje Angeles100% (6)
- Week 3Documento3 páginasWeek 3api-482599157Ainda não há avaliações
- Feedback: Feedback Specifics For Each Subject 1. ReadingDocumento2 páginasFeedback: Feedback Specifics For Each Subject 1. ReadingMonica DanielAinda não há avaliações
- TSL3108 Grammar Rules Language FormationDocumento4 páginasTSL3108 Grammar Rules Language FormationKing Gilgamesh0% (1)
- Topic 12Documento7 páginasTopic 12Teresa Pajarón LacaveAinda não há avaliações
- 5 3-6 EALD Progression by Mode SpeakingDocumento1 página5 3-6 EALD Progression by Mode SpeakingS TANCREDAinda não há avaliações
- Y2 GrammarDocumento2 páginasY2 Grammarapi-208000806Ainda não há avaliações
- Marking RubricDocumento6 páginasMarking RubricKim Louise Hartley100% (1)
- Grade 2 Reading Writing Language StandardsDocumento6 páginasGrade 2 Reading Writing Language StandardsDenver TamayoAinda não há avaliações
- ESIO Trot Unit-Leanne WilliamsonDocumento17 páginasESIO Trot Unit-Leanne WilliamsonS TANCRED100% (2)
- Portuguese A Language ObjectivesDocumento10 páginasPortuguese A Language ObjectivesmarianaosantosAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 1 Learning OutcomesDocumento4 páginasGrade 1 Learning Outcomesapi-293668836100% (1)
- Year 1 English v9Documento5 páginasYear 1 English v9api-256832695Ainda não há avaliações
- K To 12 English Competencies Grade 1 3Documento11 páginasK To 12 English Competencies Grade 1 3Lcsb FucultyAinda não há avaliações
- The Language Lab: Step-by-Step Guide to Improving Language AbilitiesNo EverandThe Language Lab: Step-by-Step Guide to Improving Language AbilitiesAinda não há avaliações
- Expressing ThemselvesDocumento2 páginasExpressing Themselvesapi-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Thinking Imaginatively and CreativelyDocumento3 páginasThinking Imaginatively and Creativelyapi-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Reflecting On LearningDocumento4 páginasReflecting On Learningapi-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Spelling Scope and Sequence 2014Documento4 páginasSpelling Scope and Sequence 2014api-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Expressing ThemselvesDocumento2 páginasExpressing Themselvesapi-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Reading and Viewing 1Documento5 páginasReading and Viewing 1api-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Handwriting and Digital Technologies 2014Documento2 páginasHandwriting and Digital Technologies 2014api-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Writing and Representing 1 2014Documento3 páginasWriting and Representing 1 2014api-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Speaking and Listening 2 Scope and Sequence 2014Documento5 páginasSpeaking and Listening 2 Scope and Sequence 2014api-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- k-10 Lit Cont OverviewDocumento5 páginask-10 Lit Cont Overviewapi-226169467Ainda não há avaliações
- Wonders Grammar Student WorkbookDocumento33 páginasWonders Grammar Student WorkbookMartha BarraganAinda não há avaliações
- Types of senten-WPS OfficeDocumento6 páginasTypes of senten-WPS OfficeAsad AsadAinda não há avaliações
- (Sem1) English Language Proficiency 1Documento27 páginas(Sem1) English Language Proficiency 1Mohd Awie RaniAinda não há avaliações
- English 7-Q3-M14Documento15 páginasEnglish 7-Q3-M14Joams artsAinda não há avaliações
- Sentence StructureDocumento11 páginasSentence StructureDennis Ebenezer DhanarajAinda não há avaliações
- Primary Eng Paper 1 PDFDocumento114 páginasPrimary Eng Paper 1 PDFatef84% (25)
- My Elder BrotherDocumento19 páginasMy Elder BrotherSanjeevSharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Fia Mock Test 2Documento11 páginasFia Mock Test 2Tariq Ali BoukAinda não há avaliações
- LP For Coordinating ConjunctionsDocumento3 páginasLP For Coordinating Conjunctionsmajenta 19Ainda não há avaliações
- Writing Chapter One Introducing YourselfDocumento42 páginasWriting Chapter One Introducing YourselfArefAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar For Descriptive TextDocumento10 páginasGrammar For Descriptive TextEko SuwignyoAinda não há avaliações
- Commas With Complex Sentences PDFDocumento2 páginasCommas With Complex Sentences PDFLal Bux SoomroAinda não há avaliações
- Time Is A Great TeacherDocumento17 páginasTime Is A Great TeacherMuhammad Hamza HamzaAinda não há avaliações
- Sen. Tella Nelson Femi GST 111 Questions and AnswersDocumento28 páginasSen. Tella Nelson Femi GST 111 Questions and Answersmcpaulo495Ainda não há avaliações
- GramUnit 1 PDFDocumento12 páginasGramUnit 1 PDFJanineP.DelaCruzAinda não há avaliações
- PAPER 1 TM Code 42 Session 2 Set W 2 24.02.2018 PDFDocumento58 páginasPAPER 1 TM Code 42 Session 2 Set W 2 24.02.2018 PDFsriramAinda não há avaliações
- Sentence Patterns 1-20.pdf - TeacherDocumento4 páginasSentence Patterns 1-20.pdf - Teachermahmud1974alam100% (1)
- Types of sentences and complements with examplesDocumento16 páginasTypes of sentences and complements with examplesDung Nguyễn HoàngAinda não há avaliações
- Team 5 - Writing NextDocumento25 páginasTeam 5 - Writing NextMERI CAHYANIAinda não há avaliações
- Answer: A. Direct - Indirect SentencesDocumento4 páginasAnswer: A. Direct - Indirect SentencesCloud ProjectAinda não há avaliações
- Review BookDocumento242 páginasReview Booksofia londoñoAinda não há avaliações
- GrammarDocumento45 páginasGrammarkomilboy001Ainda não há avaliações
- English Revision BookletDocumento20 páginasEnglish Revision BookletBlack Ink Tutorials & Services96% (46)
- Compare sentence typesDocumento3 páginasCompare sentence typesElena N.Ainda não há avaliações
- English Midterm Exam QuestionsDocumento3 páginasEnglish Midterm Exam Questionsnabila putriAinda não há avaliações
- Adjective Clause Worksheet EslDocumento6 páginasAdjective Clause Worksheet EslHugh YipAinda não há avaliações
- Constituent Analysis of The SentenceDocumento10 páginasConstituent Analysis of The SentenceАнастасия ЗаворотнаяAinda não há avaliações
- Complex SentenceDocumento2 páginasComplex SentenceThời PhạmAinda não há avaliações
- Subject Terminology For English Lang and LitDocumento3 páginasSubject Terminology For English Lang and Litapi-200352820Ainda não há avaliações
- Noun/Pronoun Verb: (On Board) Basic Sentence Patterns in EnglishDocumento16 páginasNoun/Pronoun Verb: (On Board) Basic Sentence Patterns in EnglishRocky C PlataAinda não há avaliações