Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Piglabinfo
Enviado por
api-244598990Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Piglabinfo
Enviado por
api-244598990Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Organ and Pig Info
Cuts:
anterior/rostral: front face
posterial/caudal: back side
lateral: side, "towards the side face
medial: towards the middle, center
dorsal: on the top, "head
ventral: on the bottom
sagittal: divides the left and right sides (x-axis)
frontal/coronal: perpendicular to the sagittal (y-axis)
horizontal: divides the top and bottom sides (z-axis)
Random Info
Pig is mammal
mammals have hair and mammary glands
mammals have two or more types of teeth for example molars and canines. 2 sets. Milk teeth
and permanent teeth.
Red blood cells do not have nucleus and are round
Pigs members of artiodactyla. Have even toes. Cows and deer as well.
omnivores
can live 15-20 years. bacon before though
adults reach weight up to 400 kg (approximately 900 lbs.)
time of development of fetus is 112-11.
7-12 offsprings per litter
similar to man
pigs used to test drugs, surgical techniques
pig body parts transported to humans. Valves, skin
to figure out pig age you measure from tip of nose to tail for example 1cm=20 days
skin important organ
2 layers epidermis and dermis
Pig can be divided into 4 sections=head, neck, trunk, and tail
trunk divided into thorax and abdomen
thorax region that contains ribs
forelegs connected to shoulders
abdomen were teats (mammary papillae)
Both male and female have teats males don't work
placenta is a fetal organ that serves as interaction between mothers and fetuses circulatory
system
umbilical cord attached to this ^
InternaI Anatomy
To view internal anatomy tie up pig and make cut along mid-ventral line of body on stomach
As lengthen incision toward thoracic cavity will feel resistance from ribs and sternum
Fetal pigs ribs and sternum still composed of cartilage
Cut through rib cage expose organs
see heart enclosed in whitish sac-like membrane, (pericardium).
whitish tube size pencil=trachea
Thymus endocrine gland involved in immune system response during infancy lies on either side
of trachea and extends of heart.
thyroid brown oval structure lying on top of trachea
peritoneum=white shiny/cut far enough
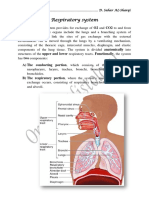
Respiratory system
Begins with larynx enlarged region of trachea inside is fibrous cords that vibrate when air passes
over them producing sounds.
tracheas tube that connects the lungs with nasopharynx reinforced with cartilage that keep it
from collapsing. lined with cells that trap mucus and foreign particles and pass them back to the
oral cavity
dorsal to trachea lies second tube esophagus part of digestive system as well.
Trachea branches into two tubes. each known as bronchus or both as bronchi
inside lungs bronchial tubes divide further into secondary bronchi then into bronchioles then into
very fine tubes that give rise? to microscopic air sacs known as alveoli
gasses exchange occurs in alveoli
Each lung divided into sections known as lobes four lobes on right and three on left
lungs cradle heart
Lungs and blood vessels merge under heart this is where pulmonary viens and arteries enter
and leave the lungs.
Diaphragm separates abdominal cavity from thoracic cavity. lungs and heart anterior from
diaphragm
Diaphragm responsible for moving air in and out of lungs
alveoli where exchange occurs
Digestive system
begins with mouth
food broken up by teeth
saliva aids in lubrication of food and contains enzymes that break down complex molecules into
simple ones so that they can be absorbed later on
food prevented from entering nasal cavity by hard and soft plates
breathing is stopped for a little to swallow food.
epiglottis: flap of cartilage at the root of the tongue, used to cover the windpipe and push food into
esophagus
esophagus: muscular tube which connects the mouth to stomach, passes behind the trachea
and attaches to stomach
liver is used in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, formation of some blood
proteins, secretion of bile, filters/breaks downs toxins produced during protein metabolism,
produces glycogen (carb used for energy)
gall bladder: small, sac-like structure used to store bile
bile: digestive juice produced by the liver, emulsifies fat (keeps it from mixing)
stomach: sac-like muscular organ used in the storage and digestion of food
glands in stomach lining secrete digestive juices such as hydrochloric acid and pepsin, mixes
gastric juices with salivary juices and foods
pyloric sphincter: junction between stomach and small intestine
spleen: brown, oblong, firm organ found along greater curvature of stomach designed to filter the
blood, produces antibodies and white blood cells
pancreas: exocrine organ which secretes pancreatic juice used in the digestion of food,
endocrine organ which produces hormones used to regulate blood sugar (insulin, glucagon,
somatostatin)
small intestine: slender tube which emerges from the stomach, breaks down protein, fats and
starches with the liver and pancreas
large intestine: organ which is primarily concerned with consolidating waste and removing
remaining water, leads to the rectum and anus which gets rid of the waste
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- NCP CopdDocumento10 páginasNCP Copdarnnie100% (2)
- Respiratory SystemDocumento12 páginasRespiratory SystemHema Kamat100% (1)
- Bronchiectasis: Citadel B. Rabanes, MD First Year JRRMMC-Department of RadiologyDocumento34 páginasBronchiectasis: Citadel B. Rabanes, MD First Year JRRMMC-Department of Radiologyadhik_deepak100% (1)
- Normal Chest RadiographDocumento108 páginasNormal Chest RadiographVenu Madhav100% (1)
- B Inggris Halim NCP Asma BronchialDocumento28 páginasB Inggris Halim NCP Asma BronchialAbdul HlmAinda não há avaliações
- Pne67!2!08pozzi ReviewDocumento10 páginasPne67!2!08pozzi ReviewmunirdayaniAinda não há avaliações
- Conchiolinum. - The Encyclopedia of Pure Materia Medica by Timothy F. Allen, A.m., M.DDocumento7 páginasConchiolinum. - The Encyclopedia of Pure Materia Medica by Timothy F. Allen, A.m., M.DAmjad KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Benign Lung TumorDocumento16 páginasBenign Lung TumorAbdul Mubdi ArdiansarAinda não há avaliações
- Acid Rain - Biological Effects and ImplicationsDocumento15 páginasAcid Rain - Biological Effects and Implicationsamir sultanAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Notes: Bell High SchoolDocumento42 páginasBiology Notes: Bell High SchoolRichard Ye93% (14)
- Answers of Histology SlidesDocumento38 páginasAnswers of Histology SlidesJiyaa PatelAinda não há avaliações
- ANAPHY Lec Session #18 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Documento7 páginasANAPHY Lec Session #18 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaAinda não há avaliações
- Post Tubercular Sequelae.123175034Documento29 páginasPost Tubercular Sequelae.123175034Andre Prasetyo MahesyaAinda não há avaliações
- Science Class 5 NotesDocumento27 páginasScience Class 5 NotesHarshil PatelAinda não há avaliações
- MCQS Snell Anatomy 9th EditionDocumento65 páginasMCQS Snell Anatomy 9th EditionUsama198750% (2)
- Respiratory System: A) The Conducting Portion, Which Consists of The Nasal CavitiesDocumento7 páginasRespiratory System: A) The Conducting Portion, Which Consists of The Nasal CavitiesSalmah Alimah FitriAinda não há avaliações
- The Respiratory SystemDocumento18 páginasThe Respiratory SystemTamilore WilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- Pathology of The Lungs 3rd Ed (PDF) (Tahir99) VRGDocumento746 páginasPathology of The Lungs 3rd Ed (PDF) (Tahir99) VRGCosmin SilviuAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocumento9 páginasPathophysiology of PneumoniaJeanette IrambonaAinda não há avaliações
- Life Processes 2Documento30 páginasLife Processes 2Generic nameAinda não há avaliações
- EPISTAXIS-bleeding From The Nose (Most Common) Etiology (Cause)Documento34 páginasEPISTAXIS-bleeding From The Nose (Most Common) Etiology (Cause)Julliza Joy PandiAinda não há avaliações
- Mrcs Part B Osce-AnatomyDocumento392 páginasMrcs Part B Osce-AnatomyWaeel Hamouda100% (3)
- AICE Bio Notes Pages 186-190: Gas ExchangeDocumento2 páginasAICE Bio Notes Pages 186-190: Gas ExchangeSanzida HossainAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Module Activity Respiratory SystemDocumento8 páginasLab Module Activity Respiratory SystemJecel LazarraAinda não há avaliações
- Respirator LangmanDocumento10 páginasRespirator LangmanSavu MalinaAinda não há avaliações
- COPDDocumento50 páginasCOPDalilnaAinda não há avaliações
- Iodine Toxicity in RuminantsDocumento9 páginasIodine Toxicity in RuminantsNilesh BariAinda não há avaliações
- Toxic Responses of Respiratory System (Pulmonotoxicity)Documento41 páginasToxic Responses of Respiratory System (Pulmonotoxicity)Mand BadyAinda não há avaliações
- Recognizing Interstitial Versus Airspace Disease: in Slide Show Mode, Advance The Slides by Pressing The SpacebarDocumento32 páginasRecognizing Interstitial Versus Airspace Disease: in Slide Show Mode, Advance The Slides by Pressing The SpacebarCheska TumulakAinda não há avaliações
- BIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 7Documento32 páginasBIOLOGY Form 4 Chapter 7Shephard Png85% (13)