Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Notes Template - Plate Tectonics
Enviado por
api-227609796Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Notes Template - Plate Tectonics
Enviado por
api-227609796Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Name: ___________________________________________
Date: __________________________ Period: ___________
Plate Tectonics
The Physical Setting: Earth Science
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
I.
Continental Drift
Continental Drift - !_____________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Pangaea - ! ___________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Alfred Wegner (1915)
German ___________________ and ____________________
Proposed the theory of !__________________________________________________________
Hypothesized a ! ________________________________________________________________
Evidence of Continental Drift:
1. !______________________________________________________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
2. !______________________________________________________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
3. !______________________________________________________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
Leigh-Manuell - 1
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
II. Crustal Activity
Plate Tectonics - !______________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Plate - ! ______________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Lithosphere - !_________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Asthenosphere - !______________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Earths surface consists of a dozen major plates and some minor ones
The plates are moving at rates close to ___________ cm/year
Iceland
Hot Spot
as
t
f
st A
Pe
Easter Island
Hot Spot
idge
ou
the
Galapagos
Hot Spot
Pa
cifi
cR
Indian-Australian
Plate
Pacific
Plate
Tasman
Hot Spot
Ind
ia n
Ridg
Nazca
Plate
Antarctic
Plate
Leigh-Manuell - 2
South
American
Plate
St. Helena
Hot Spot
Scotia
Plate
st
Ea
Antarctic
Plate
African
Plate
an
ibbe
Car late
P
Cocos
Plate
hile Tren
u-C
ch
Ea
Fiji Plate
To n g a
Tr e n c h
rican Ri
f
dian Ridge
-In
Hawaii
Hot Spot
Canary
Islands
Hot Spot
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
a
Tr ria n a
e n ch
ian
ab
Ar late
P
an
i
nd
tI
s
e
we g
th id
ou R
Yellowstone
Hot Spot
Juan de
Fuca Plate
San Andreas
Fault
Philippine
Plate
Mi
d
Eurasian
Plate
cR
idg
e
Aleutian
ch
Tren
North American
Plate
Mid
-A
tla
nti
Eurasian
Plate
Bouvet
Hot Spot
Sandwich
Plate
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
Convection Currents - ! _________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Magma heats up causing it to ___________________ and ____________________
Magma cools down causing it to ___________________ and ____________________
The plates are moving on top of the asthenosphere due to density differences
The idea of continental drift had been around since the 1900s, but lacked enough scientic evidence to support the theory
New advancements after World War II help provide the evidences needed to validate the Theory of
Plate Tectonics
Earthquake Evidence
Scientists noticed that earthquakes do not occur at random locations, but throughout the
world along __________________________________
When plotted on a map they outline the !____________________________________________
(dots represent earthquake epicenter locations)
Volcanic Evidence
Occurs at plate boundaries where plates are interacting
Ring of Fire - ! __________________________________________________________________
!__________________________________________________________________
Leigh-Manuell - 3
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
Rock Evidence
Sedimentary deposits and igneous lava ows are usually placed down in horizontal layers
Sometimes movement along boundaries causes these layers to ! ______________________
or ________________________
Mountain Evidence
As plates collide they sometimes are pushed ! _______________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
! ______________________________________________________________________________
Leigh-Manuell - 4
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
III.
Crustal Boundaries
Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting
As they move across the _______________________________ and form plate boundaries they interact in various ways
Types of plate boundaries:
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
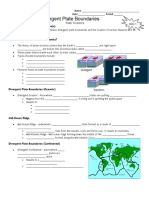
Convergent Boundary - !________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Example: the India Plate pushing upward into Eurasian Plate and creating the Himalayan
Mountains
Subduction - !_________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Example: the Nazca Plate being consumed under the South American Plate
Three Types of Convergent Boundaries
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
Leigh-Manuell - 5
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
Divergent Boundary - !__________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Example: part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge emerges from the ocean and splits Iceland in half
Sea-Floor Spreading - ! __________________________________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
Mid-Ocean Ridge - ! _____________________________________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
Mid-Atlantic Ridge - ! ____________________________________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
Separates the N. and S. American Plates from the Eurasian and African Plates
Rift Valley - !____________________________________________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
Divergent Plate Boundary Evidence
Scientists dragged a ______________________
across the ocean oor and discovered a unique
magnetic pattern where stripes of
___________________ and ___________________
polarity parallel the mid-ocean ridge ipping every
76 million years
Rock samples of the deep ocean oor show that basaltic oceanic crust becomes
progressively ____________________ as you approach the mid-ocean ridge
Leigh-Manuell - 6
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
Transform Boundary - ! _________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Example: the San Andreas Fault is 800 km long and runs throughout California
Tectonic Plates
Iceland
Hot Spot
as
t
Pe
Easter Island
Hot Spot
idge
rican Ri
f
f
st A
Ea
Galapagos
Hot Spot
Tasman
Hot Spot
Ind
ia n
Ridg
Antarctic
Plate
Key
South
American
Plate
St. Helena
Hot Spot
Scotia
Plate
st
Ea
Antarctic
Plate
Relative motion at
plate boundary
Nazca
Plate
Pa
cifi
cR
ou
the
To n g a
Tr e n c h
Indian-Australian
Plate
Pacific
Plate
African
Plate
an
ibbe
Car late
P
Cocos
Plate
hile Tren
u-C
ch
dian Ridge
-In
Fiji Plate
Canary
Islands
Hot Spot
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
a
Tr ria n a
e n ch
ian
ab
Ar late
P
S
Hawaii
Hot Spot
ia
nd
tI
es ge
w
d
th i
ou R
Yellowstone
Hot Spot
Juan de
Fuca Plate
San Andreas
Fault
Philippine
Plate
Mi
d
Eurasian
Plate
cR
idg
e
h
Aleutian Trenc
North American
Plate
Mid
-A
tla
nti
Eurasian
Plate
Bouvet
Hot Spot
Sandwich
Plate
overriding
plate
Transform plate boundary
(transform fault)
Divergent plate boundary
(usually broken by transform
faults along mid-ocean ridges)
subducting
plate
Convergent plate boundary
(subduction zone)
Leigh-Manuell - 7
Complex or uncertain
plate boundary
Mantle
hot spot
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
IV. Earths Interior
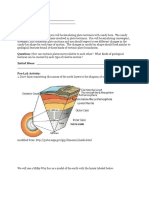
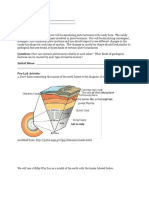
Earths interior structures are known through the study of " ___________________________________
Seismic waves refract, _________________________, __________________________ and are absorbed depending on the material they are transmitted through
Lithosphere - !_________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Continental Crust - !__________________________________________________________
!___________________________________________________________________________
Oceanic Crust - !_____________________________________________________________
!___________________________________________________________________________
MOHO - thin interface separating the lithosphere from the asthenosphere
Asthenosphere - !______________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Discovery: a decrease in velocity from earthquake waves
Mantle - !_____________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Outer Core - ! _________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Discovery: absorption and refraction of earthquake waves
Inner Core - !__________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Discovery: an increase in velocity from earthquake waves
Leigh-Manuell - 8
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
TIC
LAN
AT
AN
OCE
DENSITY (g/cm3)
IC
TLANT
MID-A GE
RID
CASCADES
9.912.2
REL)
COICKE
&
LE
NT
MA
RE )
COICKEL
TRENCH
12.813.1
IN N
(IRO ER
N&
N
PACIFIC
OCEAN
3.45.6
RO
N
STI
FF
ER
LA
(P
OU
TE
(I
LI
}
NO
SP
HE
R
CR
RIG UST
ID
MA
NT
AS
TH
LE
E
NO
RT
H
AM
ER
IC
A
)
RE
T LE
HE
AN
SP
M
O
IC
TH
ST
2.7 granitic continental crust
3.0 basaltic oceanic crust
MOHO
V. Earthquakes
Earthquake - !_________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Most earthquakes are caused by a movement along a fault where ! _____________________
energy is given off as a seismic wave
Epicenter - !___________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Focus - !______________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Seismometer - ! _______________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Seismogram - !________________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
Leigh-Manuell - 9
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
Mercalli Scale - scale that measures the _______________________ of an earthquake based on the
effects to Earths surface, humans, objects in nature, and other man-made structures
The values will differ based on the distance from the epicenter
!_________________________________________________________________
!_________________________________________________________________
Intensity
Type of Damage
Instrumental
II
Feeble
III
Slight
IV
V
Rather Strong
VI
VII
Very Strong
VIII
IX
Ruinous
Disastrous
XI
Very Disastrous
XII
Richter Scale - logarithmic scale that measures the _____________________________________ released during an earthquake
Magnitude - a number to quantify the amount of ________________________________ released
from an earthquake
The Richter Scales magnitude is determined from the following measurements:
!___________________________________________________________________________
!___________________________________________________________________________
!___________________________________________________________________________
Leigh-Manuell - 10
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
Primary Wave (P-wave)
___________________________________________
Travel through __________________, __________________, and __________________
Compressional - ! _______________________________________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
Secondary Wave (S-wave)
___________________________________________
Travel through __________________ only
Shear - ! _______________________________________________________________________
!______________________________________________________________________________
Compressional Wave (P-wave)
Shear Wave (S-wave)
Seismic waves radiate away from the focus
Leigh-Manuell - 11
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
Shadow Zone - !_______________________________________________________________________
!_____________________________________________________________________________________
P-waves are ____________________ when they reach the liquid outer core
S-waves are ____________________ when they reach the outer core and are not transmitted through to the other side
P-wave Shadow Zone
S-wave Shadow Zone
Epicenters are located using the velocity differences between the p-wave and s-wave
Since the p-waves travel ____________________ then s-waves, as your distance
_____________________ from the earthquake's epicenter the arrival time between the two
waves will be __________________
Leigh-Manuell - 12
Class Notes: Plate Tectonics
Distance to the epicenter is determined by comparing the arrival times and the E.S.R.T.
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
TRAVEL TIME (min)
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
10
EPICENTER DISTANCE ( 103 km)
To nd the epicenter location you need to triangulate a position using ___________________ different seismometer stations
Leigh-Manuell - 13
Você também pode gostar
- Aural History, Regional Studies and Literature in British ColumbiaNo EverandAural History, Regional Studies and Literature in British ColumbiaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Geological Maps and Structures: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesNo EverandIntroduction to Geological Maps and Structures: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Convergent Plate Boundaries Guided NotesDocumento2 páginasConvergent Plate Boundaries Guided NotesTracy NewKirkAinda não há avaliações
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Geologic Time ScaleDocumento4 páginasGENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Geologic Time ScalelouAinda não há avaliações
- K10 Quarter 1 Module 1 Activity No. 2Documento5 páginasK10 Quarter 1 Module 1 Activity No. 2Daniel TabingaAinda não há avaliações
- G11 EarSci Q2 W3Documento6 páginasG11 EarSci Q2 W3Grace SagosoAinda não há avaliações
- Motion of The SunDocumento3 páginasMotion of The SunBrianThompsonAinda não há avaliações
- Evidence of Evolution Guided Notes StudentDocumento3 páginasEvidence of Evolution Guided Notes Studentapi-290100812Ainda não há avaliações
- Review Packet-Earth ScienceDocumento10 páginasReview Packet-Earth Sciencemsthomas79Ainda não há avaliações
- Science Grade VDocumento4 páginasScience Grade VNabeela KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet 1: Types of Plate BoundariesDocumento6 páginasWorksheet 1: Types of Plate BoundariesNoeljaysel AlejoAinda não há avaliações
- Divergent Plate Boundaries Guided NotesDocumento1 páginaDivergent Plate Boundaries Guided NotesTracy NewKirkAinda não há avaliações
- Transform Plate Boundaries Guided NotesDocumento1 páginaTransform Plate Boundaries Guided NotesTracy NewKirkAinda não há avaliações
- Activity No. - : LET'S MARK BOUNDARIES Objectives:: Group No. - Section: - ScoreDocumento2 páginasActivity No. - : LET'S MARK BOUNDARIES Objectives:: Group No. - Section: - ScoreshizukikuroAinda não há avaliações
- Changes To The Earth's Surface?Documento1 páginaChanges To The Earth's Surface?Federico MazzaAinda não há avaliações
- Science Mock ExamDocumento4 páginasScience Mock ExamJaslyn Claire CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Building Pangaea SEDocumento4 páginasBuilding Pangaea SEShirin HaddadinAinda não há avaliações
- Class Notes: Minerals and Rocks: The Physical Setting: Earth ScienceDocumento16 páginasClass Notes: Minerals and Rocks: The Physical Setting: Earth Sciencepaulchristian satoAinda não há avaliações
- Glgq1g10 Sci Las Set 4 ColoredDocumento4 páginasGlgq1g10 Sci Las Set 4 ColoredPogi AkoAinda não há avaliações
- Guided Notes PlatetectonicunitDocumento2 páginasGuided Notes Platetectonicunitapi-351897877Ainda não há avaliações
- Civics: Weather Climate Rainfall Weather Revolution Orbits Temperature Rotation Humidity PagasaDocumento4 páginasCivics: Weather Climate Rainfall Weather Revolution Orbits Temperature Rotation Humidity PagasaTalah SeseAinda não há avaliações
- Portfolio inDocumento31 páginasPortfolio inThess Tecla Zerauc AzodnemAinda não há avaliações
- Layers of Earth WRKSHTDocumento5 páginasLayers of Earth WRKSHTapi-531818627Ainda não há avaliações
- Q1 Module 4 Lesson 7 AnswersheetDocumento3 páginasQ1 Module 4 Lesson 7 AnswersheetLennie DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Esch 065 KeyDocumento2 páginasEsch 065 KeyJonathan TabbunAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 Geosphere Review Sheet - AcademicDocumento4 páginasUnit 4 Geosphere Review Sheet - AcademicNyla Robinson-PartridgeAinda não há avaliações
- l2 Candybar Tectonics Worksheet AnswersDocumento5 páginasl2 Candybar Tectonics Worksheet AnswersJoy Ann Akia PasigonAinda não há avaliações
- l2 Candybar Tectonics Worksheet AnswersDocumento5 páginasl2 Candybar Tectonics Worksheet AnswerssayAinda não há avaliações
- Earth and Life Science Q1 Week 722Documento13 páginasEarth and Life Science Q1 Week 722urhjnlbrgts11Ainda não há avaliações
- Earth Science Q2 Week 6 - REFINED - EDITEDDocumento12 páginasEarth Science Q2 Week 6 - REFINED - EDITEDJay Buiza NozalAinda não há avaliações
- Plate Tectonics Review WebquestDocumento10 páginasPlate Tectonics Review WebquestDELILAH MAXWELLAinda não há avaliações
- Tectonic Plates Are Plates That Make Up The Earth's SurfaceDocumento3 páginasTectonic Plates Are Plates That Make Up The Earth's SurfaceBliss Dizon-BicaldoAinda não há avaliações
- ReportDocumento72 páginasReportJessareth CapacioAinda não há avaliações
- BuildingPangaeaSEDocumento7 páginasBuildingPangaeaSETieghan MorrisAinda não há avaliações
- Building Pangaea GizmosDocumento4 páginasBuilding Pangaea GizmosNora PonceAinda não há avaliações
- Yr8 The World Beneath UsDocumento40 páginasYr8 The World Beneath UsMaria JiaAinda não há avaliações
- 1-3 Drifting Continents PDFDocumento5 páginas1-3 Drifting Continents PDFGeorge Chandler100% (1)
- History of The Earth Evolution Fill-In NotesDocumento20 páginasHistory of The Earth Evolution Fill-In Notesapi-622033028Ainda não há avaliações
- Oceanography Study GuideDocumento9 páginasOceanography Study Guideapi-199925868100% (1)
- Continentaldrifthypothesis JeffreyyuDocumento2 páginasContinentaldrifthypothesis Jeffreyyuapi-341861410Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit Plan ActivitiesDocumento10 páginasUnit Plan Activitiesapi-639531624Ainda não há avaliações
- G /: - D: - S: - Plate Tectonics (Activity 3.2)Documento3 páginasG /: - D: - S: - Plate Tectonics (Activity 3.2)anieleAinda não há avaliações
- EqtsunamiDocumento7 páginasEqtsunamiapi-251874912Ainda não há avaliações
- Science 10 Answersheets Week 7 To 8Documento4 páginasScience 10 Answersheets Week 7 To 8Misis AdaAinda não há avaliações
- Guided NotesDocumento2 páginasGuided Notesapi-242744059Ainda não há avaliações
- Luigi Oliveira (Student MHS) - Plate Tectonics Web-QuestDocumento8 páginasLuigi Oliveira (Student MHS) - Plate Tectonics Web-QuestLuigi Oliveira (Student MHS)Ainda não há avaliações
- Sea-Floor Spreading B WKSHTDocumento3 páginasSea-Floor Spreading B WKSHTapi-251874912Ainda não há avaliações
- Momentum QuestionsDocumento5 páginasMomentum QuestionsAda BrigoleAinda não há avaliações
- SSss T1-U1Documento7 páginasSSss T1-U1Elimer Ag.Ainda não há avaliações
- LC 1 Learning Task 2 Lets Mark The BoundariesDocumento4 páginasLC 1 Learning Task 2 Lets Mark The BoundariesAldrin Manalo SabinoAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Minerals and RocksDocumento12 páginas5 Minerals and RocksMark Allen JugalbotAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 Magnetism Student Note PackageDocumento18 páginasUnit 5 Magnetism Student Note Packageapi-604347267Ainda não há avaliações
- Globe - Latitudes and LongitudesDocumento2 páginasGlobe - Latitudes and LongitudesNeeraja RanjithAinda não há avaliações
- China DBQ CcssDocumento15 páginasChina DBQ Ccssapi-245681790Ainda não há avaliações
- Actvity Worksheet - LMS-NAT22222Documento6 páginasActvity Worksheet - LMS-NAT22222Maestro de Grapico0% (1)
- Actvity Worksheet - LMS-NAT22222Documento6 páginasActvity Worksheet - LMS-NAT22222Marlon Joseph ManzanoAinda não há avaliações
- Class 5 Sst3Documento1 páginaClass 5 Sst3Ajay MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Geology of Istarú QuadrangleDocumento54 páginasGeology of Istarú QuadranglePabloAinda não há avaliações
- History - WorksheetsDocumento4 páginasHistory - WorksheetsMaria Jose FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Starburst Rock Cycle LabDocumento3 páginasStarburst Rock Cycle Labapi-4340089340% (1)
- Shear Riedel StyleDocumento20 páginasShear Riedel Style13092014Ainda não há avaliações
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Movements of Plates and Formation of Folds and FaultsDocumento23 páginasEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 10: Movements of Plates and Formation of Folds and Faultshara azurAinda não há avaliações
- Earth and Space Science Grade 10 Quarter 1 Modules 2, 3 Weeks 4, 5, 6 Long Quiz 2 Direction: Read Each Question and Write TheDocumento2 páginasEarth and Space Science Grade 10 Quarter 1 Modules 2, 3 Weeks 4, 5, 6 Long Quiz 2 Direction: Read Each Question and Write TheJasmine SaligaoAinda não há avaliações
- Plate Boundaries ObservationDocumento26 páginasPlate Boundaries ObservationPatrick Casquejo AndalesAinda não há avaliações
- Plate Tectonics QuizDocumento3 páginasPlate Tectonics QuizJeffery Lee Boggan Jr.Ainda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesDocumento7 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) : Knowledge Skills Attitudes ValuesAndrie Vonn Perocho NerpiolAinda não há avaliações
- Geothermal Energy Technology and Current Status - An OverviewDocumento63 páginasGeothermal Energy Technology and Current Status - An OverviewRickAinda não há avaliações
- World Stress MapDocumento55 páginasWorld Stress MapTarun SinghalAinda não há avaliações
- Plate Tectonic Theory and Continental Drift TheoryDocumento4 páginasPlate Tectonic Theory and Continental Drift TheoryLoui Mark Loui MarkAinda não há avaliações
- Science10 Q1 Mod2 Plate BoundariesDocumento25 páginasScience10 Q1 Mod2 Plate BoundariesMomshie Ella82% (11)
- Duad - GeologyDocumento13 páginasDuad - GeologyPrince SanjiAinda não há avaliações
- Q1 Summative-Test Science-10Documento5 páginasQ1 Summative-Test Science-10Nheil Ayrton CañeteAinda não há avaliações
- New Curr 2019 GeoDocumento166 páginasNew Curr 2019 GeoDealAinda não há avaliações
- Interactive Map QuestionsDocumento4 páginasInteractive Map Questionsapi-251874912Ainda não há avaliações
- GRADE 10 Plate-BoundariesDocumento23 páginasGRADE 10 Plate-BoundariesGilbert Monterde BaflorAinda não há avaliações
- Evidence: The Continental Jigsaw PuzzleDocumento6 páginasEvidence: The Continental Jigsaw PuzzleChristopher Shane GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Plate Tectonics AnswerDocumento4 páginasPlate Tectonics AnswerthAinda não há avaliações
- EARTH SCIENCE ReviewerDocumento11 páginasEARTH SCIENCE ReviewerLeira EroaAinda não há avaliações
- Convergent Boundaries: Divergent BoundaryDocumento3 páginasConvergent Boundaries: Divergent BoundaryTrishia PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Complete Book ChaptersDocumento0 página1 Complete Book ChaptersAadilIftikharAinda não há avaliações
- LR ModuleDocumento10 páginasLR ModuleDaniel NacordaAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 10 June Exam Marking Guideline 2023-2Documento9 páginasGrade 10 June Exam Marking Guideline 2023-2Masimo SeforaAinda não há avaliações
- 11212021091341M3 EARTH SCIENCE Deformation of The Earths CrustDocumento14 páginas11212021091341M3 EARTH SCIENCE Deformation of The Earths CrustJhon PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Faults: Fault TerminologyDocumento35 páginasFaults: Fault TerminologyJuan David Velez HoyosAinda não há avaliações
- Earth'S Materials and Processes: Marilyn P. MifuelDocumento57 páginasEarth'S Materials and Processes: Marilyn P. MifuelSheyah Villanueva100% (1)
- Structure of The EarthDocumento47 páginasStructure of The Earthapi-270383743100% (1)
- Strike SlipDocumento5 páginasStrike SlipClarisse Fernandes100% (1)
- Summative QuizDocumento2 páginasSummative QuizDarryl CalimlimAinda não há avaliações
- G10-Science-Q1-Module 2Documento19 páginasG10-Science-Q1-Module 2Xiomara Jude SolonAinda não há avaliações
- UPCAt Earth Science Module 1Documento14 páginasUPCAt Earth Science Module 1fodavila50% (2)