Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Prenatal Development
Enviado por
api-246379610Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Prenatal Development
Enviado por
api-246379610Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
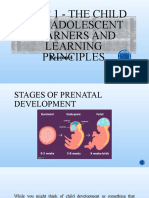
There are 3 basic periods of prenatal development: A.
Germinal Period 8 to 10 days to 2 weeks; ends with egg attachment to uterine wall. Cleavage the mitotic division of the zygote into several cells; begins at 24 hours after conception. Division rates are different and this yields heterogeneity variability in the rate of change of different parts. 1. As cleavage occurs, a cluster of cells called the morula take shape in the zona pellucida. After the 5th day post-conception,
the cells begin taking in nutrients; this is the first interaction with the environment (the fallopian tube). 2. A fluid filled cavity forms in the morula thus facilitating the change into a blastocyst hollow sphere of cells. The blastocyst has two kinds of cells. One set of small cells are the inner cell mass, which gives rise to the organisms, whereas the other set of flat cells surrounding the inner cell mass called the trophoblast, form a protective barrier b/w the inner cell mass and the environment. 3. As the blastocyst moves further into the uterus, the trophoblast cells branch out into the mothers uterus to the blood vessels. This begins implantation, the process by which the blastocyst becomes attached to the uterus. This action marks the transition to the embryonic period. B. Embryonic Period up to 8 weeks; ends when all major organs have formed. The embryo is surrounded by the amnion, a thin, tough, transparent membrane that holds the amniotic fluid, which protects the embryo from damaging movements. 1. Surrounding the amnion is the chorion, the precursor to the placenta, a complex organ of tissue from mom and embryo that acts as a filter allowing oxygen, nutrients, and waste to be exchanged. Waste is filtered through moms kidneys and excreted. 2. While the trophoblast is forming the placenta and other membranes, the inner cell mass is busy evolving into organs. Then the inner cell mass separates into two layers: a. ectoderm outer; skin, nails, teeth, eye lens, inner ear, and nervous system b. endoderm inner; digestive system and lungs Then a third layer develops b/w these two: c. mesoderm middle; muscles, circulatory system & inner skin
3. Organogenesis process of organ formation that takes place during first two prenatal months. 4. Human growth follows two patterns from now until adolescence: a. cephalocaudal head to toe (arms then legs) b. proximodistal inside to out (shoulder before wrists) C. Fetal Period from 9 weeks to birth (30 weeks); bones harden and infant is able to survive outside mother. At 17 to 18 weeks fetal activity declines as the higher regions of the brain develop. This period of inhibited activity persists until six months. Then activity increases. 1. At this point the fetus experiences endogenous (internal to fetus) and exogenous (external) movement. Movement is essential for limb development. Adverse Factors Affecting Fetal Development Although the womb provides protection, the fetus remains indirectly connected to the outside world through its mother. Several factors that are linked to the mother can harm the fetus: Poor nutrition Use of alcohol Smoking Use of certain prescription or over-the-counter drugs Use of recreational drugs such as cocaine, sedatives, and narcotics X-rays and other kinds of radiation Ingested toxins, such as lead Illnesses such as AIDS, German measles, syphilis, cholera, smallpox, mumps, or severe flu Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Mothers who drink heavily during pregnancy may have babies with fetal alcohol syndrome. Babies with this syndrome may have problems such as
slow physical growth, small head size, heart defects, irritability, hyperactivity, mental retardation, or slowed motor development.
Resources: Berk, L. E. (2013).Child development. (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson. Mossler, R.A. (2011). Child and adolescent development. Bridgepoint Education, Inc.
Você também pode gostar
- DevelopmentDocumento2 páginasDevelopmentMichelle UpodAinda não há avaliações
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento20 páginasPrenatal DevelopmentVictoria AntonetteAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Paul Rockwell, A New York Physician, Made This Profound Observation After His AmazingDocumento12 páginasDr. Paul Rockwell, A New York Physician, Made This Profound Observation After His AmazingJosephine ArcibalAinda não há avaliações
- Development of the Child from Prenatal to ToddlerhoodDocumento21 páginasDevelopment of the Child from Prenatal to ToddlerhoodMay ann AntonioAinda não há avaliações
- Pre NatalDocumento30 páginasPre Natalelna troganiAinda não há avaliações
- Development of The Learners at The Various StagesDocumento32 páginasDevelopment of The Learners at The Various StagesMelanie SerquiñaAinda não há avaliações
- Fertilisation, implantation and development of the embryo and fetusDocumento39 páginasFertilisation, implantation and development of the embryo and fetusJanae CampbellAinda não há avaliações
- MODULE 11 v3 LatestDocumento50 páginasMODULE 11 v3 LatestBrigette Kim Lumawas100% (3)
- Developmental StagesDocumento17 páginasDevelopmental StagesAhmer AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2Documento15 páginasUnit 2Tanvi ManjrekarAinda não há avaliações
- Principles Of Early Childhood DevelopmentDocumento14 páginasPrinciples Of Early Childhood DevelopmentMelAinda não há avaliações
- Foundation ReviewerDocumento8 páginasFoundation ReviewerYhang KasanAinda não há avaliações
- Prenatal Development StagesDocumento11 páginasPrenatal Development StagesAnanya GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- Module 6 - Development of The Learners at Various StagesDocumento25 páginasModule 6 - Development of The Learners at Various StagesRachelle DalingAinda não há avaliações
- Biophysical Aspects of PregnancyDocumento34 páginasBiophysical Aspects of PregnancyRucrispi VirayoAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation Group 1Documento29 páginasPresentation Group 1SABAHAT SHAHID BS Applied PsychologyAinda não há avaliações
- Prenatal Development and Birth: Prepared by Ms. Sana AslamDocumento12 páginasPrenatal Development and Birth: Prepared by Ms. Sana AslamAmatul MusawarAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento24 páginasEssential Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentMylene MahinayAinda não há avaliações
- Educ 101 ReviewerDocumento27 páginasEduc 101 ReviewerRolando AmadAinda não há avaliações
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento33 páginasPrenatal DevelopmentDexter Nario0% (1)
- Photo By: Soupstock: BlastocystDocumento11 páginasPhoto By: Soupstock: BlastocystZain Ul abideenAinda não há avaliações
- Competency 3 DoneDocumento2 páginasCompetency 3 Doneapi-264474189Ainda não há avaliações
- Prenatal and Postnatal: DevelopmentDocumento22 páginasPrenatal and Postnatal: DevelopmentenergygapAinda não há avaliações
- Prenat DevelDocumento3 páginasPrenat DevelenergygapAinda não há avaliações
- The development of life in the wombDocumento19 páginasThe development of life in the wombJessabelle D CasanovaAinda não há avaliações
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento66 páginasPrenatal DevelopmentBlessie NgitngitAinda não há avaliações
- Normal PregnancyDocumento65 páginasNormal PregnancyRhesie Joyce AguilarAinda não há avaliações
- Embryonic Development and Fetal Growth StagesDocumento8 páginasEmbryonic Development and Fetal Growth StagesCarenza AlainAinda não há avaliações
- Prenatal Development (Child Psychology)Documento37 páginasPrenatal Development (Child Psychology)Yel BaldemorAinda não há avaliações
- Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento4 páginasStages of Prenatal DevelopmentJinli BalaticoAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Natal DevelopmentDocumento44 páginasPre Natal DevelopmentLisa Gurrea100% (2)
- Developmental Psychology Lecture 1 MidtermsDocumento3 páginasDevelopmental Psychology Lecture 1 MidtermsAngelo SumaoyAinda não há avaliações
- Pre-natal Development StagesDocumento5 páginasPre-natal Development StagesRachel Joy SaldoAinda não há avaliações
- Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento17 páginasStages of Prenatal DevelopmentMary Ellen Martillos AguinilloAinda não há avaliações
- Educ 1 - 4Documento71 páginasEduc 1 - 4Rolando T. Jaravata Jr.Ainda não há avaliações
- Biological and Environmental Causes of Developmental DisabilitiesDocumento9 páginasBiological and Environmental Causes of Developmental DisabilitiesAngelica MadronaAinda não há avaliações
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento20 páginasPrenatal DevelopmentJosephine ArcibalAinda não há avaliações
- Stages of Human Development Before BirthDocumento3 páginasStages of Human Development Before BirthAaronotix GamingAinda não há avaliações
- NMD-4 Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento49 páginasNMD-4 Prenatal DevelopmentYorgos TheodosiadisAinda não há avaliações
- Childhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions ManualDocumento12 páginasChildhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions ManualJenniferAguilarrfiax100% (10)
- Module #4 Educ Iii Prenatal PeriodDocumento10 páginasModule #4 Educ Iii Prenatal PeriodGinaly PicoAinda não há avaliações
- Development of The Learners at Various Stage: Submitted byDocumento22 páginasDevelopment of The Learners at Various Stage: Submitted byArly Boy TadumanAinda não há avaliações
- Lifespan Psychology chp3Documento5 páginasLifespan Psychology chp3khadijahAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 6Documento9 páginasUnit 6Amjad PathanAinda não há avaliações
- EmbryogenesisDocumento9 páginasEmbryogenesisSanchita SabatAinda não há avaliações
- Dwnload Full Childhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions Manual PDFDocumento36 páginasDwnload Full Childhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions Manual PDFdoughnut.synocilj084s100% (8)
- Childhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions ManualDocumento36 páginasChildhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions Manualaudiblycaribbeeuwiq100% (14)
- Chapter 29 - Development and Inheritance: ST ND RD STDocumento5 páginasChapter 29 - Development and Inheritance: ST ND RD STtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayAinda não há avaliações
- Prof Ed2editedDocumento60 páginasProf Ed2editedEdelyn CuriosoAinda não há avaliações
- Cad Module 11 23 Unit1 Unit5 ReviewerDocumento47 páginasCad Module 11 23 Unit1 Unit5 ReviewerJelmar CastuloAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Outline - Conception - Periods of Prenatal DevelopmentDocumento28 páginasLecture Outline - Conception - Periods of Prenatal DevelopmentaEnahAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1.1 SummaryDocumento2 páginasModule 1.1 SummaryElijah RevillaAinda não há avaliações
- General Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekDocumento141 páginasGeneral Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third Weekmutumamiguel15Ainda não há avaliações
- AnswersDocumento2 páginasAnswersPAULAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityDocumento62 páginasUnit 2 - Fertilization, Impantation, Development of Placenta and Its Function, AbnormalityN. Siva100% (1)
- Child and Adolescent Learners Module 4Documento11 páginasChild and Adolescent Learners Module 4Markhill Veran TiosanAinda não há avaliações
- EmbryologyDocumento9 páginasEmbryologyRuhul Qudus NaimAinda não há avaliações
- DevPsych NewDocumento15 páginasDevPsych NewRea Grace YosoresAinda não há avaliações
- Embryological Developemnt PDTCDocumento14 páginasEmbryological Developemnt PDTCJoy JoycAinda não há avaliações
- How To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornNo EverandHow To Have an Easy and Safe Pregnancy and Bring Forth a Healthy Baby: A Pregnancy Book for First Time Moms for a Successful and Healthy Journey through Pregnancy, Childbirth and NewbornAinda não há avaliações
- Infant and ToddlerhoodDocumento8 páginasInfant and Toddlerhoodapi-246379610Ainda não há avaliações
- Resources Used FinalDocumento2 páginasResources Used Finalapi-246379610Ainda não há avaliações
- AdolescenceDocumento6 páginasAdolescenceapi-246379610Ainda não há avaliações
- Self-Regulation NewsletterDocumento2 páginasSelf-Regulation Newsletterapi-246379610Ainda não há avaliações
- Early ChildhoodDocumento7 páginasEarly Childhoodapi-246379610Ainda não há avaliações
- Middle ChildhoodDocumento6 páginasMiddle Childhoodapi-246379610Ainda não há avaliações
- Parent Presentation FinalDocumento20 páginasParent Presentation Finalapi-246379610Ainda não há avaliações
- USA Vs Andrei KulagoDocumento260 páginasUSA Vs Andrei KulagoAndrew KerrAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Lesson 2 Video Asa Aas HL NotesDocumento2 páginasUnit 3 Lesson 2 Video Asa Aas HL Notesapi-264764674Ainda não há avaliações
- BIO125 Syllabus Spring 2020Documento3 páginasBIO125 Syllabus Spring 2020Joncarlo EsquivelAinda não há avaliações
- Reflection Paper About Educational Administration (Ivy M. Peralta)Documento1 páginaReflection Paper About Educational Administration (Ivy M. Peralta)Ivy peraltaAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Physics - Chapter 27Documento67 páginasModern Physics - Chapter 27Hamza PagaAinda não há avaliações
- Slides Iso 17021 Be LacDocumento117 páginasSlides Iso 17021 Be Lacjorge.s1943Ainda não há avaliações
- A LITTLE CHEMISTRY Chapter 2-1 and 2-2Documento5 páginasA LITTLE CHEMISTRY Chapter 2-1 and 2-2Lexi MasseyAinda não há avaliações
- Test Booklet Primary-1 PDFDocumento53 páginasTest Booklet Primary-1 PDFReynold Morales Libato100% (1)
- Program Python by ShaileshDocumento48 páginasProgram Python by ShaileshofficialblackfitbabaAinda não há avaliações
- Interventional Radiology & AngiographyDocumento45 páginasInterventional Radiology & AngiographyRyBone95Ainda não há avaliações
- 2022 Australian Grand Prix - Race Director's Event NotesDocumento5 páginas2022 Australian Grand Prix - Race Director's Event NotesEduard De Ribot SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Provide feedback on BS 7671 18th EditionDocumento5 páginasProvide feedback on BS 7671 18th EditionYashveer TakooryAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Transfer DoeDocumento32 páginasHeat Transfer DoeArt RmbdAinda não há avaliações
- Wa0000.Documento6 páginasWa0000.Sanuri YasaraAinda não há avaliações
- Reading SkillsDocumento37 páginasReading SkillsShafinaz ZhumaAinda não há avaliações
- Malunggay cooking oil substituteDocumento5 páginasMalunggay cooking oil substitutebaba112Ainda não há avaliações
- Practical Exercise - Analysis of The Collapse of Silicon Valley BankDocumento2 páginasPractical Exercise - Analysis of The Collapse of Silicon Valley Bankhanna.ericssonkleinAinda não há avaliações
- Topographic Map of New WaverlyDocumento1 páginaTopographic Map of New WaverlyHistoricalMapsAinda não há avaliações
- Stages On The Empirical Program of RelativismDocumento9 páginasStages On The Empirical Program of RelativismJorge Castillo-SepúlvedaAinda não há avaliações
- GUIDE FOR ROOM EXAMINER - 2023-05 Revised (CSE-Pen & Paper Test) - ModifiedDocumento14 páginasGUIDE FOR ROOM EXAMINER - 2023-05 Revised (CSE-Pen & Paper Test) - ModifiedLeilani BacayAinda não há avaliações
- METACOGNITION MODULEDocumento4 páginasMETACOGNITION MODULEViolet SilverAinda não há avaliações
- ACE Personal Trainer Manual Chapter 13Documento59 páginasACE Personal Trainer Manual Chapter 13Đạt NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Verify File Integrity with MD5 ChecksumDocumento4 páginasVerify File Integrity with MD5 ChecksumSandra GilbertAinda não há avaliações
- Agriculture DisciplineDocumento3 páginasAgriculture DisciplineUmair FaheemAinda não há avaliações
- Getting More Effective: Branch Managers As ExecutivesDocumento38 páginasGetting More Effective: Branch Managers As ExecutivesLubna SiddiqiAinda não há avaliações
- Cotton-Top Tamarin - Husbandry - ManualDocumento98 páginasCotton-Top Tamarin - Husbandry - Manualjoaquin chan100% (1)
- Under DronesDocumento336 páginasUnder DronesRobert LewisAinda não há avaliações
- Controlled Vadose Zone Saturation and Remediation (CVSR)Documento35 páginasControlled Vadose Zone Saturation and Remediation (CVSR)FranciscoGarciaAinda não há avaliações
- William Gilpin On Picturesque TravelDocumento7 páginasWilliam Gilpin On Picturesque Travelcordia ghoshAinda não há avaliações
- Research On Water Distribution NetworkDocumento9 páginasResearch On Water Distribution NetworkVikas PathakAinda não há avaliações