Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Literacy Groups Program t2
Enviado por
api-2436006390 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
27 visualizações4 páginasTítulo original
literacy groups program t2
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
27 visualizações4 páginasLiteracy Groups Program t2
Enviado por
api-243600639Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 4
Literacy Groups Term 2
Outcomes Assessment overview
English K-10
EN3-1A communicates effectively for a variety of audiences and purposes using increasingly
challenging topics, ideas, issues and language forms and features
EN3-2A composes, edits and presents well-structured and coherent texts
EN3-3A uses an integrated range of sills, strategies and nowledge to read, view and
comprehend a wide range of texts in different media and technologies
EN3-!" thins imaginatively, creatively, interpretively and critically a#out information and ideas
and identifies connections #etween texts when responding to and composing texts
EN3-$% identifies and considers how different viewpoints of their world, including aspects of
culture, are represented in texts
&tudents will complete various assessments at the end of 'erm to trac
their improvement in literacy(
Unit overview
)iteracy *roups are an important part of our morning routine( *roups are a#ility #ased and grouped according to scores from assessment tass( +ne *roup is woring at a
,ear ! level, three at a ,ear - level, one at a ,ear . level and one at a ,ear 3 level( &tudents rotate daily and are expected to complete activities at their level(
ontent
Stage 3 - Speaking and listening
use appropriate metalanguage to identify and descri#e
relationships #etween and among texts
use metalanguage to descri#e the effects of ideas, text
structures and language features on particular audiences
/A"E)'1!0-1
participate in and contri#ute to discussions, clarifying and
interrogating ideas, developing and supporting arguments,
sharing and evaluating information, experiences and opinions
/A"E),1!201
Stage 3 - Writing and representing
understand and appreciate the way texts are shaped through
exploring a range of language forms and features and ideas
experiment and use aspects of composing that enhance
learning and en3oyment
identify and explore underlying themes and central storylines in
imaginative texts
understand and use the ey elements of planning, composing,
reviewing and pu#lishing in order to meet the increasing
demands of topic, audience and language
plan, draft and pu#lish imaginative, informative and persuasive
texts, choosing and experimenting with text structures,
language features, images and digital resources appropriate
to purpose and audience /A"E),1!2., A"E),1!1.1
understand, interpret and experiment with the use of imagery in
imaginative texts, poetry and songs, eg similes, metaphors,
personification and sound devices such as alliteration
investigate how complex sentences can #e used in a variety of
ways to ela#orate, extend and explain ideas /A"E)A1-221
compose imaginative and informative texts that show evidence
of developed ideas
compose increasingly complex print, visual, multimodal and
digital texts, experimenting with language,
design, layout and graphics
reread and edit students4 own and others4 wor using agreed
criteria and explaining editing choices /A"E),1!2-,
A"E),1!1-1
develop a handwriting style that is legi#le, fluent and automatic
and varies according to audience and purpose /A"E),1!25,
A"E),1!151
Stage 3 - Reading and viewing
understand how texts vary in purpose, structure and topic
as well as the degree of formality /A"E)A1-2.1
appreciate how demanding texts, eg extended novels and
informative texts, contain increasing levels of complexity
and a#straction to enhance en3oyment
analyse how text structures and language features wor
together to meet the purpose of a text /A"E),1!111
recognise and compare how composers use a range of
language features, including connectives, topic sentences
and active and passive voice, to achieve their purposes
recognise how grammatical features help to #uild
meaning in texts, including reference lins and adver#ial
and ad3ectival phrases
recognise evaluative language, including emotive
language and modality
understand, interpret and experiment with sound devices
and imagery, including simile, metaphor and
personification, in narratives, shape poetry, songs,
anthems and odes /A"E)'15111
select, navigate and read texts for a range of purposes,
applying appropriate text processing strategies and
interpreting structural features, for example ta#le of
contents, glossary, chapters, headings and su#headings
/A"E),1!121
navigate and read texts for specific purposes applying
appropriate text processing strategies, for
example predicting and confirming, monitoring
meaning, simming and scanning /A"E),1!221
use comprehension strategies to interpret and analyse
information and ideas, comparing content from a variety
of textual sources including media and digital texts
/A"E),1!23, A"E),1!131
recognise how aspects of personal perspective influence
responses to text
summarise a text and evaluate the intended message or
theme
analyse and evaluate the way that inference is used in a
text to #uild understanding in imaginative, informative and
persuasive texts
Stage 3 - Thinking imaginatively, creatively,
interpretively and critically
recognise and explain creative language features in imaginative,
informative and persuasive texts that contri#ute to engagement
and meaning
interpret events, situations and characters in texts
thin critically a#out aspects of texts such as ideas and events
thin imaginatively when engaging with texts, using prediction, for
example, to imagine what happens to characters after the text
understand how authors often innovate on text structures and
play with language features to achieve particular aesthetic,
humorous and persuasive purposes and effects /A"E)A1-1$1
create literary texts that adapt or com#ine aspects of texts
students have experienced in innovative ways /A"E)'1512,
A"E)'151$1
adapt aspects of print or media texts to create new texts #y
thining creatively and imaginatively a#out character, setting,
narrative voice, dialogue and events
Stage 3 - Expressing themselves
recognise that ideas in literary texts can #e conveyed from
different viewpoints, which can lead to different inds of
interpretations and responses /A"E)'15121
consider how texts a#out local events and issues in the media are
presented to engage the reader or viewer
mae connections #etween students4 own experiences and those
of characters and events represented in texts drawn from
different historical, social and cultural contexts /A"E)'15131
identify aspects of literary texts that convey details or information
a#out particular social, cultural and historical contexts
/A"E)'152$1
recognise how the use of language and visual features can
depict cultural assumptions in texts
identify language features used to position the reader6viewer in a
wide variety of communication activities for a range of purposes,
including de#ates, formal tals, interviews, explanations,
anecdotes and recitations
discuss and explore moral, ethical and social dilemmas
encountered in texts
discuss aspects of literature from a range of cultures to explore common
experiences and ideas as well as recognising difference
Timeta!le
Monday Wednesday Thursday Friday
Group 1
Comprehension Novel Grammar Writing
Group 2
Novel Grammar Writing Comprehension
Group 3
Grammar Writing Comprehension Novel
Group 4
Writing Comprehension Novel Grammar
Group 5
Comprehension Novel Grammar Writing
Group 6
Novel Grammar Writing Comprehension
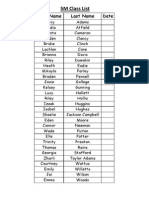
Groups
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3
Isobel Mikayla Emma
Darcy Emily Heath
Elle Brianna Josie
Georgia Bridie Jayden
Wade Riley D
Zharli Connor
Group 4 Group 5 Group 6
Lachlan rinity Riley H
homas !haelie Eden
L"cy Cla"dia Jai
Co"rtney Jack I#aak
Jack $elsey
Você também pode gostar
- Sailing Sinking SoaringDocumento21 páginasSailing Sinking Soaringapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Visual Arts t4Documento7 páginasVisual Arts t4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Fundamental Movement Skills Term 4 Stage 3Documento2 páginasFundamental Movement Skills Term 4 Stage 3api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Reflections Term 4Documento3 páginasReflections Term 4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Sport Program Term 4Documento1 páginaSport Program Term 4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Health Program Term 4Documento23 páginasHealth Program Term 4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Computer Program - Term 4Documento1 páginaComputer Program - Term 4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Thebushwackersofficialdancebook FreedownloadDocumento30 páginasThebushwackersofficialdancebook Freedownloadapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Dance Program Term 4Documento1 páginaDance Program Term 4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Grammar Unit Term 4Documento14 páginasGrammar Unit Term 4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Literacy Unit Writing To Inform NewspapersDocumento12 páginasLiteracy Unit Writing To Inform Newspapersapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Combined Split List Term 4Documento8 páginasCombined Split List Term 4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Literacy Groups Program t4Documento4 páginasLiteracy Groups Program t4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Group 5Documento12 páginasGroup 5api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Spelling Activities Program t4Documento2 páginasSpelling Activities Program t4api-243600639100% (1)
- Maths ProgramDocumento14 páginasMaths Programapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Hsie - Rainforests t4Documento3 páginasHsie - Rainforests t4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Spelling Term 4 Yr 5Documento11 páginasSpelling Term 4 Yr 5api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Spelling Groups Term 4Documento1 páginaSpelling Groups Term 4api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Combined GeneralDocumento11 páginasCombined Generalapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Combined Ilps and PlpsDocumento57 páginasCombined Ilps and Plpsapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Spelling Term 4 Yr 6Documento10 páginasSpelling Term 4 Yr 6api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Term 3 Lucy Individual Learning PlanDocumento4 páginasTerm 3 Lucy Individual Learning Planapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Term 3 Claudia Individual Learning PlanDocumento4 páginasTerm 3 Claudia Individual Learning Planapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Sport t3Documento2 páginasSport t3api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Literacy Unit Persuasive Texts Real Estatetheme ParkDocumento6 páginasLiteracy Unit Persuasive Texts Real Estatetheme Parkapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Term 3 Group 5 Literacy Personalised Learning PlanDocumento4 páginasTerm 3 Group 5 Literacy Personalised Learning Planapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Term 3 Maths Individual Learning PlanDocumento3 páginasTerm 3 Maths Individual Learning Planapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Term 3 Group 6 Literacy Personalised Learning PlanDocumento4 páginasTerm 3 Group 6 Literacy Personalised Learning Planapi-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Yr5 t3 PDH 2014Documento5 páginasYr5 t3 PDH 2014api-243600639Ainda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Vocabulary For Writing Task 1Documento11 páginasVocabulary For Writing Task 1Anmol singhAinda não há avaliações
- Malteska GramatikaDocumento120 páginasMalteska GramatikaMarina Ristić Ex NikolićAinda não há avaliações
- t2 e 1118 Using Subordinate Clauses Teaching Powerpoint Ver 1Documento6 páginast2 e 1118 Using Subordinate Clauses Teaching Powerpoint Ver 1Mai - Patcharee RushAinda não há avaliações
- GrammarDocumento30 páginasGrammarHaji ZadaAinda não há avaliações
- IngDocumento2 páginasIngHoracio Jesus Prado GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Focgb3 Ak GQ 1Documento2 páginasFocgb3 Ak GQ 1GardezAinda não há avaliações
- M Business Communication 3rd Edition Rentz Test Bank 1Documento36 páginasM Business Communication 3rd Edition Rentz Test Bank 1johnnypachecorgsnwcfjyi100% (21)
- English Lesson Plan Form 4 (Literature: "The Living Photograph")Documento2 páginasEnglish Lesson Plan Form 4 (Literature: "The Living Photograph")Maisarah Mohamad100% (3)
- 21st Century Lit DLL Quarter 2, Week 1Documento116 páginas21st Century Lit DLL Quarter 2, Week 1SORAHAYDA ENRIQUEZAinda não há avaliações
- EXERCISE Already Yet Still AnymoreDocumento2 páginasEXERCISE Already Yet Still AnymoreGeorge P.AbbsAinda não há avaliações
- Ore No Imouto Ga Konna Ni Kawaii Wake Ga Nai 5Documento203 páginasOre No Imouto Ga Konna Ni Kawaii Wake Ga Nai 5neonplayzyt1Ainda não há avaliações
- Purdue OWL - APA Formatting and Style GuideDocumento3 páginasPurdue OWL - APA Formatting and Style Guideldub4455Ainda não há avaliações
- English AssignmentDocumento3 páginasEnglish AssignmentRuha ShimeAinda não há avaliações
- 04 Planning Business MessagesDocumento52 páginas04 Planning Business MessagesThùy DươngAinda não há avaliações
- Asignment Barriers To CommunicationDocumento4 páginasAsignment Barriers To CommunicationRAZZAQ ULHAQAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Swifter, Higher, Stronger VocabularyDocumento34 páginasUnit 2 Swifter, Higher, Stronger VocabularySavithaAinda não há avaliações
- No. Nisn Nama Akidah-Akhlak Al Quran-Hadis Pengetahuan Keterampilan PengetahuanDocumento5 páginasNo. Nisn Nama Akidah-Akhlak Al Quran-Hadis Pengetahuan Keterampilan PengetahuanHabib RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Hobbies: A. Complete The Sentences With The Correct Hobbies BelowDocumento6 páginasHobbies: A. Complete The Sentences With The Correct Hobbies BelowGretchen MarquinaAinda não há avaliações
- Soal Grammar Kode BDocumento3 páginasSoal Grammar Kode BYanto BudayaAinda não há avaliações
- Soal B. IngDocumento10 páginasSoal B. IngSiti Maulani irawanAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas Uts SyntaxDocumento11 páginasTugas Uts SyntaxDella Zalfia angrainiAinda não há avaliações
- TesztsorokDocumento11 páginasTesztsorokeviAinda não há avaliações
- Entrance Exam ReviewerDocumento24 páginasEntrance Exam ReviewerBhenice AmparoAinda não há avaliações
- Edmund Spenser in Context - Allegory - Theory and Practice (2017)Documento9 páginasEdmund Spenser in Context - Allegory - Theory and Practice (2017)samaneh zandiAinda não há avaliações
- Key 2 SyllabusDocumento2 páginasKey 2 SyllabusMarisaAinda não há avaliações
- Tenses, Objective First, Cambridge English, B2Documento4 páginasTenses, Objective First, Cambridge English, B2Maja PericAinda não há avaliações
- Actual FLAT TemplateDocumento2 páginasActual FLAT TemplateAl Patrick ChavitAinda não há avaliações
- QMI 1500 TextbookDocumento448 páginasQMI 1500 TextbookC Shebo StheAinda não há avaliações
- Adverbs Exercises For Class 8Documento2 páginasAdverbs Exercises For Class 8Alna Rahman100% (2)
- Types of Sentence: 1. Simple SentencesDocumento2 páginasTypes of Sentence: 1. Simple SentencesRahmat HaryadiAinda não há avaliações