Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NSD With Iufd Pathophysiology
Enviado por
kaye0403Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NSD With Iufd Pathophysiology
Enviado por
kaye0403Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
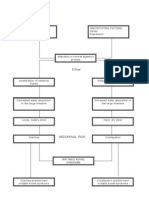
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF INTRAUTERINE FETAL DEMISE
Fertilization
(Union of sperm and ovum)
Zygote - Unicellular
(Intermingling of haploid paternal 23 X or Y and maternal 23 X chromosomes)
Series of Mitotic Cell division - Cleavage
(In 24 hours become two cell organism)
In 72 hours become 16 cell organism called Morula
Morula enters the uterus on the 3rd day through peristaltic movement
Separate into two parts by fluid from the uterus on the 4th day
The outer layer gave rise to the placenta The inner layer gave rise to the embryo
( trophoblast ) ( embryoblast )
blastocytes attaches to endometrium on the 6th day
Implantation
Embryonic development begins during
the second week and continues through
the eighth week
3 Stages
• 1st stage – increase in cell number and with Fetal Development is from ninth week to birth
elaboration of cell products
• 2ndstage – morphogenesis / includes mass cell
• 3rdstage – differentiation or maturation of
physiologic processes
Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors
Age: 31 y/o Ineffective role performance
AOG: 31 wks. Anxiety/stress in work
Congenital anomalies
Abnormal Pattern of Fetal Development Normal Pattern of Fetal Development
arising from
Congenital Anomalies
resulting to
Abnormal Fetal Heart Rate pattern
Ominous Patterns
Late Decelerations Variable Decelerations
due to due to
uteroplacental insufficiency Cord Compression
decreased blood flow and Oxygen
supply to fetus
increased peripheral resistance
Fetal Hypertension
stimulates
baroreceptors in aortic arc and carotid arteries
decreased heart rate
(bradycardia)
If untreated If treated
Extreme vagal inhibition Maternal inhalation of oxygen
Scalp stimulation test
Fetal scalp blood sampling
Total cardiac arrest medications as ordered
Intrauterine Fetal Demise
Stabilization of Fetal heart rate
Immediate/ Forced Normal
Vaginal delivery
Continuous FHR monitoring until delivery
Você também pode gostar
- Pathophysiology of NSVDDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of NSVDLenjun83% (6)
- Pathophysiology of NSDDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of NSDJNDNNSBM50610% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta PathophysiologyDocumento4 páginasAbruptio Placenta Pathophysiologyjamie carpioAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeRosemarie CarpioAinda não há avaliações
- ABORTION PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasABORTION PathophysiologyChiara FajardoAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study On Intrauterine Fetal Demise (Final Draft)Documento11 páginasCase Study On Intrauterine Fetal Demise (Final Draft)Anne Mosquite82% (11)
- Chapter 24: Nursing Care of A Family During A Surgical Intervention For BirthDocumento22 páginasChapter 24: Nursing Care of A Family During A Surgical Intervention For BirthAlyssaGrandeMontimorAinda não há avaliações
- Iii. Textbook Discussion A. Definition: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsDocumento3 páginasIii. Textbook Discussion A. Definition: Predisposing Factors Precipitating FactorsVianne ArcenioAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care of Hydatidiform MoleDocumento23 páginasNursing Care of Hydatidiform MoleKristel Rivamonte100% (1)
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocumento19 páginasAbnormal Uterine BleedingDelphy Varghese100% (1)
- REFERAT - Ppt.pathophysiology of PROM-noviDocumento16 páginasREFERAT - Ppt.pathophysiology of PROM-noviFrisma Indah Permatasari100% (1)
- Discharge PlanningDocumento3 páginasDischarge PlanningAlex Marie100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyLiza MinonaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Pathophysiology PreeclampsiaDocumento4 páginasAnatomy Pathophysiology PreeclampsiaKeith Wesley YbutAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramQuintin MangaoangAinda não há avaliações
- Concept of unitive and procreative healthDocumento5 páginasConcept of unitive and procreative healthDONITA DALUMPINESAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan AbortionDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan AbortionJane Casiquin100% (1)
- Nursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocumento2 páginasNursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionJustin PasaronAinda não há avaliações
- GENERIC NAME: Co-Amoxiclav (Amoxicillin & Clavulanic Acid) BRAND NAMES: Natravox, AddexDocumento4 páginasGENERIC NAME: Co-Amoxiclav (Amoxicillin & Clavulanic Acid) BRAND NAMES: Natravox, AddexDRAAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care of The Client With High-Risk Labor & DeliveryDocumento10 páginasNursing Care of The Client With High-Risk Labor & DeliveryWilbert CabanbanAinda não há avaliações
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYDocumento2 páginasPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYryeAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasNursing Care PlanArvan James Cabugayan TalboAinda não há avaliações
- Ectopic Pregnancy Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasEctopic Pregnancy Nursing Care PlanKim GalamgamAinda não há avaliações
- NSVD Case Study FinalDocumento60 páginasNSVD Case Study Finaljints poterAinda não há avaliações
- Essential newborn care steps in first 90 minutesDocumento1 páginaEssential newborn care steps in first 90 minutesGabriel Anthony ArtizaAinda não há avaliações
- Unang Yakap: Essential Newborn Care (ENC) ProtocolDocumento13 páginasUnang Yakap: Essential Newborn Care (ENC) ProtocolJan Oliver YaresAinda não há avaliações
- CPD: Cephalo-Pelvic Disproportion PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasCPD: Cephalo-Pelvic Disproportion PathophysiologyTeanne Bathan100% (1)
- NCM 109N: Frameworks For Maternal & Child Health NursingDocumento37 páginasNCM 109N: Frameworks For Maternal & Child Health NursingZudotaAinda não há avaliações
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocumento5 páginasEctopic Pregnancy Pathophysiologyjoyrena ochondraAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDocumento35 páginasNormal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryJohn Edward EscoteAinda não há avaliações
- Placenta Previa PhatoDocumento2 páginasPlacenta Previa PhatoMarl Jarl E BayanesAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDocumento5 páginasPathophysiology EclampsiaYael EzraAinda não há avaliações
- Maternal Risk AssessmentDocumento3 páginasMaternal Risk AssessmentMark FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- 1 and 11.1 ABDOMINAL LAYERS AND CESAREAN SECTIONDocumento14 páginas1 and 11.1 ABDOMINAL LAYERS AND CESAREAN SECTIONKim Sunoo100% (1)
- Care of Pregnant FamilyDocumento17 páginasCare of Pregnant FamilyKaryll RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- I. Pathophysiology: Fetal Swallowing Renal Disorder of Fetus Premature Rupture of MembraneDocumento3 páginasI. Pathophysiology: Fetal Swallowing Renal Disorder of Fetus Premature Rupture of MembraneSTEFFI GRACE TANAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study On NSVDDocumento50 páginasCase Study On NSVDNyj Quiño100% (2)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaDocumento5 páginasPATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaFretzgine Lou Manuel100% (2)
- Incompetent Cervix Case Analysis Subgroup 2Documento44 páginasIncompetent Cervix Case Analysis Subgroup 2bunso padillaAinda não há avaliações
- Gestational AgeDocumento6 páginasGestational AgemhuniswellAinda não há avaliações
- Retained Placental FragmentsDocumento9 páginasRetained Placental FragmentsHannah Laput100% (2)
- NURSING CARE PLAN ON FOUL-SMELLING LOCHIADocumento3 páginasNURSING CARE PLAN ON FOUL-SMELLING LOCHIANE Tdr100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Incomplete Abortion: Risk Factors and ManagementDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Incomplete Abortion: Risk Factors and ManagementClaire Nimor Ventulan50% (4)
- I. Framework For Maternal and Child Health Nursing (MCN) Focusing On At-Risk, High Risk, and Sick ClientsDocumento5 páginasI. Framework For Maternal and Child Health Nursing (MCN) Focusing On At-Risk, High Risk, and Sick ClientsSophia Loraine Dorone Jesura100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionVincent Paul SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Postpartum Hemorrhage: A.Personal DataDocumento55 páginasPostpartum Hemorrhage: A.Personal DataEmmanuel Recodo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology NSD FinalDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology NSD FinalDaniel Tan Galindez80% (5)
- Case Study (Preeclampsia)Documento6 páginasCase Study (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingDocumento6 páginasDrug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingAudrie Allyson GabalesAinda não há avaliações
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Documento1 páginaDysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Bheru LalAinda não há avaliações
- Multivitamin with iron relieves deficienciesDocumento3 páginasMultivitamin with iron relieves deficienciesAngelique Ramos PascuaAinda não há avaliações
- Incomplete AbortionDocumento22 páginasIncomplete AbortionAJ Dalawampu100% (2)
- OB - Abortion (NER)Documento6 páginasOB - Abortion (NER)gellie gellesAinda não há avaliações
- 6 PathophysiologyDocumento2 páginas6 PathophysiologyAJ SnowhiAinda não há avaliações
- Last-minute Biology revision guide for Class XII students in Jaipur regionDocumento18 páginasLast-minute Biology revision guide for Class XII students in Jaipur regionghjAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology (Normal Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery)Documento2 páginasPathophysiology (Normal Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery)Jose Bryan NacillaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology (Normal Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery)Documento2 páginasPathophysiology (Normal Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery)Jose Bryan NacillaAinda não há avaliações
- Blastocyst Development and Implantation (ANA 205Documento27 páginasBlastocyst Development and Implantation (ANA 205Ogundipe olorunfemiAinda não há avaliações
- MCHN 3RD LectDocumento9 páginasMCHN 3RD LectZahAinda não há avaliações
- Maternal Health: Pregnancy Signs and StagesDocumento9 páginasMaternal Health: Pregnancy Signs and StagesjisooAinda não há avaliações
- Malaria PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaMalaria Pathophysiologykaye040375% (4)
- NCP Normal Spontaneous Delivery Disturbed Sleeping PatternDocumento2 páginasNCP Normal Spontaneous Delivery Disturbed Sleeping Patternkaye040389% (27)
- Pa Tho Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocumento1 páginaPa Tho Irritable Bowel Syndromekaye0403Ainda não há avaliações
- Learning DisabilitiesDocumento40 páginasLearning Disabilitieskaye0403Ainda não há avaliações
- Temenoff BiomaterialsDocumento0 páginaTemenoff BiomaterialsJason Chou0% (9)
- Syllabus of BS English (Language & Literature) Implemented From 1 Semester Fall 2021Documento95 páginasSyllabus of BS English (Language & Literature) Implemented From 1 Semester Fall 2021Lahore PunjabAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study For Engineering ProblemDocumento37 páginasCase Study For Engineering ProblemAfiq AfifeAinda não há avaliações
- Specific Gravity by Pycnometer MethodDocumento4 páginasSpecific Gravity by Pycnometer Methodأحمد جاسم محمدAinda não há avaliações
- Physiotherapy's Role in Rehabilitation and Health Promotion Across the LifespanDocumento3 páginasPhysiotherapy's Role in Rehabilitation and Health Promotion Across the LifespanMariana OspinaAinda não há avaliações
- Shukr Thankfulness To Allah Grade 12Documento21 páginasShukr Thankfulness To Allah Grade 12Salman Mohammed AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Customer Satisfaction and Firm Performance: Insights From Over A Quarter Century of Empirical ResearchDocumento22 páginasCustomer Satisfaction and Firm Performance: Insights From Over A Quarter Century of Empirical ResearchMohamedAliBenAmorAinda não há avaliações
- Sector:: Automotive/Land Transport SectorDocumento20 páginasSector:: Automotive/Land Transport SectorVedin Padilla Pedroso92% (12)
- Magic Writ: Textual Amulets Worn On The Body For Protection: Don C. SkemerDocumento24 páginasMagic Writ: Textual Amulets Worn On The Body For Protection: Don C. SkemerAsim HaseljicAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Management Accounting: ConceptsDocumento47 páginasAdvanced Management Accounting: ConceptsGEDDIGI BHASKARREDDYAinda não há avaliações
- Case 3:09 CV 01494 MODocumento13 páginasCase 3:09 CV 01494 MOAnonymous HiNeTxLMAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus Mac1105 M 530 - 8 PM 203080Documento6 páginasSyllabus Mac1105 M 530 - 8 PM 203080api-261843361Ainda não há avaliações
- ALL INDIA NURSING TEST REVIEWDocumento102 páginasALL INDIA NURSING TEST REVIEWDr-Sanjay SinghaniaAinda não há avaliações
- AC413 Operations Auditing Outline & ContentDocumento29 páginasAC413 Operations Auditing Outline & ContentErlie CabralAinda não há avaliações
- Maternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancyDocumento10 páginasMaternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancymanognaaaaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-1 of F.mensurationDocumento8 páginasChapter-1 of F.mensurationpradeeppoddarAinda não há avaliações
- Why Men Are The Submissive SexDocumento8 páginasWhy Men Are The Submissive SexWilliam Bond89% (9)
- ESL S9 W3 P14-15 Project Challenge Part 2Documento27 páginasESL S9 W3 P14-15 Project Challenge Part 2Emma Catherine BurkeAinda não há avaliações
- Terese LiteDocumento211 páginasTerese Liteoguruma100% (1)
- ME8513 & Metrology and Measurements LaboratoryDocumento3 páginasME8513 & Metrology and Measurements LaboratorySakthivel KarunakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Sanitation LessonDocumento4 páginasEnvironmental Sanitation LessonMARIS GRACE CARVAJALAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 006Documento50 páginasChap 006Martin TrịnhAinda não há avaliações
- Teresa R. Ignacio, Represented by Her Attorney-In-fact, Roberto R. Ignacio, Petitioner, V. Office of The City Treasurer of Quezon City, Et. Al.Documento2 páginasTeresa R. Ignacio, Represented by Her Attorney-In-fact, Roberto R. Ignacio, Petitioner, V. Office of The City Treasurer of Quezon City, Et. Al.Pam Otic-ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- DIASS - Quarter3 - Module1 - Week1 - Pure and Applied Social Sciences - V2Documento18 páginasDIASS - Quarter3 - Module1 - Week1 - Pure and Applied Social Sciences - V2Stephanie Tamayao Lumbo100% (1)
- Objective/Multiple Type QuestionDocumento14 páginasObjective/Multiple Type QuestionMITALI TAKIAR100% (1)
- Definitions - Estoppel PDFDocumento4 páginasDefinitions - Estoppel PDFsrrockygAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Laryngitis in CHU Yalgado Ouedraogo: Epidemiological and Diagnostic AspectsDocumento4 páginasChronic Laryngitis in CHU Yalgado Ouedraogo: Epidemiological and Diagnostic AspectsMarlina ElvianaAinda não há avaliações
- HDPS 1303 - 930425105424Documento6 páginasHDPS 1303 - 930425105424Cheryl LimAinda não há avaliações
- QDEGNSWDocumento2 páginasQDEGNSWSnehin PoddarAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Verb TensesDocumento4 páginasSummary of Verb TensesRamir Y. LiamusAinda não há avaliações