Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Pa Tho Physiology of Pneumonia
Enviado por
joyasejoDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Pa Tho Physiology of Pneumonia
Enviado por
joyasejoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
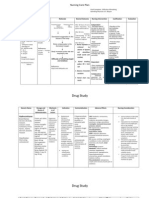
Pathophysiology
Pneumonia
Predisposing factors
Precipitating Factors: Age
Etiology: altered state of immunity
exposure to pathogen
Upper respiratory tract infection • streptococcus polluted environment (smoking,
pneumonia noxious gases, etc)
Pathogens invade the respiratory tract/ infect airways
Bronchi
Bronchiole
terminal bronchiole
Spread to the alveoli
Release biochemical mediators of Cell injury Injured respiratory mucosa (goblet cells)
inflammation and the
inflammatory response occurs
Capillary vasodilation WBC activation Increase capillary
permeability secrete large amounts of
Chemotaxis and mucous
Increase phagocytosis of
bloodflow pathogens
Swelling / mucosal edema
Fluid and exudates
Fever Endogenous Crackles and
accumulation
pyrogens Wheezing
Airway Alveoli lose air spaces and solidify
(bronchioles or because the space which air must
terminal bronchioles) occupy
. SOB \ SOB is filled with fluids and exudates
with exudates and
fluids (consolidation)
Dullness during
percussion
Decrease oxygen and carbon dioxide
exchange in
the alveoli
The body compensates
the decrease in oxygen that
reaches the alveoli by increasing
the respiratory rate Ventilation – perfusion
mismatch
Hypoxemia. less oxygen is also
delivered to body
Tachypnea tissues and organs
The heart compensates by
increasing the heart rate
Hypoxia
pale and dusky
skin
Tachycardia
Death
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Epid 1.1Documento194 páginasEpid 1.1devtarioAinda não há avaliações
- Susbtance Relared Disorders (PPT Transcript)Documento11 páginasSusbtance Relared Disorders (PPT Transcript)SOLEIL LOUISE LACSON MARBASAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneDocumento4 páginasDrug Study Amlodipine & HydrocortisoneJohn Kristoffer JisonAinda não há avaliações
- Test Yourself: MCQ and Extended MatchingDocumento2 páginasTest Yourself: MCQ and Extended MatchingPhil ChanAinda não há avaliações
- AlexithymiaDocumento10 páginasAlexithymiaCassiopea AndromedaAinda não há avaliações
- RCSI Bahrain ConnectED Newsletter Winter 2022-23Documento32 páginasRCSI Bahrain ConnectED Newsletter Winter 2022-23Yousif YousifAinda não há avaliações
- EXERCISE THERAPY Assignment-Elastic BandDocumento9 páginasEXERCISE THERAPY Assignment-Elastic BandApoorv100% (1)
- Medication Research Card SampleDocumento1 páginaMedication Research Card SamplekennybooboooAinda não há avaliações
- Class 12 Physical Education Chapter 1 Planning in Sports Question/AnswerDocumento7 páginasClass 12 Physical Education Chapter 1 Planning in Sports Question/AnswerPihoo MohanAinda não há avaliações
- Veterinary Neurologic Rehabilitation The Rationale For ADocumento9 páginasVeterinary Neurologic Rehabilitation The Rationale For ACarolina Vargas VélezAinda não há avaliações
- Mann Assessment of Swallowing AbilityDocumento9 páginasMann Assessment of Swallowing Abilityluca bastianiAinda não há avaliações
- Tupoksi & Indikator TO PMDT Prov - Sultra TW3Documento192 páginasTupoksi & Indikator TO PMDT Prov - Sultra TW3AryoWibowoAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Emergency NursingDocumento41 páginasLesson Plan Emergency NursingSwapnil Mahapure100% (1)
- First Aid: By: Sem. Winmark S. PerdiganDocumento18 páginasFirst Aid: By: Sem. Winmark S. PerdiganWinsley RazAinda não há avaliações
- The Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) On Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)Documento8 páginasThe Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) On Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)nadia rukmanaAinda não há avaliações
- Company Profile Indo Medika InternationalDocumento12 páginasCompany Profile Indo Medika InternationalshavinravizaAinda não há avaliações
- Orientation ResidenecyDocumento18 páginasOrientation ResidenecyReeMii AngeLa100% (1)
- Marketing Plan Sensodyne ToothpasteDocumento22 páginasMarketing Plan Sensodyne ToothpasteMd. Azad HossainAinda não há avaliações
- The Mental Workload of Nurses in The Role of Nursing Care ProvidersDocumento8 páginasThe Mental Workload of Nurses in The Role of Nursing Care ProvidersDede NunuAinda não há avaliações
- Muhamad Lutfi ParatuberculosisJournalDocumento17 páginasMuhamad Lutfi ParatuberculosisJournalLutfi AlkaAinda não há avaliações
- Balance and Vestibular Rehabilitation: Presented By: Neha Tabbassum Khan M.P.T. 1 Yr (Neuro)Documento25 páginasBalance and Vestibular Rehabilitation: Presented By: Neha Tabbassum Khan M.P.T. 1 Yr (Neuro)Vidya VenkitaramanAinda não há avaliações
- NGT PowerpointDocumento19 páginasNGT Powerpointسانو روديلAinda não há avaliações
- Pap SmearDocumento3 páginasPap SmearcziehjheyAinda não há avaliações
- AnesthesiaDocumento26 páginasAnesthesiaezkina14Ainda não há avaliações
- Week 5 Case Study Instructions NR 507Documento3 páginasWeek 5 Case Study Instructions NR 507Benedict KakaiAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Case SheetDocumento5 páginasMedical Case SheetMary CaldwellAinda não há avaliações
- Antipsycotic DrugDocumento21 páginasAntipsycotic DrugShashank SatheAinda não há avaliações
- GCC Guidelines For Ectd SubmissionDocumento18 páginasGCC Guidelines For Ectd SubmissionSatadal Deb RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Handbook of Insomnia PDFDocumento73 páginasHandbook of Insomnia PDFAmira FathidzkiaAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Features of GingivitisDocumento27 páginasClinical Features of Gingivitisfreeda.ampottiAinda não há avaliações