Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP Cholangitis
Enviado por
Janica C. BayauaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NCP Cholangitis
Enviado por
Janica C. BayauaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
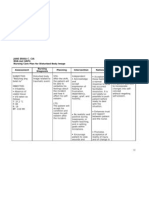
NURSING CARE PLAN
CUES
NURSING
DIAGNOSIS
ANALYSIS GOAL & OBJECTIVES INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective:
The patient
verbalized:
Masakit tiyan
ko
Objective
Observed
evidence of
pain
Guarding
behavior
Frequently
changing
position to
avoid pain
Irritability
Facial grimace
Acute pain
related to
spasms and
abdominal
pain.
Cholangitis
is the most
serious
complicatio
n of
gallstones
and more
difficult to
diagnose. It
is caused
by
impacted
stone in
the
common
bowel
duct,
resulting in
bile stasis,
bacteremia
and
septicemia
if left
untreated.
It is more
ikely to
occur when
an already
infected
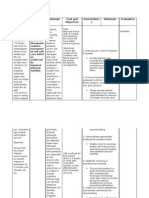
Goal: After 3 hours of nursing
interventions the client will be
free from experiencing pain in
the abdomen.
Objectives:
1. After 40 minutes
of assessment, the
client will be able
to describe the
characteristic,
onset, location,
duration, severity,
and precipitating
factors of pain.
2. After 15 minutes
of assessing for
the presence of
fear or anxiety,
the client will be
able to verbalize if
shes feeling
>Assess the client of
pain to include the
characteristic, onset,
location, duration,
severity, and
precipitating factors
of pain.
>Assess for the
presence of fear or
anxiety.
>Pain is a subjective
experience and must
be described by the
patient in order to
plan effective
treatment.
(http://wps.prenhall.
com/wps/media/obje
cts/3918/4012970/N
ursingTools/ch46_NC
P_AcutePain)
>Fear and anxiety
can alleviate clients
perception of pain.
(http://bja.oxfordjour
nals.org/content/87/
1/144.full)
__Met
__Partially met
__Unmet
bile duct
becomes
obstructed.
Patients
having
cholangitis
is suffering
from
severe
abdominal
pain.
(All-in-one
Care
Planning
Resource
by
Swearinge
n; page
453)
anxious.
3. After 15 minutes
of assessing for
clients
discomfort, client
will verbalize the
cause of
discomort.
4. After 10 minutes
of monitoring the
patient for pain,
the client will be
able to verbalize
the rate of pain
she is
experiencing.
5. After 30 minutes
of deep breathing
>Assess causes of
possible discomfort.
>Monitor patient for
pain or other
discomfort. Devise a
pain scale with
patient, rating
discomfort on a scale
of 0 (no pain) to 10
(worst pain)
> Encourage use of
relaxation techniques
> Discomfort can be
caused or aggravated
by presence of
nonpatent indwelling
catheters causing
bladder pain, NG
tube resulting in
gastric fluid and gas
accumulation, or
parenteral lines that
have infiltrated IV
fluids or medications.
(Nursing Care Plans
by Doenges, 8
th
ed;
page 798)
>Enables more
precise measurement
of discomfort and
relief obtained.
(All-in-one Care
Planning Resource by
Swearingen; page
454)
> Relieves muscle
and emotional
exercise and doing
the bent-knee
position, the client
will be able to
verbalize that the
abdominal tension
will be
relieved/reduced.
6. 30 minutes after
administering
analgesics, client
will report
reduced
abdominal pain.
such as deep-
breathing exercises.
>Position the client in
a bent-knee position.
>Administer
analgesics as
prescribed.
tension; enhances
sense of control and
may improve coping
abilities.
>This position
decreases tension on
abdominal contents
to promote comfort.
(All-in-one Care
Planning Resource by
Swearingen; page
454)
>Nonsteroidal
antiinflammantory
drugs (NSAIDs) or
opioid analgesics
may be indicated,
depending on
severity of the pain.
For the postoperative
patient, continuous
IV of opioid
analgesics are used
with increasing
frequency and
efficacy.
(All-in-one Care
7. After 40 minutes
of nursing
interventions the
client will be able
to verbalize
willingness to
alleviate pain.
> Note clients
attitude towards pain
and use of pain
medications.
> Evaluate clients
response to
analgesics and assist
in transitioning or
altering drug
regimen, based on
individual needs and
protocols.
Planning Resource by
Swearingen; page
455)
>To promote
wellness
Você também pode gostar
- CAREPLAN For CholangitisDocumento3 páginasCAREPLAN For CholangitisNatty-oneBonafide100% (2)
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocumento1 páginaThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Physical Mobility...Documento3 páginasImpaired Physical Mobility...Christy BerryAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Acute Pain RT CancerDocumento3 páginasNCP Acute Pain RT CancerCharissa Magistrado De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- NCP PancreatitisDocumento2 páginasNCP PancreatitisJeanelle Generoso100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationVecky TolentinoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP LymphedemaDocumento1 páginaNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- Fernando - NCP & Drud Study (Colostomy)Documento4 páginasFernando - NCP & Drud Study (Colostomy)Cyril Joy N. FernandoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP LymphomaDocumento3 páginasNCP Lymphomamahmoud fuqahaAinda não há avaliações
- Lung Cancer (Nursing Care)Documento5 páginasLung Cancer (Nursing Care)heiyuAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPeun kyung shinAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPChrisTine M. MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocumento4 páginasNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implemantation Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implemantation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie Rosalejos100% (1)
- NCP Epidural HemDocumento32 páginasNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Documento3 páginasPathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Katherine Clarisse Carvajal Lavarias100% (1)
- Colorectal Cancer NCP and FDAR FinalDocumento8 páginasColorectal Cancer NCP and FDAR Finalnot your medz duranAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Crohn'sDocumento2 páginasNCP Crohn'sJanice Marco100% (1)
- Ineffective Role Perf Romance FinalDocumento1 páginaIneffective Role Perf Romance Finalasymptomaticcrisis0% (1)
- NCP For Cervical SpondylosisDocumento3 páginasNCP For Cervical Spondylosishannah0% (1)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento7 páginasImpaired Physical MobilityVianah Eve EscobidoAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPbjhilario100% (1)
- You Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeDocumento2 páginasYou Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeWen Silver100% (1)
- Fistula NCPDocumento1 páginaFistula NCPHasna LisnaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Acute Pain NCPDocumento2 páginas1 Acute Pain NCPFilipinas BelzaAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Acute ConfusionDocumento2 páginasRisk For Acute ConfusionChar PereaAinda não há avaliações
- Patriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. YingDocumento1 páginaPatriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. Yingjanna mae patriarca100% (2)
- NCP For Ears Nose ThroatDocumento1 páginaNCP For Ears Nose ThroatMcmac YangoAinda não há avaliações
- N1007 Week Two - Nurse Care Plan - Diabetes - James ScalesDocumento1 páginaN1007 Week Two - Nurse Care Plan - Diabetes - James Scalesjumpshooter88100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 páginaNursing Care PlanSHeenah Qo100% (1)
- Teaching PlanDocumento4 páginasTeaching PlanPagodAinda não há avaliações
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Documento2 páginasCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16Ainda não há avaliações
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento1 páginaAcute Pain NCPJed AvesAinda não há avaliações
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocumento6 páginasWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrAinda não há avaliações
- NCP pAlPITATIONSDocumento3 páginasNCP pAlPITATIONSHazel PalomaresAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Physical Mobility CholecystectomyDocumento2 páginasImpaired Physical Mobility CholecystectomyPrincess Danica Purcia100% (1)
- BPH NCPDocumento1 páginaBPH NCPJayson BenitezAinda não há avaliações
- Seborr NCPDocumento2 páginasSeborr NCPBianca Monis0% (1)
- Care Plan ExampleDocumento2 páginasCare Plan Exampleincess27100% (1)
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDocumento2 páginasCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAngie MandeoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For FallsDocumento1 páginaRisk For FallsEugene UCAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Risk For Acute PainDocumento3 páginasNCP For Risk For Acute PainAngelgodess Athena-envyAinda não há avaliações
- Copd Case StudyDocumento5 páginasCopd Case StudyJake Yvan DizonAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For CamoxDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan For CamoxRolena Johnette B. PiñeroAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 páginasNursing Care PlanJoy Callo100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis For CataractDocumento3 páginasNursing Diagnosis For CataractZainul HazwanAinda não há avaliações
- Breast Cancer Risk For InfectionDocumento6 páginasBreast Cancer Risk For Infectionam peAinda não há avaliações
- Post-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasPost-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanCyrus De AsisAinda não há avaliações
- Breast Ca NCPDocumento3 páginasBreast Ca NCPThirdy AquinoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocumento5 páginasNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlansDocumento4 páginasNursing Care PlansanreilegardeAinda não há avaliações
- NCP 1Documento1 páginaNCP 1hsiriaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceDocumento8 páginasNCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceWyen Cabatbat100% (2)
- CP AmoebaDocumento3 páginasCP AmoebaJoy G. NomilAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - PainDocumento3 páginasNCP - PainAdrian Mallar100% (2)
- NCP For Acute PainDocumento3 páginasNCP For Acute PainAneeta Tamo - Aviles67% (3)
- NCP - CruzDocumento2 páginasNCP - CruzAlvin CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRomeo Avecilla CabralAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Acute Pain: Assessment Evaluation PlanningDocumento9 páginasNursing Care Plan Acute Pain: Assessment Evaluation PlanningAngelokeizer GavinoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasNursing Care PlanJonie AgcongAinda não há avaliações
- Avian Anatomy 1Documento50 páginasAvian Anatomy 1Le KhaiAinda não há avaliações
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocumento9 páginasExcretory Products and Their EliminationBiju MylachalAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 11 Introduction To EpidemiologyDocumento38 páginasUnit 11 Introduction To EpidemiologyhumaAinda não há avaliações
- DafpusDocumento1 páginaDafpusJeliny Bintan MaisuriAinda não há avaliações
- Health Crisis Slams Disney, But More Bloodletting Ahead: For Personal, Non-Commercial Use OnlyDocumento30 páginasHealth Crisis Slams Disney, But More Bloodletting Ahead: For Personal, Non-Commercial Use OnlyMiguel DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Obstetrics & GynecologyDocumento10 páginasObstetrics & GynecologyRaul DoctoAinda não há avaliações
- Liver CancerDocumento16 páginasLiver CancerMark James MelendresAinda não há avaliações
- Human Digestive SystemDocumento13 páginasHuman Digestive SystemEvansAinda não há avaliações
- Patofisiologi Kanker RahimDocumento98 páginasPatofisiologi Kanker RahimOjo Nesu100% (1)
- (11anh1) Practice Test 3Documento5 páginas(11anh1) Practice Test 3nhuAinda não há avaliações
- Comprehensive Diabetes Checklist Joslin Diabetes CenterDocumento2 páginasComprehensive Diabetes Checklist Joslin Diabetes CenterAbraham DíazAinda não há avaliações
- HRCA GK Quiz Syllabus Class 7-8Documento19 páginasHRCA GK Quiz Syllabus Class 7-8Sualiha MalikAinda não há avaliações
- NRC Guidelines GujrathDocumento68 páginasNRC Guidelines GujrathNirajkumar KondekarAinda não há avaliações
- Evidence-Based Decision Making in Dentistry - Multidisciplinary Management of The Natural DentitionDocumento143 páginasEvidence-Based Decision Making in Dentistry - Multidisciplinary Management of The Natural DentitiontayabakhanAinda não há avaliações
- A To Z Orthodontics - Vol 9 - Preventive and Interceptive OrthodonticsDocumento37 páginasA To Z Orthodontics - Vol 9 - Preventive and Interceptive OrthodonticsĐạt HuỳnhAinda não há avaliações
- Headache and Joint PainDocumento13 páginasHeadache and Joint PainJosiah Noella BrizAinda não há avaliações
- History and Physical Exam GuidelinesDocumento5 páginasHistory and Physical Exam GuidelinesPrincella MonicaAinda não há avaliações
- Wildlife Fact File - Mammals, Pgs. 111-120Documento20 páginasWildlife Fact File - Mammals, Pgs. 111-120ClearMind84100% (2)
- Forgotten CropsDocumento48 páginasForgotten CropsbhollisAinda não há avaliações
- Cysteamine - Full Profile - 170917Documento11 páginasCysteamine - Full Profile - 170917Walter MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Language and The BrainDocumento8 páginasLanguage and The BrainAntonio GoqueAinda não há avaliações
- Water HomeostasisDocumento9 páginasWater HomeostasisRini MagfirahAinda não há avaliações
- Ethical Judgments Limit The Methods Available in The Production of Knowledge in Both The Arts and The Natural SciencesDocumento5 páginasEthical Judgments Limit The Methods Available in The Production of Knowledge in Both The Arts and The Natural SciencesMilena ŁachAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical Site Infection Investigation Tool: AHRQ Safety Program For SurgeryDocumento5 páginasSurgical Site Infection Investigation Tool: AHRQ Safety Program For SurgeryDewi ListyoriniAinda não há avaliações
- Essay 3. The CNN HeroesDocumento3 páginasEssay 3. The CNN HeroesMARIA JOSE CARAVEO GUERREROAinda não há avaliações
- Dos 773 Csi Plan Study-1Documento7 páginasDos 773 Csi Plan Study-1api-504593245Ainda não há avaliações
- Urinary System and Disorders IntroductionDocumento23 páginasUrinary System and Disorders IntroductionHananya ManroeAinda não há avaliações
- The Diet Solution Metabolic Typing TestDocumento10 páginasThe Diet Solution Metabolic Typing TestkarnizsdjuroAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Nursing Services Scheduling PolicyDocumento7 páginas5 Nursing Services Scheduling PolicyVin BitzAinda não há avaliações
- Nematode Parasites of RiceDocumento2 páginasNematode Parasites of RiceCPS_IRRIAinda não há avaliações