Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Alkane, Alkene, Alkyne
Enviado por
burgesss870 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
125 visualizações6 páginasBonding in Hydrocarbons-basic concepts of organic Chemistry
Título original
Alkane,Alkene,Alkyne
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoBonding in Hydrocarbons-basic concepts of organic Chemistry
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
125 visualizações6 páginasAlkane, Alkene, Alkyne
Enviado por
burgesss87Bonding in Hydrocarbons-basic concepts of organic Chemistry
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 6
Bonding in Hydrocarbons
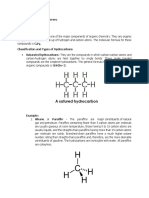
Alkanes are hydrocarbons with all single bonds
between all carbon atoms
Alkanes can be either straight-chain or
branched-chain
Alkanes are also called as Paraffins
Generally the molecular formula of Alkanes is
C
n
H
2n+2
Where n is the Number of carbons
Few examples of Alkanes in increasing order of
carbon number are Methane, ethane, propane,
butane, pentane etc.
Alkenes are hydrocarbons with at least one
carbon-carbon double bond
Alkenes are also called as Olefins.
Generally the molecular formula of Alkanes is
C
n
H
2n
Where n is the Number of carbons (n>1)
Few examples of Alkenes in increasing order
of carbon number are Ethene, propene,
butene, pentene etc.
Alkynes are hydrocarbons with at least one
carbon-carbon triple bond.
Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes.
Generally the molecular formula of Alkanes is
C
n
H
2n-2
Where n is the Number of carbons (n>1)
Few examples of Alkynes in increasing order of
carbon number are ethyne, propyne, butyne etc.
Basic understanding of hydrocarbon classification
is useful to solve chemistry home work problems.
Alkanes
Alkenes
Alkynes
Você também pode gostar
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryNo EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- UntitledDocumento1 páginaUntitledकुॅं राज बन्नाAinda não há avaliações
- Naming Organic Aliphatic CompoundsDocumento27 páginasNaming Organic Aliphatic CompoundsAikaterine SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Nomenclature of Alkane,Alkene & AlkyneDocumento19 páginasNomenclature of Alkane,Alkene & Alkynea6446674Ainda não há avaliações
- Review of Naming HydrocarbonsDocumento5 páginasReview of Naming HydrocarbonsHalima Al-MohammadAinda não há avaliações
- Chemia 1Documento3 páginasChemia 1juliaAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry SummaryDocumento8 páginasOrganic Chemistry SummaryZeath ElizaldeAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesDocumento11 páginasAlkanes, Alkenes, AlkynesRosalia JasmineAinda não há avaliações
- AlkanesDocumento4 páginasAlkanesjeffersonmanalo787Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture-10 (Organic Chemistry and Hidrocarbon) - 1Documento75 páginasLecture-10 (Organic Chemistry and Hidrocarbon) - 1Permadi BagasAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 15 Intro To OrganicDocumento8 páginasChapter 15 Intro To OrganicLisa DentonAinda não há avaliações
- Janina Cassandra T. GuerreroDocumento3 páginasJanina Cassandra T. GuerreroJanina GuerreroAinda não há avaliações
- Natural Science PrelimDocumento26 páginasNatural Science PrelimMew GulfAinda não há avaliações
- Alkenes AlkynesDocumento40 páginasAlkenes AlkynesHanindya NugrahaAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols - Written Report - SolidumDocumento13 páginasHydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols - Written Report - SolidumAva Mae SolidumAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Compounds and Nomenclature: Classifying Organic StructuresDocumento22 páginasOrganic Compounds and Nomenclature: Classifying Organic StructuresNunaAinda não há avaliações
- Alkane Structure and PropertiesDocumento17 páginasAlkane Structure and PropertiesAneesa JalilAinda não há avaliações
- NomenclatureDocumento2 páginasNomenclaturedaramolamekaiahAinda não há avaliações
- AlkanesDocumento61 páginasAlkanesFrancis LaoAinda não há avaliações
- Alkenes GroupDocumento8 páginasAlkenes GroupHanna GalatiAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes: The Basics of Saturated HydrocarbonsDocumento16 páginasAlkanes: The Basics of Saturated Hydrocarbonsfumerojr5164Ainda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry NomenclatureDocumento8 páginasOrganic Chemistry NomenclaturetasneemAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction Organic ChemistryDocumento5 páginasIntroduction Organic ChemistryMUNSURUL HAQUEAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes To Alkynes and AromaticsDocumento48 páginasAlkanes To Alkynes and AromaticswallabooAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes 2Documento3 páginasAlkanes 2Efren TurajaAinda não há avaliações
- AlkanesDocumento8 páginasAlkanesBenjamen FolarinAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesDocumento65 páginasAlkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesTeresita CamachoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocumento18 páginasIntroduction To Organic ChemistryElmarAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chem U-2 Functional GroupDocumento34 páginasOrganic Chem U-2 Functional Groupsinte beyuAinda não há avaliações
- The Saturated Hydrocarbons: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Contrasts Between Organic and Inorganic MoleculesDocumento9 páginasThe Saturated Hydrocarbons: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Contrasts Between Organic and Inorganic MoleculesNaveenAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry 1Documento110 páginasOrganic Chemistry 1Mahmoud RslanAinda não há avaliações
- Text of ReportDocumento3 páginasText of Reportismhael baldomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Alkenes and Alkynes Structure, Naming, and ReactionsDocumento25 páginasAlkenes and Alkynes Structure, Naming, and ReactionsMa. Angelica Claire LuayonAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Revision NotesDocumento63 páginasCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Revision NotesAjitesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Organic ChemistryDocumento11 páginasOrganic Chemistryapi-546066323Ainda não há avaliações
- Alkenes: Organic ChemistryDocumento21 páginasAlkenes: Organic ChemistryMelissa Marie CustodioAinda não há avaliações
- 5 +Alkenes+and+AlkynesDocumento53 páginas5 +Alkenes+and+AlkynesSantiago ValadezAinda não há avaliações
- AlkynesDocumento3 páginasAlkynesabdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Families of Organic CompoundsDocumento8 páginasFamilies of Organic CompoundsJessa Mae LangcuyanAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Key Carbon Compounds ConceptsDocumento9 páginasSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Key Carbon Compounds ConceptsSofiyyahOpieAinda não há avaliações
- Santos AlkanealkenesalkynesDocumento28 páginasSantos AlkanealkenesalkynesApril JoyAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Objectives: Understanding Carbon CompoundDocumento20 páginasLearning Objectives: Understanding Carbon Compoundheryana8100% (3)
- Functional G Chem 15th FebDocumento64 páginasFunctional G Chem 15th FebAndrew GordonAinda não há avaliações
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocumento48 páginasCarbon and Its Compoundsmadhus1778Ainda não há avaliações
- Study Notes On HydrocarbonsDocumento1 páginaStudy Notes On HydrocarbonsChristian Josef AvelinoAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes: A Guide to Hydrocarbon Structures and ReactionsDocumento28 páginasAlkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes: A Guide to Hydrocarbon Structures and ReactionsRanier Factor AguilarAinda não há avaliações
- Alkane, Alkene, Alkyne PDFDocumento17 páginasAlkane, Alkene, Alkyne PDFEra MelaniaAinda não há avaliações
- Organic ChemistryDocumento45 páginasOrganic ChemistryShiv PriyamAinda não há avaliações
- Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Alkenes and Alkynes Aromatic CompoundDocumento4 páginasUnsaturated Hydrocarbons Alkenes and Alkynes Aromatic CompoundGAinda não há avaliações
- 25.2: Introduction To Hydrocarbons: Learning ObjectivesDocumento2 páginas25.2: Introduction To Hydrocarbons: Learning ObjectivesshasagailAinda não há avaliações
- NotesDocumento7 páginasNotesAmahAinda não há avaliações
- Hydroc'sDocumento7 páginasHydroc'ssrtgrwl1971Ainda não há avaliações
- Bonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanDocumento33 páginasBonding of Hydrocarbons: Presented by Rina Mae Manceras Benjamin BagayanIce BearAinda não há avaliações
- ALKENEDocumento7 páginasALKENEKrystel Ann Demaosa CarballoAinda não há avaliações
- Module 2Documento12 páginasModule 2AbhijeetAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Organic CompoundsDocumento20 páginasAn Introduction To Organic CompoundsJotillnaimAinda não há avaliações
- Alkenes Guide: Properties, Preparation & Uses in 40 CharactersDocumento5 páginasAlkenes Guide: Properties, Preparation & Uses in 40 CharactersSafa MarwanAinda não há avaliações
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionNo EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Assembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsNo EverandAssembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsAinda não há avaliações
- Binomial Theorem: Simple Formulas Which Are Helpful To Solve Algebra ProblemsDocumento5 páginasBinomial Theorem: Simple Formulas Which Are Helpful To Solve Algebra Problemsburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Arithmetic ProgressionsDocumento6 páginasArithmetic Progressionsburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Surds and IndicesDocumento5 páginasSurds and Indicesburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Simple Concepts, Which Are Helpful To Solve Simple Chemistry ProblemsDocumento7 páginasSimple Concepts, Which Are Helpful To Solve Simple Chemistry Problemsburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Geographic Coordinate SystemDocumento6 páginasGeographic Coordinate Systemburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Tests of DivisibilityDocumento6 páginasTests of Divisibilityburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- How To Calculate Day of The Week With Given DateDocumento6 páginasHow To Calculate Day of The Week With Given Dateburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of MeanDocumento5 páginasTypes of Meanburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Surds and IndicesDocumento5 páginasSurds and Indicesburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Trigonometric Formula ProofDocumento6 páginasTrigonometric Formula Proofburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Binomial Theorem: Simple Formulas Which Are Helpful To Solve Algebra ProblemsDocumento5 páginasBinomial Theorem: Simple Formulas Which Are Helpful To Solve Algebra Problemsburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- How To Calculate Day of The Week With Given DateDocumento6 páginasHow To Calculate Day of The Week With Given Dateburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Partial Pressure ConceptDocumento6 páginasPartial Pressure Conceptburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações
- Pythagoras Theorem ProofDocumento5 páginasPythagoras Theorem Proofburgesss87Ainda não há avaliações