Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
21 Faradays Law
Enviado por
api-235269401Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
21 Faradays Law
Enviado por
api-235269401Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
N S
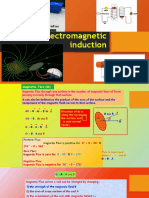
Electromagnetic induction
Electric current can be generated in a coil by pushing
a magnet into a coil.
When it is pulled out of the coil a current (in the
opposite direction) is then set up.
N S
Reverse the polarity,
change magnets & the
speed & number of coils
and see how the induced
current is affected.
Note: There is only an induced current while there is
movement of the magnet relative to the coil & vice versa.
Electromagnetic induction
1
Cutting through field lines
When a magnet is moved in a coil, the wires of the coil cut
through the field lines, thus producing an induced current.
When a conductor cuts through field lines, a potential difference is
induced across the ends of the conductor.
This is called electromagnetic induction.
The size of the induced potential difference is determined by:
The strength of the field lines i.e. the strength of
the magnet
How many lines are cut the speed of the magnet
How quickly they are cut the speed of the magnet
The number of turns of wire in the coil.
Electromagnetic induction
2
Faradays law of
Electromagnetic Induction
A potential difference is induced in a conductor when
magnetic field lines are cut by the conductor. The size
of the potential difference is directly proportional to the
rate at which the lines are cut.
The rate is increased by:
Using a stronger magnet
Having more turns in the coil
Moving the magnet faster
Factors affecting electromagnetic induction
3
Direction of induced current
N S
S N
As N pole moves into
coil N pole formed at
near end of coil to
oppose the incoming N
pole and thus set up an
induced current in the
coil.
As S pole is moved out
of coil S pole formed
at near end of coil &
thus a reversal of
direction of current in
coil.
Inducing current
4
Finding direction of induced current
Clasp the solenoid with the thumb pointing to the
induced North pole of the solenoid.
The direction in which the fingers curl about
solenoid, provides the direction of the induced
current in the solenoid.
N S N
Direction of induced current flow
5
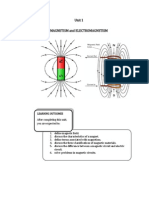
Important magnetism terms.
Magnetic flux ( pronounced fie) means the total
magnetic field that passes through a loop of wire. It
is a measure of the field lines passing through the
loop and is measured in weber (Wb)
Magnetic flux density (B) is a measure of the
strength and direction of the magnetic field i.e. it is
the magnetic flux per square metre of area that it
passes through and is measured in tesla (T).
Magnetic field and flux
6
Important magnetism terms.
Normal
B
Z
Loop of
wire
= BA cos Z
= magnetic flux in webers
B = magnetic flux density in tesla
A = area of loop in m
2
Z = angle between field & normal to loop
7
Faradays law of
Electromagnetic Induction
Definition:
An emf is induced in a conductor when the magnetic
field surrounding it changes. The size of the induced
emf () is directly proportional to the rate of change
of the magnetic flux linkage.
is emf
- indicates current is induced
N is number of turns or loops
change in magnetic flux
t change in time.
Calculating emf
8
Você também pode gostar
- Nagnetic InductionDocumento102 páginasNagnetic InductionAyush ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetism 29 JULY 2014 Lesson Description: Magnetic Effect of An Electric CurrentDocumento5 páginasElectromagnetism 29 JULY 2014 Lesson Description: Magnetic Effect of An Electric CurrentHAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 15 Class 10th PDFDocumento12 páginasChapter 15 Class 10th PDFMuneer Kaleri75% (4)
- CH6 Formula SheetDocumento11 páginasCH6 Formula SheetNancy SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic CircuitsDocumento38 páginasMagnetic CircuitsHanan KemalAinda não há avaliações
- Group 1 1.3Documento27 páginasGroup 1 1.3Krista Joy PetalioAinda não há avaliações
- MagnetismDocumento10 páginasMagnetismIvan TzAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 EMIDocumento52 páginasChapter 3 EMIMayank MeghaniAinda não há avaliações
- Electromgnetic InductionDocumento5 páginasElectromgnetic InductionGhanshyam SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetism CSEC NotesDocumento10 páginasElectromagnetism CSEC NotesCornflakes ToastedAinda não há avaliações
- Year 12 E-Note PhyDocumento77 páginasYear 12 E-Note Phyjeffersonawesome28Ainda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocumento13 páginasMagnetic Effect of Electric Currentanjupal100% (4)
- Unit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)Documento43 páginasUnit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)UpasnaAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical 1 PDFDocumento53 páginasElectrical 1 PDFMdmashihaAinda não há avaliações
- 8.3 Electromagnetic InductionDocumento117 páginas8.3 Electromagnetic InductionPAKK20622 CHARLENE LIONG YAN TINGAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1Documento13 páginasElectromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1midhunesh41Ainda não há avaliações
- Electrical Machines 3rd Sem AsgnmntDocumento95 páginasElectrical Machines 3rd Sem AsgnmntNivedAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 12th ProjectDocumento11 páginasPhysics 12th ProjectVed RameshAinda não há avaliações
- Elect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldDocumento8 páginasElect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldIsmail MzavaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-13 Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocumento19 páginasChapter-13 Magnetic Effect of CurrentSuhani GosainAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3B Electromagnetic InductionDocumento6 páginasChapter 3B Electromagnetic InductionTaonga NhambiAinda não há avaliações
- ch4 CL 10Documento6 páginasch4 CL 10jaiathihyadAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetic EffectsDocumento34 páginas5 Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetic EffectsDevAinda não há avaliações
- CH 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NotesDocumento12 páginasCH 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NotesAkshithAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetism Chap 2 Wildi: ELET 4143 Electrical Machines and ControlsDocumento26 páginasElectromagnetism Chap 2 Wildi: ELET 4143 Electrical Machines and ControlsVijayakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Physics ProjectDocumento15 páginasPhysics ProjectDebkanti Gupta Bhaya0% (1)
- Electromagnetic InductionDocumento18 páginasElectromagnetic InductionShailesh MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5Documento21 páginasChapter 5badrilaminAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocumento53 páginasUnit 1 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismOdellien SajaAinda não há avaliações
- Faraday's LawDocumento35 páginasFaraday's LawMasterArvinAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic InductionDocumento11 páginasElectromagnetic InductionblueegofxAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic InductionDocumento5 páginasElectromagnetic InductionLakshmi MenonAinda não há avaliações
- MAGNETISMDocumento64 páginasMAGNETISMjonathane nhlaneAinda não há avaliações
- X-Magnetic Effect of Electric Current PDFDocumento36 páginasX-Magnetic Effect of Electric Current PDFBilal kaziAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic Induction Physics Investigatory FileDocumento8 páginasElectromagnetic Induction Physics Investigatory Filethe best ofAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture3 - Magnetism and Electromagnetism PDFDocumento8 páginasLecture3 - Magnetism and Electromagnetism PDFOcwich FrancisAinda não há avaliações
- 1.magnetic CircuitsDocumento21 páginas1.magnetic Circuitsp2345715Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 Magnetic Induction, Inductance, Ac and LC CircuitsDocumento13 páginasChapter 7 Magnetic Induction, Inductance, Ac and LC CircuitsShara TayonaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Project Report On Electromagnetic InductionDocumento6 páginasPhysics Project Report On Electromagnetic InductionSwarup RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Notes Fbise FSC 2 CHAPTER - 14 MAGNETISM AND ELECTRODocumento6 páginasPhysics Notes Fbise FSC 2 CHAPTER - 14 MAGNETISM AND ELECTROflyfalconAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Notes Chpt2Documento11 páginasMagnetic Effect of Electric Current Notes Chpt2Sarathrv Rv100% (2)
- Samplenote f5 Chapter 3 Notes 1558234679 5ce0c63729aaa 42548Documento29 páginasSamplenote f5 Chapter 3 Notes 1558234679 5ce0c63729aaa 42548Pavithra RaviAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento37 páginasChapter 1playerAinda não há avaliações
- CH 13Documento12 páginasCH 13charanAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetics CH 1Documento55 páginasMagnetics CH 1NAHOM ANTENEHAinda não há avaliações
- CH 1 MachineDocumento18 páginasCH 1 MachineTeshale AlemieAinda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetism Short NotesDocumento10 páginasElectromagnetism Short Notespadhaai karoAinda não há avaliações
- Motors GeneratorsDocumento14 páginasMotors Generatorsatiggy05Ainda não há avaliações
- Study About Magnetic FieldsDocumento5 páginasStudy About Magnetic Fieldsbazooka wrongAinda não há avaliações
- SUMMARY of Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocumento9 páginasSUMMARY of Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentTajiriMollelAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3: Electromagnetism: Magnetic Field PatternDocumento29 páginasChapter 3: Electromagnetism: Magnetic Field PatternNur ArafahAinda não há avaliações
- Group 3 PresentsDocumento18 páginasGroup 3 PresentsShannie Longakit RacomaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics NotesDocumento85 páginasPhysics NotesJfoxx Samuel0% (1)
- Magneticeffectofelectriccurrent 1 130509054452 Phpapp02Documento29 páginasMagneticeffectofelectriccurrent 1 130509054452 Phpapp02Devika ManiAinda não há avaliações
- Walker, Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday's Law of InductionDocumento31 páginasWalker, Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday's Law of InductionMohsin RazaAinda não há avaliações
- Notes PPT UNIT-2Documento21 páginasNotes PPT UNIT-2ajha88475Ainda não há avaliações
- Review ExamDocumento9 páginasReview ExamasdasdasdaAinda não há avaliações
- Phy Topic 2 F4Documento12 páginasPhy Topic 2 F4Kandrossy GlassAinda não há avaliações
- 1.1: Discuss The Effect On The Magnitude of The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor of Variations inDocumento20 páginas1.1: Discuss The Effect On The Magnitude of The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor of Variations inYousef YohannaAinda não há avaliações
- Invisalign 947Documento3 páginasInvisalign 947api-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- Ceramic Braces 809Documento2 páginasCeramic Braces 809api-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- How To Use A Student PlannerDocumento35 páginasHow To Use A Student Plannerapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- Inman Aligners 781Documento3 páginasInman Aligners 781api-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- g12m FunctionsDocumento34 páginasg12m Functionsapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- g12m Differential CalculusDocumento66 páginasg12m Differential Calculusapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- g12m Counting ProbabilityDocumento31 páginasg12m Counting Probabilityapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- g11 1 Exponents and SurdsDocumento31 páginasg11 1 Exponents and Surdsapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- g11 5 FunctionsDocumento76 páginasg11 5 Functionsapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- g11 9 Finance Growth and DecayDocumento25 páginasg11 9 Finance Growth and Decayapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 06 PH Newton Law of Universal GravitationDocumento12 páginas06 PH Newton Law of Universal Gravitationapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- g11 10 StatisticsDocumento49 páginasg11 10 Statisticsapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- g11 6 TrigonometryDocumento73 páginasg11 6 Trigonometryapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 14 Snells LawDocumento8 páginas14 Snells Lawapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 07 CH Chemical Bonds and Shapes of MoleculesDocumento13 páginas07 CH Chemical Bonds and Shapes of Moleculesapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 05 PH Newtons LawsDocumento22 páginas05 PH Newtons Lawsapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 18 Coulombs LawDocumento7 páginas18 Coulombs Lawapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 23 Power and EnergyDocumento5 páginas23 Power and Energyapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 19 Electric FieldsDocumento11 páginas19 Electric Fieldsapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 27 Exploiting The Lithosphere or Earths CrustDocumento15 páginas27 Exploiting The Lithosphere or Earths Crustapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 25 Acids and BasesDocumento20 páginas25 Acids and Basesapi-235269401Ainda não há avaliações
- 02 PH Addition of Vectors in 2 Dimensions 2Documento12 páginas02 PH Addition of Vectors in 2 Dimensions 2api-2352694010% (1)
- 10K Ductile Cast Iron Gate Valve (Flange Type) TOYO VALVE Gate ValvesDocumento4 páginas10K Ductile Cast Iron Gate Valve (Flange Type) TOYO VALVE Gate ValvesFredie LabradorAinda não há avaliações
- Mark Scheme (Results) October 2020: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level in Core Mathematics C34 (WMA02) Paper 01Documento29 páginasMark Scheme (Results) October 2020: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level in Core Mathematics C34 (WMA02) Paper 01nonAinda não há avaliações
- Button - Head - Socket - Screws - Metric - Spec - SheetDocumento1 páginaButton - Head - Socket - Screws - Metric - Spec - SheetXto PeregrinAinda não há avaliações
- Pokropivny 2007Documento4 páginasPokropivny 2007vasanthanilAinda não há avaliações
- Safety Alarms Chiller and StarterDocumento5 páginasSafety Alarms Chiller and StarterRaghavendra KaleAinda não há avaliações
- Cytomat Software InformationDocumento34 páginasCytomat Software InformationCarlosReisAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Casing Running Speed - QuartzDocumento1 página12 Casing Running Speed - QuartzRebarAinda não há avaliações
- Inductiveand Deductive Reasoning in Geometry October 27 2022Documento9 páginasInductiveand Deductive Reasoning in Geometry October 27 2022Seif DelawarAinda não há avaliações
- Trane ComercialDocumento152 páginasTrane ComercialMartin Bourgon100% (2)
- Exciter Field - Cat GeneratorDocumento5 páginasExciter Field - Cat Generatorwagner_guimarães_10% (1)
- Huaweigpon PDFDocumento1 páginaHuaweigpon PDFRobAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 1research MethodologyDocumento2 páginasPaper 1research MethodologySg_manikandanAinda não há avaliações
- ISUOG Basic Training: Fetal Biometry - Dating, Assessing Size & Estimating Fetal WeightDocumento33 páginasISUOG Basic Training: Fetal Biometry - Dating, Assessing Size & Estimating Fetal WeightRolando DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Programming: Simplex Method: Dr. R. K Singh Professor, Operations Management MDI, GurgaonDocumento58 páginasLinear Programming: Simplex Method: Dr. R. K Singh Professor, Operations Management MDI, GurgaonvsyoiAinda não há avaliações
- EO Gaddis Java Chapter 06 6e-ClassesObjectsPart2Documento48 páginasEO Gaddis Java Chapter 06 6e-ClassesObjectsPart2nyle90009Ainda não há avaliações
- Design and Fabrication of Solar Powered Waste Management SystemDocumento10 páginasDesign and Fabrication of Solar Powered Waste Management SystemAnonymous lPvvgiQjRAinda não há avaliações
- Fuels and Combustion (Unit-Viii) 1. (A) Explain How Fuels Are Classified With Suitable ExamplesDocumento15 páginasFuels and Combustion (Unit-Viii) 1. (A) Explain How Fuels Are Classified With Suitable ExamplesengineeringchemistryAinda não há avaliações
- M.C.a.sem III Operation Research 1Documento50 páginasM.C.a.sem III Operation Research 1Pankaj SatkarAinda não há avaliações
- Onion Ring Magic SquareDocumento8 páginasOnion Ring Magic SquareMJ Foust100% (2)
- HW7 A SolutionsDocumento6 páginasHW7 A Solutionsmmsingh91100% (1)
- Drive Shafts For Steel Production/ Industrial EquipmentDocumento36 páginasDrive Shafts For Steel Production/ Industrial EquipmentEdna Odette Melo UscangaAinda não há avaliações
- C Programming Board Solve PDFDocumento12 páginasC Programming Board Solve PDFEstiak Hossain ShaikatAinda não há avaliações
- Oracle Ebs InstallationDocumento22 páginasOracle Ebs InstallationMr. JalilAinda não há avaliações
- Monsoon Booklet 19 FinalDocumento64 páginasMonsoon Booklet 19 Finalsantosh kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Way4 Manager Menu Editor: Openway Group System Administrator ManualDocumento47 páginasWay4 Manager Menu Editor: Openway Group System Administrator ManualEloy Escalona100% (1)
- Directional & Horizontal DrillingDocumento23 páginasDirectional & Horizontal DrillingMuhammad shahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 4 Positioining V2Documento39 páginasTopic 4 Positioining V2Aqilah Taufik100% (2)
- LYNQ 2020 Installation GuideDocumento16 páginasLYNQ 2020 Installation GuideasdfsadfasdfAinda não há avaliações
- CAT 2020 QUANT Previous Year QuestionsDocumento49 páginasCAT 2020 QUANT Previous Year QuestionsApoorva SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of The Cone and Edge On The Acoustic Characteristics Ofa Cone LoudspeakerDocumento13 páginasEffects of The Cone and Edge On The Acoustic Characteristics Ofa Cone LoudspeakerJavierAinda não há avaliações