Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Notes Scimethod
Enviado por
api-2632308400 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
245 visualizações24 páginasTítulo original
notes scimethod
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
245 visualizações24 páginasNotes Scimethod
Enviado por
api-263230840Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 24
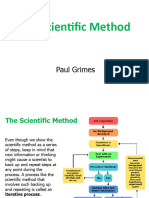
The Scientific Method
Steps to the Scientific Method
(PRHEAD)
Problem State the problem
Research
Hypothesis form a hypothesis
Experiment design & conduct experiment
Analyze Collected Data
Draw Conclusion support or reject
hypothesis
P-Problem State the Problem
Gives you a reason for doing
the experiment
This question MUST be
testable/measurable
Ex: Which car oil will allow
my car to get the best gas
mileage?
Process ItTestable or Not?
Do cats make better pets than
dogs?
Process ItTestable or Not?
How do different types of
movement/activity affect human
heart rate?
Process ItWhich is testable?
A. Which is the tastiest soda?
B. How many people will choose Dr.
Pepper over Coke?
R-Research
In order to make an
educated guess
(hypothesis), you need to
find out more information
about the problem you
are trying to solve.
Ex: research various oils
and their properties.
H-Hypothesis form a hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated
guess about the solution to your
problem based on your
research.
This is done with an if / then
statement. .
Ex: If I use Havoline car oil then
my Lamborghini Diablo will get
better gas mileage.
Hypothesis MUST be:
1. Testable/ Fact-based-Dr. Pepper is the
tastiest soda is not fact-based, its based
on opinion, and therefore can not be a
hypothesis.
2. A sentence, not a question!!
Process ItTestable or Not?
If I use Havoline car oil then it
will be better than Mobile
Oil.
Process ItTestable or Not?
If I use Havoline car oil then
my Lamborghini Diablo will
get better gas mileage.
E-Experiment Design and
conduct experiment
This is done to test the hypothesis.
Design an experiment that will
provide data to support or reject
your hypothesis.
Ex: Test four different car oils found
during research
Parts of an Experiment
Independent Variable The part of an experiment
that you change.
EX: car oil
Dependent Variable- What you are
recording/observing. It changes according to how
the independent variable changes
Ex: gas mileage
ONLY test one variable at a time!!!!!!!!!!
Parts of an Experiment
Constant variables- quantities that remain
constant (the same) aka controlled
variables
Ex: same car, same road
Control group- what is used to COMPARE
the results to. It is the variable in which no
independent variable has been applied.
Ex: test run with the original brand of oil in
the car
A-Analyze Collected Data
Observations are recorded
facts about what you see
during the experiment.
Graph: IVs go on the x-axis
DVs go on y-axis
D-Draw Conclusion Support
or reject hypothesis
This is a brief statement about the results
of the experiment.
In the conclusion state if the hypothesis
was correct (supported) or incorrect
(rejected).
Claim, evidence, reasoning
TYPES OF DATA
Observation or Inference
Observation- See with own eyes
(ex; the apple is red, it is raining outside,
the window is 6ft long
Inference: What you think might
be true but not sure.
(ex: She is wiping her eyes, she is crying, He
has hair on his shirt, he owns a cat)
Types of Observations
Qualitative Results are
descriptive.
ex: the litmus paper turned red
Quantitative Results are
numerical and have a unit.
ex: 5 meters, 45 seconds
Accuracy vs Precision
Accuracy- nearness to the actual value
Precision- how close the data is together
Accuracy and precision: the target example
Precise, but not
accurate
Accuracy and precision: the target example
Accurate,
not precise
Accuracy and precision: the target example
Neither
accurate,
nor precise
Accuracy and precision: the target example
Accurate
and
precise
Você também pode gostar
- Scientific MethodDocumento12 páginasScientific Methodapi-94846453100% (1)
- 6 Steps in Decision MakingDocumento5 páginas6 Steps in Decision MakingNefvi Desqi AndrianiAinda não há avaliações
- K.T. Decision Analysis Techniques for Solving ProblemsDocumento8 páginasK.T. Decision Analysis Techniques for Solving ProblemsnaveengkotaAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific Method NXPowerLiteDocumento21 páginasScientific Method NXPowerLiteJullie Ann AcuninAinda não há avaliações
- AQA Psychology A Level – Research Methods: Practice QuestionsNo EverandAQA Psychology A Level – Research Methods: Practice QuestionsAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific EnquiryDocumento34 páginasScientific EnquiryCarl BlakeAinda não há avaliações
- MarketingProjectDocumento19 páginasMarketingProjectSouvik Mitra ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific Investigation Grade 7Documento4 páginasScientific Investigation Grade 7Anne Hazel Roldan100% (1)
- Scientific Method StepsDocumento31 páginasScientific Method Stepsanonymous manAinda não há avaliações
- 08-Alfa-Alan Richardson-Creating Yourself As A Tester 0Documento60 páginas08-Alfa-Alan Richardson-Creating Yourself As A Tester 0anon_246356152Ainda não há avaliações
- IFTSensory Science Part IIDocumento21 páginasIFTSensory Science Part IINikKiCasiñoAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific Method and Basic SkillsDocumento31 páginasScientific Method and Basic SkillsDaniela Cordovez HidalgoAinda não há avaliações
- Unit IIDocumento125 páginasUnit IISanthos Kumar.kAinda não há avaliações
- Exploring Marketing Research: Problem Definition and The Research ProposalDocumento28 páginasExploring Marketing Research: Problem Definition and The Research ProposalsaikrishnakodaliAinda não há avaliações
- Pass The Civil Professional Engineering (PE) Exam Guide Book by Mark F. DeSantis - 4th Ed-2015-1621419452 (Full Permission)Documento138 páginasPass The Civil Professional Engineering (PE) Exam Guide Book by Mark F. DeSantis - 4th Ed-2015-1621419452 (Full Permission)Mohamed HelmyAinda não há avaliações
- Scale Development Guide for Construct MeasurementDocumento15 páginasScale Development Guide for Construct MeasurementRicha Mukhi100% (1)
- Midterm Exam Review Session: What You've Learned So FarDocumento12 páginasMidterm Exam Review Session: What You've Learned So FarImperator FredericusAinda não há avaliações
- Confirmatory Factor AnalysisDocumento43 páginasConfirmatory Factor AnalysisJasmineNadjaPinuguAinda não há avaliações
- AFQT Test Strategy: Winning Multiple Choice Strategies for the Armed Forces Qualification TestNo EverandAFQT Test Strategy: Winning Multiple Choice Strategies for the Armed Forces Qualification TestAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific MethodDocumento17 páginasScientific Methodapi-261393595Ainda não há avaliações
- Scientific Method NXPowerLiteDocumento18 páginasScientific Method NXPowerLiteEnrique DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Experiment2 PDFDocumento9 páginasMarketing Experiment2 PDFgskAinda não há avaliações
- What is Sensory EvaluationDocumento21 páginasWhat is Sensory EvaluationS Sonia SathiavathyAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific Method: The 7-Step Process To Scientific InvestigationsDocumento13 páginasScientific Method: The 7-Step Process To Scientific Investigationsahmad alfi wirantanaAinda não há avaliações
- Six-step problem solvingDocumento37 páginasSix-step problem solvingblablagm100% (1)
- .... Week 8Documento25 páginas.... Week 8sufyanAinda não há avaliações
- Presenting Your Result / DiscussionDocumento36 páginasPresenting Your Result / DiscussionSofea IzyanAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Scientific Method 2014Documento77 páginas1 Scientific Method 2014api-251060011Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson 6 - Confirmatory Factor AnalysisDocumento43 páginasLesson 6 - Confirmatory Factor AnalysisJasmineNadjaPinuguAinda não há avaliações
- Think Fast Act Faster: How to Generate Innovative Ideas and Make Them HappenNo EverandThink Fast Act Faster: How to Generate Innovative Ideas and Make Them HappenAinda não há avaliações
- Probsolv2010 - Engineering Design Processes ReviewDocumento13 páginasProbsolv2010 - Engineering Design Processes ReviewMsmutok1Ainda não há avaliações
- BRM (Unit 1) - 3Documento21 páginasBRM (Unit 1) - 3Abhi LawandAinda não há avaliações
- SpeedometryActivitiesAtHome PDFDocumento13 páginasSpeedometryActivitiesAtHome PDFid.nurhidayatAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Bayesian Adaptive MethodsDocumento64 páginasIntroduction to Bayesian Adaptive MethodsSergioDragomiroffAinda não há avaliações
- Univ of Chicago - Case Interviewing Tips (2010-2011)Documento16 páginasUniv of Chicago - Case Interviewing Tips (2010-2011)aeonassocAinda não há avaliações
- Experiments Handbook: An overview of how and when to validate hypotheses. And whith whom.No EverandExperiments Handbook: An overview of how and when to validate hypotheses. And whith whom.Ainda não há avaliações
- Scientific MethodDocumento20 páginasScientific MethodmaniasjAinda não há avaliações
- The Scientific Method Short VersionDocumento19 páginasThe Scientific Method Short VersionkamilsmudaAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific Investigation 2Documento23 páginasScientific Investigation 2Riyanka MAinda não há avaliações
- 2business Research Methods2Documento40 páginas2business Research Methods2Gaurav AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Steps of Scientific MethodDocumento18 páginasSteps of Scientific MethodbarranquitasAinda não há avaliações
- Root Cause AnalysisDocumento28 páginasRoot Cause Analysisaftabseven2Ainda não há avaliações
- Root Cause AnalysisDocumento28 páginasRoot Cause AnalysisRashid Saleem100% (2)
- Criterion B and C Summative Assessment: Factors Affecting Heart RateDocumento8 páginasCriterion B and C Summative Assessment: Factors Affecting Heart RateTej Bains100% (1)
- Overview of Project:: BCBT 100: Science of Cooking Individual Experimental Lab Unit 5Documento1 páginaOverview of Project:: BCBT 100: Science of Cooking Individual Experimental Lab Unit 5Haley SwailsAinda não há avaliações
- Go Forwards Go Backwards Exit: This IconDocumento27 páginasGo Forwards Go Backwards Exit: This IconIvy Delos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Dimensional Analysis PowerpointDocumento32 páginasDimensional Analysis PowerpointVijay Sai100% (1)
- Week 4 Concept FanDocumento19 páginasWeek 4 Concept FanAdryanisah Aanisah100% (1)
- Ia WorkbookDocumento11 páginasIa Workbookapi-188978784Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Scientific MethodDocumento21 páginasIntroduction To Scientific MethodDean JezerAinda não há avaliações
- Hypothesis Testing in Business DecisionsDocumento11 páginasHypothesis Testing in Business DecisionsPreethiAinda não há avaliações
- Science and You WorksheetDocumento4 páginasScience and You Worksheetl WhoDex lAinda não há avaliações
- Ap Environmental Science Summer WorkDocumento2 páginasAp Environmental Science Summer Workapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Ecological SuccessionDocumento18 páginasEcological Successionapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Word AssociationDocumento1 páginaWord Associationapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- MeiosisDocumento7 páginasMeiosisapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- The Skeletal SystemDocumento19 páginasThe Skeletal Systemapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Biology Bootcamp Flyer 2015Documento2 páginasBiology Bootcamp Flyer 2015api-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Neuron NotesDocumento10 páginasNeuron Notesapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Structures of Nervous SystemDocumento12 páginasStructures of Nervous Systemapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Jeopardy Test Review Digestive SystemDocumento69 páginasJeopardy Test Review Digestive Systemapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- The Muscular SystemDocumento11 páginasThe Muscular Systemapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System NotesDocumento17 páginasCirculatory System Notesapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System NotesDocumento11 páginasRespiratory System Notesapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Digestive System NotesDocumento13 páginasDigestive System Notesapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Mendelian Genetics Vocab ListDocumento1 páginaMendelian Genetics Vocab Listapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Darwin and Natural SelectionDocumento20 páginasDarwin and Natural Selectionapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- More Complex GeneticsDocumento13 páginasMore Complex Geneticsapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- My Cell MembraneDocumento33 páginasMy Cell Membraneapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Evidence of EvolutionDocumento7 páginasEvidence of Evolutionapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Proteins and Amino Acids NotesDocumento10 páginasProteins and Amino Acids Notesapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- MitosisDocumento10 páginasMitosisapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- CH 8 Mendelian Genetics IntroDocumento18 páginasCH 8 Mendelian Genetics Introapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Energy and Living ThingsDocumento22 páginasEnergy and Living Thingsapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Cell Coloring WorksheetDocumento2 páginasCell Coloring Worksheetapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Dna Test ReviewDocumento16 páginasDna Test Reviewapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Lipids and Nucleic Acids NotesDocumento7 páginasLipids and Nucleic Acids Notesapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Organic Compound NotesDocumento13 páginasOrganic Compound Notesapi-263230840100% (1)
- Carbohydrate Mcas Questions 1 2015Documento3 páginasCarbohydrate Mcas Questions 1 2015api-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- I Am Joes Cell Article and QuestionsDocumento5 páginasI Am Joes Cell Article and Questionsapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Symbiotic RelationshipsDocumento7 páginasSymbiotic Relationshipsapi-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary 2 2Documento1 páginaVocabulary 2 2api-263230840Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecturenote - 1573170473OR MODULE MengistuDocumento163 páginasLecturenote - 1573170473OR MODULE MengistuZena Selfu100% (5)
- Paano Ba Gumawa NG Research PaperDocumento7 páginasPaano Ba Gumawa NG Research Papernydohavihup2100% (2)
- Chapter 5 Evaluation by FUENTES, THEA JYDEE 9 STE ADocumento4 páginasChapter 5 Evaluation by FUENTES, THEA JYDEE 9 STE AThea Jydee FuentesAinda não há avaliações
- Demystifying Ontologyand EpistemologyinresearchmethodsDocumento12 páginasDemystifying Ontologyand EpistemologyinresearchmethodsasaibAinda não há avaliações
- Economic Valuation of Protected AreasDocumento1 páginaEconomic Valuation of Protected AreasEnp Gus AgostoAinda não há avaliações
- 117th ACAD Course at BPATCDocumento41 páginas117th ACAD Course at BPATCPronoy BiswasAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Cardava Banana in Isabela, Philippines: Counting Method Vs Metric SystemDocumento12 páginasMarketing Cardava Banana in Isabela, Philippines: Counting Method Vs Metric SystemRandy Teofilo MbaAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Bahasa Inggris 2Documento16 páginasJurnal Bahasa Inggris 2Gabriel ArmandoAinda não há avaliações
- The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of TechnologyDocumento20 páginasThe Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of TechnologyDeyanira ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- EMSD - PGDE - Lesson TwoDocumento11 páginasEMSD - PGDE - Lesson TwoCharleneAinda não há avaliações
- Verbal Reports ResearchDocumento36 páginasVerbal Reports ResearchChim Cánh CụtAinda não há avaliações
- Application Form For Ethiopian UniversitiesDocumento2 páginasApplication Form For Ethiopian UniversitiesDutta SauravAinda não há avaliações
- Christoph Schmidt Agile Software Development TeamsDocumento195 páginasChristoph Schmidt Agile Software Development TeamsJohny Baca100% (1)
- Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Universitas Islam Indragiri Mid TestDocumento3 páginasProgram Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Universitas Islam Indragiri Mid TestRizky Nur AmaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Sustainability Marketing Strategy: An Analysis of Recent LiteratureDocumento25 páginasSustainability Marketing Strategy: An Analysis of Recent LiteratureNazanin SabetAinda não há avaliações
- Zaleski (1994) Psyc. of Fut OrientationDocumento231 páginasZaleski (1994) Psyc. of Fut Orientationzirpo0% (1)
- Does Psychological Capital and Social Support Impact Burnout in Online Distance Learning StudentsDocumento9 páginasDoes Psychological Capital and Social Support Impact Burnout in Online Distance Learning Studentsalifianda qistiAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Career Plan Template (Published)Documento26 páginasSample Career Plan Template (Published)alex_grgAinda não há avaliações
- Pluralism, Diversity, and Sophistication in Family Therapy ResearchDocumento16 páginasPluralism, Diversity, and Sophistication in Family Therapy ResearchUmi NurhidayahAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Communication (Lynn H. Turner Richard West)Documento676 páginasAn Introduction To Communication (Lynn H. Turner Richard West)abubakarsuleiman5206100% (1)
- Chapter 7Documento26 páginasChapter 7harshal49Ainda não há avaliações
- Mineralogical Controls on Sb RecoveryDocumento152 páginasMineralogical Controls on Sb RecoveryDaniAinda não há avaliações
- Knowledge and Compliance with COVID-19 ProtocolsDocumento28 páginasKnowledge and Compliance with COVID-19 Protocolsivandave27145 encisoAinda não há avaliações
- Neuroscience X CitiesDocumento67 páginasNeuroscience X CitiesSergio Martty Ehecatl Orozco MejíaAinda não há avaliações
- Factors Influencing the Adoption of Autonomous DrivingDocumento18 páginasFactors Influencing the Adoption of Autonomous Drivingvinoham666Ainda não há avaliações
- Fishbone PulverizerDocumento26 páginasFishbone PulverizerFernan MacusiAinda não há avaliações
- Relationship of Political Science With Other Social ScienceDocumento5 páginasRelationship of Political Science With Other Social ScienceShadab AnwarAinda não há avaliações
- Supporting Assessment in Undergraduate MathematicsDocumento247 páginasSupporting Assessment in Undergraduate MathematicsMathematical Association of America100% (6)
- Tourism Demand ProposalDocumento34 páginasTourism Demand ProposalBabu GeorgeAinda não há avaliações
- Ethical Dilemmas of Human Resource Professional in Davao CityDocumento92 páginasEthical Dilemmas of Human Resource Professional in Davao CityCathy Joyce SumandeAinda não há avaliações