Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
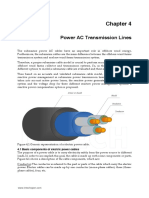
Sag-Corona: Factors, Effects, Loss
Enviado por
Waqar UddinDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sag-Corona: Factors, Effects, Loss
Enviado por
Waqar UddinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Sag In Transmission Line And
Corona Effect
Group Members
Asad Mahmood Jadoon
Waqar
Hasnain Bashir
What Is Sag In Transmission Line?
Sag is defined as the difference in level
between point of support and the
lowest point of conductor.
Actual Picture Of Sag In a Transmission Line
General Figure Of Line Sag
Formula For Sag Calculation
cable Tension of T
span length of L
conductor weight of w
sag S
T
wL
S
8
2
Factors Affecting Sag In Transmission Line
Temperature
Aging
Wind
Ice
Effect Of Temperature On Sag
Effect Of Temperature On Sag
As the temperature increases, the outstretched conductor
length will increase by an amount equal to:
L =TS
Where
= the coefficient of thermal expansion
T = the temperature increase in oC
S = the span length in meters
This will result in increase in sag and decrease in
conductor tension
Effect Of Age On Sag
Conductor sag over time may increase
due to the effects of strand settling in and
metallurgical creep. A higher tension may be
used when the conductor is first erected to
allow for settling in of conductor strands
and for subsequent metallurgical creep of
the conductor material
Effect Of Age Of Line On Sag
Effect Of Wind & Ice On Sag
A wind load on the conductor will increase the
apparent weight of the conductor resulting in an in
increase in tension Whereas Ice build up on the
conductor will increase the apparent diameter and
weight of the conductor
Calculation of Weight of Ice
ice ckness of radial thi r
r f conducto diameter o D
m
kg
r D r w meter of ice per weight
i
3 . 890 , 2
Calculation of Weight of Wind
Combine Effect Of Wind And Ice
the Ice weight of w
tor the conduc weight of w
weight Resultant w
w w w w
i
c
r
w i c r
2 2
ht ltant weig is an resu ertical ax een the v angle betw
w
w w
r
i c
1
cos
Tension T
the span length of L
weight resultant w
T
L w
sag Vertical
r
r
cos
8
2
the Ice weight of w
tor the conduc weight of w
weight Resultant w
w w w w
i
c
r
w i c r
2 2
Sag Due To Different Levels Of Height
Sag Due To Different Levels Of Height
line tension of T
conductor weight of w
o Supports between tw in level Difference h
B e at point Sag of lin S
A e at point Sag of lin S
h Span lengt L
nt A and O etween poi distance b x
wL
Th L
x
2
1
2
T
wx
S
2
2
1
T
x L w
S
2
2
2
Clearance Determination
Line Clearance
What Is Corona ?
The phenomenon of violet glow, hissing
sound & production of ozone gas in over
head Transmission Line is known as Corona.
Effect of Corona
A Violet glow
Hissing Sound
Produces Ozone Gas
Max at Rough & Dirty surface of conductor
Power Loss
Factor affecting Corona
Atmosphere
Conductor
Spacing Between Conductor
Line Voltage
Atmosphere Affect
Breakdown voltage inversely proportional to
Density(number of Ions) of Air
Eg in Stormy Weather the number of ions
may be more then normal so corona occur at
less voltage
Conductor
Affect
Corona depends on
size(diameter),shape(stranded/smooth) &
surface condition(dirty/clean)
Corona Is Inversely proportional to Diameter
Stranded conductor give rise to more corona
then solid conductor
Dirt increases irregularity and thereby
Decreases breakdown voltage
Corona Is Inversely proportional to Spacing between
the conductor
Line Voltage Affect
Line Voltage Directly Proportional to Corona
Spacing Affect Between Conductor
Advantages Of Corona
Vitual Diameter Of Conductor Increases &
reduces electrostatic stress
Corona reduces the effect of transients
produced by surges
Disadvantages Of Corona
Corona causes power losses that affects
transmission efficiency
Ozone Production causes corrosion of
conductor due to chemical reaction
Non sinusoidal voltage drop occurs in the
line cause the inductive interference with the
communication line.
Corona power loss
Corona has power loss which has effect on
the efficiency of transmission line
The power loss is effected both by
atmospheric and line condition
In case of fair weather
Phase Km KW V V
d
r
f P
d ph c
5 2
10 25
244
0
of system Frequency f
r f conducto diameter o d
conductor Radius of r
voltage critical Disriptive V
age phase Volt V
Phase Km KW V V
d
r
f P
o
d
ph
d ph c
10 8 . 0 25
244
5 2 '
0
In case of fair weather
Phase Km KW V V
d
r
f P
d ph c
5 2
10 25
244
0
In case of stormy weather
Factor effecting corona Loss
Effect of conductivity of air:
Effect of density of air
Effect of conductor surface
Effect of conductor radius
Effect of atmospheric condition
Effect of load condition
Effect of load current
Bundling of conductors
Methods of Reducing Corona
Effect
Critical voltage will increase by increasing
the spacing between the conductor.
By using the bundle conductor corona loss is
decrease.
Corona loss can be decreased by increasing
the diameter of the conductor.
Corona discharge images under different gaps (applied voltage: 120 kV, 1 kHz). The discharge length from 1020 cm
gaps is 6.5 cm (10 cm), 5 cm (12 cm), 4 cm (14 cm), 2.5 cm (16 cm), 2 cm (18 cm) and 2 cm (20 cm)
Você também pode gostar
- Corona, Sag and Conductor Vibration: Batch IXDocumento15 páginasCorona, Sag and Conductor Vibration: Batch IXShyamala Chettiraj100% (1)
- Kelvin LawDocumento6 páginasKelvin LawAbdul AlimAinda não há avaliações
- Cascade Arrangements of TransformersDocumento3 páginasCascade Arrangements of TransformerstutorrituAinda não há avaliações
- Module 4 - Conduction and Breakdown in Solid DielectricsDocumento49 páginasModule 4 - Conduction and Breakdown in Solid DielectricsFah Rukh0% (1)
- Presentation On PMU Based Transmission Line Protection Scheme (A Paper Summary)Documento16 páginasPresentation On PMU Based Transmission Line Protection Scheme (A Paper Summary)samuelAinda não há avaliações
- Elektronika Daya Kuliah Ke 2Documento39 páginasElektronika Daya Kuliah Ke 2Hafizh Al KhawarizmiAinda não há avaliações
- Transient Recovery Voltages During The Switching Under Out-of-Phase ConditionsDocumento5 páginasTransient Recovery Voltages During The Switching Under Out-of-Phase ConditionsRoberto SuAinda não há avaliações
- Eeda 512 - Ac/Dc Machinery (Lecture) Lesson 3: Transformers and RegulatorsDocumento4 páginasEeda 512 - Ac/Dc Machinery (Lecture) Lesson 3: Transformers and RegulatorsPatrick NavaAinda não há avaliações
- Nadar Saraswathi College of Engineering and Technology, TheniDocumento5 páginasNadar Saraswathi College of Engineering and Technology, TheniAbhishek Vikram Godse PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Course Syllabus of Hydropower and Renewal EnergyDocumento3 páginasCourse Syllabus of Hydropower and Renewal Energydrbhatta100% (1)
- EHVAC NotesDocumento36 páginasEHVAC NotesVenkatAinda não há avaliações
- EEE 465 Breakdown MechanismsDocumento16 páginasEEE 465 Breakdown MechanismsMd IbtidaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment - I 26 04 2020Documento2 páginasAssignment - I 26 04 2020JackAinda não há avaliações
- Setting Directional Over Current Relays As The LocDocumento6 páginasSetting Directional Over Current Relays As The LocAnonymous yvo84B5Ainda não há avaliações
- Sub-Stations: Departmental of Electrical EngineeringDocumento41 páginasSub-Stations: Departmental of Electrical EngineeringJAYESHAinda não há avaliações
- Calculate Numbers of Plate - Pipe - Strip Earthings (Part-3) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocumento11 páginasCalculate Numbers of Plate - Pipe - Strip Earthings (Part-3) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesMohamad HishamAinda não há avaliações
- Ps2113 Distributed Generation and Microgrid 2013 14Documento2 páginasPs2113 Distributed Generation and Microgrid 2013 14Eric Hernandez0% (1)
- ICL8038 Linear Sweep Function Generator CCTDocumento2 páginasICL8038 Linear Sweep Function Generator CCTian_new100% (1)
- Basic Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocumento25 páginasBasic Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVAinda não há avaliações
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR)Documento8 páginasSilicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR)dcyomamaAinda não há avaliações
- WG CF&E-CoronaGuideKuffel July2012Documento33 páginasWG CF&E-CoronaGuideKuffel July2012vairam_eee01Ainda não há avaliações
- Capacitor BankDocumento16 páginasCapacitor BankKyaw Soe0% (1)
- HVDC transmission line from Ethiopia to Isinya (KenyaDocumento9 páginasHVDC transmission line from Ethiopia to Isinya (KenyakarthikAinda não há avaliações
- Se 02 PDFDocumento40 páginasSe 02 PDFk rajendra100% (1)
- 2-Charge Formation in Clouds-1Documento26 páginas2-Charge Formation in Clouds-1Gokulraja GokulAinda não há avaliações
- Transformers: Understanding the Heart of AC Power SystemsDocumento28 páginasTransformers: Understanding the Heart of AC Power SystemsGirish Shankar MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Sri Sivasubramaniyanadar College of Engineering, Kalavakkam - 603 110Documento2 páginasSri Sivasubramaniyanadar College of Engineering, Kalavakkam - 603 110Rajalakshmi TVAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - Basics of ProtectionDocumento42 páginas3 - Basics of ProtectionSarthak VatsAinda não há avaliações
- Three-phase power flow analysisDocumento6 páginasThree-phase power flow analysishockpinAinda não há avaliações
- EE296 Lightning Overvoltage Simulation of Wind FarmDocumento30 páginasEE296 Lightning Overvoltage Simulation of Wind FarmPaolo Josemari ZafraAinda não há avaliações
- EDC Notes PDFDocumento377 páginasEDC Notes PDFscribdcurrenttextAinda não há avaliações
- Transmission LinesDocumento40 páginasTransmission LinesKuronix ArcayaAinda não há avaliações
- Induction Relay Types - Disc, Cup & Their WorkingDocumento8 páginasInduction Relay Types - Disc, Cup & Their WorkinghilalsherAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Power Theft Monitoring SystemDocumento3 páginasWireless Power Theft Monitoring SystemVIVA-TECH IJRIAinda não há avaliações
- HIPASE-E 001-AB-310 Application Board ExcitationDocumento3 páginasHIPASE-E 001-AB-310 Application Board ExcitationChi PhamAinda não há avaliações
- Power AC Transmission Lines: 3.4 Chapter ConclusionsDocumento49 páginasPower AC Transmission Lines: 3.4 Chapter ConclusionsHassenAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-I: Introduction of BJTDocumento56 páginasUnit-I: Introduction of BJThodeegits9526Ainda não há avaliações
- 534621ijsetr1142 259Documento7 páginas534621ijsetr1142 259Hannu PortilloAinda não há avaliações
- Scientech 2266Documento33 páginasScientech 2266sarikapravinAinda não há avaliações
- Lightning AnalysisDocumento21 páginasLightning AnalysisDanialMdNoorAinda não há avaliações
- Do Capacitor Switching Transients Still Cause ProblemsDocumento5 páginasDo Capacitor Switching Transients Still Cause Problemsaris09yekofAinda não há avaliações
- Auto Selection of Any Available PhaseDocumento16 páginasAuto Selection of Any Available PhaseRyan HarrisAinda não há avaliações
- Ferroresenance Phenomena of A Station Service Transformer During Black Start and Its Investigatio1Documento4 páginasFerroresenance Phenomena of A Station Service Transformer During Black Start and Its Investigatio1pongpumAinda não há avaliações
- 221 Townsend Full NoteDocumento12 páginas221 Townsend Full NoteKhairul AkmalAinda não há avaliações
- Defining Size and Location of Capacitor in Electrical System 1Documento7 páginasDefining Size and Location of Capacitor in Electrical System 1Prince BlissfulAinda não há avaliações
- Integrated Solar Power Plants (ISCC)Documento13 páginasIntegrated Solar Power Plants (ISCC)carzanteAinda não há avaliações
- Is 2309 1989Documento72 páginasIs 2309 1989Jagdish PalariyaAinda não há avaliações
- A2125040331 - 14289 - 12 - 2018 - Transformer & MotorDocumento97 páginasA2125040331 - 14289 - 12 - 2018 - Transformer & MotorRaj RathoreAinda não há avaliações
- Eee-V-dcmachines and Synchronous Machines (10ee54) - SolutionDocumento73 páginasEee-V-dcmachines and Synchronous Machines (10ee54) - SolutionchaitanyaAinda não há avaliações
- High Impedance FaultsDocumento3 páginasHigh Impedance FaultsGary GrubbsAinda não há avaliações
- Earthing Guide: Methods, Sizes & InstallationDocumento6 páginasEarthing Guide: Methods, Sizes & InstallationAditya SinghaniaAinda não há avaliações
- 6.1 Leakage Flux and Leakage InductanceDocumento29 páginas6.1 Leakage Flux and Leakage InductancePrema ElizabethAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Earth Testing 2010Documento68 páginas1 Earth Testing 2010Ramy DiabAinda não há avaliações
- Gopal Seminar Report PDFDocumento14 páginasGopal Seminar Report PDFKarthik OberioAinda não há avaliações
- Power Quality and The Philippine Grid CodeDocumento15 páginasPower Quality and The Philippine Grid CodeYellow LanternAinda não há avaliações
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityNo EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityAinda não há avaliações
- Real-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsNo EverandReal-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsAinda não há avaliações
- Biogas Potential For Electrical Power Generation in PakistanDocumento9 páginasBiogas Potential For Electrical Power Generation in PakistanWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Development Board User ManualDocumento29 páginasDSP Development Board User ManualWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- Code For Getting Data Points From GraphDocumento1 páginaCode For Getting Data Points From GraphWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 01 Submission Date: 25/04/2014 Q1:: T P T PDocumento1 páginaQuiz 01 Submission Date: 25/04/2014 Q1:: T P T PWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- 01 A Overview of MicrohydelDocumento44 páginas01 A Overview of MicrohydelWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- Matlab Finite Element Modeling For Materials Engineers Using MATLABDocumento74 páginasMatlab Finite Element Modeling For Materials Engineers Using MATLABPujara ManishAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Transformers (2) 11Documento25 páginasLecture Transformers (2) 11Waqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- Questionnaire: Adress of ClientDocumento7 páginasQuestionnaire: Adress of ClientWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- Wind PowerDocumento12 páginasWind PowerWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S1364032114001154 MainDocumento18 páginas1 s2.0 S1364032114001154 MainWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S1364032108001603 MainDocumento6 páginas1 s2.0 S1364032108001603 MainWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- BiogasDocumento9 páginasBiogasWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- Energy and Renewable Energy Scenario of PakistanDocumento10 páginasEnergy and Renewable Energy Scenario of Pakistanfardasa123Ainda não há avaliações
- Boiler Models For System Dynamic Performance StudiesDocumento9 páginasBoiler Models For System Dynamic Performance Studiesiacobmihai70Ainda não há avaliações
- Inverse of A 3x3 MatrixDocumento3 páginasInverse of A 3x3 MatrixMthokozisi Cecil MkandlaAinda não há avaliações
- EditDocumento2 páginasEditWaqar UddinAinda não há avaliações
- L1 1KeyTermCrosswordDocumento2 páginasL1 1KeyTermCrosswordIsabella DivilovaAinda não há avaliações
- MNBC 2012 Provisional Part 5B (Electrical & Allied Installation)Documento101 páginasMNBC 2012 Provisional Part 5B (Electrical & Allied Installation)Htoo Kyi WynnAinda não há avaliações
- Generator Technical Operation & Maintenance ManualDocumento68 páginasGenerator Technical Operation & Maintenance ManualRaul BalboaAinda não há avaliações
- PIRELLI Marine CablesDocumento28 páginasPIRELLI Marine CablesDan GhimbasanuAinda não há avaliações
- Cost Data FY 2018-19Documento109 páginasCost Data FY 2018-19ganesh2428364Ainda não há avaliações
- Stock-Material-and-Febricated-Material SOR-2016-17Documento35 páginasStock-Material-and-Febricated-Material SOR-2016-17souvikbesu89Ainda não há avaliações
- L s8 Lightning Protection System Using Stranded G.I. WiresDocumento4 páginasL s8 Lightning Protection System Using Stranded G.I. WiresTan Kang YaoAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 4 Power SystemDocumento45 páginasChap 4 Power SystemArife AbdulkerimAinda não há avaliações
- RME Refresher April 4 2009 PEC 5 KeyDocumento7 páginasRME Refresher April 4 2009 PEC 5 KeyCharlene Mae Sta Teresa-ZambaleAinda não há avaliações
- NORSOK U CR 006r1 - Subsea Production Control UmbilicalDocumento14 páginasNORSOK U CR 006r1 - Subsea Production Control UmbilicalNils Antoine FreundAinda não há avaliações
- VCTF10KDocumento2 páginasVCTF10KgeekcourseonlineAinda não há avaliações
- Fictitious Calculation Method: A. 4x4 MM CU/XLPE/SWA/PVC 0.6/1 KVDocumento3 páginasFictitious Calculation Method: A. 4x4 MM CU/XLPE/SWA/PVC 0.6/1 KVosama100% (1)
- Field Test PlanDocumento8 páginasField Test PlanMohammed TauseefAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentation Cables: BS 5308, Part 1 BS 5308, Part 2 and Gen. To BS 5308, Part 1Documento88 páginasInstrumentation Cables: BS 5308, Part 1 BS 5308, Part 2 and Gen. To BS 5308, Part 1Raj ChavanAinda não há avaliações
- Line Up TerminalDocumento10 páginasLine Up TerminalAdam SatrioAinda não há avaliações
- Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis-Part I Review of Principle and MethodsDocumento18 páginasBioelectrical Impedance Analysis-Part I Review of Principle and MethodslayzarleskaAinda não há avaliações
- Onshore CablesDocumento184 páginasOnshore CablesHarish Sundar100% (1)
- Close Exam 12Documento4 páginasClose Exam 12sieged_rj3165Ainda não há avaliações
- Ranger2 TerminationsDocumento6 páginasRanger2 TerminationsMoisésIxbaAinda não há avaliações
- L1 Che Spe 017Documento7 páginasL1 Che Spe 0174493464Ainda não há avaliações
- Minimum Ground Clearance As Per IEDocumento3 páginasMinimum Ground Clearance As Per IEJeya KannanAinda não há avaliações
- Supporting Doc For 210.19 (A) (5) - NEC 250.4 (A) (5) Et AlDocumento1 páginaSupporting Doc For 210.19 (A) (5) - NEC 250.4 (A) (5) Et AlPaul KeleherAinda não há avaliações
- EB CablesDocumento1 páginaEB CablesVijay KarthikeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Earthing and Lightning Protection MetricDocumento40 páginasEarthing and Lightning Protection MetricbalabhaviniAinda não há avaliações
- Amperage Selection GuideDocumento4 páginasAmperage Selection GuideMohan SAinda não há avaliações
- Transfer of Heat Energy - Check Your UnderstandingDocumento2 páginasTransfer of Heat Energy - Check Your UnderstandingAlyssa Cole100% (1)
- Características Cable DCDocumento2 páginasCaracterísticas Cable DCpablo luis andreattaAinda não há avaliações
- Motor Thermal ModelDocumento15 páginasMotor Thermal ModelnagarajasarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Bus Bar Types and TestsDocumento13 páginasBus Bar Types and TestsRANGASWAMY SAinda não há avaliações