Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Isometric Drawing G-Wlearning Com
Enviado por
api-265554570Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Isometric Drawing G-Wlearning Com
Enviado por
api-265554570Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 1
Chapter 3
Introduction to Isometric Drawings
The most common type of pictorial drawing used in the drafting industry
is the isometric drawing. See Figure 3B-1. This supplement focuses on tools
and drawing aids that help you create 2D isometric views that look 3D, as if the
object tilts toward you. However, a 3D model provides a better way to display
isometric views, for most applications. AutoCAD and Its Applications
Advanced describes how to construct 3D models.
pictorial drawing: A drawing that shows the height, width, and depth of an object in a single view.
isometric drawing: A view in which all three axes appear at equal 120 angles with the plane of projection.
2. REMOVE ALL BURRSAND SHARP EDGES.
1. DIMENSIONSAND TOLERANCESPER ASME Y14.5M-2009.
NOTES:
MADSEN DESIGNS INC.
DIMENSIONSAREIN INCHES(IN.)
1 1
0
IAA-018-01
1:1
B
DAM
SLIDER HINGE CONNECTOR
ALL OVER
TITANIUM
DPM
DPM
10'
REV
DATE
SHEET
DWG NO. SIZE
SCALE
CAGECODE
TITLE
CHECKED
DRAWN
APPROVALS
.X
.XX
TOLERANCES:
UNLESSOTHERWISESPECIFIED
.1
.01
MATERIAL
APPROVED
FINISH
ANGULAR:
FINISH:
THIRD ANGLEPROJ ECTION
62IN.
.005 .XXX
DO NOTSCALEDRAWING OF
.984
2X .394 R
) (.541
3.937
3.543
.394
2.657
.394
1.772
.394
.886
.394
.984
.492
.197 .394
.197 THRU 5X
) 4X .541(=2.165 .886
B
C
C B A .005
A
.394
8X .394 1.969
8X .197 R
8X .394 R
.005
B A .005
M M
M
M
Isometric drawing view
Figure 3B-1. An example of a 2D mechanical part drawing with an isometric view used to help
visualize the product.
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 2
Chapter 3
The term isometric means equal (iso) measure (metric). An isometric drawing
has no perspective, and therefore edges that are equal in length are drawn equal
in length. The angles between the three principle planes and edges of an object
are equal. See Figure 3B-2A. The vertical edges of an object are parallel to each
other and form measurable isometric lines 90 from horizontal. The horizontal
edges of an object are parallel to each other and form measurable isometric lines
30 from horizontal. All other lines are nonisometric lines. See Figure 3B-2B.
Circular features appear elliptical in an isometric drawing. The Isocircle
option of the ELLIPSE tool, described in Chapter 4, allows you to construct
isometric circles and arcs easily. Isometric text uses a specic obliquing angle
and rotation depending on the plane and drawing application. Chapters 9 and
10 cover AutoCAD text.
90
120
120 120
30
30
Right
isometric
plane
Nonisometric
lines
Left
isometric
plane
Top isometric
plane
isometric lines: Lines that are parallel to an axis in an isometric drawing.
nonisometric lines: Lines that are not parallel to the axes in an isometric drawing.
Figure 3B-2. AAn isometric drawing creates equal angles between the three principle planes
and edges of an object. BAn example of an isometric drawing with isometric and nonisometric
lines.
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 3
Chapter 3
Isometric Snap
Once you understand the geometric layout of an isometric view, you can use
any point entry method to construct an isometric drawing. Polar coordinates and
dynamic input or dimensional input are common basic point entry options for
isometric construction because they allow you to specify angles. Polar tracking set
to 30 increment angles is also an effective method. One of the most useful aids for
isometric drawing is the Isometric snap option of Snap and Grid modes.
Use the Snap and Grid tab of the Drafting Settings dialog
box to set Isometric snap. See Figure 3B-3. A quick way
to access the Snap and Grid tab is to right-click on the Grid
Display or Snap Mode button on the status bar and select
Settings. Pick the Isometric snap radio button in the Snap
Type
DSETTINGS
DS
SE
D
S
E
T
T
I
N
G
S
Isometric
crosshairs
Pick to set
isometric
snap
Grid
rotates 30
Specify the
grid spacing
Check when
using
isometric snap
to display the
grid as a
pattern of dots
Turn snap on and off Turn grid on and off
Specify the isometric
snap increment
Figure 3B-3. Use the Snap and Grid tab of the Drafting Settings dialog box to specify isometric
grid and snap settings.
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 4
Chapter 3
type area to activate Isometric snap. Then specify the snap increment using the
Snap Y spacing: text box of the Snap spacing area, and the grid spacing using
the Grid Y spacing: text box of the Grid spacing area. You can only set the Y snap
and grid spacing. The X spacing is not applicable because the X axis relates to
horizontal measurements. For this same reason, you must also check 2D model
space in the Grid style area to display the grid as a pattern of dots.
Activate Grid and Snap modes and you are ready to begin
drawing. As shown in Figure 3B-3, the grid and crosshairs
rotate to an isometric orientation that aids in drawing objects
at isometric angles. Figure 3B-4 shows the steps required
to construct an isometric cube using the LINE tool. Apply
the same techniques to drawing other objects. Notice that
isometric snap can be very helpful when you are constructing
isometric lines.
Specifying the Isometric Plane
Isometric grid and snap modes orient the grid and snap
to isometric angles. You can align the crosshairs with the
left, right, or top isoplane, depending on the plane on which
you plan to draw. See Figure 3B-5. Changing the isoplane
is not required when drawing isometric lines, but doing so
can be helpful for visualization and drawing ease. You must
change the isoplane orientation to construct isometric circles and arcs using the
Isocircle option of the ELLIPSE tool, described in Chapter 4. Press [F5] repeat-
edly to cycle through the isoplanes, or access the ISOPLANE tool and specify the
Left, Top, or Right option, depending on the isoplane orientation appropriate for
the isometric plane on which you plan to draw.
Type
GRID
[F7] G
R
I
D
Type
SNAP
SN
[F9]
S
N
A
P
Type
ISOPLANE
[F5]
I
S
O
P
L
A
N
E
isoplane: One of the three isometric planes: left, right, or top.
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Ands jspois a thspo
cnb angoxu ig
cuostues tre poiust
piod agousgas on
few ousi zougosa eos
sougsgo.
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 5
Chapter 3
Figure 3B-4. Creating a 2 unit 2 unit cube using isometric grid and snap. Other default
drawing aids are also on to help describe the construction process.
NOTE
When using Isometric snap, the crosshairs is always
oriented with the specified isoplane. The isoplane does
not apply to window or crossing selection and similar
operations that use a box to make a selection.
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Ands jspois a thspo
cnb angoxu ig
cuostues tre poiust
piod agousgas on
few ousi zougosa eos
sougsgo.
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 6
Chapter 3
Left Isoplane
150 X axis
90 Y axis
Right Isoplane
30 X axis
90 Y axis
Top Isoplane
150 X axis
30 Y axis
Figure 3B-5. Adjusting the isoplane orientation of the crosshairs to match a specific isometric
plane.
NOTE
Some of the following activities require the use of a
decimal-unit isometric template with active isometric grid
and snap modes. If you do not have such a template, create
it now. Then use it as indicated in these activities.
1. Start a new drawing from scratch using the imperial format.
2. Access the Drafting Settings dialog box. On the Snap and Grid tab,
pick the Isometric snap radio button, enter .25 for the Y snap and grid
spacing values, and pick the 2D model space check box.
3. Toggle Grid mode on from the status bar if it is not active.
4. Toggle Snap mode on from the status bar if it is not active.
(Continued.)
Activity 3B-1
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 7
Chapter 3
5. Access the LINE tool and use grid and snaps to draw the isometric
view shown below. Change the isoplane orientation as appropriate
for drawing objects on each isometric plane. Do not dimension the
drawing.
6. Save the drawing as ACT3B-1.
Activity 3B-1
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 8
Chapter 3
For each of the following isometric drawings, start a new drawing using a
decimal-unit isometric template that includes active isometric grid and snap
modes. Draw an isometric part view similar to each drawing using dimen-
sions of your choice. Save the drawings using the file names shown.
1.
File name: ACT3B-2A
2.
File name: ACT3B-2B
(Continued.)
Activity 3B-2
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 9
Chapter 3
3.
File name: ACT3B-2C
4.
File name: ACT3B-2D
(Continued.)
Activity 3B-2
SUPPLEMENTAL
MATERI ALS
AutoCAD
and Its Applications
B A S I C S
Student Web Si t e
Copyright by Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. Introduction to Isometric Drawings, page 10
Chapter 3
5.
File name: ACT3B-2E
6.
File name: ACT3B-2F
Activity 3B-2
Você também pode gostar
- CATIA Exercise Book PDFDocumento33 páginasCATIA Exercise Book PDFNikhil Raj83% (153)
- Assembly DrawingDocumento55 páginasAssembly DrawingKantharaj ChinnappaAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To Aux ViewsDocumento20 páginasIntro To Aux ViewsBhuban LimbuAinda não há avaliações
- W 7 IsometricdrawingDocumento8 páginasW 7 Isometricdrawingapi-265554570Ainda não há avaliações
- Isometric in AutocadDocumento13 páginasIsometric in Autocadapi-265554570Ainda não há avaliações
- Multiviews Isometric ExercisesDocumento4 páginasMultiviews Isometric Exercisesapi-265554570Ainda não há avaliações
- Isometric Draw Problems Cha Engr Sjsu Edu-Mjonhson-Autocad-Cha PDFDocumento52 páginasIsometric Draw Problems Cha Engr Sjsu Edu-Mjonhson-Autocad-Cha PDFapi-265554570Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter7 Demtol1 - Dimensioning StandardsDocumento100 páginasChapter7 Demtol1 - Dimensioning Standardsapi-265554570Ainda não há avaliações
- Autocad Assig1Documento5 páginasAutocad Assig1api-265554570Ainda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Risus - Silverlode 1908Documento9 páginasRisus - Silverlode 1908lutherAinda não há avaliações
- Look - Back - in - Anger General NoteDocumento4 páginasLook - Back - in - Anger General NoteWungreiyon moinao100% (1)
- Kourtessi Philippakis PDFDocumento2 páginasKourtessi Philippakis PDFcatalinAinda não há avaliações
- Reflective Essay.1Documento31 páginasReflective Essay.1Nora Lyn M. TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Calypso GenreDocumento14 páginasCalypso GenreLucky EluemeAinda não há avaliações
- Reiki Master Handbook-Full InglesDocumento44 páginasReiki Master Handbook-Full Inglesanon-523638100% (13)
- Ricoh Error CodeDocumento7 páginasRicoh Error CodeMarxe Ozil MurimiAinda não há avaliações
- Listening exercise present continuous sentences questionsDocumento3 páginasListening exercise present continuous sentences questionsLmd DomerAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Aqueous Titrations & Complexometric TitrationsDocumento8 páginasNon-Aqueous Titrations & Complexometric TitrationsAmit GautamAinda não há avaliações
- Drawing List (II) : Alam Sutera CondominiumDocumento1 páginaDrawing List (II) : Alam Sutera CondominiumDenyAinda não há avaliações
- Dissertation PDFDocumento61 páginasDissertation PDFÍtalo R. H. Ferro100% (1)
- Jingle Bells - Natal (Impressão)Documento1 páginaJingle Bells - Natal (Impressão)Virginia Aparecida Kloster SalonskiAinda não há avaliações
- Brazil Badlands Landscapes RevealedDocumento42 páginasBrazil Badlands Landscapes RevealedIvamauro SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Pastyme ScoreDocumento2 páginasPastyme ScoreMatthew JelfAinda não há avaliações
- How Values and Virtues Shape Our Thoughts and ActionsDocumento11 páginasHow Values and Virtues Shape Our Thoughts and ActionsLovely Platon CantosAinda não há avaliações
- How To Batch Separate & Crop Multiple Scanned PhotosDocumento5 páginasHow To Batch Separate & Crop Multiple Scanned PhotosAnonymous Re62LKaACAinda não há avaliações
- Joseph Brodsky - A Room and A HalfDocumento5 páginasJoseph Brodsky - A Room and A Halfkottzebue0% (1)
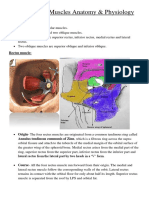
- Extraocular Muscle Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocumento13 páginasExtraocular Muscle Anatomy and Physiology NotesRahul Jasu100% (1)
- Tribute Albums: Leonard CohenDocumento12 páginasTribute Albums: Leonard CohentoypomAinda não há avaliações
- Yogacara BuddhismDocumento2 páginasYogacara BuddhismV.F.Ainda não há avaliações
- (Jim Surmanek) Introduction To Advertising Media (BookFi) PDFDocumento393 páginas(Jim Surmanek) Introduction To Advertising Media (BookFi) PDFIoana-Nely MilitaruAinda não há avaliações
- MMW Module 1 - Patterns, Transformation & FractalsDocumento17 páginasMMW Module 1 - Patterns, Transformation & Fractalscai8viaAinda não há avaliações
- Title Sequence Timeline - TintinDocumento3 páginasTitle Sequence Timeline - TintinMichelleAinda não há avaliações
- Parasitic ArchitectureDocumento4 páginasParasitic ArchitecturehopeAinda não há avaliações
- Make a 3D Text in GimpDocumento19 páginasMake a 3D Text in GimpAlyssa Jed TenorioAinda não há avaliações
- UST Paskuhan 2017 Concert Hosts' ScriptDocumento9 páginasUST Paskuhan 2017 Concert Hosts' ScriptElijah PunzalanAinda não há avaliações
- Rizal's Life in Asian CountriesDocumento3 páginasRizal's Life in Asian CountriesJenemar0% (1)
- Why You Need To Buy A New VW Beetle?Documento3 páginasWhy You Need To Buy A New VW Beetle?Carlos RocaAinda não há avaliações
- Report - Paints & VarnishesDocumento11 páginasReport - Paints & VarnishesShruthadev BantwalAinda não há avaliações
- Pre K Kindergarten Alphabet Letter TracingDocumento28 páginasPre K Kindergarten Alphabet Letter TracingNeha RawatAinda não há avaliações