Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Unit4dna2014 15
Enviado por
api-2619420100 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
44 visualizações35 páginasTítulo original
unit4dna2014-15
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
44 visualizações35 páginasUnit4dna2014 15
Enviado por
api-261942010Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 35
Journal Entry 1
What do you know about DNA?
Tell me at least
two things you know
about DNA.
Journal Entry 2
Draw a picture of DNA and label
Nucleotide
adenine
guanine
cytosine
thymine
sugar
phosphate
hydrogen bond
Journal Entry 3
Summarize and explain the process of
DNA replication.
Chapter 10 Objectives
By the end of this unit I will be able to
Describe the three parts of a nucleotide
Relate the role of base pairing rules to the
structure of DNA
Summarize and explain the process of
DNA replication
Chapter 10 Objectives
By the end of this unit I will be able to
Identify the role of enzymes in the
replication of DNA
Outline the flow of genetic information in
cells from DNA to protein
Compare the structure of DNA with that of
RNA
Summarize the process of transcription.
Chapter 10
Nucleic Acids and Protein
Synthesis
What is a nucleic acid?
A complex organic (carbon)
macromolecule
DNA= Deoxyribonucleic Acid
RNA= Ribonucleic Acid
What are the two main
functions of DNA?
1. To store information and to direct
activities of the cell.
-tells which proteins to make
2. To copy itself exactly for new cells that
are created
What are DNA molecules
made of?
Two strands of repeating nucleotides
A nucleotide has three parts:
1. Deoxyribose =a sugar
2. Phosphate =PO4
3. Nitrogen Base
What are DNA molecules
made of?
A= Adenine
T= Thymine
C= Cytosine
G= Guanine
Adenine and Guanine have two rings of
carbon and are called Purines
Thymine and Cytosine have one ring of
carbon and are called Pyrimidines
What does the DNA molecule
look like?
A twisted ladder (double helix) helical
What are the base pairing
rules?
Adenine always bonds with Thymine
Cytosine always bonds with Guanine
Who discovered the structure
of DNA?
In 1953 Francis Crick and
James Watson
They proposed a model of
DNA in which two nucleotide
chains wrap around each
other to form a double spiral-
similar to a spiral staircase
They called it a Double Helix
Who discovered the
structure of DNA?
They relied heavily on scientific evidence
reported by other scientists to construct
their model. Evidence like the X-ray
diffraction photo of DNA studied by
Rosaline Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
Crick, Watson, & Wilkins received the
Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1962
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4PKj
F7OumYo
What is DNA replication and
what happens during it?
The process of copying DNA in a cell is
called replication.
What is DNA replication and
what happens during it?
1. The two chains of DNA separate at
the replication fork by enzymes
called Helicase. They break the
hydrogen bonds between the
complementary base pairs.
What is DNA replication and
what happens during it?
2. Enzymes called DNA Polymerase move
down each half strands and binds the new
nucleotides to the existing DNA chains.
What is DNA replication and
what happens during it?
3. When replication is
completed, two new exact
copies of the original DNA
molecule are produced
and the cell is ready to
divide.
What is a mutation?
A mistake in the nucleotide sequence at even
one location will cause a mutation and can
have serious effects in new cells.
Chemicals and ultraviolet radiation from the
sun can damage DNA which can lead to
cancer.
Enzymes called DNA polymerase are
constantly proofreading and repairing errors
that occur.
What are some differences
between RNA and DNA?
RNA DNA
1. Sugar is ribose
2. One strand
3. Uracil
4. Can be found in the
nucleus or the
cytoplasm
1. Sugar is deoxyribose
2. Two strands
3. Thymine
4. Can only be found in
the nucleus
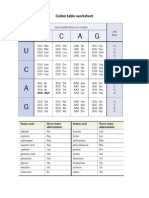
What are the three kinds of RNA?
1. Messenger RNA
2. Transfer RNA
3. Ribosomal RNA
What is Protein Synthesis and
where does it take place?
The making of proteins and it takes
place on the ribosomes
How does Protein Synthesis
occur?
1. Transcription- genetic information is
copied from DNA to mRNA
2. Messenger RNAs code is in three
base groups called codons
3. Codons attach to ribosomes and each
one codes for an amino acid.
How does Protein Synthesis
occur?
4. Translation- the process of assembling
the protein from information encoded in
Messenger RNA. This process begins
when the mRNA leaves the nucleus
through pores in the nuclear membrane
and then migrates to a ribosome.
How does Protein Synthesis
occur?
5. Amino acids floating freely in the
cytosol are transported to the
ribosome by the tRNA.
6. The tRNA has a sequence of three
nucleotides called an anti-codon which
is complementary to and pairs with its
corresponding codons.
Protein Synthesis
http://www.dnai.org/a/index.html
Lets watch this in action!
What joins the amino acids
together to form a protein?
A peptide bond joins amino acids to
make a polypeptide chain.
Where do the amino acids come
from floating in the cytosol of
our cells?
The food we eat
(proteins)
What are some important
proteins that we make?
Functional Proteins
1. Hemoglobin -found in our red blood
cells; function in carrying oxygen
2. Antibodies -help fight off viruses and
bacteria that invade the body.
3. Enzymes -control chemical reactions
in the body.
What are some important
proteins that we make?
Structural Proteins
1. Keratin -water proofing protein on our
skin.
2. Actin and Myosin -proteins which
make up our muscles
3. Collagen- found in cartilage and other
connective tissue
The Human Genome
The Human Genome
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Unit Calendar Chapter 7Documento2 páginasUnit Calendar Chapter 7api-261942010Ainda não há avaliações
- VocabularyDocumento1 páginaVocabularyapi-261942010Ainda não há avaliações
- Transcription Translation Practice WorksheetDocumento2 páginasTranscription Translation Practice Worksheetapi-2619420100% (1)
- Codon Table WorksheetDocumento4 páginasCodon Table Worksheetapi-261942010Ainda não há avaliações
- Worksheet - Dna Strucuture and ReplicationDocumento3 páginasWorksheet - Dna Strucuture and Replicationapi-261942010Ainda não há avaliações
- Dnaunitcalendar 1Documento1 páginaDnaunitcalendar 1api-261942010Ainda não há avaliações
- LabrubricDocumento1 páginaLabrubricapi-261942010Ainda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Exercise-01: JEE-PhysicsDocumento52 páginasExercise-01: JEE-Physicsjk rAinda não há avaliações
- Precision Machine Components: NSK Linear Guides Ball Screws MonocarriersDocumento564 páginasPrecision Machine Components: NSK Linear Guides Ball Screws MonocarriersDorian Cristian VatavuAinda não há avaliações
- SolBridge Application 2012Documento14 páginasSolBridge Application 2012Corissa WandmacherAinda não há avaliações
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) : Mfos Kras Objectives Timeline Weight Per KRADocumento4 páginasIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form (Ipcrf) : Mfos Kras Objectives Timeline Weight Per KRAChris21JinkyAinda não há avaliações
- Ovr IbDocumento27 páginasOvr IbAriel CaresAinda não há avaliações
- Nokia CaseDocumento28 páginasNokia CaseErykah Faith PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio Analysis of PIADocumento16 páginasRatio Analysis of PIAMalik Saad Noman100% (5)
- 4 Factor DoeDocumento5 páginas4 Factor Doeapi-516384896Ainda não há avaliações
- U2 All That You Can't Leave BehindDocumento82 páginasU2 All That You Can't Leave BehindFranck UrsiniAinda não há avaliações
- Qad Quick StartDocumento534 páginasQad Quick StartMahadev Subramani100% (1)
- Managerial EconomicsDocumento3 páginasManagerial EconomicsGuruKPOAinda não há avaliações
- CALCULUS PHYSICS MIDTERMDocumento41 páginasCALCULUS PHYSICS MIDTERMMACARIO QTAinda não há avaliações
- Form 709 United States Gift Tax ReturnDocumento5 páginasForm 709 United States Gift Tax ReturnBogdan PraščevićAinda não há avaliações
- Lewis Corporation Case 6-2 - Group 5Documento8 páginasLewis Corporation Case 6-2 - Group 5Om Prakash100% (1)
- eHMI tool download and install guideDocumento19 páginaseHMI tool download and install guideNam Vũ0% (1)
- Guia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFDocumento118 páginasGuia de Usuario GPS Spectra SP80 PDFAlbrichs BennettAinda não há avaliações
- Factors of Active Citizenship EducationDocumento2 páginasFactors of Active Citizenship EducationmauïAinda não há avaliações
- 3d Control Sphere Edge and Face StudyDocumento4 páginas3d Control Sphere Edge and Face Studydjbroussard100% (2)
- (123doc) - Chapter-24Documento6 páginas(123doc) - Chapter-24Pháp NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Ansible Playbook for BeginnersDocumento101 páginasAnsible Playbook for BeginnersFelix Andres Baquero Cubillos100% (1)
- British Universal Steel Columns and Beams PropertiesDocumento6 páginasBritish Universal Steel Columns and Beams PropertiesjagvishaAinda não há avaliações
- LEARNING ACTIVITY Sheet Math 7 q3 M 1Documento4 páginasLEARNING ACTIVITY Sheet Math 7 q3 M 1Mariel PastoleroAinda não há avaliações
- Certification Presently EnrolledDocumento15 páginasCertification Presently EnrolledMaymay AuauAinda não há avaliações
- Embryology-Nervous System DevelopmentDocumento157 páginasEmbryology-Nervous System DevelopmentGheavita Chandra DewiAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 14 Ergonomics Design: AND ProductDocumento24 páginasUnit 14 Ergonomics Design: AND ProductRämêşh KątúřiAinda não há avaliações
- AVR Instruction Set Addressing ModesDocumento4 páginasAVR Instruction Set Addressing ModesSundari Devi BodasinghAinda não há avaliações
- Composite Structures: A. Grimaldi, A. Sollo, M. Guida, F. MaruloDocumento15 páginasComposite Structures: A. Grimaldi, A. Sollo, M. Guida, F. MaruloSharan KharthikAinda não há avaliações
- Flexible Regression and Smoothing - Using GAMLSS in RDocumento572 páginasFlexible Regression and Smoothing - Using GAMLSS in RDavid50% (2)
- UD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GDocumento164 páginasUD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GMahmoud Mady100% (3)
- Eye Bags ReliefDocumento27 páginasEye Bags ReliefNatsu DragneelAinda não há avaliações