Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Proteins Question Package
Enviado por
api-2395370020 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
377 visualizações6 páginasTítulo original
proteins question package
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
377 visualizações6 páginasProteins Question Package
Enviado por
api-239537002Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 6
Biology 12
Protein Synthesis & Mutations Question Package
1. An error occurred when DNA was being transcribed to mRNA and the sixth nucleotide was left
out by accident on the mRNA strand.
a) What kind of genetic mutation is this? ________________________________
b) What is the result of this type of mutation?
2. An error occurred when DNA was being transcribed to mRNA. The original DNA sequence was
TAC GGA ACA and a G was placed in the sixth nucleotide position instead of an A. HINT: you
must convert the DNA sequence to a mRNA sequence in order to read the codon chart.
a) What kind of genetic mutation is this? _________________________________
b) What is the result of this type of mutation?
3. What happens when a nonsense mutation occurs in DNA?
4. Can an amino acid have more than one codon? Explain.
Biology 12
5. Can a codon have more than one amino acid? Explain.
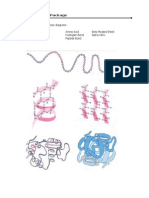
6. Add the following labels to the diagram below:
peptide bond, dipeptide, ribosome, incoming tRNA-amino acid complex, outgoing empty tRNA,
amino acid, anticodon, codon
7. List the steps involved in transcription?
Biology 12
8. Explain the 3 main steps involved in the translation of a protein. Use clear point form.
Step 1: ____________________________
Step 2: ____________________________
Step 3: ________________________
9. Complete the following chart:
Template
strand of DNA
TAC AAA TTT CGC ATT
mRNA (codons)
tRNA
(anticodons)
Amino acid
sequence
Biology 12
Protein Synthesis & Mutations Question Package Key
1. An error occurred when DNA was being transcribed to mRNA and the sixth nucleotide
was left out by accident on the mRNA strand.
a) What kind of genetic mutation is this? FRAMESHIFT DELETION
b) What is the result of this type of mutation?
A completely non-functional protein because the sequence of codons is changed
and no longer is the correct set of instructions for the original protein being
made.
2. An error occurred when DNA was being transcribed to mRNA. The original DNA sequence
was TAC GGA ACA and a G was placed in the sixth nucleotide position instead of an A.
a) What kind of genetic mutation is this? POINT MUTATION
b) What is the result of this type of mutation?
DNA TAC GGG etc
mRNA AUG CCC instead of AUG CCU, but CCU and CCC both code for
Proline, so this is a SILENT MUTATION
3. What happens when a nonsense mutation occurs in DNA?
- A nonsense mutation is when a codon is changed to a stop codon and protein
synthesis stops before the protein is completed
4. Can an amino acid have more than one codon? Explain.
Yes. According to the table there are multiple codons for some amino acids.
E.g. AGA and AGG both code for arginine
E.g. CCU, CUC, CUA, CUG all code for leucine
** The only amino acid which has one codon is methionine (start codon)
Biology 12
5. Can a codon have more than one amino acid? Explain.
NO. Every codon codes for one and only one amino acid, or STOP codon.
6. Add the following labels to the diagram below:
peptide bond, dipeptide, ribosome, incoming tRNA-amino acid complex, outgoing empty tRNA,
amino acid, anticodon, codon
7. List the steps involved in transcription.
RNA polymerase identifies the TATA box (promoter site) on the DNA and unwinds a section
of the DNA
Free floating complementary RNA nucleotides bond with one strand of the open section of
DNA until the RNA polymerase reaches the termination site (end of the gene)
mRNA breaks free of the DNA and travels out to the cytoplasm
8. Explain the 3 main steps involved in the translation of a protein. Use clear point form.
Step 1: Initiation
A small ribosomal subunit attaches to the mRNA molecule at the site of
the start codon (AUG).
The first tRNA pairs with the start codon.
Then a large ribosomal subunit joins to the small subunit to form a
functional ribosome.
Biology 12
Step 2: Elongation
The polypeptide chain lengthens one amino acid at a time.
An incoming tRNA-amino acid complex bonds to its matching codon on
mRNA
The amino acid carried by the first tRNA-amino acid complex is passed to
the amino acid of the incoming tRNA and forms a peptide bond creating
the beginning of a polypeptide chain.
The empty tRNA then detaches off of the mRNA and goes back into the
cytoplasm to pick up another amino acid.
This process repeats over and over.
Step 3: Termination
The polypeptide chain continues to grow until a STOP or termination
codon is reached on the mRNA.
Instead of carrying an amino acid, the tRNA with the correct anitcodon for
the STOP codon on mRNA carries a release factor which cuts the
polypeptide chain from the last tRNA.
The ribosome and mRNA then break apart and are recycled until another
protein is needed.
9. Complete the following chart:
Template
strand of DNA
TAC AAA TTT CGC ATT
mRNA (codons) AUG UUU AAA GCG UAA
tRNA
(anticodons)
UAC AAA UUU CGC AUU
Amino acid
sequence
Methionine Phenyl Alanine Lysine Alanine -
Stop
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Devlin Biochemistry With Clinical CorrelationsDocumento1.241 páginasDevlin Biochemistry With Clinical CorrelationsJorge100% (5)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Csir Life Sciences Fresh Instant NotesDocumento4 páginasCsir Life Sciences Fresh Instant NotesAlps Ana33% (3)
- PRP Slide PresentationDocumento29 páginasPRP Slide Presentationtricia isabella100% (2)
- Problem Set 1Documento4 páginasProblem Set 1annon55555Ainda não há avaliações
- Introductory Human Physiology DUKE UNIVERSITYDocumento15 páginasIntroductory Human Physiology DUKE UNIVERSITYMagdalena Misirlou Aliaj QirkoAinda não há avaliações
- Penn Foster Biology ExaminatonDocumento4 páginasPenn Foster Biology ExaminatonRobert KikahAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleic Acid Question Package Without Dna RnaDocumento1 páginaNucleic Acid Question Package Without Dna Rnaapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Protein Synthesis - StudentDocumento7 páginasProtein Synthesis - Studentapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab - Extracting Dna From StrawberriesDocumento4 páginasLab - Extracting Dna From Strawberriesapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Protein Review PackageDocumento2 páginasProtein Review Packageapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Inquiry Project RubricDocumento2 páginasInquiry Project Rubricapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- The Nervous System Notes For InquiryDocumento11 páginasThe Nervous System Notes For Inquiryapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 3a The Respiratory SystemDocumento11 páginasUnit 3a The Respiratory Systemapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Inquiry QuestionDocumento1 páginaInquiry Questionapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Checklist For Evaluating Internet SourcesDocumento1 páginaChecklist For Evaluating Internet Sourcesapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System Reveiw QuestionsDocumento4 páginasRespiratory System Reveiw Questionsapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Part 1 Enzyme Lock and Key ModelDocumento2 páginasPart 1 Enzyme Lock and Key Modelapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Kidney LabDocumento5 páginasKidney Labapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Carbohydrates Lipids Question PackageDocumento2 páginasCarbohydrates Lipids Question Packageapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- l3 Biological Molecules - Without DnaDocumento16 páginasl3 Biological Molecules - Without Dnaapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Dna Dna ReplicationDocumento10 páginasDna Dna Replicationapi-239537002Ainda não há avaliações
- Genetic Variation in Drug Disposition: Balmukunda Regmi and Laxman BharatiDocumento11 páginasGenetic Variation in Drug Disposition: Balmukunda Regmi and Laxman BharatiAnsiSilambiAinda não há avaliações
- PmCherry-C1 Vector InformationDocumento3 páginasPmCherry-C1 Vector InformationrsmbgssAinda não há avaliações
- tp53 Concept MapDocumento1 páginatp53 Concept Mapapi-449993710Ainda não há avaliações
- DPP 1 Cell BiologyDocumento2 páginasDPP 1 Cell Biology1149 Vanshika BAinda não há avaliações
- AP Biology Course at A Glance 0Documento3 páginasAP Biology Course at A Glance 0Omar SaiedAinda não há avaliações
- Development of Cell Theory Robert HookeDocumento3 páginasDevelopment of Cell Theory Robert HookeKarmelle GabrielAinda não há avaliações
- Grupa 1Documento7 páginasGrupa 1nazwa użytkownikaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Biology1Documento4 páginasCell Biology1Ashlee TalentoAinda não há avaliações
- Santa Cruz Biotechnology ProtocolsDocumento18 páginasSanta Cruz Biotechnology ProtocolsserbusabinaAinda não há avaliações
- Vanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 15Th Edition Widmaier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento68 páginasVanders Human Physiology The Mechanisms of Body Function 15Th Edition Widmaier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFgadsmanoutfitqcs100% (4)
- Cellular RespirationDocumento18 páginasCellular RespirationConcepcion, Jemaelah P.Ainda não há avaliações
- Biology Olympiad Placement TestDocumento5 páginasBiology Olympiad Placement Testharry yangAinda não há avaliações
- Imaginarium - Class 9 - April - 2019Documento66 páginasImaginarium - Class 9 - April - 2019Kshitij Raj0% (1)
- Biochemistry Concepts and Connections 1st Edition Appling Solutions ManualDocumento7 páginasBiochemistry Concepts and Connections 1st Edition Appling Solutions Manualscarletwilliamnfz100% (32)
- v11 Biomodulacao Celular o Futuro Da DermatologiaDocumento8 páginasv11 Biomodulacao Celular o Futuro Da DermatologiaFabiana BAinda não há avaliações
- Science of Hyaluronic Acid Beyond Filling - Fibroblasts and Their Response To The Extracellular MatrixDocumento8 páginasScience of Hyaluronic Acid Beyond Filling - Fibroblasts and Their Response To The Extracellular MatrixAnonymous LnWIBo1GAinda não há avaliações
- Comparative Human Salivary and Plasma Proteomes: Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & MedicineDocumento8 páginasComparative Human Salivary and Plasma Proteomes: Critical Reviews in Oral Biology & MedicinerenattoAinda não há avaliações
- ProteomicsDocumento30 páginasProteomicsArjun D Law100% (2)
- PHD Credit Seminar 2 Punjab Agricultural University, LudhianaDocumento141 páginasPHD Credit Seminar 2 Punjab Agricultural University, LudhianaSUSHANT DHARAinda não há avaliações
- From Twiggy To Tubby:: The Progression of Insulin Resistance and Type II DiabetesDocumento9 páginasFrom Twiggy To Tubby:: The Progression of Insulin Resistance and Type II DiabetesMelissa RivasAinda não há avaliações
- Proteins: Their Biological Functions and Primary StructureDocumento59 páginasProteins: Their Biological Functions and Primary StructureIsha BhartiAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map For Animal CellDocumento5 páginasConcept Map For Animal CellJennifer Pangilinan67% (3)
- 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocumento12 páginas3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsPrince TeodocioAinda não há avaliações
- Application of Tissue EngineeringDocumento3 páginasApplication of Tissue Engineeringtahomag44Ainda não há avaliações