Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Answer The Charles Darrin Packet
Enviado por
Nicholas CoxDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Answer The Charles Darrin Packet
Enviado por
Nicholas CoxDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chapter 16 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
247
Darwins Theory
of Evolution
Evolution
Q: What is natural selection?
16.1 What
patterns of
biodiversity did
Darwin observe
aboard the Beagle?
WHAT I KNOW
SAMPLE ANSWER: On each island
that Darwin visited, he saw
different species of plants and
animals.
WHAT I LEARNED
SAMPLE ANSWER: Darwin noticed
that different, yet similar,
species inhabited separated,
but similar, habitats around
the globe. Also, different, yet
related, species often occupied
different habitats within a
local area.
16.2 How did
other scientists
work help Darwin
develop his theory
of natural selection?
SAMPLE ANSWER: Other scientists
did research on how
organisms inherited different
traits.
SAMPLE ANSWER: Hutton and
Lyell concluded that Earth is
extremely old. Lamarck
suggested that species are
not fixed. Malthus reasoned
larger populations would
deplete resources.
16.3 What is
Darwins theory of
evolution by natural
selection?
SAMPLE ANSWER: Organisms that
are best adapted to their
environment survive longer
and have more offspring.
SAMPLE ANSWER: Natural
selection is the process by
which organisms with
variations most suited to their
local environment survive and
leave more offspring. Over
time, beneficial traits
accumulate in a population.
16.4 What are
the main lines of
scientific evidence
that support
Darwins theory of
evolution by natural
selection?
SAMPLE ANSWER: Fossils show
how organisms have changed
over time.
SAMPLE ANSWER: Biogeography,
fossils, homologous structures,
similarities in embryological
development, the universal
genetic code, homologous
molecules, and field studies
provide evidence of evolution.
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.1 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
248
16.1 Darwins Voyage of Discovery
Lesson Objectives
State Charles Darwins contribution to science.
Describe the three patterns of biodiversity noted by Darwin.
Lesson Summary
Darwins Epic Journey Darwin developed a scientific theory to explain how evolution, or
change over time, occurs in living things. Darwins theory explains how modern organisms
have evolved over long periods of time through descent from common ancestors.
Observations Aboard the Beagle During his five-year trip on the Beagle, Darwin
made many observations and collected a great deal of evidence.
He noticed that many different, yet ecologically similar, animal and plant species
occupied different, yet ecologically similar, habitats around the globe.
On the Galpagos Islands, Darwin noticed that the traits of many organismssuch as
the shell shapes of tortoisesvaried from island to island. He noticed that different, yet
related, animal and plant species occupied different habitats within a local area.
Darwin collected fossils, the preserved remains of ancient organisms. He noticed that
some fossils of extinct species resembled living species.
Darwins findings led him to think that species are not fixed and that they could change by
some natural process.
Darwins Epic Journey
1. On the map below, (1) find and label the Galpagos Islands (2)
circle the names of three large land masses Darwin did not visit on his voyage.
North
America
Atlantic
British
Isles
Europe
Asia
Ocean Pacific
Ocean
Galapagos
Darwins
voyage
South
America
Rheas
Cape
Horn
Africa
Ostriches
Cape of
Good Hope
Australia
Emus
N
W E
Indian
S
Ocean
New
Zealand
0 2000 km
0 1000 mi
Antarctica
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.1 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
249
For Questions 24, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words. Refer to
the map on the previous page as needed.
2. Darwin spent most of his time exploring the continent of
South America
; he did not
visit
North America
,
Asia
, or
Antarctica
.
3. During Darwins time, geologists were suggesting that Earth was
ancient
and
changed over time
.
4. Darwins work offers insight into the living world by showing organisms are constantly
changing or evolving
.
Observations Aboard the Beagle
Use the drawings of the tortoises to answer Questions 5 and 6.
Isabela Island tortoise Hood Island tortoise
5. What important information about the Galpagos Islands tortoises did Darwin learn?
Darwin learned that the shell shape of a tortoise could be used to identify the island
it inhabited.
6. Given its body structure, which tortoise above would require a habitat where food is
easy to reach?
Because the Isabela Island tortoise has a short neck that restricts the movement of its
head, it would require a habitat where food is easy to reach.
Use the map on the previous page to answer Questions 7 and 8.
7. On the map, place the labels Rheas, Emus, and Ostriches on the continents where they
are found. Why were the similarities among rheas, ostriches, and emus surprising to
Darwin? It was surprising because these different birds lived so far away from each
other.
8. Why might Darwin come to think that the finches of the Galpagos Islands might be related
to the finches of South America, despite how different the birds were in appearance?
The islands are very close to the coast of South America and so the birds may have
migrated from there.
9. Darwin observed that the birds he would eventually discover were finches had differently
shaped beaks. What might this suggest about the eating habits of the birds? Explain.
Because birds use their beaks to eat or capture food, differently shaped beaks might
mean that the birds lived on different diets.
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.1 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
250
10. What did the similarities between fossil animals and modern animals, like the glyptodont
and armadillo, suggest to Darwin?
The similarities suggested to Darwin that the modern species may be related to the
extinct fossil species.
11. Complete the graphic organizer by listing three ways that species vary. For each pattern
of biodiversity, list an example that Darwin observed.
vary
an example of which is an example of which is an example of which is
12. When Darwin returned to England, he learned that the small brown birds he observed on
the Galpagos Islands were all finches. They resembled South American finches. What
hypothesis does this observation support?
The birds are descended from South American ancestors that traveled to the
Galpagos Islands. The species have changed over time as they adapted to particular
niches on each island.
Glyptodonts
and armadillos
Rheas and
ostriches
Galpagos
tortoises
Loc ally Globally Over Time
Species
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.2 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
251
16.2 Ideas That Shaped Darwins Thinking
Lesson Objectives
Identify the conclusions drawn by Hutton and Lyell about Earths history.
Describe Lamarcks hypothesis of evolution.
Describe Malthuss view of population growth.
Explain the role of inherited variation in artificial selection.
Lesson Summary
An Ancient, Changing Earth In Darwins day, most Europeans believed that Earth and
all its life forms were only a few thousand years old and had not changed very much in that
time. Several scientists who lived around the same time as Darwin began to challenge these
ideas. These scientists had an important influence on the development of Darwins theory of
evolution.
Geologists James Hutton and Charles Lyell argued that Earth is many millions of
years old.
They also argued that the processes changing Earth today, like volcanism and erosion, are
the same ones that changed Earth in the past.
Knowing that Earth could change over time helped Darwin realize that species might change
as well. Knowing that Earth was very old convinced Darwin that there had been enough
time for life to evolve.
Lamarcks Evolutionary Hypothesis Jean-Baptiste Lamarck was one of the first scien-
tists to propose hypotheses about how evolution occurred.
To explain evolution, Lamarck hypothesized that all organisms have an inborn drive to
become more complex and perfect. According to Lamarck, an organism could gain or lose
traits during its lifetime by using or not using certain organs.
Lamarck also hypothesized that acquired characteristics could be passed on to an
organisms offspring leading to evolution of the species.
Scientists now know that most of Lamarcks ideas about evolution are incorrect.
However, he correctly suggested that life is not fixed and was the first to offer a natural
and scientific explanation for evolution. Further, he recognized that an organisms traits
are linked to its environment.
Population Growth Thomas Malthus thought that if the human population continued to
grow unchecked, it would run out of living space and food. Darwin realized that this was
true of all organisms, not just humans.
Artificial Selection Plant and animal breeders in Darwins time used a process now known
as artificial selection to improve their crops and livestock. In artificial selection, nature
provides the variations, and humans select those they find desirable. Darwin experimented
with artificial selection. The results from his experiments indicated natural variation was very
important because it provided the raw material for evolution.
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.2 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
252
An Ancient, Changing Earth
1. In what two ways did an understanding of geology influence Darwin?
Knowing that Earth could change over time helped Darwin believe that life might
change as well. Knowing that Earth was very old assured Darwin that there had been
enough time for life to change.
For Questions 25, write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the
underlined word or words to make the statement true.
older
slowly
the same as
True
2. Hutton realized that Earth was much younger than previously
believed.
3. Lyell thought most geological processes operated extremely quickly.
4. The processes that changed Earth in the past are different from the
processes that operate in the present.
5. Lyells work explained how large geological features could be built
up or torn down over long periods of time.
Lamarcks Evolutionary Hypotheses
6. How did Lamarck propose that species change over time?
Lamarck proposed that by selective use or nonuse of organs, organisms acquired or
lost certain traits during their lifetime. These traits could then be passed on to their
offspring. Over time, this process led to change in a species.
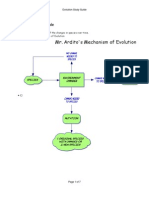
Use the diagram to answer Questions 78.
1.
2.
7. According to Lamarcks hypothesis, what occurs
3.
between steps 2 and 3 in the diagram above to
make the crabs claw grow larger?
The crab selectively uses its left claw more. This
increased use causes the claw to grow in size.
8. Which step in the diagram above shows the inheritance of acquired traits as proposed
by Lamarck?
Step 3 shows the inheritance of acquired traits by the young.
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.2 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
253
9. How did Lamarck pave the way for the work of later biologists?
Lamarck was one of the first to develop scientific hypotheses about evolution and to
realize that organisms change over time.
10. Which of Lamarcks ideas turned out to be true? Which turned out to be false?
Lamarcks ideas that evolution occurs and that an organisms traits are linked to its
environment are true. Lamarcks idea that acquired characteristics can be inherited is
false. Also, Lamarcks idea that species have an inborn drive to become more complex
and perfect is false.
11. How would Lamarck have explained the length of a giraffes neck?
A giraffe could have acquired a long neck because it began to stretch its neck upward
to reach higher and higher on trees looking for leaves to eat. As the giraffe stretched
toward leaves on higher branches, its neck would grow a little longer. Giraffes could
then pass on their long neck to their offspring who could further lengthen their necks
during their lifetimes.
Population Growth
For Questions 1214, write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left.
A
12. Which observation caused Thomas Malthus to form his theory about population
growth?
A. Human birth rate was higher than the death rate.
B. War caused the death of thousands of people.
C. Famines were common in England in the 1800s.
D. The offspring of most species survived into adulthood.
D
13. Which of the following is an idea attributed to Malthus?
A. As a population decreases in size, warfare and famine become
more common.
B. As a population increases in size, the percentage of offspring that survive
also increases.
C. If the human population grew unchecked, its rate of evolution would increase
geometrically.
D. If the human population grew unchecked, there wouldnt be enough living
space and food for everyone.
C
14. Malthuss ideas led Darwin to conclude that
A. Earth is much older than previously thought.
B. the size of the human population can grow indefinitely.
C. many more organisms are born than will survive and reproduce.
D. organisms are able to evolve through a process known as
artificial selection.
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.2 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
254
Articial Selection
15. How do humans affect artificial selection? What role does nature play?
Darwin stated that nature provides the variation among organisms, and humans
select and breed for the variations they find useful or appealing.
16. What is another name for artificial selection?
selective breeding
17. Describe how you could use artificial selection to breed pigeons with large beaks.
Find pigeons that naturally have larger than normal beaks. Mate these pigeons.
Repeat this process over several generations until you achieve the desired beak size.
18. Complete the table about scientists who contributed to the development of the theory of
evolution.
Scientists Who Contributed to Darwins Theory of Evolution
Scientist Contribution to Darwins Theory
James Hutton Hutton argued that Earth is many millions of years old. Knowing
that Earth was very old convinced Darwin that there had been
enough time for life to evolve.
Charles Lyell Lyell argued that the processes that changed Earth in the past
were the same as the processes that are still changing Earth in
the present. Knowing that Earth could change over time helped
Darwin realize that life might change as well.
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck Lamarck was one of the first scientists to recognize that evolution
has occurred and that organisms change to live more success-
fully in their environment. His general ideas about evolution and
adaptation influenced Darwin.
Thomas Malthus Malthus thought that if the human population continued to grow
unchecked, it would run out of living space and food. Darwin
realized that this was true of all organisms, not just humans.
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.3 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
255
16.3 Darwin Presents His Case
Lesson Objectives
Describe the conditions under which natural selection occurs.
Explain the principle of common descent.
Lesson Summary
Evolution by Natural Selection Darwin published On the Origin of Species in 1859.
In the book, Darwin describes and provides evidence for his explanation of how
evolution occurs. He called this process natural selection because of its similarities to
artificial selection. Darwins theory of evolution by natural selection can be summed up
as follows:
More offspring are produced than can survive to reproduce. There is competition for
limited resources, or a struggle for existence.
Individuals exhibit variation in their traits and some of these differences can be passed on
to their offspring.
Inherited traits that increase an organisms ability to survive and reproduce are called
Differences among adaptations affect an individuals fitnessthe ability to survive and
reproduce in a specific environment.
Only the fittest organisms live to reproduce and pass on their adaptive traits to offspring.
This is known as the survival of the fittest.
From generation to generation, populations continue to evolve as they become better
adapted, or as their environment changes.
Common Descent Darwin argued that all species are descended, with modification, from
common ancestors. Through descent with modification, all organismsliving and extinct
are linked on a single tree of life.
Evolution by Natural Selection
1. What does the phrase struggle for existence mean?
It means that members of a population compete regularly to obtain food, living
space, and other necessities of life.
2. Why is camouflage considered an adaptation?
Camouflage is a heritable trait that can help an organism avoid predation and
thereby increases the chances of its survival.
3. How does an animals level of fitness relate to its chances of survival and reproduction?
The higher an animals level of fitness in its particular environment, the better its
chances for survival and reproduction.
adaptations
.
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.3 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
256
For Questions 46, write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the
underlined word or words to make the statement true.
inherited
True
fitness
4. Natural selection acts on acquired traits.
5. Any inherited characteristic that increases an organisms chance
of survival is considered an adaptation.
6. Natural selection is the ability of an individual to survive and
reproduce in its specific environment.
7. Below is a partially completed flowchart that models how natural selection drives
evolution. The missing steps are listed below, out of order, and lettered AD. Write
the letter of the missing step in a blank box in the flowchart.
A. Adaptations are passed on to the next generation.
B. The accumulation of adaptations may lead to the evolution of a new species.
C. These offspring have few or no offspring of their own.
D. Some offspring inherit traits that increase fitness (adaptations).
Individuals in a population have many
variations.
Some offspring inherit traits that decrease
fitness.
D
C
A
Over time, adaptations accumulate in a
population.
B
Name Class Date
Lesson 16.3 Workbook A Copyright by Pearson Education, Inc., or its afliates. All Rights Reserved.
257
Common Descent
For Questions 813, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words.
8. Natural selection depends on the ability of organisms to
leave descendants.
reproduce
, which means to
9. Every organism alive
today reproduced.
descended
from ancestors who survived and
10. Over many generations, adaptation could cause successful species
to new species.
11. Common descent suggests that all species, living and extinct, are
evolve
related
.
into
12. The principle that living species descend, with changes, from other species over time
is
referred to as
descent with modification
.
13. The
fossil record
provides physical evidence of descent with modification over long
periods of time.
14. In the three boxes on the left, draw an example of natural selection that might occur in a
population of frogs. Then, on the lines at right, describe each stage.
SAMPLE ANSWER: A population of frogs has a large number
of offspring. Only a small fraction of these offspring will
survive.
SAMPLE ANSWER: In this population of frogs, heritable
variation includes short tongues and long tongues. Long
tongues are an adaptation: The frogs with long tongues
are able to catch more flies than frogs with short tongues.
Long-tongued frogs eat more and so survive and reproduce
more often than short-tongued frogs do.
SAMPLE ANSWER: Long-tongued frogs become more common
than short-tongued frogs in this population over time
because (1) more frogs are born than can survive,
(2) individuals vary in tongue-length and tongue-length
is a heritable trait, and (3) long-tongued individuals
have higher fitness in this particular environment.
Name Class Date
V
a
r
i
a
t
i
o
n
a
n
d
A
d
a
p
t
i
o
n
/
S
u
r
v
i
v
a
l
o
f
t
h
e
F
i
t
t
e
s
t
T
h
e
S
t
r
u
g
g
l
e
f
o
r
E
x
i
s
t
e
n
c
e
N
a
t
u
r
a
l
S
e
l
e
c
t
i
o
n
Você também pode gostar
- Chapter 12 Homeostasis - Lecture NotesDocumento6 páginasChapter 12 Homeostasis - Lecture Notesapi-3728508100% (3)
- Natural Selection Lesson ElementDocumento11 páginasNatural Selection Lesson ElementAbir OmarAinda não há avaliações
- Examining Plant and Animal Cells LabDocumento2 páginasExamining Plant and Animal Cells LabAhsan AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- AP Psych CH 2 Study Guide-Myers 8th EditionDocumento7 páginasAP Psych CH 2 Study Guide-Myers 8th Editionlcbell92Ainda não há avaliações
- Pedigree Chart WorksheetDocumento72 páginasPedigree Chart Worksheetapi-3075658820% (1)
- Genetics Chapter 2 - ProProfs QuizDocumento9 páginasGenetics Chapter 2 - ProProfs QuizlifecostAinda não há avaliações
- Pogil Photosynthesis and Respiration-SDocumento6 páginasPogil Photosynthesis and Respiration-Sapi-2623786400% (1)
- BLANK Biology EOC - Review - Packet by StandardDocumento14 páginasBLANK Biology EOC - Review - Packet by StandardmspallardAinda não há avaliações
- Mitosis: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase TelophaseDocumento5 páginasMitosis: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase TelophaseJohn0% (1)
- Evidence For Evolution Foldable Use This OneDocumento9 páginasEvidence For Evolution Foldable Use This Oneapi-271661638Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 Plant System NotesDocumento2 páginas1 Plant System NotesAdeyemi AdamsAinda não há avaliações
- Evolution - Part 1Documento29 páginasEvolution - Part 1Wei Zhang100% (1)
- Evolution Study GuideDocumento7 páginasEvolution Study Guidegmanb5100% (3)
- Experimental Design POGIL 2013Documento3 páginasExperimental Design POGIL 2013Steffi Basnet0% (1)
- Dyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry PaperworkDocumento7 páginasDyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry Paperworkapi-250608665Ainda não há avaliações
- Biology 11 Wolkow PDFDocumento653 páginasBiology 11 Wolkow PDFمنیر سادات100% (7)
- Chapter 13 Nervous System in Mammals - Worksheet (Answers)Documento2 páginasChapter 13 Nervous System in Mammals - Worksheet (Answers)api-3728508100% (2)
- Ocean ActivitesDocumento7 páginasOcean ActivitesritakeskitaloAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Pearson HL Chapter 3 AnswersDocumento4 páginasBio Pearson HL Chapter 3 AnswersKunakorn KunthamasAinda não há avaliações
- Mitosis and Meiosis WorksheetsDocumento3 páginasMitosis and Meiosis WorksheetsVinson Eric50% (2)
- University of Phoenix Material: Biological Psychology Worksheet PSY/340Documento3 páginasUniversity of Phoenix Material: Biological Psychology Worksheet PSY/340Jarra37100% (2)
- Evolution Study Guide Answer Key - Verona School DistrictDocumento21 páginasEvolution Study Guide Answer Key - Verona School DistrictEfimios Neos100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Thinking Critically With Psychological Science, Myers 8e PsychologyDocumento26 páginasChapter 1 Thinking Critically With Psychological Science, Myers 8e Psychologymrchubs100% (7)
- Psychology Chapter 11Documento3 páginasPsychology Chapter 11cardenass100% (4)
- Biology WorkbookDocumento193 páginasBiology Workbookabisantiago6131100% (4)
- 4 Membrane Structure-SDocumento6 páginas4 Membrane Structure-SjulitaaaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell and Cell TheoryDocumento13 páginasCell and Cell TheoryAnaJeanJumawidMaranan100% (1)
- How Do Genes Affect AddictionDocumento7 páginasHow Do Genes Affect AddictionIvy Maril De GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Guided Notes-Teacher LectureDocumento8 páginasGuided Notes-Teacher Lectureapi-417232384Ainda não há avaliações
- Dehydration Synthesis SEDocumento5 páginasDehydration Synthesis SEsaianuj0% (3)
- The Nervous System: The Central Processing UnitDocumento85 páginasThe Nervous System: The Central Processing UnitGeoffrey MilesAinda não há avaliações
- Mitosis and Meiosis WebquestDocumento3 páginasMitosis and Meiosis Webquestapi-3156932390% (1)
- Diffusion WorksheetDocumento1 páginaDiffusion Worksheetsandsphilip0% (1)
- Experiments For IB Psychology SLDocumento23 páginasExperiments For IB Psychology SLHilda HiongAinda não há avaliações
- Answering Exam Questions On CellsDocumento4 páginasAnswering Exam Questions On CellsTamicka Bonnick100% (1)
- Enzymes Virtual LabDocumento4 páginasEnzymes Virtual Labapi-34000547527% (11)
- Bio Module 1 WorksheetsDocumento11 páginasBio Module 1 WorksheetsKevin100% (2)
- Biology Chapter 1 Notes (Grade 11)Documento4 páginasBiology Chapter 1 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (11)
- IB Psychology HL Biological LOADocumento11 páginasIB Psychology HL Biological LOAgfore3Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 Scientific Inquiry-S PDFDocumento6 páginas2 Scientific Inquiry-S PDFDonna N0% (1)
- Abo Blood Type Worksheet 0Documento2 páginasAbo Blood Type Worksheet 0api-233187566Ainda não há avaliações
- 6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesDocumento82 páginas6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesEvangelene Esquillo SanaAinda não há avaliações
- 18 Notes Introduction To Ecology PDFDocumento14 páginas18 Notes Introduction To Ecology PDFAnonymous STRYVGKAinda não há avaliações
- IB Biology Cells 2010Documento13 páginasIB Biology Cells 2010tr4l100% (1)
- North Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideDocumento38 páginasNorth Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideRaquel Galdamez-GaldamezAinda não há avaliações
- LAB - Meiosis ModelingDocumento7 páginasLAB - Meiosis ModelingDaniel CondreayAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrient Cycle WorksheetDocumento8 páginasNutrient Cycle Worksheetapi-2348912390% (1)
- IB Biology Assessment Statements - DrawDocumento33 páginasIB Biology Assessment Statements - DrawSchuyler Huff100% (1)
- Sbi3u Unit Plan Wolinski: Download NowDocumento5 páginasSbi3u Unit Plan Wolinski: Download NowAbhishek SainiAinda não há avaliações
- 16.1 PowerpointDocumento15 páginas16.1 PowerpointMcpsed McpsAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 - The Theory of EvolutionDocumento35 páginasChapter 10 - The Theory of EvolutionmaleskunAinda não há avaliações
- 16.1 Darwin's Voyage of DiscoveryDocumento3 páginas16.1 Darwin's Voyage of DiscoveryAbdul Mohti ShahineAinda não há avaliações
- Bio 1 Ck12-EvolutionDocumento3 páginasBio 1 Ck12-Evolutionirfan khuhroAinda não há avaliações
- CH 15 WorkbookDocumento10 páginasCH 15 Workbookapi-237586441100% (1)
- B 10 VRV 5161Documento21 páginasB 10 VRV 5161Reaper-sanAinda não há avaliações
- Name: - Section: - ScoreDocumento4 páginasName: - Section: - ScoreHonleth Jheney MamarilAinda não há avaliações
- B 10 VRV 5161Documento21 páginasB 10 VRV 5161api-283593849Ainda não há avaliações
- Biological EvolutionDocumento54 páginasBiological EvolutionMa. Krizia Tiny ParconAinda não há avaliações
- Research On Dog Behaviour at Max Planch InstituteDocumento3 páginasResearch On Dog Behaviour at Max Planch InstituteChristopher MendezAinda não há avaliações
- Ruth Garrett Millikan Varieties of Meaning The 2002 Jean Nicod Lectures 2004Documento255 páginasRuth Garrett Millikan Varieties of Meaning The 2002 Jean Nicod Lectures 2004legeh5781100% (3)
- PBOT111 - Topic 1 Basic Concepts To Understand Plants Part 1Documento42 páginasPBOT111 - Topic 1 Basic Concepts To Understand Plants Part 1Kath Del FinAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis Statement Evolution Vs CreationDocumento8 páginasThesis Statement Evolution Vs Creationafkodpexy100% (2)
- Outdoor Education: Beating The Effects of Techno-Immersion in An Over-Urbanised EnvironmentDocumento13 páginasOutdoor Education: Beating The Effects of Techno-Immersion in An Over-Urbanised EnvironmentGunter SwobodaAinda não há avaliações
- Species ConceptsDocumento33 páginasSpecies ConceptsBlexx LagrimasAinda não há avaliações
- Recent Advances in Understanding StreptomycesDocumento16 páginasRecent Advances in Understanding StreptomycesPushpendra ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- ch.01 - Introduction To Ecology - PDFDocumento10 páginasch.01 - Introduction To Ecology - PDFKaiAinda não há avaliações
- Designing Social InquiryDocumento259 páginasDesigning Social InquiryBruno CrasnekAinda não há avaliações
- CASScheduler - SPECIAL PROBLEM PDFDocumento155 páginasCASScheduler - SPECIAL PROBLEM PDFLorena TeofiloAinda não há avaliações
- Anthropological PerspectiveDocumento14 páginasAnthropological PerspectiveGerundio, Jean Liven H.Ainda não há avaliações
- Enviromental Science Lesson 1Documento43 páginasEnviromental Science Lesson 1Willer Jay Rosas BersabaAinda não há avaliações
- ZenetosDocumento43 páginasZenetosKalliopyKavouraAinda não há avaliações
- LeaP-Science-G10-Week 5-Q3Documento4 páginasLeaP-Science-G10-Week 5-Q3Eunice Kathleen M. JavelosaAinda não há avaliações
- Architects of Light Manual - TextDocumento41 páginasArchitects of Light Manual - TextStephen J. Roberts75% (4)
- Ian Roxborough - Theories of Underdevelopment (1981)Documento182 páginasIan Roxborough - Theories of Underdevelopment (1981)Barna BoseAinda não há avaliações
- CIEF S 13 00234 Mulawarman KamayantiDocumento41 páginasCIEF S 13 00234 Mulawarman KamayantiRusman SEAinda não há avaliações
- History of BiologyDocumento2 páginasHistory of BiologyyoyoyoiAinda não há avaliações
- Scientific American 1993-2013 Article IndexDocumento147 páginasScientific American 1993-2013 Article IndexamlferreiraAinda não há avaliações
- Hermann Joseph Muller: 1967) by G. PontecorvoDocumento10 páginasHermann Joseph Muller: 1967) by G. PontecorvoKeny Ruslan MowilosAinda não há avaliações
- Human Evolution and Development: Nico M. Van Straalen and Dick RoelofsDocumento297 páginasHuman Evolution and Development: Nico M. Van Straalen and Dick RoelofsafrozqadeerAinda não há avaliações
- Vega-Redondo F. Evolution, Games, and Economic Behaviour (OUP, 1996) (ISBN 0198774737) (O) (222s) - GG - PDFDocumento222 páginasVega-Redondo F. Evolution, Games, and Economic Behaviour (OUP, 1996) (ISBN 0198774737) (O) (222s) - GG - PDFBabarKalamAinda não há avaliações
- CMRDocumento9 páginasCMRNakul Jain100% (1)
- Teoría Tradicional William Stead The ORIGIN and Erratic Spread of TuberculosisDocumento13 páginasTeoría Tradicional William Stead The ORIGIN and Erratic Spread of TuberculosisLucia ZatarainAinda não há avaliações
- Structure of Ethics ManagementDocumento5 páginasStructure of Ethics ManagementIulia T Popa100% (1)
- Mcat2015 ContentDocumento128 páginasMcat2015 ContentRon HardeoAinda não há avaliações
- Homo BiologicusDocumento3 páginasHomo BiologicusCarolina Roldán0% (1)
- Em 135 2007 03 PDFDocumento24 páginasEm 135 2007 03 PDFbzvsbhanAinda não há avaliações
- Living in The IT Era Exams and Quizzes Complete: By: Shaira AlmocedaDocumento11 páginasLiving in The IT Era Exams and Quizzes Complete: By: Shaira AlmocedaCarlo Aprado100% (1)
- Studentdatainterp Sexual-SelectionDocumento5 páginasStudentdatainterp Sexual-SelectionParnoor SinghAinda não há avaliações