Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
2013 IntroductiontoPetroleumandNaturalGas New
Enviado por
Mgn San0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
26 visualizações36 páginasgas
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentogas
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
26 visualizações36 páginas2013 IntroductiontoPetroleumandNaturalGas New
Enviado por
Mgn Sangas
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPTX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 36
Exploring Oil & Gas
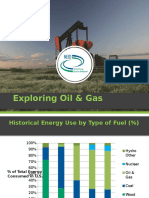
Historical Energy Use by Type of Fuel (%)
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
1850 1900 1950 2000 2010
% of Total
Energy
Consumed in
U.S.
Wood
Coal
Oil & Gas
Nuclear
Hydro
Other
Data: Energy Information Administration
Where are the fossils in Fossil Fuels?
Fossil fuels were forming before dinosaurs lived
Formation
Hydrocarbons
The NEED Project
Methane
The NEED Project
History of Oil
Edwin Drake and Henry Ford
History of Natural Gas
First U.S. Natural Gas Well
In 1821, William Hart dug the first natural gas well in Fredonia,
NY.
The NEED Project
Where are Oil and Gas found in the U.S.?
The NEED Project
Oil and gas are found on land and under
water
Sedimentary Rock and Petroleum Traps
Exploratio
n
Production Transport Refining
Chemical
Manufacturing
Uses
Oil and Gas Process
Exploration by Geologists
Seismic Technology
Land Water
Seabed Seismic
Visualization
The NEED Project
Core Samples
Exploration and Production by Drilling
The NEED Project
Drilling Process
Place the drill bit, collar, and drill pipe in the hole.
Attach the kelly and turntable and begin drilling.
As drilling progresses, circulate mud through the pipe
and out of the bit to float the rock cuttings out of the
hole.
Add new sections (joints) of drill pipes as the hole
gets deeper.
Remove (trip out) the drill pipe, collar and bit when the
preset depth (anywhere from a few hundred to a
couple thousand feet) is reached.
Parts of a Well
Horizontal Drilling and
Hydraulic Fracturing
Increased technology
allows us to retrieve
tight formations.
The drilling process is
similar, except for a
specialized bit that
allows for horizontal
drilling.
If oil and gas are
trapped, fracturing may
be used to allow liquids
to flow.
Production
Christmas Tree Horse Head Pump
Enhanced Oil Recovery
Oil Transport
Natural Gas Transport
The NEED Project
Refining of Petroleum
Fractionating Tower
What does a barrel of crude oil provide?
Note: A 42-U.S. gallon barrel
of crude oil yields about 45
gallons of petroleum
products.
Data: Energy Information Administration
Petroleum
Products
Data: Energy Information Administration
Petroleum Products
by Type, 2011
Gasoline 42.02%
Diesel / Heating Oil 26.99%
Other 14.36%
(asphalt, feedstock, paraffin)
Jet Fuel 8.80%
Refinery Fuel 4.11%
Liquefied Petroleum Gas 3.73%
Processing of Natural Gas
A natural gas compressor
Uses of Petroleum and Natural Gas
Data: Energy Information Administration
Residential,
2.48%
Commercial,
1.79%
Industrial,
20.39%
Transportation,
74.48%
Electric, 0.85%
Petroleum Consumption by Sector of the
Economy, 2011
Residential
38%
Commercial
10%
Industrial
26%
Transportation
2%
Electric
24%
Natural Gas Consumption by Sector
of the Economy, 2011
Summary of Oil and Natural Gas
Advantages
Widely available
Simple combustion
process can directly heat
or generate electricity
Inexpensive
Easily distributedgood
infrastructure in place
High energy content
Disadvantages
Nonrenewable
Greenhouse Gases(CO
2
)
Air pollution (byproducts
released during
combustion)
Price instability and costs
rising
Reliance upon imports
Environmental impacts
For More Information
The NEED Project
www.need.org
info@need.org
1-800-875-5029
Energy Information Administration
U.S. Department of Energy
www.eia.gov
The NEED Project
Você também pode gostar
- Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Study: Dr. AADocumento75 páginasHazard and Operability (HAZOP) Study: Dr. AAjoenediath9345100% (1)
- 2013 - IntroductiontoPetroleumandNaturalGas NewDocumento36 páginas2013 - IntroductiontoPetroleumandNaturalGas NewZynAbidinAinda não há avaliações
- Coalbed Methane As Unconventional GasDocumento32 páginasCoalbed Methane As Unconventional GasSuska AgustaAinda não há avaliações
- Efficient Ammonia Production: Jim Gosnell 13 October 2005 Hydrogen Conference Argonne National LaboratoryDocumento76 páginasEfficient Ammonia Production: Jim Gosnell 13 October 2005 Hydrogen Conference Argonne National LaboratoryPermata AdindaAinda não há avaliações
- Petroleum - Geology-Lecture 1 IntroductionDocumento32 páginasPetroleum - Geology-Lecture 1 IntroductionGoldenSun2012100% (2)
- Petroleum Geology - Lecture 1 08Documento34 páginasPetroleum Geology - Lecture 1 08adlisrodAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To HydrocarbonDocumento89 páginasIntroduction To Hydrocarbongege-mzAinda não há avaliações
- Shale Gas 2016 - FinalDocumento33 páginasShale Gas 2016 - FinalNandani SudamaAinda não há avaliações
- OIL & GAS: Qa/QcDocumento20 páginasOIL & GAS: Qa/QcSurjit DuttaAinda não há avaliações
- Gas - To - Liquid Technologies: Recent Advances, Economics, ProspectsDocumento36 páginasGas - To - Liquid Technologies: Recent Advances, Economics, ProspectsMohamad TarmiziAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Oil Sands and Sustainable DevelopmentDocumento36 páginasEnergy Oil Sands and Sustainable Developmentkamranonline999Ainda não há avaliações
- Oil and Gas IndustryDocumento23 páginasOil and Gas IndustryJoshwin JacobAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Nonrenewable EnergyDocumento56 páginas10 Nonrenewable Energyabbicox.stlAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction of Petroleum Industry - PdkhanhDocumento49 páginasIntroduction of Petroleum Industry - PdkhanhNguyễnBìnhPhương100% (1)
- Petroleum Refining Engineering: Dr. TVN. Padmesh Week 2Documento57 páginasPetroleum Refining Engineering: Dr. TVN. Padmesh Week 2Saswiny RitchieAinda não há avaliações
- Eric K. Albert, PHD: and Some of The Career Opportunities Created by The IndustryDocumento39 páginasEric K. Albert, PHD: and Some of The Career Opportunities Created by The IndustryAnonymous kbPP3CCcAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4 Air, Gas, Mist DrillingDocumento82 páginasLesson 4 Air, Gas, Mist DrillingSerkan CenberlitasAinda não há avaliações
- OIL and GAS IntroductionDocumento28 páginasOIL and GAS IntroductionShaliniIlavarapuAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 27 SolutionDocumento11 páginasUnit 27 Solutionapi-3704862Ainda não há avaliações
- آبار النفط والغاز الطبيعيDocumento23 páginasآبار النفط والغاز الطبيعيASOMA .YAinda não há avaliações
- Konsep Energi Terbarukan Dan BiodieselDocumento311 páginasKonsep Energi Terbarukan Dan BiodieselFadhilah NurulhaqAinda não há avaliações
- Eagle Ford Fact Book FinalDocumento20 páginasEagle Ford Fact Book FinalKumaren MaruthamuthooAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Generation From Crude OilDocumento9 páginasEnergy Generation From Crude OilOgunsua AdewoleAinda não há avaliações
- © 2017, John R. Fanchi All Rights Reserved. No Part of This Manual May Be Reproduced in Any Form Without The Express Written Permission of The AuthorDocumento36 páginas© 2017, John R. Fanchi All Rights Reserved. No Part of This Manual May Be Reproduced in Any Form Without The Express Written Permission of The AuthorsifatAinda não há avaliações
- FrackingDocumento391 páginasFrackingVo HaianhAinda não há avaliações
- Opportunity Analysis For Recovering Energy From Industrial Waste Heat and EmissionsDocumento24 páginasOpportunity Analysis For Recovering Energy From Industrial Waste Heat and EmissionsAshish FandeAinda não há avaliações
- Apr Jun 2012Documento76 páginasApr Jun 2012suraj99s_99Ainda não há avaliações
- Oil Recovery (Oil Production) ProcessDocumento7 páginasOil Recovery (Oil Production) ProcessLathifa Rahma AstutiAinda não há avaliações
- Crude Oil Assay (Assignment 1) (FINAL)Documento12 páginasCrude Oil Assay (Assignment 1) (FINAL)Fabliha KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Petro Mo To - 2 PDFDocumento4 páginasPetro Mo To - 2 PDFMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Exploitation of Gas Hydrates As An Energy ResourceDocumento37 páginasExploitation of Gas Hydrates As An Energy ResourceaargovindAinda não há avaliações
- Nadeem - Performance Evaluation of An Industrial BoilerDocumento44 páginasNadeem - Performance Evaluation of An Industrial Boilervazzoleralex6884Ainda não há avaliações
- Ames Virosco NexantDocumento31 páginasAmes Virosco NexantAzizol WahabAinda não há avaliações
- Petroleum - Oil and Natural Gas: Skip To ContentDocumento3 páginasPetroleum - Oil and Natural Gas: Skip To ContentslawiAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Oil and Gas Industry1Documento35 páginasFundamentals of Oil and Gas Industry1Chandan Narang100% (1)
- Non Traditional Fuel Landfill Gas ProjectDocumento46 páginasNon Traditional Fuel Landfill Gas ProjectAnonymous fS6Znc9Ainda não há avaliações
- 444Documento81 páginas444sangeetha saraswathyAinda não há avaliações
- Canada Oil SandsDocumento21 páginasCanada Oil SandsdoombuggyAinda não há avaliações
- Coal and Liquid Fuels: Richard A. Bajura Edward M. EyringDocumento31 páginasCoal and Liquid Fuels: Richard A. Bajura Edward M. EyringSubhradeep MajumderAinda não há avaliações
- Coal GasificationDocumento72 páginasCoal GasificationguymailyAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Tech 2009 - Economical Option For CO2-Methane Separation in Produced Gas Containing A High CO2Documento12 páginasGas Tech 2009 - Economical Option For CO2-Methane Separation in Produced Gas Containing A High CO2Lim Eng SoonAinda não há avaliações
- TCT2 - TP 2 Library of Congress Oil Gas IndustryDocumento6 páginasTCT2 - TP 2 Library of Congress Oil Gas IndustryRomanAinda não há avaliações
- CL304 - Introduction SlidesDocumento56 páginasCL304 - Introduction Slidesshivurkolli07Ainda não há avaliações
- Inf Shail OilDocumento8 páginasInf Shail OilkonstantinovvAinda não há avaliações
- George Koperna's CO2-EOR Presentation MAR 2009Documento38 páginasGeorge Koperna's CO2-EOR Presentation MAR 2009Bill Christensen100% (1)
- Drilling Source Book - Jim ShortDocumento588 páginasDrilling Source Book - Jim Shortprem_1975Ainda não há avaliações
- Principle of Petroleum EngineeringDocumento33 páginasPrinciple of Petroleum EngineeringHemenMoAinda não há avaliações
- ZefinalDocumento14 páginasZefinalapi-194340850Ainda não há avaliações
- Xay Dung Nha May5-Dr Muhammad SaleemDocumento36 páginasXay Dung Nha May5-Dr Muhammad SaleemVăn Đại - BKHNAinda não há avaliações
- LNGDocumento52 páginasLNGRama Moorthy100% (6)
- Fuels & Combustion: Dr. Thangaraja JDocumento17 páginasFuels & Combustion: Dr. Thangaraja JsheenAinda não há avaliações
- Oil and Gas FacilitiesDocumento11 páginasOil and Gas FacilitiesDemzy Adeniyi100% (4)
- Global Energy Crisis: ENV200 Environmental Studies Lecture SlidesDocumento165 páginasGlobal Energy Crisis: ENV200 Environmental Studies Lecture SlidestejuAinda não há avaliações
- Enhanced Oil Recovery - Department of EnergyDocumento4 páginasEnhanced Oil Recovery - Department of Energytsar_philip2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Pakistan Energy SectorDocumento80 páginasPakistan Energy SectorAsim Riaz100% (2)
- Lesson 12 FinalDocumento32 páginasLesson 12 FinalMabel DilaoAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrostatic and Hydro-Testing in the Oil and Gas FieldNo EverandHydrostatic and Hydro-Testing in the Oil and Gas FieldNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (2)
- Thermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualNo EverandThermodynamic Design Data for Heat Pump Systems: A Comprehensive Data Base and Design ManualAinda não há avaliações
- Bulletin EQM 89 - 5S PDFDocumento23 páginasBulletin EQM 89 - 5S PDFMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Operator Asset Ownership This Is My Equipment Part 1 98Documento7 páginasOperator Asset Ownership This Is My Equipment Part 1 98Mgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- 2012 02 Brady 5S HandBookDocumento23 páginas2012 02 Brady 5S HandBookAlexandruAinda não há avaliações
- Countries Plants Products Month DayDocumento2 páginasCountries Plants Products Month DayMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- KKC Media 2017 M1Documento6 páginasKKC Media 2017 M1Mgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Inventário - Pessoal: Item Descrição Do Categoriac ItemDocumento8 páginasInventário - Pessoal: Item Descrição Do Categoriac ItemMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- 2017 GTS Training Catalog Moz PDFDocumento30 páginas2017 GTS Training Catalog Moz PDFMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Countries Plants Equipments ProductsDocumento34 páginasCountries Plants Equipments ProductsMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Countries Plants Equipments ProductsDocumento5 páginasCountries Plants Equipments ProductsMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Countries Plants Products Month: Total Total Total Total Total Total TotalDocumento2 páginasCountries Plants Products Month: Total Total Total Total Total Total TotalMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Employee Time Sheet: Employee Name: Etelvino Santiago Department: Start Day: 3/4/2002Documento1 páginaEmployee Time Sheet: Employee Name: Etelvino Santiago Department: Start Day: 3/4/2002Mgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Countries Plants Equipments ProductsDocumento3 páginasCountries Plants Equipments ProductsMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Disposal and Utilization of Fly Ash To Protect The EnvironmentDocumento8 páginasDisposal and Utilization of Fly Ash To Protect The EnvironmentMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- PipelinesDocumento12 páginasPipelinesSidick DaoussaAinda não há avaliações
- Oil and Gas SeparatorsDocumento7 páginasOil and Gas SeparatorsMgn San100% (1)
- Cem I CEM II/A 42,5 Çimento TipiDocumento8 páginasCem I CEM II/A 42,5 Çimento TipiMgn SanAinda não há avaliações
- Comparison of Waste Oil TreatmentDocumento5 páginasComparison of Waste Oil TreatmentFernando SImonelliAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 10-12 Geography - Manufacturing in Zambia and The Sub-Region-1Documento9 páginasGrade 10-12 Geography - Manufacturing in Zambia and The Sub-Region-1Prof Samuel Kashina100% (1)
- AnsiDocumento4 páginasAnsiHendrie NMcAinda não há avaliações
- Downstream Oil Industry Deregulation Act of 1998.Documento24 páginasDownstream Oil Industry Deregulation Act of 1998.Kriz MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Vel CVDocumento4 páginasVel CVKaranSinglaAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Crude Oil and Product Markets Primer Low PDFDocumento39 páginasUnderstanding Crude Oil and Product Markets Primer Low PDFrohanpujari100% (1)
- Chemical Engineering Journal: SciencedirectDocumento12 páginasChemical Engineering Journal: Sciencedirectpsnmurthy333Ainda não há avaliações
- Atlas - Case Study - English VersionDocumento5 páginasAtlas - Case Study - English Versionasmelash gideyAinda não há avaliações
- HydrocarbonEngineering 2023-03Documento92 páginasHydrocarbonEngineering 2023-03jmod7867Ainda não há avaliações
- PCU PresentationDocumento34 páginasPCU Presentationade agung laksonoAinda não há avaliações
- MOGAS Refining Valve Application GuideDocumento28 páginasMOGAS Refining Valve Application Guidecristi_molinsAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Sector of Pakistan & PGNiG OverviewDocumento27 páginasEnergy Sector of Pakistan & PGNiG OverviewNaba ZaidiAinda não há avaliações
- Re RefiningDocumento68 páginasRe RefiningBibhu PratapAinda não há avaliações
- (Magazine) Hydrocarbon Processing 01 2014Documento103 páginas(Magazine) Hydrocarbon Processing 01 2014Huy Văn ĐoànAinda não há avaliações
- SZ Sales ProgramDocumento28 páginasSZ Sales ProgramrossifrancescoAinda não há avaliações
- Petrochemical, Oil & Gas DictionaryDocumento79 páginasPetrochemical, Oil & Gas DictionaryErica LindseyAinda não há avaliações
- ENI Raffineria Eni Venezia 07.12.16Documento5 páginasENI Raffineria Eni Venezia 07.12.16rishikeshmandawadAinda não há avaliações
- CV of Izazur RahmanDocumento5 páginasCV of Izazur RahmanAjit EnterpriseAinda não há avaliações
- The Design and Layout of Vertical Thermosyphon ReboilersDocumento39 páginasThe Design and Layout of Vertical Thermosyphon Reboilerskphk1979Ainda não há avaliações
- Petron Corporation - Company AnalysisDocumento13 páginasPetron Corporation - Company AnalysisKristianne ClaireAinda não há avaliações
- Flare System Study EpaDocumento130 páginasFlare System Study Epahk168100% (2)
- 2016 July PDFDocumento108 páginas2016 July PDFmnasiroleslamiAinda não há avaliações
- Trislot Reactor Internal Part PDFDocumento12 páginasTrislot Reactor Internal Part PDFjonathanAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0098135423000467 MainDocumento19 páginas1 s2.0 S0098135423000467 MainFrank Joel Herrera ApaesteguiAinda não há avaliações
- SAN307 NotesDocumento10 páginasSAN307 NotesChristineNyambeAinda não há avaliações
- Fact Sheet MOSH and MOAHDocumento4 páginasFact Sheet MOSH and MOAHWayneAinda não há avaliações
- The Role of Oxygen and Hydrogen in Refining - tcm17-416854Documento8 páginasThe Role of Oxygen and Hydrogen in Refining - tcm17-416854alhag alhebirAinda não há avaliações
- Cs B Final Report Valero SunrayDocumento65 páginasCs B Final Report Valero Sunraysayed1234Ainda não há avaliações
- CrackingDocumento156 páginasCrackingImah MahdiAinda não há avaliações