Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Biological Evaluation
Enviado por
ahmrak0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
11 visualizações1 páginaof Different Betaine Sources
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoof Different Betaine Sources
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
11 visualizações1 páginaBiological Evaluation
Enviado por
ahmrakof Different Betaine Sources
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
Biological Evaluation of Different Betaine Sources
Suarez B.J. 1*, Van der Aa A. 1, Rovers M. 2, Kampf D. 2, De Kimpe N. 3,
Mangelinckx S. 3** and Segers L. 2
1. Excentials B.V., Cordoba, Argentina
2. Orffa International B.V. Werkendam, The Netherlands
3. Ghent University, Department of Sustainable Organic Chemistry and Technology,
Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Gent, Belgium.**Postdoctoral Fellow of the
Research Foundation - Flanders (FWO)
Corresponding author: Suarez@excentials.com
Abstract
Betaine is a functional nutrient commonly used as a feed additive in animal nutrition, mainly
as methyl donor. In the past betaine was available as betaine anhydrous extracted from
sugar beets; nowadays is present in different chemical forms and produced by different
methods. Concern was raised regarding the biological properties (bioactivity) of different
sources and production methods. Several publications had shown osmoregulatory effects of
betaine anhydrous, assisting animals during heat stress. The osmoregulatory properties of
betaine hydrochloride were point of discussion. State of the art research was setup in order to
evaluate the biological equivalence of different sources (monohydrate & anhydrous betaine
produced by extraction vs. hydrochloride & anhydrous betaine, produced by chemical
synthesis). Samples were dissolved in a water-hydrochloride solution (pH 2.3= gastric
conditions) to mimic gastric passage and analyzed by high-performance liquid
chromatography - electrospray ionization mass spectrometric (LC-MS) and direct mass
spectrometric (MS) analysis. After gastric passage both molecules remained identical,
showing that irrespective of the ionic form and production method (natural extraction vs.
chemical synthesis) different sources of betaine gave the same analytical LC-MS and MS
results (same m/z retention time pairs); therefore no difference in biological activity should
be expected. Further in vivo research (Haldar, 2011) carried out with broilers confirmed in
vitro findings and indicated that betaine hydrochloride is also effective as osmoregulator to
overcome heat stress in broiler chickens.
Key Words: Betaine, sources, biological equivalences.
Você também pode gostar
- Metabolites 09 00165 v2Documento15 páginasMetabolites 09 00165 v2Ignacio Pérez-VictoriaAinda não há avaliações
- HTTP WWW - Sciencedirect.com Science Ob MImg& Imagekey B6T6P-4VJ0CWR-5-7& Cdi 5036& User 687350& Search& CoverDate 06/30/2009& Ie SdarticleDocumento5 páginasHTTP WWW - Sciencedirect.com Science Ob MImg& Imagekey B6T6P-4VJ0CWR-5-7& Cdi 5036& User 687350& Search& CoverDate 06/30/2009& Ie SdarticlePaola CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Journal Pre-Proofs: Haematococcus LacustrisDocumento34 páginasJournal Pre-Proofs: Haematococcus LacustrisAlpa IgniAinda não há avaliações
- Reuteri 2-20B and Pediococcus Acidilactici 0-11A Isolated From FuraDocumento9 páginasReuteri 2-20B and Pediococcus Acidilactici 0-11A Isolated From FuramostecocAinda não há avaliações
- Comparative Study of Biogas Production From Different Food WastesDocumento6 páginasComparative Study of Biogas Production From Different Food WastesAngel LaneAinda não há avaliações
- Food Chemistry: Matthias Berger, Torben Ku Chler, Andrea Maaßen, Mechthild Busch-Stockfisch, Hans SteinhartDocumento6 páginasFood Chemistry: Matthias Berger, Torben Ku Chler, Andrea Maaßen, Mechthild Busch-Stockfisch, Hans SteinhartBryam David Ramirez ErazoAinda não há avaliações
- 015 Icbem2012 C00002Documento6 páginas015 Icbem2012 C00002jubatus.libroAinda não há avaliações
- Cholesterol Assimilation by Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bifidobacteria Isolated From The Human GutDocumento5 páginasCholesterol Assimilation by Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bifidobacteria Isolated From The Human GutmicrozasterAinda não há avaliações
- Production of Probiotic Cabbage Juice by Lactic Acid BacteriaDocumento5 páginasProduction of Probiotic Cabbage Juice by Lactic Acid BacteriaAsra Zafar khanAinda não há avaliações
- Probiotic Bacteria May Become Dormant During StoraDocumento3 páginasProbiotic Bacteria May Become Dormant During StoraAgus Prihanto PurnomoAinda não há avaliações
- Escherichia Coli O157:H7, Salmonella Enteritidis, and Listeria Monocytogenes On The Surfaces of TomatoesDocumento9 páginasEscherichia Coli O157:H7, Salmonella Enteritidis, and Listeria Monocytogenes On The Surfaces of TomatoesRuL'zAinda não há avaliações
- JB 82 4 582-588 1961Documento7 páginasJB 82 4 582-588 1961laasyagudiAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Different Fermentation Temperatures On Metabolites of KimchiDocumento7 páginasEffects of Different Fermentation Temperatures On Metabolites of KimchiAngela ValdiviesoAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal and Energetic Studies of Cellular Biological SystemsNo EverandThermal and Energetic Studies of Cellular Biological SystemsA. M. JamesAinda não há avaliações
- Quantification of Biotin in Feed, Food, Tablets, and Premixes Using HPLC-MS/MSDocumento9 páginasQuantification of Biotin in Feed, Food, Tablets, and Premixes Using HPLC-MS/MSSean Loh Wei JianAinda não há avaliações
- Physical-Chemical Properties of Foods: New Tools for PredictionNo EverandPhysical-Chemical Properties of Foods: New Tools for PredictionAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics of Kombucha Fermentation From DiffDocumento9 páginasCharacteristics of Kombucha Fermentation From Diffheinz strunkAinda não há avaliações
- Removal of Estrogens by Activated Sludge Under Different Conditions Using Batch ExperimentsDocumento12 páginasRemoval of Estrogens by Activated Sludge Under Different Conditions Using Batch ExperimentsReni AfrianiAinda não há avaliações
- Multimarker Responses of Zebrafish To The Effect of Ibuprofen and Gemfibrozil in Environmentally Relevant ConcentrationsDocumento9 páginasMultimarker Responses of Zebrafish To The Effect of Ibuprofen and Gemfibrozil in Environmentally Relevant ConcentrationssymchakrAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S2405844021007350 MainDocumento6 páginas1 s2.0 S2405844021007350 MainSantiago DangerAinda não há avaliações
- Motility Evaluation and Cryopreservation of Fish Sperm Exposed by Waterborne and Foodborne BoronDocumento8 páginasMotility Evaluation and Cryopreservation of Fish Sperm Exposed by Waterborne and Foodborne BoronjaefrAinda não há avaliações
- Foods 11 02054 v3Documento15 páginasFoods 11 02054 v3Yến BùiAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Water Avtivity On Carotenoid DegradationDocumento7 páginasEffect of Water Avtivity On Carotenoid DegradationEdgar Gamboa TerronesAinda não há avaliações
- Cricketbioaccessibility 2017 DavidDocumento7 páginasCricketbioaccessibility 2017 DavidDavid BarriosAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrogen Production From Food Waste in Anaerobic Mesophilic and Thermophilic AcidogenesisDocumento9 páginasHydrogen Production From Food Waste in Anaerobic Mesophilic and Thermophilic AcidogenesisĐêmTrắngAinda não há avaliações
- SuitaetalDocumento11 páginasSuitaetalJunar GiloAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical and Biological Variability of Hot Pepper FruitsDocumento9 páginasChemical and Biological Variability of Hot Pepper FruitsTatiane AraujoAinda não há avaliações
- SporeDocumento8 páginasSporepedroloxxxAinda não há avaliações
- The Study of Shelf Life For Liquid Biofertilizer From Vegetable WasteDocumento6 páginasThe Study of Shelf Life For Liquid Biofertilizer From Vegetable WasteFadhilah SurotoAinda não há avaliações
- Vishnuvardhan Reddy 2008 Isolation of PHA Bacteria From SewagesludgeDocumento7 páginasVishnuvardhan Reddy 2008 Isolation of PHA Bacteria From SewagesludgeASWINI J SAinda não há avaliações
- 401323v1 FullDocumento12 páginas401323v1 FullNew CertificateAinda não há avaliações
- Protein Deposition in Animals: Proceedings of Previous Easter Schools in Agricultural ScienceNo EverandProtein Deposition in Animals: Proceedings of Previous Easter Schools in Agricultural ScienceAinda não há avaliações
- A Case Study of Physico-Chemical and Bacteriological Analysis of Ajnal River at Harda M P During Monsoon SeasonDocumento4 páginasA Case Study of Physico-Chemical and Bacteriological Analysis of Ajnal River at Harda M P During Monsoon SeasonEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Degradation of Monoaromatics by Bacillus Pumilus MVSV3Documento18 páginasDegradation of Monoaromatics by Bacillus Pumilus MVSV3Davidsantiago Murillo AvilaAinda não há avaliações
- Refrigerated Chicken Meat Freshness Correlation BeDocumento8 páginasRefrigerated Chicken Meat Freshness Correlation BeElena EnacheAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S2665927123000771 MainDocumento13 páginas1 s2.0 S2665927123000771 MainSuthida PinyarukAinda não há avaliações
- Bioponics For Lettuce Production in A Plant Factory With Artificial LightingDocumento6 páginasBioponics For Lettuce Production in A Plant Factory With Artificial LightingvennithayumanavanAinda não há avaliações
- Betalainic and Nutritional Profiles of Pigment-Enriched Red Beet RootDocumento12 páginasBetalainic and Nutritional Profiles of Pigment-Enriched Red Beet RootDorin PopescuAinda não há avaliações
- Media Preparation and Bioreactors For Upstream Bioprocess DevelopmentDocumento11 páginasMedia Preparation and Bioreactors For Upstream Bioprocess DevelopmentGamze HatlarAinda não há avaliações
- Food Chemistry: S. Carneado, E. Hernández-Nataren, J.F. López-Sánchez, A. SahuquilloDocumento7 páginasFood Chemistry: S. Carneado, E. Hernández-Nataren, J.F. López-Sánchez, A. SahuquilloŞebnem İlarslanAinda não há avaliações
- Notes: Notes On Food, Beverages and Fomites Contaminated With Vibrio CholeraeDocumento10 páginasNotes: Notes On Food, Beverages and Fomites Contaminated With Vibrio CholeraeMoonsoul ChildAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Temperature On Microbial Changes During Kimchi FermentationDocumento6 páginasEffect of Temperature On Microbial Changes During Kimchi FermentationAditya Dian TjokroatmodjoAinda não há avaliações
- Joc - 7099Documento8 páginasJoc - 7099Diogo DiasAinda não há avaliações
- Study of PH Changes in Media During Bacterial Growth of Several Environmental StrainsDocumento5 páginasStudy of PH Changes in Media During Bacterial Growth of Several Environmental StrainsBagas Rahman SantosaAinda não há avaliações
- Tmp90a3 TMPDocumento11 páginasTmp90a3 TMPFrontiersAinda não há avaliações
- Study Kinetics Hazardous Pollutants Adsorption and Desorption by Biomass: Mechanistic ConsiderationsDocumento15 páginasStudy Kinetics Hazardous Pollutants Adsorption and Desorption by Biomass: Mechanistic ConsiderationsLaura MolanoAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0032579119537130 MainDocumento12 páginas1 s2.0 S0032579119537130 MainMuslima RakhimovaAinda não há avaliações
- Production of Bioorganic Liquid Fertilizer From Cow Manure and Groundnut HuskDocumento5 páginasProduction of Bioorganic Liquid Fertilizer From Cow Manure and Groundnut Huskmd kamal AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0144861707006601 MainDocumento7 páginas1 s2.0 S0144861707006601 MainIngrid DantasAinda não há avaliações
- Journal RosettoDocumento9 páginasJournal RosettoBrad PorneaAinda não há avaliações
- Uamerica 23 02043Documento6 páginasUamerica 23 02043Rimy Cruz GambaAinda não há avaliações
- Kim 2019Documento8 páginasKim 2019Shirley EspirituAinda não há avaliações
- 23 15 15 DrinkingwaterDocumento7 páginas23 15 15 DrinkingwaterPrecious Marie AgabeAinda não há avaliações
- 23 15 15 DrinkingwaterDocumento7 páginas23 15 15 DrinkingwaterPrecious Marie AgabeAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Ri, Sulawesi Tenggara, 93231Documento6 páginasDepartment of Chemistry, Faculty of Ri, Sulawesi Tenggara, 93231Alvio AndriantoAinda não há avaliações
- Lyngby ADocumento12 páginasLyngby ANatalia DonțuAinda não há avaliações
- Intermediate Moisture Meat Product: Biological Evaluation of Charqui Meat Protein QualityDocumento5 páginasIntermediate Moisture Meat Product: Biological Evaluation of Charqui Meat Protein QualityHarry YucraAinda não há avaliações
- An Exopolysaccharide From A Probiotic - Biosynthesis Dynamics, Composition and Emulsifying ActivityDocumento5 páginasAn Exopolysaccharide From A Probiotic - Biosynthesis Dynamics, Composition and Emulsifying ActivityWFreeAinda não há avaliações
- Arc Amts 4Documento9 páginasArc Amts 4AnilKumarAinda não há avaliações
- Universal Buffers For Use in Biochemistry and Biophysical ExperimentsDocumento7 páginasUniversal Buffers For Use in Biochemistry and Biophysical Experimentsعـَــٻاس مَـــشتاقAinda não há avaliações
- Protease Can Alleviate Negative Effects of CoccidiosisDocumento9 páginasProtease Can Alleviate Negative Effects of CoccidiosisahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- FT42 Broz PDFDocumento8 páginasFT42 Broz PDFahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- 335Documento10 páginas335ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Franklin 2005Documento10 páginasFranklin 2005ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Anesthesia-Responding To ComplicationsDocumento6 páginasAnesthesia-Responding To ComplicationsTELGE GIN 1Ainda não há avaliações
- 001 Boerderij Download Wp6381d01Documento2 páginas001 Boerderij Download Wp6381d01ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Anesthetic 1Documento19 páginasAnesthetic 1ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Zhan 2006Documento6 páginasZhan 2006ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Live Yeast and Mannan-Oligosaccharides On Performance of Early-Lactation Holstein Dairy CowsDocumento7 páginasEffect of Live Yeast and Mannan-Oligosaccharides On Performance of Early-Lactation Holstein Dairy CowsahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Jas 78 8 2039Documento16 páginasJas 78 8 2039ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- At 11 P 127Documento10 páginasAt 11 P 127ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Aflatoxin in Dairy FeedsDocumento4 páginasAflatoxin in Dairy FeedsahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Supplementation of Enzyme Complex On Growth Performance of Crossbred PigsDocumento5 páginasEffect of Supplementation of Enzyme Complex On Growth Performance of Crossbred PigsahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- 150 TassinariDocumento6 páginas150 TassinariahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Detection of Alpha ToxinDocumento1 páginaDetection of Alpha ToxinahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Held in Conjunction With The American Association of Avian Pathologists and The American Veterinary Medical Associatio 11PSA001Documento4 páginasHeld in Conjunction With The American Association of Avian Pathologists and The American Veterinary Medical Associatio 11PSA001ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- 31 1389780240Documento6 páginas31 1389780240ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Broiler Immune HealthDocumento3 páginasBroiler Immune HealthahmrakAinda não há avaliações
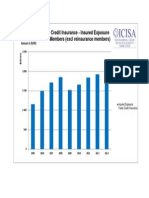
- Trade Credit Insurance - Insured Exposure ICISA Members (Excl Reinsurance Members)Documento1 páginaTrade Credit Insurance - Insured Exposure ICISA Members (Excl Reinsurance Members)ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- IAF - Radioökologie: 96132 SchlüsselfeldDocumento1 páginaIAF - Radioökologie: 96132 SchlüsselfeldahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- LSU AgCenter - Printable Copyasd PDFDocumento2 páginasLSU AgCenter - Printable Copyasd PDFahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Poultry Broiler FarmingDocumento16 páginasPoultry Broiler FarmingB.p. MugunthanAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Betaine Source On Nutrient Utilisation of Broilers Challenged With CoccidiaDocumento3 páginasEffect of Betaine Source On Nutrient Utilisation of Broilers Challenged With CoccidiaahmrakAinda não há avaliações
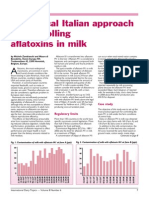
- A Practical Italian Approach To Controlling Aflatoxins in MilkDocumento3 páginasA Practical Italian Approach To Controlling Aflatoxins in MilkahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Pub 2897 Broiler PRDocumento8 páginasPub 2897 Broiler PRahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Al 703 e 00Documento4 páginasAl 703 e 00ahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Pro-Lyte Plus Product InfoDocumento2 páginasPro-Lyte Plus Product InfoahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- DR - Mahmoud El KelawayDocumento9 páginasDR - Mahmoud El KelawayahmrakAinda não há avaliações
- Supersect, ADWIA (Powder) : CompositionDocumento1 páginaSupersect, ADWIA (Powder) : CompositionahmrakAinda não há avaliações