Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
The Human Body System
Enviado por
api-269312030Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The Human Body System
Enviado por
api-269312030Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The Human Body
System
Katherine Salgado
Interesting Facts about the Respiratory System:
The human respiratory system is a series of organs responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling
carbon dioxide. The primary organs of the respiratory system are lungs, which carry out this exchange
of gases as we breathe.
As we breathe, oxygen enters the nose or mouth and passes the sinuses, which are hollow spaces in the
skull. Sinuses help regulate the temperature and humidity of the air we breathe.
The alveolar walls are extremely thin (about 0.2 micrometers). These walls are composed of a single
layer of tissues called epithelial cells and tiny blood vessels called pulmonary capillaries.
Red blood cells collect the oxygen from the lungs and carry it to the parts of the body where it is needed.
During the process, the red blood cells collect the carbon dioxide and transport it back to the lungs,
where it leaves the body when we exhale.
Interesting Facts about the Muscular System:
The focusing muscles in your eyes move around 100,000
times a day. To give your leg muscles the same workout,
youd need to walk 50 miles.
Our muscles are actually incredibly more powerful than they
appear to be. Human strength is limited to protect our
tendons and muscles from harming themselves. This
limitation can be removed during an adrenaline rush, during
which some people have lifted boulders or even cars off
themselves.
For every pound of fat or muscle gained, your body creates
seven miles of new blood vessels
The focusing muscles of the eyes move around 100,000 times
a day. To give your leg muscles the same workout, you would
need to walk 80km (50 miles) every day.
The hardest bone in the human body is the jawbone. The
next time someone suggests you take it on the chin, you
might be well advised to take their advice as the jawbone is
one of the most durable and hard to break bones in the body.
Interesting Facts about the Lymphatic System:
The primary function of the lymphatic system is to transport lymph, a clear, colorless fluid
containing white blood cells that helps rid the body of toxins, waste and other unwanted
materials.
The lymphatic system, which is a subset of the circulatory system, has a number of functions,
including the removal of interstitial fluid, the extracellular fluid that bathes most tissue. It
also acts as a highway, transporting white blood cells to and from the lymph nodes into the
bones, and antigen-presenting cells to the lymph nodes.
The lymphatic system is a network of tissues and organs that primarily consists of lymph
vessels, lymph nodes and lymph. The tonsils, adenoids, spleen and thymus are all part of the
lymphatic system.
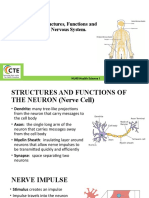
Interesting Facts about the Nervous System:
The nervous system is a complex collection of nerves and
specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals
between different parts of the body. It is essentially the bodys
electrical wiring.
Structurally, the nervous system has two components: the
central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
Functionally, the nervous system has two main subdivisions:
the somatic, or voluntary, component; and the autonomic, or
involuntary, component.
There are a number of tests and procedures to diagnose
conditions involving the nervous system. In addition to the
traditional X-ray, a specialized X-ray called a fluoroscopy
examines the body in motion, such as blood flowing through
arteries.
Interesting Facts about Skeletal System:
An adult's skeletal system consists 206 bones, 32 teeth and a network of other structures that connect the bones
together. This system performs a number of vital functions, such as giving the body its form, assisting with bodily
movements and producing new blood cells.
The skeletal system performs vital functions support, movement, protection, blood cell production, calcium
storage and endocrine regulation that enable us to move through our daily lives.
Animals with internal skeletons made of bone, called vertebrates, are actually the minority, as 98 percent of all
animals are invertebrates, meaning they do not have internal skeletons or backbones.
Human infants are born with 300 to 350 bones, some of which fuse together as the body develops. By the time
most children reach the age of 9 they have 206 bones.
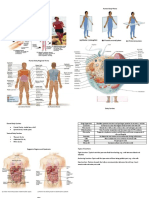
Interesting Facts about Cardiovascular System:
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and the approximately 5 liters of blood
that the blood vessels transport. Responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and
cellular waste products throughout the body, the cardiovascular system is powered by the bodys
hardest-working organ the heart, which is only about the size of a closed fist.
The heart is a muscular pumping organ located medial to the lungs along the bodys midline in the
thoracic region.
Blood vessels are the bodys highways that allow blood to flow quickly and efficiently from the heart to
every region of the body and back again. The size of blood vessels corresponds with the amount of
blood that passes through the vessel. All blood vessels contain a hollow area called the lumen through
which blood is able to flow
Blood circulates through a network of vessels throughout the body to provide individual cells with
oxygen and nutrients and helps dispose of metabolic wastes. The heart pumps the blood around the
blood vessels.
Interesting Facts about Digestive System:
The digestive tract, also known as the gastrointestinal (GI)
tract, starts at the mouth, continues to the esophagus,
stomach, small intestine, large intestine (commonly
referred to as the colon) and rectum, and ends at the anus.
The entire system from mouth to anus is about 30
feet (9 meters) long.
Digestion begins with chewing. Teeth, which are part of
the skeletal system, play a key role in digestion. In
carnivores, teeth are designed for killing and breaking
down meat. Herbivores teeth are made for grinding plants
and other food to ease them through the digestion process.
Saliva, which is secreted by the salivary glands in the
mouth, contains an enzyme, salivary amylase, which
breaks down starch.
Many problems can affect the GI tract, including:
abdominal pain, blood in the stool, bloating, constipation,
diarrhea, heartburn, incontinence, nausea and vomiting
and difficulty swallowing.
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Maximizing Growth Factors for Height IncreaseDocumento29 páginasMaximizing Growth Factors for Height IncreaseMegaV100% (2)
- The Developing Child - The First Seven Years - EbookDocumento141 páginasThe Developing Child - The First Seven Years - Ebookall-natural-nutAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- NCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Documento51 páginasNCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Richelle Joy Durano RegatunaAinda não há avaliações
- Digestion SystemDocumento15 páginasDigestion Systemapi-269312030Ainda não há avaliações
- Client 2 TrishaDocumento8 páginasClient 2 Trishaapi-277938821Ainda não há avaliações
- Hbs Unit 1 Identity SummaryDocumento29 páginasHbs Unit 1 Identity Summaryapi-269312030Ainda não há avaliações
- Skeleton Scavenger HuntDocumento11 páginasSkeleton Scavenger Huntapi-269312030Ainda não há avaliações
- Human TissuesDocumento7 páginasHuman Tissuesapi-269312030Ainda não há avaliações
- Skeletal System Tie-InsDocumento1 páginaSkeletal System Tie-Insapi-269312030Ainda não há avaliações
- Plant Cell Vs SmartphoneDocumento10 páginasPlant Cell Vs Smartphoneapi-269312030Ainda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis Question Booklet: Name . .Documento16 páginasPhotosynthesis Question Booklet: Name . .ajithaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology PDFDocumento1.447 páginasBiology PDFPrincess Ethel Atillo100% (2)
- Assignment Lec 4Documento3 páginasAssignment Lec 4morriganAinda não há avaliações
- Pete Pfitzinger Advanced Marathoning Training 88K-1Documento8 páginasPete Pfitzinger Advanced Marathoning Training 88K-1Phan ToanAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Chapter 8 - Cell CommunicationDocumento8 páginasBiology Chapter 8 - Cell CommunicationDonnabelle VaronaAinda não há avaliações
- Paragraph Development ExerciseDocumento6 páginasParagraph Development ExerciseSYAFINAS SALAM100% (1)
- Tetanus Neonatorum LectureDocumento11 páginasTetanus Neonatorum LectureJackAinda não há avaliações
- Musculoskeletal System Lecture NotesDocumento169 páginasMusculoskeletal System Lecture Noteszygote0711578796% (28)
- Fruit and Vegetable Diseases PDFDocumento563 páginasFruit and Vegetable Diseases PDFgrigorasalexandru100% (1)
- Manajemen Pre-Operatif Pasien Dengan DMDocumento12 páginasManajemen Pre-Operatif Pasien Dengan DMyanayas28Ainda não há avaliações
- CSIR UGC JRF Subjetive Model Test PaperDocumento17 páginasCSIR UGC JRF Subjetive Model Test PaperManu Mallahalli ShanthappaAinda não há avaliações
- NTSE Stage 1 State Level Model Paper 14Documento4 páginasNTSE Stage 1 State Level Model Paper 14AmanAinda não há avaliações
- Modul Anatomi Blok 7Documento27 páginasModul Anatomi Blok 7Dewandaru I A BAinda não há avaliações
- 3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocumento38 páginas3.03 Understand Structures, Functions and Disorders of The Nervous SystemLoriwinchesterAinda não há avaliações
- Overview of Complications Occurring in The Post-Anesthesia Care UnitDocumento14 páginasOverview of Complications Occurring in The Post-Anesthesia Care UnitShahabuddin ShaikhAinda não há avaliações
- CM All Compiled NotesDocumento100 páginasCM All Compiled NotesKatrina Mae PatalinghugAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDocumento12 páginasAnatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDeity Ann ReuterezAinda não há avaliações
- How Can We Use Neurotransmitters in Emotion and Reward System To Study DepressionDocumento22 páginasHow Can We Use Neurotransmitters in Emotion and Reward System To Study DepressionGlobal Research and Development ServicesAinda não há avaliações
- Altered Body TemperatureDocumento27 páginasAltered Body TemperatureAnusikta PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Abdominal SurgeryDocumento166 páginasAbdominal SurgeryIndera VyasAinda não há avaliações
- Fta Dna ExtractionDocumento20 páginasFta Dna Extractionnorma eunice gonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Key For Comprehensive Exam XVDocumento18 páginasAnswer Key For Comprehensive Exam XVQharts SajiranAinda não há avaliações
- ANAESTHESIOLOGYDocumento38 páginasANAESTHESIOLOGYcollinsmagAinda não há avaliações
- Meridians and Points PDFDocumento35 páginasMeridians and Points PDFHamdon Hamad100% (9)
- BioSignature Review - Are Hormones The Key To Weight LossDocumento19 páginasBioSignature Review - Are Hormones The Key To Weight LossVladimir OlefirenkoAinda não há avaliações
- Pancoast Tumour: Rare Lung Cancer FormDocumento2 páginasPancoast Tumour: Rare Lung Cancer FormobligatraftelAinda não há avaliações