Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Human Tissues
Enviado por
api-269312030Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Human Tissues
Enviado por
api-269312030Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Human Tissues
KATHERINE SALGADO
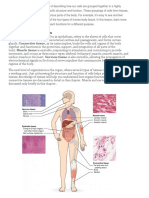
Tissues
In tissues the simplest combination is called a membrane, or a sheet of
tissues which cover or line the body surface or divide organs into parts.
Examples include the mucous membrane which lines body cavities.
Tissues combine to form organs. An organ is a part of the body which
performs a definite function. The final units of organization in the body
are called systems. A system is a group of organs each of which
contributes its share to the function of the body as a whole.
Connective Tissues
Connective tissue is the most abundant and the most widely
distributed of the tissues. Connective tissues perform a variety of
functions including support and protection. The following tissues are
found in the human body, ordinary loose connective tissue, fat tissue,
dense fibrous tissue, cartilage, bone, blood, and lymph, which are all
considered connective tissue.
Epithelial Tissues
Epithelial tissue covers the body surface and forms the lining for
most internal cavities. The major function of epithelial tissue includes
protection, secretion, absorption, and filtration. The skin is an organ
made up of epithelial tissue which protects the body from dirt, dust,
bacteria and other microbes that may be harmful. Cells of the
epithelial tissue have different shapes as shown on the student's
worksheet. Cells can be thin, flat to cubic to elongated.
Muscle Tissues
There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth, and
cardiac.
Skeletal muscle is a voluntary type of muscle tissue that is used in the
contraction of skeletal parts.
Smooth muscle is found in the walls of internal organs and blood
vessels. It is an involuntary type.
The cardiac muscle is found only in the walls of the heart and is
involuntary in nature.
Nervous Tissues
Nerve tissue is composed of specialized cells which not only receive
stimuli but also conduct impulses to and from all parts of the body.
Nerve cells or neurons are long and string-like. Nervous tissue is the
main component of the two parts of the nervous system; the brain and
spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS), and the branching
peripheral nerves of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which
regulates and controls bodily functions and activity.
Sources
http://www.msnucleus.org/membership/html/k-6/lc/humanbio/4/lchb4_3
a.html
Você também pode gostar
- Nselec TissueDocumento6 páginasNselec TissueClaire funtilarAinda não há avaliações
- Four Types of Tissue: Austin Sebastian Stem 12-2 HeaDocumento5 páginasFour Types of Tissue: Austin Sebastian Stem 12-2 HeaAustin SebastianAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Documento3 páginasAnimal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Amor Panopio MagtibayAinda não há avaliações
- Cell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationDocumento11 páginasCell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationSyuri MustikaAinda não há avaliações
- Anaphy ReportingDocumento8 páginasAnaphy ReportingRushyl Angela FaeldanAinda não há avaliações
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocumento9 páginasExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamental Types of Animal TissuesDocumento12 páginasFundamental Types of Animal TissuesBriana Franshay Aguilar SiotingAinda não há avaliações
- Specificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalDocumento22 páginasSpecificatio N: Tissues: Epithelial: Simple (CuboidalFatma AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Speech SciebnceDocumento2 páginasSpeech SciebnceluisAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Animal TissueDocumento8 páginas01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesDocumento3 páginasAnimal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesJamesAinda não há avaliações
- Epithelium: Source: Wikipedia - Bioligical TissueDocumento2 páginasEpithelium: Source: Wikipedia - Bioligical TissueMark PangilinanAinda não há avaliações
- Human Body TissuesDocumento6 páginasHuman Body Tissuesapi-269552822Ainda não há avaliações
- The Report of Animal Tissue Observation ResultDocumento4 páginasThe Report of Animal Tissue Observation Resulthilmisifa0% (1)
- Animal TissueDocumento3 páginasAnimal TissueAkmal MusyaffaAinda não há avaliações
- Is Cell Important For HumansDocumento2 páginasIs Cell Important For HumansniallevetriscaAinda não há avaliações
- Tissue Form & FunctionDocumento14 páginasTissue Form & FunctionLi KimAinda não há avaliações
- The Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoverDocumento9 páginasThe Four Types of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue, Also Referred To As Epithelium, Refers To The Sheets of Cells That CoveraudreyAinda não há avaliações
- TissuesDocumento4 páginasTissuesJaveria ZaidiAinda não há avaliações
- Why Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Documento37 páginasWhy Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Nuraini Zul100% (3)
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocumento8 páginasBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiAinda não há avaliações
- That Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDocumento3 páginasThat Means That Underlying The Cells That Are The Cellular Component of The Epithelial TissueDivine HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Human AnatomyDocumento6 páginasHuman AnatomyRazel PiñeroAinda não há avaliações
- From Cells To Tissue To Organs To Organ Systems: LS1.A: Structure and FunctionDocumento3 páginasFrom Cells To Tissue To Organs To Organ Systems: LS1.A: Structure and FunctionSaleh AlsowayanAinda não há avaliações
- Group 7Documento9 páginasGroup 7Prinz ToshAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Documento14 páginasUnit Iv Soft Tissue Mechanics The Soft Tissues of The Body:: Kripa's Notes.Kripa NAinda não há avaliações
- Cell and Tissues ResubDocumento9 páginasCell and Tissues Resubsilly GooseAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueDocumento10 páginasCHAPTER V: Tissues: Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous TissueAem TalAinda não há avaliações
- Basic AnatomyDocumento2 páginasBasic Anatomyafriesen72Ainda não há avaliações
- Gen Bio Module 4Documento8 páginasGen Bio Module 4rodriguezelmind20Ainda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento23 páginasAnatomy and Physiologyapi-464344582100% (1)
- Animal Tissues 1. EpithelialDocumento3 páginasAnimal Tissues 1. EpithelialRogeimar Claire MangomayaoAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocumento58 páginasLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Modifications and TissuesDocumento4 páginasCell Modifications and TissuesElla PascuaAinda não há avaliações
- Tissues and Cells Part 1 - Grade 7 - BiologyDocumento4 páginasTissues and Cells Part 1 - Grade 7 - BiologyYasmina Jamal GholoumAinda não há avaliações
- Class Discussion On TissueDocumento2 páginasClass Discussion On TissueKristhine Abegail Manangan-GamiaoAinda não há avaliações
- This Article Is About Biological Tissue. For Other Uses, SeeDocumento5 páginasThis Article Is About Biological Tissue. For Other Uses, Seerjohn 7Ainda não há avaliações
- Sri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Documento22 páginasSri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Sriarliza FebrianiAinda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Word - TISSUES OF THE BODY - MEDICS 20102011Documento5 páginasMicrosoft Word - TISSUES OF THE BODY - MEDICS 20102011AJAY KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- Animal TissueDocumento28 páginasAnimal TissueArjunAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Tissue and Animal TissueDocumento2 páginasPlant Tissue and Animal TissueJibril Halim SilaoAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocumento12 páginasAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- Activity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsDocumento7 páginasActivity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsAryan Jovic DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1Documento6 páginasPlant Tissues and Animal Tissues 1PawanAinda não há avaliações
- Organ System 1Documento15 páginasOrgan System 1LeoAinda não há avaliações
- College Level Anatomy and Physiology: Essential Knowledge for Healthcare Students, Professionals, and Caregivers Preparing for Nursing Exams, Board Certifications, and BeyondNo EverandCollege Level Anatomy and Physiology: Essential Knowledge for Healthcare Students, Professionals, and Caregivers Preparing for Nursing Exams, Board Certifications, and BeyondAinda não há avaliações
- Animal TissuesDocumento17 páginasAnimal TissuesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- TissuesDocumento33 páginasTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Proper For Week 7Documento5 páginasLesson Proper For Week 7Merlyn NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionDocumento8 páginasAssignment # 5: Body Covering and ProtectionJefferAinda não há avaliações
- The Physiologic Support SystemDocumento45 páginasThe Physiologic Support SystemModesto MasangkayAinda não há avaliações
- Abella, Franz Karl - Zoology Reviewer Pt. 1Documento4 páginasAbella, Franz Karl - Zoology Reviewer Pt. 1Franz AbellaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueDocumento6 páginasPlant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueBhoomika GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- Animal TissuesDocumento1 páginaAnimal TissuesIan BergadoAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiDocumento22 páginasBiology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiYaqeen AlaidyAinda não há avaliações
- Tissues 2Documento48 páginasTissues 2chikwatumilessAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Proper For Week 9Documento5 páginasLesson Proper For Week 9Merlyn NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- Animal TissuesDocumento13 páginasAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraAinda não há avaliações
- Histology Notes: Epithelial TissueDocumento4 páginasHistology Notes: Epithelial TissueSteph AsideAinda não há avaliações