Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Angle of Equilibrium - Derived Wind Heeling Arm
Enviado por
yuniardimzDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Angle of Equilibrium - Derived Wind Heeling Arm
Enviado por
yuniardimzDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
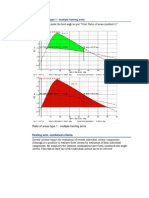
Angle of equilibrium - derived wind heeling arm
The derived wind heeling criterion is used to check that the steady heel angle due to wind
pressure exceeds a certain value. The steady heel arm is derived from a gust of specified
ratio. The wind gust will cause the vessel to heel over to the lesser of a specified heel
angle, angle of the first GZ peak, angle of maximum GZ or the first downflooding angle.
The vessel is assumed to be safe from gusts up to the specified ratio, if the angle of
steady heel is greater than the angle. This means that the lesser of: a specified heel angle,
first peak in GZ curve, angle of maximum GZ or the first downflooding angle, should be
large enough to withstand a gust from a steady wind heeling angle larger than .
Angle of equilibrium - derived wind heeling arm
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Weather Watch Study NotesDocumento5 páginasWeather Watch Study Notesapi-336664994Ainda não há avaliações
- 100-T-1100 Methanol Tank SampleDocumento3 páginas100-T-1100 Methanol Tank SampleSachinl PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Turbomachines Explained: Energy Transfer, Classification, EfficienciesDocumento254 páginasTurbomachines Explained: Energy Transfer, Classification, Efficienciesyash_ganatra0% (1)
- D790 02Documento9 páginasD790 02Arlene AriasAinda não há avaliações
- RRRRRRR RRRRRRR RRRRRRRRDocumento1 páginaRRRRRRR RRRRRRR RRRRRRRRyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- UuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuDocumento1 páginaUuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- HohohohohoDocumento1 páginaHohohohohoyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- NGOGKLDMFLKSMNFKLSMFLSMFSDocumento1 páginaNGOGKLDMFLKSMNFKLSMFLSMFSyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- THFTRHBRH rtjt535369999999999Documento1 páginaTHFTRHBRH rtjt535369999999999yuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Eeeeeeeeeeeeeee Eeeeeeeeeeeeeee EeeeDocumento1 páginaEeeeeeeeeeeeeee Eeeeeeeeeeeeeee EeeeyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- THFTRHBRH rtjt535369999999999Documento1 páginaTHFTRHBRH rtjt535369999999999yuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- OkeokeokeokeokeDocumento1 páginaOkeokeokeokeokeyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Range of Positive Stability - General Heeling ArmDocumento1 páginaRange of Positive Stability - General Heeling ArmyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- YtutuyuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuDocumento1 páginaYtutuyuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- JJJJJJJOOOOOOOOOOKOOKOKOKOOKKDocumento1 páginaJJJJJJJOOOOOOOOOOKOOKOKOKOOKKyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Other Criteria - STIXDocumento2 páginasOther Criteria - STIXyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- NgfngfmjyghdfshdfsrhfthDocumento1 páginaNgfngfmjyghdfshdfsrhfthyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- DRGDRGDFG 12 D 31 G 2 D 351321Documento1 páginaDRGDRGDFG 12 D 31 G 2 D 351321yuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Candidate Form: Personal DetailsDocumento1 páginaCandidate Form: Personal DetailsyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Value of GMT atDocumento1 páginaValue of GMT atyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Minimum Freeboard at EquilibriumDocumento1 páginaMinimum Freeboard at EquilibriumyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Angle of Deck Edge ImmersionDocumento1 páginaAngle of Deck Edge ImmersionyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Option Description Units: Value of GZ atDocumento1 páginaOption Description Units: Value of GZ atyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio of Areas Type 1 - Multiple Heeling ArmsDocumento1 páginaRatio of Areas Type 1 - Multiple Heeling ArmsyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio of Areas Type 1 - General Cos+sin Heeling ArmDocumento1 páginaRatio of Areas Type 1 - General Cos+sin Heeling ArmyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Angle of Maximum GZ Above Heeling Arm - General Heeling ArmDocumento1 páginaAngle of Maximum GZ Above Heeling Arm - General Heeling ArmyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Other Criteria - STIXDocumento2 páginasOther Criteria - STIXyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Ratio of GZ Values at Phi1 and Phi2 - General Heeling ArmDocumento1 páginaRatio of GZ Values at Phi1 and Phi2 - General Heeling ArmyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Maximum Freeboard at EquilibriumDocumento1 páginaMaximum Freeboard at EquilibriumyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Angle of Equilibrium - High-Speed Turn Heeling ArmDocumento1 páginaAngle of Equilibrium - High-Speed Turn Heeling ArmyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Value of GMT atDocumento1 páginaValue of GMT atyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Angle of Equilibrium - Passenger Crowding Heeling ArmDocumento1 páginaAngle of Equilibrium - Passenger Crowding Heeling ArmyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Angle of Deck Edge ImmersionDocumento1 páginaAngle of Deck Edge ImmersionyuniardimzAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Fog Formation ExplainedDocumento2 páginasTypes of Fog Formation ExplainedImane Aly Saroit Ismail100% (1)
- 2 Constitutive Models: Theory and Implementation: Section 2.2.1Documento144 páginas2 Constitutive Models: Theory and Implementation: Section 2.2.1mybestloveAinda não há avaliações
- GPAT Physical Pharmacy SyllabusDocumento2 páginasGPAT Physical Pharmacy Syllabuskumar Harsh100% (1)
- LIST OF SYMBOLS AND ROLLING BEARING ANALYSIS TABLEDocumento2 páginasLIST OF SYMBOLS AND ROLLING BEARING ANALYSIS TABLEotokar2Ainda não há avaliações
- Week 3 Lectures - Differential AnalysisDocumento19 páginasWeek 3 Lectures - Differential AnalysisboogolamAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 6: Dew Point and Bubble Point Calculation: Assignment 1Documento2 páginasExercise 6: Dew Point and Bubble Point Calculation: Assignment 1Junaid0% (1)
- Simulation of Water-Clay Flow in Dam Break with SPHDocumento8 páginasSimulation of Water-Clay Flow in Dam Break with SPHGeorge CarmelAinda não há avaliações
- ASTM C 158 Standard Test Methods For Strength of Glass by Flexure (Determination of Modulus of RuDocumento9 páginasASTM C 158 Standard Test Methods For Strength of Glass by Flexure (Determination of Modulus of RuRyan Lasaca100% (1)
- Fatigue Properties of JIS H3300 C1220 Copper For Strain Life PredictionDocumento10 páginasFatigue Properties of JIS H3300 C1220 Copper For Strain Life PredictionnomecAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Heat Exchanger U-TUBE ReportDocumento66 páginasSample Heat Exchanger U-TUBE Report9913489806Ainda não há avaliações
- Appendix A: Dimensionless Groups: By. Robert B. HeimannDocumento2 páginasAppendix A: Dimensionless Groups: By. Robert B. HeimannGusti Ayoe NurjanahAinda não há avaliações
- 2016-1 Breno Ventorim de TassisDocumento49 páginas2016-1 Breno Ventorim de TassisMedhn AbrahaAinda não há avaliações
- Bending Dan Longitudinal BendingDocumento5 páginasBending Dan Longitudinal BendingDhebdjshdn ShxhshushdAinda não há avaliações
- Psig 1901Documento29 páginasPsig 1901Qaiser HafeezAinda não há avaliações
- Water Gas Shift Equilibria Using NIST Webbook and MatlabDocumento7 páginasWater Gas Shift Equilibria Using NIST Webbook and MatlabTaylorAinda não há avaliações
- Live load and wind pressure on sloping roofsDocumento11 páginasLive load and wind pressure on sloping roofsAbel BerhanemeskelAinda não há avaliações
- Gas TurbineDocumento9 páginasGas TurbineTian TianAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 12 Fluid FrictionDocumento4 páginasExperiment 12 Fluid FrictionHadoosh2786% (7)
- Shape Effects On DragDocumento2 páginasShape Effects On Dragshivansh231Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Plasticity Tests and Stress-Strain CurvesDocumento71 páginasChapter 3 Plasticity Tests and Stress-Strain CurvesbrettbookAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise ProblemsDocumento1 páginaExercise ProblemsVenkitaraj K PAinda não há avaliações
- Pushover AnalysisDocumento12 páginasPushover AnalysisNikhilVasistaAinda não há avaliações
- Week 9 Lecture Material - WatermarkDocumento62 páginasWeek 9 Lecture Material - WatermarkVaibhav SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Simulation of A Tensile Test For An Epoxy/E-glass Composite Strip With 0° and 45° Orientations Using ANSYS® and SolidWorks®.Documento9 páginasComputer Simulation of A Tensile Test For An Epoxy/E-glass Composite Strip With 0° and 45° Orientations Using ANSYS® and SolidWorks®.YussefRikli100% (1)
- 1.0 - Properties FluidsDocumento5 páginas1.0 - Properties Fluidsrhydnar KimAinda não há avaliações
- ENCH607-F2022-L02-Physical&Thermodynamic PropertiesDocumento81 páginasENCH607-F2022-L02-Physical&Thermodynamic PropertiesNick jamesAinda não há avaliações