Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Decreased Cardiac Output RM 7
Enviado por
api-283470660Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Decreased Cardiac Output RM 7
Enviado por
api-283470660Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
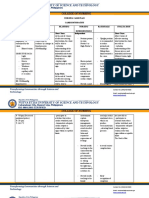
PLANNING/IMPLEMENTATION/EVALUATION (See Grading Rubric for NCP Criteria)
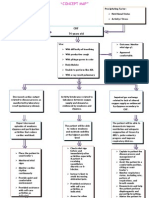
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for decreased cardiac output related to ventricular arrhythmia
Long Term Goal: Patient will maintain adequate cardiac output
Outcome Criteria
One outcome criteria for each
intervention. Number each one.
Interventions
Label each intervention as:
Assess/Monitor/Independent
Dependent/Teaching/Collaboration
Rationale
Evaluation
Answers why, how, what your interventions will Evaluate the patient
help solve, prevent or lessen the stated problem outcome NOT the
specific to this patient.
intervention
Assess/Monitor
1. Pt will not have peripheral
edema upon assessment
q4h
1. Assess peripheral edema Edema is swelling caused by excess fluid
q4h
trapped in your body's tissues. Although
edema can affect any part of your body, it's
most commonly noticed in the hands, arms,
feet, ankles and legs. The patient has CHF
which means the hearts lower chambers
lose their ability to pump blood effectively.
This causes the blood to back up in your
legs, ankles and feet (as well as other
areas), causing edema. The patient also has
acute on chronic kidney disease which
causes extra fluid and sodium in circulation
which causes edema. The edema
associated with kidney disease usually
occurs in your legs and around your eyes.
Excess peripheral edema may be improved
by taking a diuretic to decrease Na and
Met, plan ongoing
2. Patient will be free of
adventitious lung sounds
upon assessment q4h
3. Pt will have normal S1
and S2 sounds heard
without S3, S4 present
2. Assess lung sounds q4h
water via excretion such as Lasix. This
decreases blood volume which decreases
preload and afterload, improving cardiac
output.
Met, plan ongoing
Crackles reflect fluid accumulation
secondary to impaired left ventricular
emptying. Pleural effusions may also be the
result of left ventricular failure. An increase
in crackles or absent breath sounds are
cause for concern of decrease cardiac
output. The patient has chronic heart failure
which increases the likelihood that fluid will
accumulate in the lungs. The cxr showed
mild pulmonary vascular congestion with
basilar atelectasis. This means there is
engorgement of pulmonary vessels with
transudation of fluid into the alveolar and
interstitial spaces. This extra fluid makes it
harder for the heart to pump and also
indicates an ineffective pump. If the heart
does not pump adequately enough, there
will not be enough output to perfuse the
kidneys that would then excrete the extra
Met, plan ongoing
fluid from the body, thus keeping it in the
3. Assess heart sounds q4h vascular system making it harder. Clear L/S
are indicative of the extra fluid moving away
and an adequate cardiac pump.
S1 and S2 are the normal lub-dub heart
sounds heard during auscultation. Hearing
an S3 would indicate reduced left ventricular
ejection and blood sloshing within the walls
4. HR will be between 60100 bpm, BP 90/50130/80 mmHg, 12-20
resps/min, temp 96.899.5, and O2 sat 93100%
5. Pt will have urine output
of at least 240cc in 8
hours upon assessment
qshift
4. Monitor vital signs q4h
of the heart. S4 signifies reduced left
ventricular compliance due to hypertrophy
which impairs filling. Murmurs signify
abnormal flow of blood through the valves.
The MD would need to be notified of
abnormal S3 and S4 sounds being heard.
Partially met, the
pts BP was low at
96/48, however
after
discontinuation of
the Lasix, the pts
Many patients with decreased cardiac output BP improved to
have tachycardia, decreased BP, decreased 107/65. Plan
ongoing
O2 sat, and increased RR. Older patients
have a reduced response to catecholamines
resulting in a decreased response to
decreased cardiac output with less increase
in HR. The patient is experiencing PSVT
which causes episodes of tachycardia where
the heart cannot pump or fill adequately due
to the elevated heart rate. This can influence
or worsen heart failure. Changes evidencing
decreased cardiac output would first be
seen in HR, BP and RR. If abnormals in vital
signs are seen, interventions may be made Partially met, pt
had voided 150 cc
like applying/increased O2, giving a
medication like adenosine, nitroglycerin, or urine, however not
a full shift was
5. Assess urine output qshift calling the MD for further direction.
spent with her. Will
continue to
The renal system compensates for low
monitor, plan
blood pressure and decreased perfusion by
ongoing
retaining Na and water. Decreased urine
output or oliguria is a classic indicator of
decreased cardiac output. The patients
BUN and Cr are both within normal limits
and GFR does not show any acute disease.
The patient is ambulatory to the bathroom
and voids in the toilet in which her urine is
6. Pt will not use accessory
muscles to breathe upon
assessment with
interactions
7. Pt will not have a weight
gain of more than 2
pounds in 2 days upon
assessment daily
6. Assess use of accessory
muscles with interations
7. Weigh pt daily
measurable with a specipan. She should
Met, plan ongoing
have at least 240cc urine output in 8 hours
to prove adequate renal perfusion by the
heart. If there is less than 240 cc, the MD
should be notified to receive further
direction.
Heart failure means the heart is not pumping
enough blood to keep the organs alive.
Since it is unable to pump the blood fast
enough, the blood on the way to the heart
gets backed up in the veins. Reduced blood
flow to the kidneys results in water retention.
You end up with fluid in the lungs and
edema on the body. The use of accessory
muscles indicates increased work of
breathing and should be noted on
assessment. These muscles include the
Unmet, pt was not
sternocleidomastoid, upper trapezius,
weighed during our
pectoralis major, and others. If use of
accessory muscles is noted, the nurse may care. Plan ongoing
also auscultate the lung sounds, administer
a diuretic to help remove fluid, administer
oxygen, and notify the MD of the pts
distress.
Heart failure happens when your heart
muscle isn't pumping enough blood to the
rest of your body. Because the heart isn't
pumping as it should, fluids can start to build
up. This fluid presents as peripheral edema,
crackle sounds in the lungs, jugular vein
distention and more. If there is more than a
2 pound weight gain in 2 days, the MD
should be notified because that signifies that Unmet, patient had
8. Pt will not have abnormal
ECG changes including
tachycardia, pvcs, or
pacs
treatment is not effective enough for proper
cardiac function. A dose of Lasix may need
to be increased and measures can be made
such as positioning that will help blood flow
8. Monitor ECG for changes back to the heart, improve preload and
afterload.
q2h
9. BNP will return to normal
range of 0-100 pg/mL by
discharge
9. Monitor BNP level as
episodes of PSVT
with HR of over
122 with pvc
during our care.
Plan ongoing
The patient has PSVT which involves
episodes of tachycardia triggered by pacs or
pvcs. When the heart is beating this fast
(upwards of 150 bpm at times), the heart
does not have enough time to adequately
fill, and therefore adequately pump blood to
the rest of the body, leading to heart failure.
The heart becomes overworked and can
become enlarged. Noticing that the HR is
elevated on the ECG allows for interventions
to be made such as calling the MD who may
Unmet, BNP was
prescribe a medication such as adenosine.
788 upon
When the pt was experiencing a HR of 122,
admission and no
the primary RN called the MD to give the
other labs have
dose of Diltiazem early to lower the heart
been drawn. Plan
rate. Managing the heart rate allows for
better cardiac output and better perfusion to ongoing
the tissues.
ordered by MD
BNP is elevated with increased filling
pressure, volume, and stretch in the
ventricles. BNP increases Na excretion,
decreases blood volume, decreases
afterload and yield increased cardiac output.
The patients BNP is elevated to 788,
signifying heart failure. Lowering the BNP to Met, plan ongoing
an acceptable level of 0-100 will reduce
10. Pt O2 sat will be 93100% at all times upon
assessment
11. Pt BP will be between
90/50-130/80 mmHg qd
and upon assessment
stress on the heart, and signify an increase
in cardiac output. If the BNP is seen to be
rising or not improving, the MD may
prescribe a new medication or increase a
dose of something like Lasix that would
improve heart failure and improve cardiac
10. Administer O2 as needed output.
to keep sat > 93% at all
times
Patients with heart failure may not be able to
respond adequately to increased O2
demand of the heart. O2 supplementation is
necessary in these cases. The patient did
not require supplemental O2 while in my
care but her O2 sat should be monitored in Partially met: Pt BP
the case that her heart failure worsens and was 96/48, Lasix
her saturation drops. Her PSVT is still not
was DCd, BP
under control so her heart failure can be
improved to
worsening. If the O2 sats drop low, O2
supply to the heart and other body tissues is 107/65. Plan
decreasing which decreases cardiac output. ongoing
Keeping the heart oxygenated increases
cardiac output.
11. Administer furosemide
20mg/2mL soln IVP qd
Diuretic such as furosemide will reduce
circulating blood volume by increasing Na
and water excretion. The end effect is
decreased BP and decreased edema. This
decreases preload and afterload and
decreases the workload on the heart. The
patient has HF which tends to increase
edema and decrease kidney perfusion
leading to retention of fluids. Removing
Met, plan ongoing
excess fluid will decrease workload of the
heart, preload, afterload and increase
cardiac output. The patients blood pressure
was low at 96/48 upon first assessment in
the morning, therefore the doctor temporarily
discontinued the Lasix to allow the blood
pressure to increase. At 11:15 the pts blood
pressure was improved to 107/65.
12. Pt potassium level will be
between 3.6 and 5.2
mmol/L as assessed after
administration of IVF with
KCL at 100cc/hr
12. Administer D NS with
KCL 40 meq/1000 mL at
100 mL/hr
Upon admission to the emergency room the
patient was being treated with Lasix which
inhibits reabsorption of Na and Cl from the
loop of Henle and distal renal tubule. It
therefore causes an increase in the
excretion of water, Na, Cl, Mg, and K.
Met, plan resolved
Potassium is essential for proper electrical
conduction of nerve impulses in smooth
muscle such as the heart. These IV fluids
help to replace the amount of potassium lost
due to diuretic use and maintain adequate
conduction and proper cardiac output.
13. Pt will verbalize 5 signs of
decreased cardiac output
that require medical
attention prior to
discharge
13. Teach the patient signs of Signs and symptoms of decreased cardiac
decreased cardiac output output are varied and can be attributed to
requiring medical attention many things if one is not specifically looking
for them. The patient should be taught that
prior to discharge
changes in resp rate, depth, effort signal
worsening lung function that is likely due to
congestion from inadequate cardiac output.
Other symptoms to watch for include urine
output of less than 240 cc in 8 hours,
extreme fatigue/weakness, hypotension,
tachycardia, cool or clammy skin, increased
edema, increase in daily weight (2lb gain or
more in 2 days), all of which require the
Unmet, smoking
cessation was not
discussed, plan
ongoing
attention of a health care provider. Knowing
these signs and getting medical help when
needed will help to minimize complications.
14. Pt will verbalize a plan on
how to quit smoking prior
to discharge after
teaching about smoking
cessation qd
14. Teach the patient about
smoking cessation qd
15. The patient will verbalize
the importance of a
cardiac diet and what
kinds of
foods/substances she
must avoid daily
15. Teach the patient about
proper cardiac diet qd
Smoking-related coronary heart disease
contributes to congestive heart failure.
Toxins found in the blood from smoking
cigarettes contribute to the development
of atherosclerosis, which is a progressive
hardening of the arteries caused by the
deposit of fatty plaques and the scarring and
thickening of the artery wall. Inflammation of
the artery wall and the development of blood
clots can obstruct blood flow and cause
heart attacks or strokes. It also causes
increased resistance that the heart must
pump blood against so the heart is
Partially met: pt
overworking and become enlarged leading
to heart failure. The patient states she is an understands she
must avoid
occasional smoker since she was in her
teenage years. Teaching her about how it is caffeine, fatty
foods, and high
not too late to stop smoking and
sodium but
encouraging her to make a plan to stop
smoking can help her to quit and improve
reasons as to why
her cardiac output.
were not discussed
in depth. Plan
People with heart failure may improve their ongoing
symptoms by reducing the amount of
(sodium) in their diet. Sodium is a mineral
found in many foods. Eating too much salt
causes the body to keep or retain too much
water, worsening the fluid build-up
associated with heart failure that can cause
edema and adventitious lung sounds with
shortness of breath or activity intolerance.
Following a low-salt diet also helps control
high blood pressure by decreasing the
amount of circulating volume. Pts with heart
failure should consume no more than 2,000
mg of salt per day. The pt should also avoid
caffeine and other stimulants because it can
aggravate the pts PSVT and result in
tachycardia and palpitations. The pt should
also opt for a low fat diet to decrease
cholesterol and the amount of plaque
buildup in the arteries which would improve
cardiac output.
Você também pode gostar
- Nursing Care Plan HF FinalDocumento10 páginasNursing Care Plan HF FinalCristina L. JaysonAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento15 páginasNCPCamille PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP and DStudyDocumento8 páginasNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatAinda não há avaliações
- Chest Pain Care PlanDocumento2 páginasChest Pain Care Planapi-545292605Ainda não há avaliações
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocumento18 páginasNursing Care Plan Renal FailureKundan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocumento6 páginasDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiogenic ShockDocumento3 páginasCardiogenic Shockmerin sunilAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioAinda não há avaliações
- Intracranial HemorrhageDocumento41 páginasIntracranial Hemorrhagedoctormussieaberra100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related ToDocumento7 páginasIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related TohannahAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocumento4 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasAinda não há avaliações
- ISBAR DocumentationDocumento1 páginaISBAR DocumentationFrancorussAinda não há avaliações
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsDocumento4 páginasAngiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) InhibitorsPutri Mulia HasibuanAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento9 páginasNCPKarell Eunice Estrellado Gutierrez100% (1)
- Concept Map - Abby !Documento2 páginasConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento14 páginasNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- NCP PainDocumento2 páginasNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Documento9 páginasNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Gayu Patel0% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodDocumento2 páginasIneffective Tissue Perfusion Related To Decrease Hemoglobin Concentration in The BloodKit Alizon BarredoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Acute PainDocumento5 páginasNCP Acute PainEzra TuanAinda não há avaliações
- Case StudyDocumento34 páginasCase StudyBSNNursing101Ainda não há avaliações
- Actual NCPDocumento3 páginasActual NCPMabz BoholAinda não há avaliações
- Coronary Artery Disease and HypertensionDocumento8 páginasCoronary Artery Disease and HypertensionsnehaAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study RespiDocumento3 páginasCase Study RespiMark Jheran AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- CarePlan #2Documento3 páginasCarePlan #2Monika StasiakAinda não há avaliações
- Oxygen TherapyDocumento3 páginasOxygen Therapymarie100% (3)
- Non-St Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Nstemi)Documento24 páginasNon-St Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Nstemi)MHIEMHOIAinda não há avaliações
- NCP CKDDocumento3 páginasNCP CKDRiel TumandaAinda não há avaliações
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento1 páginaDecreased Cardiac OutputPrecious Heart Sotero TababaAinda não há avaliações
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 páginasDecreased Cardiac OutputCristina L. JaysonAinda não há avaliações
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocumento3 páginasSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaAinda não há avaliações
- Anxiety R:T Death ThreatDocumento8 páginasAnxiety R:T Death ThreatAlfredo BaulaAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map Finished 2Documento6 páginasConcept Map Finished 2api-352785497100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatAinda não há avaliações
- Welcome To The Case Study Presentation:-: Prostate CancerDocumento22 páginasWelcome To The Case Study Presentation:-: Prostate CancerDengo ChapatieeAinda não há avaliações
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyDocumento7 páginasNueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyKym RonquilloAinda não há avaliações
- Rhea TestDocumento3 páginasRhea Testerma090308Ainda não há avaliações
- Clinical Log Term II PDFDocumento9 páginasClinical Log Term II PDFPriscilla S100% (1)
- Drug Study On DigoxinDocumento8 páginasDrug Study On DigoxinDonald BidenAinda não há avaliações
- Post-op-Case-Conference-DM FootDocumento44 páginasPost-op-Case-Conference-DM FootShereen DS Lucman100% (1)
- NCP AneurysmDocumento4 páginasNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetDocumento5 páginasAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: STO: Within 4 Hour of DX: DX: Sto: Goal MetRussel SantosAinda não há avaliações
- 16 ARDS - Nursing Care ManagementDocumento2 páginas16 ARDS - Nursing Care ManagementTisha CarretteAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocumento19 páginasNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan EportfolioDocumento14 páginasNursing Care Plan Eportfolioapi-279212367Ainda não há avaliações
- Hypertension NclexDocumento5 páginasHypertension Nclexハニファ バランギAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Acute Pain NCSDocumento3 páginasNCP Acute Pain NCSPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Velez College of Nursing F. Ramos Street, Cebu CityDocumento57 páginasVelez College of Nursing F. Ramos Street, Cebu Cityinah krizia lagueAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento5 páginasNursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPArien CaleonAinda não há avaliações
- MI BrochureDocumento2 páginasMI BrochureAbedin Mehmedovic100% (1)
- Case Study: Congestive Heart FailureDocumento7 páginasCase Study: Congestive Heart FailureXI-E / 21 / MARY TRIANAAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 páginasNCP - Decreased Cardiac OutputIzza DeloriaAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocumento3 páginasImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliAinda não há avaliações
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento4 páginasRisk For Decreased Cardiac Outputapi-283482759Ainda não há avaliações
- Excrete Less Salt and Water. It Also Produces A Reduction in Renal Plasma Flow andDocumento3 páginasExcrete Less Salt and Water. It Also Produces A Reduction in Renal Plasma Flow andCoole PhilipAinda não há avaliações
- S RL 31072018 Desmoplastic FibromaDocumento23 páginasS RL 31072018 Desmoplastic FibromaAnonymous bE4VegCcAinda não há avaliações
- Listening Sample Test 3 Question PaperDocumento12 páginasListening Sample Test 3 Question PaperYu YuiAinda não há avaliações
- Uterine Anomaly, Fibroid Uterus, Ovarian Tumor, Uterine ProlapseDocumento30 páginasUterine Anomaly, Fibroid Uterus, Ovarian Tumor, Uterine ProlapseVijith.V.kumar80% (5)
- Effects of Implementation of Focus-Pdca Model To Decrease Patients' Length of Stay in Emergency DepartmentDocumento5 páginasEffects of Implementation of Focus-Pdca Model To Decrease Patients' Length of Stay in Emergency DepartmentMuhammad RamadhanAinda não há avaliações
- Flail ChestDocumento7 páginasFlail ChestMark Anthony IbayAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper DiabetesDocumento8 páginasResearch Paper Diabetesapi-359023534Ainda não há avaliações
- Advanced Diagnostic TechniquesDocumento19 páginasAdvanced Diagnostic TechniquesSunkara Musalaiah0% (1)
- Sop Hand HygieneDocumento3 páginasSop Hand HygieneIndri SafitriAinda não há avaliações
- Why Did You Decide To Become A NurseDocumento4 páginasWhy Did You Decide To Become A Nurseaisyah andyAinda não há avaliações
- ENT Notes For Med StudentsDocumento4 páginasENT Notes For Med Studentsnikki100% (1)
- DNR - Do Not Resuscitate Law - 2017Documento8 páginasDNR - Do Not Resuscitate Law - 2017Keelie SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Towards Improving post-SSRI Sexual Dysfunction by Using Nutriceuticals: Lessons From A Case Study - Calabrò 2019Documento8 páginasTowards Improving post-SSRI Sexual Dysfunction by Using Nutriceuticals: Lessons From A Case Study - Calabrò 2019Julio JuarezAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Tool - PCW CertificationDocumento13 páginasAssessment Tool - PCW CertificationPaula PascualAinda não há avaliações
- StrokeDocumento22 páginasStrokeAlex GasnasAinda não há avaliações
- TetanusDocumento34 páginasTetanusBintang Ruth Cecilia FebrinaAinda não há avaliações
- Extended Role of NurseDocumento7 páginasExtended Role of Nurseसपना दाहालAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid Hormone Therapy For Older Adults With Subclinical HypothyroidismDocumento11 páginasThyroid Hormone Therapy For Older Adults With Subclinical HypothyroidismAssifa RidzkiAinda não há avaliações
- PRUBSN Heatlh Enrich PlusDocumento2 páginasPRUBSN Heatlh Enrich PlusMalik TaufiqAinda não há avaliações
- FOI Response From Barnsley HospitalDocumento3 páginasFOI Response From Barnsley HospitalnhswatchukAinda não há avaliações
- Crasilneck1979 PDFDocumento9 páginasCrasilneck1979 PDFfebria fadhilahAinda não há avaliações
- Ciprofloxacin Induced Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocumento8 páginasCiprofloxacin Induced Systemic Lupus ErythematosusAvelox FloxAinda não há avaliações
- HHS Public Access: How Schizophrenia Develops: Cognitive and Brain Mechanisms Underlying Onset of PsychosisDocumento25 páginasHHS Public Access: How Schizophrenia Develops: Cognitive and Brain Mechanisms Underlying Onset of PsychosisNoriAinda não há avaliações
- Ethical Issues in The Care of Older PersonsDocumento3 páginasEthical Issues in The Care of Older PersonsGodwin Babista GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Pulmonary TuberculosisDocumento17 páginasPulmonary TuberculosisRobert Dominic GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding The Complete Blood Count (CBC) and Common Blood DeficienciesDocumento8 páginasUnderstanding The Complete Blood Count (CBC) and Common Blood DeficienciesTanveer100% (1)
- Integ 4 Answer PDFDocumento12 páginasInteg 4 Answer PDFRhasdie MandiAinda não há avaliações
- Appropriate Maximum Phlebotomy Volumes: Neonate, Infant and Pediatric PopulationDocumento2 páginasAppropriate Maximum Phlebotomy Volumes: Neonate, Infant and Pediatric PopulationEthiopia HagereAinda não há avaliações
- Project Report of A HospitalDocumento28 páginasProject Report of A HospitalsureshvgkAinda não há avaliações
- Brain DeathDocumento24 páginasBrain DeathKawaljit KaurAinda não há avaliações
- Approach To Movement Disorders ..Documento54 páginasApproach To Movement Disorders ..Ihda ParidahAinda não há avaliações