Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Circlelesson 1
Enviado por
api-267810292Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Circlelesson 1
Enviado por
api-267810292Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lesson Plan Template ED 3501 (Version C)
Lesson
Title/Focus
Circumference of Circles (Lesson #1)
Date
March 13, 2015
Subject/Grade
Level
Grade 7 Math
Time
Duration
45 min
Unit
Chapter 8 Circles
Teacher
Kathy Kawade
OUTCOMES FROM ALBERTA PROGRAM OF STUDIES
General
Learning
Outcomes:
Specific
Learning
Outcomes:
Space and Shape (Measurement)
Use direct and indirect measurement to solve problems
1.1 Describe the relationships among radius, diameter, and circumference
1.2 Relate circumference to pi
1.5 Solve problems involving the radii, diameters, and circumference of circles.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Students will:
1. Describe the relationships between radius, diameter and circumference through
experimentation
2. Understand the relationship of pi to circumference
3. Experiment with solving circumference when given 2 out of 3 needed pieces of information
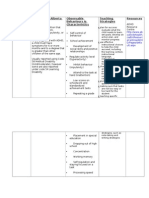
ASSESSMENTS
Observations:
Key Questions:
Products/Performances:
Did the students discover the constant relationship between the circumference and the
diameter of ANY circle?
How can we use the person at the centre of the circle to check
that the circle we made is really circular?
How many lengths of string are needed to extend all the way
across the circle while still passing through the centre?
Estimate how many lengths of our diameter string would fit
around the circumference of the circle?
Did the students discover the constant relationship between the circumference and the
diameter of ANY circle?
LEARNING RESOURCES CONSULTED
Alberta Program of Study Grade 7 Math
Learnalberta.ca
http://www.angio.net/pi/piquery (pi to 200
million)
MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT
String
Rulers
Math Notes
Calculators
PROCEDURE
Prior to lesson
Transition to Body
Body
Learning Activity #1
Have the desks all away from the walls so students can form their human circle. Have a student
in mind to be the centre.
Introduction
Time
Let students know were going to be looking at circles.
Circles are all around us: sun, plant stems, the wheels, coins,
rings, and CDs
The circle is an important symbol in many cultures. It shows
2-3 min
how everything in life is connected. In First Nations culture, the
circle can be seen in examples such as teepee bases, medicine
wheels, and ceremonial drums.
Creating a circle:
Students position themselves around the room to form a
human circle with one student as the centre of the circle.
How can we use the person at the centre of the circle
Adapted from a template created by Dr. K. Roscoe
15-20 min
Learning Activity #2
Learning Activity #3
Lesson Plan Template ED 3501 (Version C)
to check that the circle we made is really circular?
(Discuss that one of the characteristics of a circle is that any
point on the circles edge is the same distance from the
centre of the circle.
Provide the student at the centre with a string (3m maybe?)
and have him/her give the other end to a student on the
circle. The outside student must adjust his position until the
string is tight. Have the students pass the string and
continue the process until it has been passed to all students.
The student at the centre must stay in position but may have
to turn his body with the movement of the string.
Relate the Diameter and Radius of a circle:
Introduce the term Radius as the distance from the centre of
the circle to any point on that circle (write on board). What
represents the radius in our concrete circle? Once they
understand that the string is our radius, have them predict
how many lengths of string are needed to extend all
the way across the circle while still passing through
the centre. . Now prove it. Move the string from random
student to random student on the other side of the circle,
passing through centre. Note how it is exactly 2x our radius
to get the Diameter. Diameter is the entire length across the
circle, going any direction, passing through centre (write on
board).
Write on the board that diameter = 2 x radius or d = 2r
Relating Diameter, Radius, and Circumference:
Introduce Circumference as the distance around the circle
(write on board). Estimate how many lengths of our
diameter string would fit around the circumference of
the circle? After discussion have the student in the centre
take the string and use it to measure the circumference of
the circle. (Re-make the connection that the radius is twice
the diameter.) Discuss how the circumference of circles
varies depending on the radius/diameter of the circle. (Could
prove with a smaller circle if time permits)
Relating to Pi:
Introduce the term Pi (and the symbol ) and explain that the approximate
value of pi is 3.14. This number is nonrepeating and nonterminating. Pi =
C/d (write on the board). So far it has been calculated to over 200 million
digits. Could check out http://www.angio.net/pi/piquery
Look on your calculators and see if you can find the Pi button.
5-7 min
We will be typing in 3.14 instead of using the button, as the button will give
everyone minutely different answers, depending on the number of decimal
places available on each calculator.
So
We know from all of our experiments that C = approx. 3 times (roughly pi) the
D so the formula is
C = d or C = x 2r or C = 2r (write on board).
Were going to do this chapter out of order just a bit, so please turn to page 273
in your text (ch 8.2)
Go through Example 1: Use diameter to find the circumference of a traffic
5-10 min
circle showing how to substitute the known numbers into our formula.
Go through Example 2: Use radius to find circumference of a carousel
showing how to substitute the known numbers into our formula.
Closure
Homework
Feedback From Students:
Pg 278 in Mathlinks 7 textbook. #3, 4, 7, 8
Thumbs up/Thumbs down for understanding level.
Adapted from a template created by Dr. K. Roscoe
Transition To Next Lesson
Reflections from the lesson
Lesson Plan Template ED 3501 (Version C)
Tomorrow were going to create some of our own circles so please bring your
compass with you to class.
**How will I know if they learned what I taught?**
Did the students discover the constant relationship between the circumference and the
diameter of ANY circle?
Adapted from a template created by Dr. K. Roscoe
Você também pode gostar
- Computer Shortcut Keys SystemDocumento5 páginasComputer Shortcut Keys SystemNo RebelAinda não há avaliações
- Piping Presentation - PpsDocumento61 páginasPiping Presentation - PpsVijayabaraniAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Triangles (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo EverandProperties of Triangles (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankAinda não há avaliações
- 2010-12 600 800 Rush Switchback RMK Service Manual PDFDocumento430 páginas2010-12 600 800 Rush Switchback RMK Service Manual PDFBrianCook73% (11)
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 9Documento27 páginasMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 9Pat So100% (1)
- Mathematics5 Q4 Mod1 FindingTheAreaOfACircle V1Documento21 páginasMathematics5 Q4 Mod1 FindingTheAreaOfACircle V1ronald71% (14)
- Solutions Manual 4th EditionDocumento57 páginasSolutions Manual 4th Editionabdul5721100% (6)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 6Documento7 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 6Aira Jane IrarumAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Exemplar (Theorems Related To Inscribed Angle)Documento16 páginasLesson Exemplar (Theorems Related To Inscribed Angle)Gen E Sis100% (1)
- Python PPTDocumento13 páginasPython PPTSagar Tewatia63% (8)
- Final Lesson Plan Area of A CircleDocumento10 páginasFinal Lesson Plan Area of A Circleapi-289454387Ainda não há avaliações
- SDO City of Malolos Math5 Q4M2 Volume of Cube and Rectangular Prism A Afb2Documento31 páginasSDO City of Malolos Math5 Q4M2 Volume of Cube and Rectangular Prism A Afb2Kris Bernadette DavidAinda não há avaliações
- Better Volume Other Formats 19aug12Documento11 páginasBetter Volume Other Formats 19aug12VijayAinda não há avaliações
- Math 5 Q3 Week 8Documento8 páginasMath 5 Q3 Week 8Cristina Morante100% (1)
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4: CirclesDocumento20 páginasMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 4: CirclesJennyAinda não há avaliações
- Circumference of A Circle Lesson PlanDocumento8 páginasCircumference of A Circle Lesson PlanRhoda Mae CocjinAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Ed TechDocumento4 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in Ed TechJera Obsina100% (1)
- PygmyManual v2 - 31Documento67 páginasPygmyManual v2 - 31myplaxisAinda não há avaliações
- CLASSROOM OBSERVATION LESSON PLAN - Mathematics VDocumento3 páginasCLASSROOM OBSERVATION LESSON PLAN - Mathematics VMay Ann Somer-Maglahus Antiquisa67% (3)
- Volume Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasVolume Lesson Planccreeb150% (2)
- Sequence of Lesson Plans - Mackintosh AmberDocumento66 páginasSequence of Lesson Plans - Mackintosh Amberapi-266794577Ainda não há avaliações
- Final Complete Project Step 2Documento68 páginasFinal Complete Project Step 2api-252424167Ainda não há avaliações
- Perimeter and CircumferenceDocumento7 páginasPerimeter and CircumferenceGabrielAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics 2 LPDocumento6 páginasMathematics 2 LPRichell RueloAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Area Learning Module No. School Year and Quarter Teacher Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELC)Documento4 páginasLearning Area Learning Module No. School Year and Quarter Teacher Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELC)Nelson ManaloAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Middle SchoolDocumento6 páginasLesson Plan Middle Schoolapi-249598233Ainda não há avaliações
- Module in Teaching CircleDocumento19 páginasModule in Teaching CircleNiko EnclonaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: A. 1. IndicatorsDocumento10 páginasLesson Plan: A. 1. IndicatorsAlmira MyeishaAinda não há avaliações
- Lessonplan MathmarDocumento4 páginasLessonplan MathmarKlarineth DelimAinda não há avaliações
- Project Work For Additional Mathematics 2009Documento27 páginasProject Work For Additional Mathematics 2009grace77100% (7)
- Day 2 Chuck George Geometry Grade 9 and 10: Learning Goals / Guiding QuestionsDocumento5 páginasDay 2 Chuck George Geometry Grade 9 and 10: Learning Goals / Guiding Questionsapi-512649878Ainda não há avaliações
- Final Demo BlueprintDocumento2 páginasFinal Demo Blueprintjennelyn malaynoAinda não há avaliações
- UbD Lesson Plan GeometryDocumento5 páginasUbD Lesson Plan GeometryNiki TaylorAinda não há avaliações
- Micro Teach Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasMicro Teach Lesson Planapi-316460590Ainda não há avaliações
- MATH10-QUARTER2-MODULE3-The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesDocumento26 páginasMATH10-QUARTER2-MODULE3-The Relations Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesDreyzen GanotisiAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Problem PortfolioDocumento6 páginasUnit Problem Portfolioapi-491415315Ainda não há avaliações
- Add Math Project 2009 (Fully Completed)Documento20 páginasAdd Math Project 2009 (Fully Completed)yumicky100% (14)
- Math6 Q4 M3Documento12 páginasMath6 Q4 M3aljun.alpajaroAinda não há avaliações
- BTech J2 WK9Documento6 páginasBTech J2 WK9mellychemaAinda não há avaliações
- Demo Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasDemo Lesson Planjennelyn malaynoAinda não há avaliações
- SDO City of Malolos Math5 Q4M3 FindingAnd EstimatingTheVolumeofACubeAndRectagularPrism Macale CADocumento25 páginasSDO City of Malolos Math5 Q4M3 FindingAnd EstimatingTheVolumeofACubeAndRectagularPrism Macale CAKris Bernadette DavidAinda não há avaliações
- DivishaDocumento23 páginasDivishaDixit TagraAinda não há avaliações
- Math 10 LP4Documento8 páginasMath 10 LP4Jara ResurreccionAinda não há avaliações
- Area of CirclesDocumento6 páginasArea of CirclesliahliahliahAinda não há avaliações
- Sphere Lesson PlanDocumento5 páginasSphere Lesson PlanVenu VenuAinda não há avaliações
- West Virginia State University Lesson PlanDocumento10 páginasWest Virginia State University Lesson Planapi-283691486Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan, Students Worksheet, Dan GlossaryDocumento6 páginasLesson Plan, Students Worksheet, Dan GlossaryNurul IsmaAinda não há avaliações
- TTL02 - M03 - Using Open-Edned Tools in Facilitating Mathematics LearningDocumento12 páginasTTL02 - M03 - Using Open-Edned Tools in Facilitating Mathematics LearningJay-ar BeloyAinda não há avaliações
- Math5 Q4-M1Documento13 páginasMath5 Q4-M1LEILA LOPEZAinda não há avaliações
- Math5 - Q3 - Week8 (24pages) - M8-RegionDocumento24 páginasMath5 - Q3 - Week8 (24pages) - M8-RegionCastro, Brick's M.Ainda não há avaliações
- Find The Volume of A Cone: Mathematics/ Grade 8 Objective: Students Will Analyze Formulas For The Volumes of A Cone by Classifying TheDocumento8 páginasFind The Volume of A Cone: Mathematics/ Grade 8 Objective: Students Will Analyze Formulas For The Volumes of A Cone by Classifying Theapi-314454587Ainda não há avaliações
- Q4-Week 1 MATH5Documento2 páginasQ4-Week 1 MATH5Judy Anne NepomucenoAinda não há avaliações
- Circumferenceofcircle 140708163044 Phpapp02Documento5 páginasCircumferenceofcircle 140708163044 Phpapp02Donna Mae SuplagioAinda não há avaliações
- ADM G8 Q4 Week1 Week4Documento33 páginasADM G8 Q4 Week1 Week4Jp Pineda MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 7 Math Shape and SpaceDocumento4 páginasGrade 7 Math Shape and Spaceapi-376455150Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan 2 in GeometryDocumento14 páginasLesson Plan 2 in GeometrySho TiAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed LP in Math VDocumento5 páginasDetailed LP in Math Vcarolina younasAinda não há avaliações
- Edml 324 - Lesson Plan CirclesDocumento9 páginasEdml 324 - Lesson Plan Circlesapi-284982853Ainda não há avaliações
- Math Project For WebsiteDocumento5 páginasMath Project For Websiteapi-478007044Ainda não há avaliações
- Diameter of A Circle: ObjectivesDocumento3 páginasDiameter of A Circle: ObjectivesAngela DimassiAinda não há avaliações
- LP in MathDocumento6 páginasLP in MathYna mae BonsolAinda não há avaliações
- Multicultural Lesson Plan Jasmin JohnsonDocumento4 páginasMulticultural Lesson Plan Jasmin Johnsonapi-515125491Ainda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Area: Geometry Time Frame: 5 Days Developed By: Rodelene G. Saludez Date: October 2, 2017-October 4, 2017Documento6 páginasCurriculum Area: Geometry Time Frame: 5 Days Developed By: Rodelene G. Saludez Date: October 2, 2017-October 4, 2017Rosillie G. SaludezAinda não há avaliações
- DLP 4 CircleDocumento6 páginasDLP 4 CircleCOLAO, EVELYNAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Solving Problems Involving CirclesDocumento16 páginasMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 6: Solving Problems Involving CirclesJay Vincent MacadangdangAinda não há avaliações
- Measurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankNo EverandMeasurement of Length - Screw Gauge (Physics) Question BankAinda não há avaliações
- Maz-Kathy Kawade Final Write-Up 2015Documento2 páginasMaz-Kathy Kawade Final Write-Up 2015api-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 Math Year Plan 2015Documento4 páginasGrade 9 Math Year Plan 2015api-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Gail ReferenceletterDocumento1 páginaGail Referenceletterapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Ksa 1Documento1 páginaKsa 1api-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Ksa 6 ReflectionDocumento2 páginasKsa 6 Reflectionapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Adhd ToolboxDocumento2 páginasAdhd Toolboxapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Ell&esl ToolboxDocumento2 páginasEll&esl Toolboxapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Emotional DepressionDocumento3 páginasEmotional Depressionapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Cerebral PalsyDocumento2 páginasCerebral Palsyapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Autism ToolboxDocumento2 páginasAutism Toolboxapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- CognitiveintellectualDocumento2 páginasCognitiveintellectualapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- A Comprehensive ReflectionDocumento3 páginasA Comprehensive Reflectionapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Visual ImpairmentDocumento2 páginasVisual Impairmentapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Scan 0009Documento2 páginasScan 0009api-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan GR 3 FractionsDocumento5 páginasLesson Plan GR 3 Fractionsapi-267810292Ainda não há avaliações
- Summa Roll Cutters: S One - S Class 2 Series World Renowned Vinyl and Contour CuttersDocumento32 páginasSumma Roll Cutters: S One - S Class 2 Series World Renowned Vinyl and Contour CuttersPU PUAinda não há avaliações
- C++ Project For Graphic Scientific CalculatorDocumento34 páginasC++ Project For Graphic Scientific CalculatorManish DeyAinda não há avaliações
- G. Measurement of Angles and DirectionsDocumento3 páginasG. Measurement of Angles and DirectionsJasleneDimarananAinda não há avaliações
- En Novatop ElementDocumento32 páginasEn Novatop ElementLucian CiprianAinda não há avaliações
- Switchgear Manufacturing Company Pvt. LTD Smc-454-Rev-0Documento62 páginasSwitchgear Manufacturing Company Pvt. LTD Smc-454-Rev-0Suvendu Sekhar SabatAinda não há avaliações
- 2014oct FE PM QuestionDocumento34 páginas2014oct FE PM QuestionShwe Yee Win ThantAinda não há avaliações
- Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocumento13 páginasDownloaded From Manuals Search EngineSandro CoelhoAinda não há avaliações
- BFC3042 BFC31802Documento13 páginasBFC3042 BFC31802Zuliyah ZakariaAinda não há avaliações
- Difference Between CURE Clustering and DBSCAN Clustering - GeeksforGeeksDocumento3 páginasDifference Between CURE Clustering and DBSCAN Clustering - GeeksforGeeksRavindra Kumar PrajapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Vibration Absorbers: Scan This QR CodeDocumento4 páginasVibration Absorbers: Scan This QR CodeMohamed RaafatAinda não há avaliações
- Adr141c PDFDocumento11 páginasAdr141c PDFNamrata Shetti100% (1)
- Assignment 3Documento10 páginasAssignment 3Joseph PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Solved Problems in Soil Mechanics: SolutionDocumento5 páginasSolved Problems in Soil Mechanics: SolutionMemo LyAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 6.14: SolutionDocumento9 páginasPROBLEM 6.14: SolutionWilliam HendersonAinda não há avaliações
- Structural SteelDocumento17 páginasStructural SteelliAinda não há avaliações
- Aptitude Test For SimplificationDocumento24 páginasAptitude Test For SimplificationKodali NaniAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus IIIvectorcalculus 2011Documento82 páginasCalculus IIIvectorcalculus 2011Alfi LouisAinda não há avaliações
- Registro Evaluacion Ergonomica ROSADocumento6 páginasRegistro Evaluacion Ergonomica ROSAEryade Grace ValenzuelaAinda não há avaliações
- Mill Test Certificate: 唐山中厚板材有限公司 Tangshan Heavy Plate Co.,Documento1 páginaMill Test Certificate: 唐山中厚板材有限公司 Tangshan Heavy Plate Co.,engbilal.qaqc786Ainda não há avaliações
- Mech CVTDocumento15 páginasMech CVTsachin guptaAinda não há avaliações
- Second Periodical ExamDocumento19 páginasSecond Periodical ExamMaynard Lee Estrada GomintongAinda não há avaliações
- Ama WB NX PDFDocumento36 páginasAma WB NX PDFirinaAinda não há avaliações
- The Nature of Mathematics: "Nature's Great Books Is Written in Mathematics" Galileo GalileiDocumento9 páginasThe Nature of Mathematics: "Nature's Great Books Is Written in Mathematics" Galileo GalileiLei-Angelika TungpalanAinda não há avaliações