Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Csim2.92 - Hypoventilation
Enviado por
AinahMahani0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
19 visualizações1 páginaHypoventilation, also known as respiratory depression, occurs when ventilation is inadequate for gas exchange, causing increased carbon dioxide (CO2) and respiratory acidosis. Acute hypoventilation represents life-threatening emergencies, while chronic hypoventilation can result from defects in the metabolic respiratory control system, respiratory neuromuscular system, or ventilator apparatus. Common causes of chronic hypoventilation include COPD, obesity, central breathing apnea, respiratory neuromuscular disorders, and primary alveolar hypoventilation.
Descrição original:
CSIM stage 4
Título original
CSIM2.92 – HYPOVENTILATION
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoHypoventilation, also known as respiratory depression, occurs when ventilation is inadequate for gas exchange, causing increased carbon dioxide (CO2) and respiratory acidosis. Acute hypoventilation represents life-threatening emergencies, while chronic hypoventilation can result from defects in the metabolic respiratory control system, respiratory neuromuscular system, or ventilator apparatus. Common causes of chronic hypoventilation include COPD, obesity, central breathing apnea, respiratory neuromuscular disorders, and primary alveolar hypoventilation.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
19 visualizações1 páginaCsim2.92 - Hypoventilation
Enviado por
AinahMahaniHypoventilation, also known as respiratory depression, occurs when ventilation is inadequate for gas exchange, causing increased carbon dioxide (CO2) and respiratory acidosis. Acute hypoventilation represents life-threatening emergencies, while chronic hypoventilation can result from defects in the metabolic respiratory control system, respiratory neuromuscular system, or ventilator apparatus. Common causes of chronic hypoventilation include COPD, obesity, central breathing apnea, respiratory neuromuscular disorders, and primary alveolar hypoventilation.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
CSIM2.
92 HYPOVENTILATION
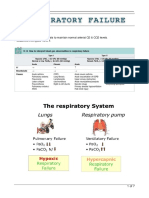
1. Also known as respiratory depression occurs when
ventilation is inadequate to perform gas exchange.
2. By definition it causes an increased concentration of
CO2 (hypercapnia) and respiratory acidosis.
3. Alveolar hypoventilation exists by definitios when
arterial PCO2 (PaCO2) increases above the normal
range of 37 to 43mmHg, but inclinically importat
hypoventilation syndromes PaCO2 is generally in the
range of 50-80mmHg.
Acute disorders
-
Which represents life-threatening emergencies.
Chronic hypoventilation
-
Can result from numerous dx entities but in all cases
the underlying mechanism involves a defect in either:
The metabolic respiratory control system
The respiratory neuromuscular system or
The ventilator apparatus
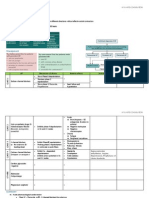
Pathophysiology of hypoventilation in syndromes related to hypoventilation
COPD
1. Inhibition of accessory and intercostal muscle breathing
2. Shallow breathing during REM sleep
3. Increase in upper airway resistance
Obesity
Central breathing apnea
Respiratory neuromuscular disorders
Primary alveolar hypoventilation
Você também pode gostar
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesNo EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsNo EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Failure: Dr. Sat Sharma Univ of ManitobaDocumento38 páginasRespiratory Failure: Dr. Sat Sharma Univ of ManitobaGonzalo Venegas RojasAinda não há avaliações
- 1.respiratory SystemDocumento42 páginas1.respiratory SystemAlexandra AlexaAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory FailureDocumento39 páginasRespiratory FailureMuntasir BashirAinda não há avaliações
- Acute RFDocumento7 páginasAcute RFLoren SangalangAinda não há avaliações
- ARDS PresentationDocumento89 páginasARDS Presentationalexandriaputera30Ainda não há avaliações
- Respiratory FailureDocumento18 páginasRespiratory FailureAyan AliAinda não há avaliações
- Lo Tropmed 1Documento49 páginasLo Tropmed 1belleAinda não há avaliações
- Control of RespirationDocumento13 páginasControl of RespirationArunchandar VelusamyAinda não há avaliações
- Running A Race at 12,000 FeetDocumento39 páginasRunning A Race at 12,000 FeetAndela Ernesto HenriqueAinda não há avaliações
- PBL #4 Respiratory Failure "Group A"Documento57 páginasPBL #4 Respiratory Failure "Group A"mohammedAinda não há avaliações
- ALCALOSIS RESPIRATORIA - VeterinariaDocumento8 páginasALCALOSIS RESPIRATORIA - VeterinariaAlanAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis Nicolaos Madias, MD ObjectivesDocumento12 páginasRespiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis Nicolaos Madias, MD Objectivesyayastoyz100% (1)
- Oxygen TherapyDocumento7 páginasOxygen TherapySudhir TyagiAinda não há avaliações
- Hypo Ventilation SyndromesDocumento22 páginasHypo Ventilation SyndromesFer45Ainda não há avaliações
- ALCALOSIS RESPIRATORIA - Veterinaria PDFDocumento6 páginasALCALOSIS RESPIRATORIA - Veterinaria PDFAlanAinda não há avaliações
- Pulmonary FailureDocumento29 páginasPulmonary FailureWengel RedkissAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory FailureDocumento7 páginasRespiratory FailureLulu100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Documento5 páginasLesson 3 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Rocelyn CristobalAinda não há avaliações
- Kaynar2018 Medscape PDFDocumento29 páginasKaynar2018 Medscape PDFberlianAinda não há avaliações
- M V ICU: Echanical Entilation INDocumento82 páginasM V ICU: Echanical Entilation INabhilashreddy45Ainda não há avaliações
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards) : Muamar Aldalaeen, RN, Mba, HCRM, Cic, Ipm, MSN, Phd. Haneen Alnuaimi, MSNDocumento59 páginasAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards) : Muamar Aldalaeen, RN, Mba, HCRM, Cic, Ipm, MSN, Phd. Haneen Alnuaimi, MSNAboodsha ShAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of Respiratory FailureDocumento8 páginasClassification of Respiratory Failurerau_rauAinda não há avaliações
- SS Visser, Pulmonology Internal Medicine UPDocumento33 páginasSS Visser, Pulmonology Internal Medicine UPRonnie JaderAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Failure: PathophysiologyDocumento5 páginasRespiratory Failure: PathophysiologyFaisal Reza AdiebAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Failure (1) .Documento36 páginasRespiratory Failure (1) .Ibrahim HemdanAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure in COPDDocumento11 páginasAcute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure in COPDbanu kuhanAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocumento3 páginasAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDIANAAinda não há avaliações
- DR Ambreen Shams NephrologistDocumento58 páginasDR Ambreen Shams NephrologistAamer NaeemAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Distress: PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaRespiratory Distress: PathophysiologyditaAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Failure: Barry WardleDocumento28 páginasRespiratory Failure: Barry Wardleapi-19826220Ainda não há avaliações
- Article 301574-PrintDocumento17 páginasArticle 301574-PrintRo RyAinda não há avaliações
- (123doc) - Tai-Lieu-Bai-Thuyet-Trinh-Tieng-Anh-De-Tai-Respiratory-AcidosisDocumento13 páginas(123doc) - Tai-Lieu-Bai-Thuyet-Trinh-Tieng-Anh-De-Tai-Respiratory-AcidosisNguyễn Hữu SangAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System: Oleh H. Errrasmus SoerasdiDocumento12 páginasRespiratory System: Oleh H. Errrasmus SoerasdiAndi TurmudziAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory FailureDocumento7 páginasRespiratory FailureJesse OnealAinda não há avaliações
- Supplementary Material 1b Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocumento7 páginasSupplementary Material 1b Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeJanela Chriselle B. TICARAinda não há avaliações
- Falla Respiratoria Fisiopato Trend Anaesth Crit Care 2013Documento5 páginasFalla Respiratoria Fisiopato Trend Anaesth Crit Care 2013Alexis Villagran ArancibiaAinda não há avaliações
- ICD IM BreathlessnessDocumento6 páginasICD IM BreathlessnessMary Christine IlangaAinda não há avaliações
- Pemicu 6 KGD AldiDocumento134 páginasPemicu 6 KGD AldiFirdaus AldyAinda não há avaliações
- 15 - Respiratory FailureDocumento33 páginas15 - Respiratory FailureSelin SakarAinda não há avaliações
- Respiration 16 Respiratory FailureDocumento31 páginasRespiration 16 Respiratory Failureapi-19641337Ainda não há avaliações
- It 25 - JHP RLDDocumento52 páginasIt 25 - JHP RLDkalajengkingkalakalaAinda não há avaliações
- SL NO Content NODocumento12 páginasSL NO Content NOPdianghunAinda não há avaliações
- Phisylogy Respiratory2 Ø Ø Ù Ù Ù Ø Ù Ù Ù ÙDocumento5 páginasPhisylogy Respiratory2 Ø Ø Ù Ù Ù Ø Ù Ù Ù Ùmaisa.alsalem4Ainda não há avaliações
- Acute Respiratory Failure LectureDocumento53 páginasAcute Respiratory Failure Lectureprototypeallhell100% (2)
- Resp InsuffDocumento30 páginasResp InsuffCLEMENTAinda não há avaliações
- L17. Askep Kritis Dan Gadar Pasien Dengan Ggguan Sistem Pernafan NontraumatikDocumento75 páginasL17. Askep Kritis Dan Gadar Pasien Dengan Ggguan Sistem Pernafan NontraumatikSepto KristianaAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory FailureDocumento8 páginasRespiratory FailureAnusha VergheseAinda não há avaliações
- 5.06b Ventilation & Sleep Apnea: I. Disorders of VentilationDocumento9 páginas5.06b Ventilation & Sleep Apnea: I. Disorders of VentilationvcAinda não há avaliações
- What Respiratory Acidosis in ABGDocumento3 páginasWhat Respiratory Acidosis in ABGBoy CartelAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory FailureDocumento22 páginasRespiratory Failuresoni gurungAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocumento8 páginasAcute Respiratory FailureCayunk NorlianaAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory FailureDocumento7 páginasRespiratory FailuremuhammadridhwanAinda não há avaliações
- 12 RLDDocumento43 páginas12 RLDNur akilaAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Failure: Presenter: Rafin, Marinel F. Ramos Marvin ODocumento28 páginasRespiratory Failure: Presenter: Rafin, Marinel F. Ramos Marvin ORenea Joy ArruejoAinda não há avaliações
- Resp 180214084710Documento72 páginasResp 180214084710Karla Geraldine Carhuas VeliAinda não há avaliações
- Management of Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocumento41 páginasManagement of Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome8515944Ainda não há avaliações
- Urinary IncontinenceDocumento1 páginaUrinary IncontinenceAinahMahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Penilaian Bahan TamhidiDocumento3 páginasPenilaian Bahan TamhidiAinahMahaniAinda não há avaliações
- CSIM2.24 - Signal TransductionDocumento6 páginasCSIM2.24 - Signal TransductionAinahMahaniAinda não há avaliações
- Penilaian Bahan MUAYYIDDocumento3 páginasPenilaian Bahan MUAYYIDAinahMahaniAinda não há avaliações
- CPTP - Pregnancy & LactatingDocumento1 páginaCPTP - Pregnancy & LactatingAinahMahaniAinda não há avaliações
- CPTP - Af & Anti CoagulationDocumento4 páginasCPTP - Af & Anti CoagulationAinahMahaniAinda não há avaliações