Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
HW #6a (Newton's Laws)
Enviado por
mathews94Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
HW #6a (Newton's Laws)
Enviado por
mathews94Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
HW #6a (Newtons Laws)
Answers
1. In the absence of an external force, a moving object will
A) stop immediately.
B) slow down and eventually come to a stop.
C) go faster and faster.
D) move with constant velocity.
Explanation: Moving objects will continue to move with a constant velocity until an
external force causes the object to accelerate.
2. A rocket moves through empty space in a straight line with constant speed. It is far
from the gravitational effect of any star or planet. Under these conditions, the force that
must be applied to the rocket in order to sustain its motion is
A) equal to its weight.
B) equal to its mass.
C) dependent on how fast it is moving.
D) zero.
Explanation: No external force is required to maintain the motion of a moving object.
The inertia of the object will keep it in motion.
3. An object sits on a frictionless surface. A 16-N force is applied to the object, and it
accelerates at 2.0 m/s2. What is the mass of the object?
A) 4.0 kg
B) 8.0 kg
C) 32 kg
D) 78 N
Explanation:Using Newtons second law F=ma, solving for m = F/a = 16N/2m/s/s=8kg
4. Starting from rest, a 4.0-kg body reaches a speed of 8.0 m/s in 2.0 s. What is the net
force acting on the body?
A) 4.0 N
B) 8.0 N
C) 16 N
D) 32 N
Explanation: F=ma = 4.0kg x (8.0m/s / 2.0s) = 4.0kg x 4.0m/s/s = 16N
5. What is the mass of an object that weighs 250 N on the surface of the Earth where the
acceleration due to gravity is 9.80 m/s2?
A) 250 kg
B) 24.5 kg
C) 25.5 kg
D) 2,450 kg
Explanation: W = mg so, m = W/g = 250N / 9.8m/s/s = 25.5kg
Free Response:
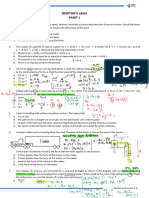
A crane is used to hoist a load of mass m1 = 500 kilograms. The load is suspended by a cable from a hook
of mass m2 = 50 kilograms, as shown in the diagram above. The load is lifted upward at a constant
acceleration of 2 m/s2.
a.
On the diagrams below draw and label the forces acting on the hook and the forces acting on the load
as they accelerate upward
T2
T1
Wh
T1
Wl
b. Determine the tension T1 in the lower cable and the tension T2 in the upper cable as the hook and and
load are accelerated upward at 2 m/s2. Use g = 10 m/s.
Wl = mg = 500kg x 10m/s/s = 5,000N
Wh= mg = 50kg x 10m/s/s = 500N
The load is accelerating upwards at 2m/s2 so there is a net force acting on the load.
Solving for the net force on the load using F=ma = 500kg x 2.0m/s/s = 1000N.
Since the load is accelerating upward the net force is directed upward as well.
So, T1 must be greater than the weight of the load by 1,000N. T1= 6,000N
The hook is accelerating upwards at 2m/s2 so there is a net force acting on the hook.
Solving for the net force on the hook using F=ma = 50kg x 2.0m/s/s = 100N
Since the hook is accelerating upward the net force is directed upward as well.
So, T2 must be greater than (T1+Wh) by 100N. T2= 6,600N
Você também pode gostar
- 3.1 ForceDocumento80 páginas3.1 ForceMuhd AfifAinda não há avaliações
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDocumento7 páginasUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnAinda não há avaliações
- As 21c Motion&ForceDocumento40 páginasAs 21c Motion&ForceHany ElGezawyAinda não há avaliações
- USTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 SolutionDocumento10 páginasUSTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 Solutionabcvn67Ainda não há avaliações
- KUE Phys 2033 Home TestDocumento3 páginasKUE Phys 2033 Home TestHailemariam WeldegebralAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocumento43 páginasNewton's Laws of MotionJhulia IlogonAinda não há avaliações
- Tut Test 4 MemoDocumento8 páginasTut Test 4 MemoVogelAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's 2nd Law of MotionDocumento14 páginasNewton's 2nd Law of MotionGarrey BrionesAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Forces Phy094Documento44 páginasChapter 3 Forces Phy094Ameera Jamal100% (1)
- Assignment 3 Solution PDFDocumento10 páginasAssignment 3 Solution PDFAhmed AttallaAinda não há avaliações
- Chap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyDocumento7 páginasChap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyTrần Hoàng Việt100% (1)
- TB Chapter4Documento18 páginasTB Chapter4Haw-ChyunAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 2Documento5 páginasQuiz 2Nurul AinAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Law of Acceleration Law of InteractionDocumento25 páginas1 Law of Acceleration Law of InteractionIah VergaraAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 4Documento5 páginasTutorial 4Winni TanAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocumento17 páginasRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBaoduy NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocumento14 páginasRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 4Documento4 páginasTutorial 4Cheryl LowAinda não há avaliações
- APPhys Newtons Laws 1Documento9 páginasAPPhys Newtons Laws 1Waleska MejiaAinda não há avaliações
- PHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsDocumento10 páginasPHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsAaisha SiddiquiAinda não há avaliações
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocumento52 páginasHapter: Conceptual ProblemsAmeen ShaikAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Sheet 3Documento5 páginasPhysics Sheet 3MariamAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer For The Test in ScienceDocumento16 páginasReviewer For The Test in ScienceKent FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- 100 Laws of Motion Practice QuestionsDocumento33 páginas100 Laws of Motion Practice QuestionsLyn RegaladoAinda não há avaliações
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections 1st Edition Katz Test Bank 1Documento35 páginasPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Foundations and Connections 1st Edition Katz Test Bank 1nell100% (44)
- Additional Applications of Newton's Laws: Conceptual ProblemsDocumento26 páginasAdditional Applications of Newton's Laws: Conceptual ProblemslizsatoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocumento10 páginasNewton's Laws of MotionkyliegAinda não há avaliações
- Examples 2 MeasurementDocumento43 páginasExamples 2 Measurementmoon starAinda não há avaliações
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 Laws of MotionDocumento29 páginasNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 Laws of MotionCREATIVE XAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Dynamics F Ma Student SlidesDocumento30 páginas1 Dynamics F Ma Student SlidesAriyah SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam Sample Physics 71Documento11 páginasFinal Exam Sample Physics 71Jay VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of MotionDocumento61 páginasChapter 4 Newton's Laws of MotionMUHAMMAD MAHMMOUD EL-QUDAFFYAinda não há avaliações
- Padilla Karl Aaron D. EN1 4STEMDocumento25 páginasPadilla Karl Aaron D. EN1 4STEMKurt Allen PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- Newtons Laws ApplicationsDocumento17 páginasNewtons Laws ApplicationsFernando AvenirAinda não há avaliações
- PhysicsDocumento5 páginasPhysicsBacillus SubtilisAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 1 Solutions November 2016Documento31 páginasPaper 1 Solutions November 2016aayush bhandariAinda não há avaliações
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 12 May Chapter 5 Laws of MotionDocumento29 páginasNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 12 May Chapter 5 Laws of Motiondaksh tyagiAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial - Newton's Law of MotionDocumento12 páginasTutorial - Newton's Law of MotionNURUL NAJIHAH KHAIRUDDINAinda não há avaliações
- ) (0.2kg) (0.4kg) / (0.4kg+0.2kg) 2.6133NDocumento2 páginas) (0.2kg) (0.4kg) / (0.4kg+0.2kg) 2.6133Nmj fullenteAinda não há avaliações
- General Physics 1 Newtons-Law-of-MotionDocumento87 páginasGeneral Physics 1 Newtons-Law-of-MotionPortia Egken100% (1)
- AssignDocumento10 páginasAssignkakaAinda não há avaliações
- Forum Diskusi 3-2 - DNDADocumento13 páginasForum Diskusi 3-2 - DNDAAayunda AriellaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Chapter 4 ProblemsDocumento22 páginasPhysics Chapter 4 ProblemscjbthegeniusAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 72 Samplex Midyear 2016Documento12 páginasPhysics 72 Samplex Midyear 2016Charmaine ColetaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Problem SetDocumento3 páginasPhysics Problem SetLilian GauiranAinda não há avaliações
- Forum Diskusi 3-2 (Force and Motion and Energy and Ork) .Id - enDocumento13 páginasForum Diskusi 3-2 (Force and Motion and Energy and Ork) .Id - enAayunda AriellaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lab Activity 4 Midterm - Group 2Documento6 páginasPhysics Lab Activity 4 Midterm - Group 2Stefhanie Brin BotalonAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 ExercisesDocumento6 páginasUnit 3 Exercises张书Ainda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstDocumento34 páginasPROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstMarj Ladica MangaAinda não há avaliações
- The Laws of Motion: Multiple ChoiceDocumento8 páginasThe Laws of Motion: Multiple Choicealiya mAinda não há avaliações
- Cavendish University Zambia: School of MedicneDocumento2 páginasCavendish University Zambia: School of MedicneMuhau ZvikomboreroAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Documento12 páginasPhysics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Emmyr FaiqAinda não há avaliações
- Ce2 Sample2Documento5 páginasCe2 Sample2ParZiValAinda não há avaliações
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocumento6 páginasTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoAinda não há avaliações
- 2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsDocumento24 páginas2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsTiff VoAinda não há avaliações
- Work and EnergyDocumento124 páginasWork and Energyjack100% (1)
- Physics 122 Problem SetDocumento86 páginasPhysics 122 Problem SetCarmen DraghiaAinda não há avaliações
- MaayohonDocumento22 páginasMaayohonkingds2006Ainda não há avaliações
- Flutter-A Scary Instability: AAE 556 - Aeroelasticity AAE 556 - AeroelasticityDocumento19 páginasFlutter-A Scary Instability: AAE 556 - Aeroelasticity AAE 556 - Aeroelasticitymathews94Ainda não há avaliações
- 8 Calorimetry 2010Documento8 páginas8 Calorimetry 2010mathews94Ainda não há avaliações
- Fox 7th ISM Ch07-13Documento1.079 páginasFox 7th ISM Ch07-13d280299100% (4)
- Problem Chapter 9Documento48 páginasProblem Chapter 9Syahid ZamaniAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 Refrigeration CyclesDocumento20 páginasChapter 11 Refrigeration Cycleskalite123Ainda não há avaliações
- Superhero ExampleDocumento8 páginasSuperhero Exampleapi-343241309Ainda não há avaliações
- Neet Test: GMM R GMM R GMM 4 RDocumento6 páginasNeet Test: GMM R GMM R GMM 4 RNavin RaiAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Machine: GovernorsDocumento68 páginasTheory of Machine: GovernorsSomnath SomadderAinda não há avaliações
- Motion Loads Pal ADocumento11 páginasMotion Loads Pal ABoris Stheven Sullcahuaman JaureguiAinda não há avaliações
- Work Power Energy JEE TestDocumento6 páginasWork Power Energy JEE TestAman RolandAinda não há avaliações
- M1 Kinematics of A Particle Moving in A Straight LineDocumento51 páginasM1 Kinematics of A Particle Moving in A Straight LineSolar Warden100% (1)
- Lab 1 Free Fall GEC - CEA21 - OERSTEDDocumento6 páginasLab 1 Free Fall GEC - CEA21 - OERSTEDLee-Ann LimAinda não há avaliações
- Electrostatics: Electrostatic Force, Field Intensity & Potential Worksheet-1Documento19 páginasElectrostatics: Electrostatic Force, Field Intensity & Potential Worksheet-1Kothari RaoAinda não há avaliações
- High Energy Physics MCQDocumento9 páginasHigh Energy Physics MCQpriyaAinda não há avaliações
- 60 ProblemsDocumento40 páginas60 ProblemsAttar Raha100% (1)
- Que. KinematicsDocumento20 páginasQue. KinematicsIqbal AdilAinda não há avaliações
- SosoDocumento2 páginasSosoChaitanya GaurAinda não há avaliações
- Pravilo Leve RukeDocumento1 páginaPravilo Leve RukeSlobodan MilosavljevicAinda não há avaliações
- NOTES - MOTION AND TIME CLASS VIIsahfghfjfgjhfgDocumento8 páginasNOTES - MOTION AND TIME CLASS VIIsahfghfjfgjhfgForex lolAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 1 - Problems With SolutionsDocumento47 páginasPhysics 1 - Problems With SolutionsMichaelAinda não há avaliações
- Static Torque PDFDocumento43 páginasStatic Torque PDFlylyho91Ainda não há avaliações
- Impulse and Momentum and Impact: Prepared By: Engr. Lucia V. Ortega 4/18/2021 1Documento12 páginasImpulse and Momentum and Impact: Prepared By: Engr. Lucia V. Ortega 4/18/2021 1Nelson FelixAinda não há avaliações
- ACTIVITY 3 - The Acceleration Due To Gravity - CRUZ ARJAYDocumento3 páginasACTIVITY 3 - The Acceleration Due To Gravity - CRUZ ARJAYArjay Francisco CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Electric Field LAb 2Documento2 páginasElectric Field LAb 2Muhammad Tayyab MadniAinda não há avaliações
- G18 - Dynamics - Work and Energy - ProblemsDocumento26 páginasG18 - Dynamics - Work and Energy - ProblemsMohammed AlryaniAinda não há avaliações
- Circular Motion (MCQ)Documento17 páginasCircular Motion (MCQ)Laxman Selvam100% (5)
- Section A (10 Marks) Instructions: Answer All The Questions in This SectionDocumento7 páginasSection A (10 Marks) Instructions: Answer All The Questions in This SectionAHMAD FAISALAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Physics Notes ch01 Electric Charges and Field PDFDocumento3 páginas12 Physics Notes ch01 Electric Charges and Field PDFVirendra GaurAinda não há avaliações
- Swings and Slides: Ann-Marie Pendrill and Gary WilliamsDocumento7 páginasSwings and Slides: Ann-Marie Pendrill and Gary WilliamsVictor CantuárioAinda não há avaliações
- PHYS Gause's LawDocumento5 páginasPHYS Gause's LawXuetong YanAinda não há avaliações
- Class Xi - Physics Set A Class Xi - Physics Set ADocumento3 páginasClass Xi - Physics Set A Class Xi - Physics Set APriyanka Mann KahlonAinda não há avaliações
- Time Distance and Train SolutionDocumento24 páginasTime Distance and Train Solutionimd mdlAinda não há avaliações
- Daya Dan Gerakan: Force and MotionDocumento21 páginasDaya Dan Gerakan: Force and MotionzinziemeewahAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Class Ix For 2017 18Documento120 páginasPhysics Class Ix For 2017 18J SoujanyaAinda não há avaliações
- Objectives - You Need To Balance Two Forks With A Toothpick in A Glass Without WaterDocumento3 páginasObjectives - You Need To Balance Two Forks With A Toothpick in A Glass Without WaterMark Joseph SorianoAinda não há avaliações