Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Impact Test
Enviado por
wayshDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Impact Test
Enviado por
wayshDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Introduction:
Materials are used to build load-bearing structures. An engineer
needs to know if the material will survive the conditions that the
structure will see in service. Important factors that adversely
affect the toughness of a structure include low-test
temperatures, extra loading and high strain rates due to over
pressurization or impacts and the effect of stress concentrations
such as notches and cracks. These all tend to encourage fracture.
To some extent, the complex interaction of these factors can be
included in the design process by using fracture mechanics
theory. Tests for the impact toughness, such as the Charpy
Impact Test , were developed before fracture mechanics theory
was available. The impact test is a method for evaluating the
relative toughness of engineering materials. The Charpy impact
test continues to be used nowadays as an economical quality
control method to assess the notch sensitivity and impact
toughness of engineering materials. It is usually used to test the
toughness of metals. Similar tests can be used for polymers,
ceramics and composites. The charpy impact test measures the
energy absorbed by the high strain rate fracture of a standard
notched specimen.
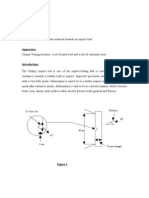
In the Charpy Impact Test, the specimen is supported as a simple
beam with a notch in the center. The specimen is supported so
that the notch is on the vertical face away from the point of
impact. Figure 3 and 4 show the dimensions of the Charpy Impact
Test specimen and the positions of the striking edge of the
pendulum and the specimen in the anvil. The specimen is broken by
the impact of a heavy pendulum hammer, falling through a fixed
distance (constant potential energy) to strike the specimen at a
fixed velocity (constant kinetic energy). Tough materials absorb
a lot of energy when fractured and brittle materials absorb very
little energy.
The Izod pendulum test configuration served as the standard in
impact testing in the plastics and metals industry for many years.
The problems with the Izod pendulum test involve several
parameters which can drastically alter the results if not strictly
controlled.
Position of the Charpy Impact Test specimen on the impact test machine
Objectives:
To test selected specimens under conditions of shock loading at
fixed temperature. Also to measure the energy absorbed in
breaking a notched specimen.
Difference between Izod and Charpy Methods
Izod vs. Charpy Methods
The izod test involved the striker, the testing material, and the
pendulum. The striker was fixed at the end of the pendulum. The
test material was fastened at a vertical position at the bottom,
and the notch was facing the striker. The striker swings
downward, hitting the test material in the middle, at the bottom
of it’s swing, and is left free at the top. The notch is placed to
concentrate the stress, and provoke delicate failure. It lowers
distortion and decreases the ductile fracture. The test was done
easily and quickly to examine the quality of the materials, and
test whether it meets the specific force of collision properties.
It is also used to evaluate the materials for overall hardiness. It
is not applicable to compound materials because of the influence
of complicated and inconsistent failure modes.
The notch is very important because it can affect the result of
the test. The making of the notch has been a problem. Initially,
the radius of the notch is crucial. The radius should not change.
It has an essential effect on the competence of the sample to
absorb the collision. The blades in the notch can overheat the
polymers, and deteriorate the materials surrounding the notch,
which could lead to an inaccurate test result. The Izod method
chose a short projection, supported at one end, to produce better
steel tools for cutting metal.
The Charpy method includes striking an appropriate test material
with a striker fastened at the end of a pendulum. The test
material is secured horizontally in place at both ends, and the
striker hits the center of the test material, behind a machined
notch. The notch is positioned away from the striker, fastened in
a pendulum. The test material usually measures 55×10x10
millimeters. The Charpy method has a machined notch across one
of the larger faces. There are two types of charpy notch, a V-
notch or a U-notch. The V-notch, or the AV-shaped notch,
measures 2 millimeters deep, with a 45 degree angle and 0.25
millimeter radius, parallel to the base. The U-notch, or keyhole
notch, is 5 millimeters deep notch, with a 1 millimeter radius at
the bottom of the notch. Higher speeds and collision energy could
be achieved in a vertical style fall. This method proved to be
reliable, and gave qualitative collision data.
Summary:
1. In the Izod method, the test material was placed in a vertical
position, while in the Charpy method, the test material was placed
horizontally.
2. The notch in the izod test is facing the striker, fastened in a
pendulum, while in the charpy test; the notch is positioned away
from the striker.
3. In the Charpy method, there are two kinds of notches, the V-
notch and the U-notch, while in the Izod method; there is only
one kind of notch.
Ductile fracture is better because of the following
reasons:
a) More energy needed in the ductile fracture because
it is a tough material
b) Brittle fracture happens quickly without warning
while the ductile fracture took a longer time before
the whole process to happen
Error source:
1. Use sensors to measure resistance of air so that we
could calculate the energy losses by friction more
accurate.
2. Try to place the centre of the notch on the specimen
to be at the centre of the impacting load.
3. The data collected should be taken carefully vertically
so that to minimize the error from reading it.
4. Using modern testing equipments that use digital
readers and load amplifiers to reach the most accurate
data.
Conclusion:
From the Charpy and izod impact test, brass undergoes
brittle fracture while the brass undergoes ductile
fracture. More energy is absorbed by steel shows that it
is more suitable to be use in the structural construction
that expose to high load for example: car body.
Você também pode gostar
- Complete Impact Test PDFDocumento9 páginasComplete Impact Test PDFKalKatu MaLam86% (22)
- Charpy Impact Test AssigmDocumento13 páginasCharpy Impact Test AssigmFaiz Sufyan0% (1)
- Impact TestDocumento8 páginasImpact TestRashid Mehmood100% (1)
- Impact TestDocumento4 páginasImpact TestKumar SamreshAinda não há avaliações
- Charpy TestDocumento10 páginasCharpy TestAsad AliAinda não há avaliações
- Impact Test Lab ReportDocumento9 páginasImpact Test Lab ReportRedzuan KamarudinAinda não há avaliações
- Title: Impact Test: Figure 1: Izod and Charpy TestDocumento9 páginasTitle: Impact Test: Figure 1: Izod and Charpy Testonkod1Ainda não há avaliações
- Charpy Impact Test - Lab ReportDocumento18 páginasCharpy Impact Test - Lab ReportChitra Nadia100% (1)
- Charpy TestDocumento7 páginasCharpy TestKa Chian100% (1)
- Iimpact TestDocumento5 páginasIimpact TestKamal JayarajAinda não há avaliações
- Impact TestDocumento8 páginasImpact TestMustafa Ani100% (1)
- Lab Report Impact Test (Strength Material)Documento13 páginasLab Report Impact Test (Strength Material)Redzuan Kamarudin0% (1)
- Vickers Hardness TestDocumento9 páginasVickers Hardness TestMoiz Amir100% (1)
- Your Name: Ulises Jose Corona Name of The Course: MAE2160 Materials Science Lab Date: Report DateDocumento7 páginasYour Name: Ulises Jose Corona Name of The Course: MAE2160 Materials Science Lab Date: Report DateUlises Corona100% (4)
- Torsion Test Discussion by ShanDocumento4 páginasTorsion Test Discussion by Shanshangovinna_1078109050% (8)
- Vickers Hardness TestDocumento9 páginasVickers Hardness TestMazlin AzuraAinda não há avaliações
- Charpy Impact TestDocumento4 páginasCharpy Impact TestChinmay Deo80% (5)
- Impact Test ReportDocumento7 páginasImpact Test Reportgammoora92% (25)
- Vicker HardnessDocumento3 páginasVicker HardnessEhsanulhaq786100% (1)
- Charpy Impact Testing Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasCharpy Impact Testing Lab ReportM Kafeel KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Torsion Test Lab Report PDFDocumento40 páginasTorsion Test Lab Report PDFengkuAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 3 Tensile TestDocumento22 páginasExp 3 Tensile TestJagathisswary SatthiAinda não há avaliações
- Objectives: Experiment: Fatigue TestingDocumento8 páginasObjectives: Experiment: Fatigue TestingShruti Raveendran100% (1)
- Tensile TestDocumento9 páginasTensile Testcheyaya80% (5)
- Testing and Evaluation of Engineering MaterialsDocumento5 páginasTesting and Evaluation of Engineering MaterialsFAHED AYYAD100% (1)
- 3-Exp#03 Tensile TestDocumento7 páginas3-Exp#03 Tensile TestD7ooM_612Ainda não há avaliações
- Charpy TestDocumento4 páginasCharpy Testcheyaya90% (10)
- Bending Test (Report) eDocumento14 páginasBending Test (Report) eWesam Maleh100% (1)
- Charpy Impact TestDocumento2 páginasCharpy Impact TestGanim Shed100% (1)
- IZod Impact TestDocumento2 páginasIZod Impact TestAnasGujjar100% (1)
- Tensile TestDocumento6 páginasTensile Testkinwai5557100% (1)
- Experiment No. (2) : Determination of Liquid Viscosity by Stock'S MethodDocumento5 páginasExperiment No. (2) : Determination of Liquid Viscosity by Stock'S MethodKawar Abid100% (1)
- Exp-04 Melt Flow IndexDocumento5 páginasExp-04 Melt Flow IndexMahazabin MimAinda não há avaliações
- 2 - Charpy - ImpactDocumento6 páginas2 - Charpy - ImpactMuzamil Hasan0% (1)
- Lab Report - Impact TestingDocumento13 páginasLab Report - Impact Testingapi-404653452100% (1)
- Hardness Test: Department of Mechanical & Manufacturing Engineering Faculty of Engineering, University of Putra MalaysiaDocumento5 páginasHardness Test: Department of Mechanical & Manufacturing Engineering Faculty of Engineering, University of Putra MalaysiaNurul Siddiqah Whakiddin100% (1)
- Tensile Test Lab ReportDocumento9 páginasTensile Test Lab ReportTan Xuennie0% (1)
- Beam Bending Lab ReportDocumento22 páginasBeam Bending Lab Reportimlioh_ih50% (2)
- Heat Treatment ReportDocumento7 páginasHeat Treatment ReportEric Fitterling0% (1)
- ME 457 Experimental Solid Mechanics (Lab) Torsion Test: Solid and Hollow ShaftsDocumento5 páginasME 457 Experimental Solid Mechanics (Lab) Torsion Test: Solid and Hollow Shaftsanon-735529100% (2)
- Hardness TestDocumento8 páginasHardness TestSyahirah JuhariAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Treatment Lab ReportDocumento12 páginasHeat Treatment Lab ReportCarl Behlmer100% (5)
- Impact Test Ravi Agarwal 09003017 Group GDocumento8 páginasImpact Test Ravi Agarwal 09003017 Group GRavi Agarwal100% (1)
- 11 Heat TreatmentDocumento5 páginas11 Heat TreatmentamokhtaAinda não há avaliações
- Rockwell Hardness Testing of Metallic Materials Lab ReportDocumento5 páginasRockwell Hardness Testing of Metallic Materials Lab ReportEmıły WınıfredAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Shubham Navnath Taware Roll No.: M2A67 Practical Classtest 8Documento3 páginasName: Shubham Navnath Taware Roll No.: M2A67 Practical Classtest 8rajeshAinda não há avaliações
- Difference Between Izod and Charpy MethodsDocumento2 páginasDifference Between Izod and Charpy Methodsvasudeva yasasAinda não há avaliações
- Impact Hardness TestDocumento7 páginasImpact Hardness TestAse Sharew100% (1)
- MOM LAB REPPORT No 4Documento10 páginasMOM LAB REPPORT No 4Faizan AnjumAinda não há avaliações
- Impact Test Lab ReportDocumento7 páginasImpact Test Lab Reportmohmmad othmanAinda não há avaliações
- Viva Voce Som LabDocumento5 páginasViva Voce Som LabSudhanshu KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Georges Augustin Albert CHARPY (1865-1945)Documento10 páginasGeorges Augustin Albert CHARPY (1865-1945)Nur Hidayatul NadhirahAinda não há avaliações
- Impact Test of Metal SpecimenDocumento18 páginasImpact Test of Metal SpecimenmosaddakAinda não há avaliações
- Impact Test: College of Engineering Salahaddin University-Erbil Academic Year 2019-2020Documento7 páginasImpact Test: College of Engineering Salahaddin University-Erbil Academic Year 2019-2020Rayan IAinda não há avaliações
- University of Jordan School of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentDocumento9 páginasUniversity of Jordan School of Engineering Mechanical Departmentjohn rozz bbAinda não há avaliações
- THE MICROSTRUCTURAL EXAMINITIONS OF METALS by Odewole TemidayoDocumento8 páginasTHE MICROSTRUCTURAL EXAMINITIONS OF METALS by Odewole Temidayostephenoladipo21Ainda não há avaliações
- Q2-Materials TestingDocumento58 páginasQ2-Materials Testingapi-348195110Ainda não há avaliações
- Materials Testing: Deadlines: Assignment 1 Submission: 22 December 2020 Assignment 2 Submission: 19 January 2021Documento41 páginasMaterials Testing: Deadlines: Assignment 1 Submission: 22 December 2020 Assignment 2 Submission: 19 January 2021Jo okAinda não há avaliações
- Material Lab 5Documento6 páginasMaterial Lab 521pwind0685Ainda não há avaliações
- Waleed Ahmed Shreim-CVDocumento3 páginasWaleed Ahmed Shreim-CVwayshAinda não há avaliações
- Waleed Ahmed Shreim - CVDocumento2 páginasWaleed Ahmed Shreim - CVwayshAinda não há avaliações
- Welding MetallurgyDocumento37 páginasWelding Metallurgyhemant1886100% (4)
- Waleed Ahmed Yousef ShreimDocumento1 páginaWaleed Ahmed Yousef ShreimwayshAinda não há avaliações
- Hardness Test: University of Jordan Mechanical Engineering Department Strength of Materials LabDocumento14 páginasHardness Test: University of Jordan Mechanical Engineering Department Strength of Materials Labwaysh88% (8)
- Rights As Bribes ResaltadoDocumento89 páginasRights As Bribes ResaltadoAndresAmarillaAinda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Vitae: Lungnila Elizabeth School of Social Work, Senapati, Manipur August 2016-June 2018Documento4 páginasCurriculum Vitae: Lungnila Elizabeth School of Social Work, Senapati, Manipur August 2016-June 2018Deuel khualAinda não há avaliações
- SDS SheetDocumento8 páginasSDS SheetΠΑΝΑΓΙΩΤΗΣΠΑΝΑΓΟΣAinda não há avaliações
- Followup Centres May12Documento14 páginasFollowup Centres May12Suresh NagpalAinda não há avaliações
- Democracy in SomalilandDocumento118 páginasDemocracy in SomalilandAbdirahman IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- LTRC FInal Report 558 Development of Performance-Based Specifications For Louisiana Asphalt MixturesDocumento149 páginasLTRC FInal Report 558 Development of Performance-Based Specifications For Louisiana Asphalt MixtureswalaywanAinda não há avaliações
- Evolution of Corporate Social Responsibility in IndiaDocumento12 páginasEvolution of Corporate Social Responsibility in IndiaVinay VinuAinda não há avaliações
- Beed 3a-Group 2 ResearchDocumento65 páginasBeed 3a-Group 2 ResearchRose GilaAinda não há avaliações
- The Effectiveness of Peppermint Oil (Mentha X Pepipirita) As Mosquito RepellentDocumento4 páginasThe Effectiveness of Peppermint Oil (Mentha X Pepipirita) As Mosquito RepellentKester PlaydaAinda não há avaliações
- Heirs of Candelaria V RomeroDocumento2 páginasHeirs of Candelaria V Romeromoniquehadjirul100% (1)
- RUBEEEEDocumento44 páginasRUBEEEEAhlyssa de JorgeAinda não há avaliações
- Child Development Assessment Tools in Low-Income and Middle-Income CountriesDocumento9 páginasChild Development Assessment Tools in Low-Income and Middle-Income Countriesalibaba1888Ainda não há avaliações
- Muslimah's Handbook of PurityDocumento60 páginasMuslimah's Handbook of PurityMuadh KhanAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 Civil Law II CasesDocumento270 páginas2016 Civil Law II CasescarinokatrinaAinda não há avaliações
- NyirabahireS Chapter5 PDFDocumento7 páginasNyirabahireS Chapter5 PDFAndrew AsimAinda não há avaliações
- BangaloreDocumento1.229 páginasBangaloreVikas RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- Call Me by Your Name-SemioticsDocumento2 páginasCall Me by Your Name-SemioticsJoevic FranciaAinda não há avaliações
- Credit Transactions Case Digestpdf PDFDocumento241 páginasCredit Transactions Case Digestpdf PDFLexa L. DotyalAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento13 páginasChapter 1Jerard AnciroAinda não há avaliações
- HaDocumento15 páginasHaNicole Easther GabilangosoAinda não há avaliações
- Per User Guide and Logbook2Documento76 páginasPer User Guide and Logbook2Anthony LawAinda não há avaliações
- A0 Unit1 Lesson3A PP GB AmbDocumento9 páginasA0 Unit1 Lesson3A PP GB AmbMasterkolo KamisAinda não há avaliações
- ADDIE - Model - For - E-Learning - Sinteza2017 - Corr-With-Cover-Page-V2 (New)Documento6 páginasADDIE - Model - For - E-Learning - Sinteza2017 - Corr-With-Cover-Page-V2 (New)arief m.fAinda não há avaliações
- Project RealDocumento4 páginasProject RealKenneth Jay BagandoAinda não há avaliações
- Adeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFDocumento12 páginasAdeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFAngel SánchezAinda não há avaliações
- Kosem SultanDocumento2 páginasKosem SultanAmaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Average and Instantaneous AccelerationDocumento35 páginasAverage and Instantaneous AccelerationaraneyaAinda não há avaliações
- Isc Class 11 Maths Sample Paper Model 1Documento2 páginasIsc Class 11 Maths Sample Paper Model 1Gaurav ShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- I. Inversion: Grammar: Expressing EmphasisDocumento7 páginasI. Inversion: Grammar: Expressing EmphasisSarah BenraghayAinda não há avaliações
- Kalki ProjectDocumento3 páginasKalki ProjectMandar SohoniAinda não há avaliações