Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
This Paper Contains FIVE Questions. You Are To Attempt FOUR
Enviado por
AmyRapaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
This Paper Contains FIVE Questions. You Are To Attempt FOUR
Enviado por
AmyRapaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
B.ENG. (HONS.) COURSE
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STREAM
YEAR II SEMESTER I
JANUARY 2005 SESSION OF EXAMINATIONS
28th January 2005
MEC 2006 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
KINEMATICS
0915 - 1145 hours
This paper contains FIVE questions. You are to attempt FOUR.
1.
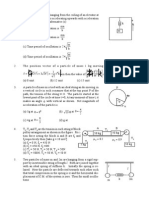
A particle of mass 10 kg is projected vertically upwards with an initial velocity of
100 m/s in a medium which exerts a resistance to the motion equal to 10v N where v is
the velocity of the particle in m/s.
Determine the maximum height reached by the particle and the time taken to attain it.
Note
xd x
= x a ln (a = x )
+ x
(25 marks)
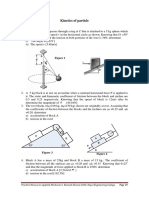
2.
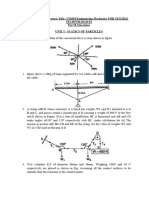
Figure 1 shows part of a mechanism in which a plate ABC of quadrant shape and
pivoted at C is moved by a linear actuator against the action of a torsion spring. The
mass of the moving part of the actuator is 2 kg and the quadrant, which may be assumed
uniform has a mass of 10 kg and radius 0.2 m. The spring has a stiffness of 250 Nm/rad
and in the position shown exerts an anticlockwise torque of 100 Nm on the quadrant.
The mechanism is contained in a horizontal plane.
If a constant force of 1000 N is applied to the ram of the actuator, determine the angular
velocity of the quadrant after 10 of rotation clockwise from the position shown.
A
0.18 m
B
10
C
Figure 1
(25 marks)
Page 1 of 3
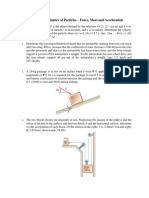
3.
In the system shown in Figure 2 the mass of the compound disc A is 90 kg and its
radius of gyration is 0.4 m. The pulley B may be assumed light and its pivot is
frictionless. The block C has a mass of 45 kg.
If disc A rolls without slip, determine the velocity of the block C 2 seconds after the
system is released from rest.
(25 marks)
B
R
r
A
r = 0.3 m
R = 0.6 m
Figure 2
4.
Figure 3 shows a test rig for inspecting steel balls. The balls are ejected at A with a
horizontal velocity of 1 m/s and after falling through 0.1 m rebound from a hard steel
surface over the guard BC. If balls having a coefficient of restitution of less than 0.8
are to be rejected, calculate the value of h and the corresponding distance s.
(25 marks)
A
1 m/s
B
H = 0.1 m
h
s
Figure 3
Page 2 of 3
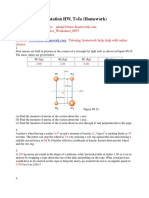
5.
In the mechanism shown in Figure 4, the driving crank CD rotates about D and when in
the position shown it has an angular velocity of 25 rad/s and an angular acceleration of
500 rad/s2 both clockwise. CD = 90 mm and AD = 120 mm.
For this position determine
(a) the velocity and acceleration of sliding between the block C and the rod AB
and
(b) the angular acceleration of the link AB.
(25 marks)
B
C
25 rad/s
500 rad/s2
60
Figure 4
Page 3 of 3
Você também pode gostar
- All AnswersDocumento22 páginasAll AnswersNadiatul JannahAinda não há avaliações
- Examples MomentumDocumento9 páginasExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- Tutorial 2 NewtonsDocumento4 páginasTutorial 2 Newtons2B Dai Ko DUPLICATEAinda não há avaliações
- T2 Force - AccelerationDocumento4 páginasT2 Force - AccelerationDipesh PanditAinda não há avaliações
- Ph.D. Qualifying Examination: Fall 2011Documento4 páginasPh.D. Qualifying Examination: Fall 2011saratAinda não há avaliações
- TUTORIAL 3 (Kinetics of Particles)Documento6 páginasTUTORIAL 3 (Kinetics of Particles)Hareez FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Semester 2 2013/2014: Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringDocumento7 páginasSemester 2 2013/2014: Faculty of Engineering Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing EngineeringBong Kuek KongAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics TutorialDocumento23 páginasMechanics TutorialDipesh PanditAinda não há avaliações
- Module 6Documento5 páginasModule 6John Kennedy EvangelistaAinda não há avaliações
- Applied MechanicsDocumento3 páginasApplied MechanicssushilAinda não há avaliações
- Es 221 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: I. Kinetics of A Particle (Force & Acceleration)Documento4 páginasEs 221 - Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: I. Kinetics of A Particle (Force & Acceleration)Jerard BalalaAinda não há avaliações
- 9A01101 Engineering MechanicsDocumento8 páginas9A01101 Engineering MechanicssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Ctut13 PDFDocumento1 páginaCtut13 PDFNik Nazri Nik GhazaliAinda não há avaliações
- Test116 3 PlusansDocumento5 páginasTest116 3 PlusansAvnish GargAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-KineticsDocumento36 páginasChapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-Kineticsعمر صرانAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 0809Documento10 páginasEngineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 0809Amirul AizatAinda não há avaliações
- 004 Problem Sheet 4 - Energy Methods For Particles DEN5108 PS4-2Documento4 páginas004 Problem Sheet 4 - Energy Methods For Particles DEN5108 PS4-2JoséRobertoAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Unit AssignmentDocumento1 página3 Unit AssignmentSagar YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Examples 2 MeasurementDocumento43 páginasExamples 2 Measurementmoon starAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 8 Motion MIDocumento3 páginasTutorial 8 Motion MIPAWAN SHRESTHAAinda não há avaliações
- Essay QuestionDocumento8 páginasEssay QuestionharshanauocAinda não há avaliações
- Honors Physics Rotation HW, T Ia (Homework) : Include File Name: Physics - Worksheet - 0057Documento4 páginasHonors Physics Rotation HW, T Ia (Homework) : Include File Name: Physics - Worksheet - 0057Jose Miguel ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment - 1 Fall 2022Documento4 páginasAssignment - 1 Fall 2022junaidAinda não há avaliações
- HW2Documento3 páginasHW2Erwin Ostol ManzanoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Newton - S Laws of Motion - Problem SetsDocumento5 páginasChapter 3 Newton - S Laws of Motion - Problem SetsSimon ManansalaAinda não há avaliações
- MomentumDocumento8 páginasMomentumPraphul Malol0% (1)
- Problem Set3Documento3 páginasProblem Set3Jonnette Luisa BacadAinda não há avaliações
- Wiley Part2Documento9 páginasWiley Part2Andrian Dean Handika CsTahtaAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial TwoDocumento5 páginasTutorial TwoParas gurungAinda não há avaliações
- R (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageDocumento4 páginasR (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageOlojo Oluwasegun EmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- MechanicsDocumento9 páginasMechanicsHarshal Dengle100% (1)
- II B.tech I Sem Question Bank For r18Documento30 páginasII B.tech I Sem Question Bank For r18saiharish634Ainda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics Q.paperDocumento8 páginasEngineering Mechanics Q.paperYogeswara KayaguralaAinda não há avaliações
- Formatted MechDocumento14 páginasFormatted MechVennela VennelaAinda não há avaliações
- R7100306 Classical MechanicsDocumento2 páginasR7100306 Classical MechanicssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Tut1 Part29Documento1 páginaTut1 Part29AnmolAinda não há avaliações
- Tut1 Part29 PDFDocumento1 páginaTut1 Part29 PDFAnmolAinda não há avaliações
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Documento5 páginasUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Vivin MathewAinda não há avaliações
- Part B Question BankDocumento9 páginasPart B Question BankSriram SrinivasanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocumento8 páginasChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Exam Covering Newtons Laws (Chapter 5 & 6 in Serway)Documento9 páginasPractice Exam Covering Newtons Laws (Chapter 5 & 6 in Serway)Hasan AlomariAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomDocumento6 páginasMechanics: Graph Paper Is Available in The Examination RoomIoana BoilaAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 2Documento3 páginasTutorial 2Muhammed IfkazAinda não há avaliações
- ENGN 37 HomeworkDocumento25 páginasENGN 37 HomeworkLucia AntoniusAinda não há avaliações
- Monowar Wadud Hridoy: Engineering DynamicsDocumento23 páginasMonowar Wadud Hridoy: Engineering DynamicsNiha chowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Cbse Xi Physics Test PapersDocumento14 páginasCbse Xi Physics Test PapersBhavesh DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Engg Mech Unit 3Documento4 páginasEngg Mech Unit 3Piyush BhandariAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocumento9 páginasMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruAinda não há avaliações
- TUTORIAL 5 (Kinetics of RBs in Plane Motion)Documento7 páginasTUTORIAL 5 (Kinetics of RBs in Plane Motion)Hareez FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- SQP Hy 11 2022 23Documento13 páginasSQP Hy 11 2022 23It's all About fitnessAinda não há avaliações
- CO-4 Assignment QuestionsDocumento7 páginasCO-4 Assignment QuestionsrajeswariAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocumento9 páginasMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruAinda não há avaliações
- Taller Fisica EcciDocumento5 páginasTaller Fisica EcciFernando TaleroAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 8Documento2 páginasTutorial 8fawwazfauzi2004Ainda não há avaliações
- r5100105 Applied MechanicsDocumento2 páginasr5100105 Applied MechanicssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Dynamics QuestionsDocumento5 páginasApplied Dynamics QuestionsKritamMaharjanAinda não há avaliações
- Fiitjee 40Documento4 páginasFiitjee 40BHAAJI0001Ainda não há avaliações
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- All Rhythm Worksheets in One FileDocumento28 páginasAll Rhythm Worksheets in One FileAmyRapa100% (1)
- Major Scale PDFDocumento1 páginaMajor Scale PDFGeraldAinda não há avaliações
- Count Rhythms With Notes 1Documento2 páginasCount Rhythms With Notes 1AmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Count Rhythms With Notes and Rests 2Documento3 páginasCount Rhythms With Notes and Rests 2AmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 1 NotesDocumento5 páginasGrade 1 NotesAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Music Theory Worksheet 14 Dotted Quarter Notes PDFDocumento1 páginaMusic Theory Worksheet 14 Dotted Quarter Notes PDFTeganMiller0% (1)
- Count Rhythms With Notes and Rests 1Documento2 páginasCount Rhythms With Notes and Rests 1AmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Theory Worksheet Major Scale Notation PDFDocumento1 páginaTheory Worksheet Major Scale Notation PDFRonan SharkeyAinda não há avaliações
- Music Theory Worksheet 9 Ledger LinesDocumento1 páginaMusic Theory Worksheet 9 Ledger LinesKaty-Gianina Strugaru83% (6)
- Music Theory Worksheet 8 Grand Staff PDFDocumento1 páginaMusic Theory Worksheet 8 Grand Staff PDFTeganMillerAinda não há avaliações
- Music Theory Worksheet 12 Eighth Notes PDFDocumento1 páginaMusic Theory Worksheet 12 Eighth Notes PDFAmyRapa100% (1)
- Music Theory Worksheet 17 Sharps PDFDocumento1 páginaMusic Theory Worksheet 17 Sharps PDFNoreen Ann Flynn0% (2)
- Music Theory Worksheet 20 Natural Minor ScaleDocumento1 páginaMusic Theory Worksheet 20 Natural Minor ScaleTeganMiller100% (1)
- Music Theory Worksheet 13 Eighth Rests PDFDocumento1 páginaMusic Theory Worksheet 13 Eighth Rests PDFAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Play This Song With The Regular Shapes of The Chords Given in This SongDocumento2 páginasPlay This Song With The Regular Shapes of The Chords Given in This Songdankor 04Ainda não há avaliações
- Kings of Leon - Sex On FireDocumento3 páginasKings of Leon - Sex On FireAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Rehearsal 1 PDFDocumento2 páginasRehearsal 1 PDFAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Music Theory Worksheet 18 Whole Half Stepsv2 PDFDocumento1 páginaMusic Theory Worksheet 18 Whole Half Stepsv2 PDFJelenaGutić67% (3)
- Music Theory Worksheet 21 Harmonic Minor ScaleDocumento1 páginaMusic Theory Worksheet 21 Harmonic Minor ScaleTeganMillerAinda não há avaliações
- Rehearsal 4Documento2 páginasRehearsal 4AmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Autumn Leaves: C F B EDocumento1 páginaAutumn Leaves: C F B EAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Happy Xmas (War Is Over)Documento2 páginasHappy Xmas (War Is Over)AmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Musical Knowledge ParametersDocumento2 páginasMusical Knowledge Parameterssrinivas_gajulAinda não há avaliações
- Part SongsDocumento2 páginasPart SongsAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Amy Rapa 2/16/2018: Designed by Checked by Approved by Date DateDocumento1 páginaAmy Rapa 2/16/2018: Designed by Checked by Approved by Date DateAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Consent Form Xewkija Forms 2 3Documento1 páginaConsent Form Xewkija Forms 2 3AmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Health and Safety Manual Company TemplateDocumento55 páginasHealth and Safety Manual Company Templatepandu_chemengAinda não há avaliações
- Drying Technology: An International JournalDocumento3 páginasDrying Technology: An International JournalAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- 1st MarchDocumento6 páginas1st MarchAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações
- Beautiful in WhiteDocumento3 páginasBeautiful in WhiteAmyRapaAinda não há avaliações