Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCP
Enviado por
dericTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCP
Enviado por
dericDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Student Nurses Community
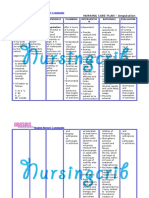
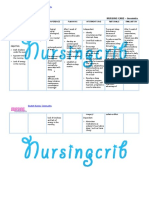
NURSING CARE PLAN Risk for Aspiration
ASSESSMENT
SUBJECTIVE:
Daughter of
patient states
that patient has
been struggling
with swallowing
and seems to
choke a lot since
her stroke.
OBJECTIVES:
Crackles noted
upon
auscultation
Diagnosis of
stroke and
right sided
paralysis
Pt exhibits
difficulty
swallowing
without
choking.
Orders to have
a speech
therapy
consult
DIAGNOSIS
Risk for
aspiration
related to
impaired
swallowing,
depressed
cough and gag
reflexes
secondary to
stroke
INFERENCE
Chronic condition
(stroke)
multiple areas of
the brain and a
series of voluntary
and involuntary
muscular
contractions are
affected
PLANNING
After 72 hours
of nursing
intervention,
risk for
aspiration will
be decreased
and the
patient will be
able to
maintain a
patent airway
as evidenced
by:
Paralysis of throat
muscles
clear breath
sounds
Impairs swallowing
and gag reflex of
patient (dysphagia)
resonant
percussion
noted over
lungs
Possibility of
material, which a
person is
swallowing to enter
Absence of
cough,
tachypnea,
and
dyspnea.
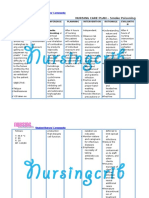
INTERVENTIONS
Independent:
Assess client's
ability to swallow
and strength of
gag reflex and
evaluate
amount/consisten
cy of secretions
RATIONALE
To determine
presence/effectiv
eness of
protective
mechanisms.
Normally the time
taken for the
bolus to move
from the point at
which the reflex
is triggered to the
esophageal entry
(pharyngeal
transit time) is (1
second). Clients
can aspirate even
if they have an
intact gag reflex
Assess ability to
swallow by
positioning
examiner's thumb
and index finger
on client's
laryngeal
protuberance. Ask
client to swallow;
feel larynx
elevate. Ask client These are all
to cough; test for
signs of
a gag reflex on
swallowing
both sides of
impairment
posterior
To remove excess
pharyngeal wall
secretions while
(lingual surface)
EVALUATION
After 72 hours
of nursing
interventions,
goal met. Clear
breath sounds,
resonant
percussion
over the lungs
are noted.
There is
absence of
cough and the
vital signs are
within normal
limits.
Student Nurses Community
TEMP: 36.5 C
the airway and
lungs
RR: 16 cpm
(Risk for aspiration)
PR: 75 bpm
BP: 110/80 mmHg
with a tongue
blade. Do not rely
on presence of
gag reflex to
determine when
to feed.
reducing
potential for
aspiration of
secretions.
To prevent foreign
aspiration
Observe for signs
To mobilize
associated with
thickened
swallowing
secretions that
problems (e.g.,
may interfere
coughing,
with swallowing.
choking, spitting
of food, drooling,
A noisy
difficulty handling
environment can
oral secretions,
be an aversive
double swallowing
stimulus and can
or major delay in
decrease
swallowing,
effective
watering eyes,
mastication and
nasal discharge,
swallowing.
wet or gurgly
Talking and
voice, decreased
laughing while
ability to move
eating increases
tongue and lips,
the risk of
decreased
aspiration
mastication of
Liquids can be
food, decreased
easily aspirated;
ability to move
thickened liquids
food to the back
form a cohesive
of the pharynx,
bolus that the
slow or scanning
client can
speech).
Student Nurses Community
perform
swallow with
increased
oropharyngeal
efficiency.
suctioning but
avoid triggering of
Food may
gag mechanism,
become pocketed
and provide oral
in the affected
hygiene as often
side and cause
as needed
stomatitis, tooth
Remove any oral
decay, and
possible later
dentures.
aspiration.
Assist in postural
An upright
drainage.
position ensures
Provide meals in a
that food stays in
quiet environment
the stomach until
away from
it has emptied
excessive stimuli
and decreases
such as a
the chance of
community dining
aspiration
room.
following meals
Avoid providing
liquids until client
is able to swallow
effectively.
Check oral cavity
for proper
emptying after
client swallows
and after client
finishes meal.
The presence of
new crackles or
wheezing, an
elevated
temperature or
white blood cell
count, and a
change in sputum
could indicate
aspiration of food
Student Nurses Community
Provide oral care
and even
at end of meal. It
pneumonia.
may be necessary
It is common for
to manually
family members
remove food from
to disregard
client's mouth. If
necessary dietary
this is the case,
restrictions and
use gloves and
give client
keep client's teeth
inappropriate
apart with a
foods that
padded tongue
predispose to
blade.
aspiration
Keep client in an
Feeding a client
upright position
who cannot
for 30 to 45
adequately
minutes after a
swallow results in
meal.
aspiration and
Auscultate lung
possibly death.
sounds after
Enteral feedings
feeding. Note new
via PEG tube are
crackles or
generally
wheezing, and
preferable to
note elevated
nasogastric tube
temperature.
feedings because
Notify physician
studies have
as needed.
demonstrated
that there is
Educate client,
increased
family, and all
nutritional status
caregivers about
and possibly
rationales for food
improved survival
Student Nurses Community
consistency and
choices.
Collaborative
Ensure proper
nutrition by
consulting with
physician for
enteral feedings,
preferably a PEG
tube in most
cases.
rates
Você também pode gostar
- NCP-RISK For ASPIRATIONDocumento3 páginasNCP-RISK For ASPIRATIONChristine S. Samaniego100% (1)
- Risk For Impaired SwallowingDocumento3 páginasRisk For Impaired SwallowingCalimlim Kim100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan ExampleDocumento5 páginasNursing Care Plan ExampleBrittanyAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Aspiration NCPDocumento2 páginasRisk For Aspiration NCPGrace Beltran67% (3)
- Risk For AspirationDocumento3 páginasRisk For Aspirationcotyboy0% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownShelli Miller Pryor82% (11)
- Risk For Aspiration Related To Impaired Swallowing Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento3 páginasRisk For Aspiration Related To Impaired Swallowing Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentChenee MabulayAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing care plan for risk of aspirationDocumento6 páginasNursing care plan for risk of aspirationWendy Escalante100% (3)
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocumento4 páginas2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedLeonardo Montemayor100% (3)
- Viii. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocumento1 páginaViii. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationJohn Linero100% (2)
- Ncp-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento3 páginasNcp-Ineffective Airway Clearancelouanne0550% (2)
- NCPDocumento9 páginasNCPTracy Camille EscobarAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocumento2 páginasImpaired Verbal CommunicationEjay Barayuga100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEDocumento3 páginasNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For StrokeDocumento4 páginasNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCOAinda não há avaliações
- #1 Risk For Aspirations DCDocumento2 páginas#1 Risk For Aspirations DCtanyav26Ainda não há avaliações
- Risk For AspirationDocumento2 páginasRisk For AspirationGly Mtg100% (6)
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 páginasPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan2 CVADocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan2 CVAhermesdave1Ainda não há avaliações
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 páginasImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- NCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T SecretionDocumento3 páginasNCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T Secretionherscentasiascribd50% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPaudreyAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - CapDocumento4 páginasNCP - CapSherryAinda não há avaliações
- Mpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasMpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanTheSweetpea5010% (2)
- Possible NCP For CVDDocumento6 páginasPossible NCP For CVDVincent Bulla50% (2)
- CVA Activity IntoleranceDocumento1 páginaCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Documento2 páginasIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Congestive Heart FailureRalph Dumawaa60% (5)
- Improving Physical Mobility Through Nursing InterventionsDocumento2 páginasImproving Physical Mobility Through Nursing InterventionsPrincess Averin Navarro50% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento13 páginasNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan - Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan - Impaired Physical MobilitySusan Croce57% (7)
- Impaired Oral Mucous MembraneDocumento2 páginasImpaired Oral Mucous Membranemai_serpic100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Goals Interventions EvaluationDocumento3 páginasNursing Diagnosis Goals Interventions EvaluationAav Canlas100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Nursing DiagnosisDocumento2 páginasIneffective Breathing Pattern Nursing DiagnosisChristianmel JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocumento2 páginasIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- Cholecystitis NCPDocumento4 páginasCholecystitis NCPdark-canales33% (3)
- NCP Impaired Swallowing.Documento3 páginasNCP Impaired Swallowing.Erliz Faye Mayor50% (2)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento4 páginasNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goal of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goal of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationHowel CristobalAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocumento8 páginasIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentDocumento17 páginasImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentAileen Lopez83% (6)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento5 páginasNursing Care PlanAnju Luchmun100% (2)
- NCP Visual SensoryDocumento2 páginasNCP Visual SensoryEugene UCAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Pleural EffusionDocumento4 páginasNCP For Pleural EffusionLilian Linogao71% (7)
- Impaired Swallowing Care PlanDocumento5 páginasImpaired Swallowing Care Planjakifer33% (3)
- Essential course on dysphagia management and feeding skillsDocumento10 páginasEssential course on dysphagia management and feeding skillsTempleknight7Ainda não há avaliações
- MG NCPDocumento9 páginasMG NCPIrene Soriano BayubayAinda não há avaliações
- 5b.ESOPHAGEAL TRAUMA AND PERFORATIONSDocumento19 páginas5b.ESOPHAGEAL TRAUMA AND PERFORATIONSHayat AL AKOUMAinda não há avaliações
- Nasogastric & Gavage - NsoDocumento5 páginasNasogastric & Gavage - NsojamesAinda não há avaliações
- Nasogastric Tube FeedingDocumento4 páginasNasogastric Tube FeedingAru VermaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Acvute PainDocumento6 páginasNCP For Acvute PainGlenn ValerioAinda não há avaliações
- Care of Patients with DysphagiaDocumento15 páginasCare of Patients with DysphagiaNeesha MAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired SwallowingDocumento2 páginasImpaired Swallowingwilz3390% (10)
- Oral and Naso Pharyngeal SuctioningDocumento10 páginasOral and Naso Pharyngeal SuctioningMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento9 páginasNursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceAngelokeizer GavinoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento1 páginaNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceImation DataAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care for Patients with Renal StonesDocumento8 páginasNursing Care for Patients with Renal StonesAnonymous dquW2YmO7Ainda não há avaliações
- RKDF Dental College: Department of Orthodontics and Dentofcaial OrthopedicsDocumento43 páginasRKDF Dental College: Department of Orthodontics and Dentofcaial Orthopedicsananya saxenaAinda não há avaliações
- Assess and Care for Impaired Oral Mucous MembranesDocumento2 páginasAssess and Care for Impaired Oral Mucous MembranesNolan Cabral100% (1)
- Neck DissectionDocumento24 páginasNeck Dissectionhayat al akoumAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDocumento5 páginasNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDocumento8 páginasNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDocumento5 páginasNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocumento14 páginasNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (23)
- Licensed Practical Nurse Knowledge & Skills Checklist: Requires Supervision/assistanceDocumento4 páginasLicensed Practical Nurse Knowledge & Skills Checklist: Requires Supervision/assistancenorthweststaffing100% (1)
- Hoja de Datos de Seguridad Removedor Adhesivo Goo GoneDocumento5 páginasHoja de Datos de Seguridad Removedor Adhesivo Goo GoneSupervisores SertresAinda não há avaliações
- 211g-Buoyant Smoke Signal JHB-4Documento3 páginas211g-Buoyant Smoke Signal JHB-4Jacqueline AblianAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines For International Arrival 20 TH October 2021Documento3 páginasGuidelines For International Arrival 20 TH October 2021Republic WorldAinda não há avaliações
- Actellic 50EC UK MSDS1 PDFDocumento14 páginasActellic 50EC UK MSDS1 PDFBán Báo DạoAinda não há avaliações
- 25 Uses Frankincense OilDocumento2 páginas25 Uses Frankincense OilkenodidAinda não há avaliações
- Toluene MSDSDocumento16 páginasToluene MSDSHari SimhaAinda não há avaliações
- MSDS AWP 140 - AwakeDocumento5 páginasMSDS AWP 140 - Awakeรอคนบนฟ้า ส่งใครมาให้ สักคนAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocumento1 páginaConcept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseWayne Calderon75% (4)
- Msds-Thinnal 4280101Documento2 páginasMsds-Thinnal 4280101محمد عزتAinda não há avaliações
- JLR-8400 INSTRUCTION MANUAL (2nd Edition)Documento218 páginasJLR-8400 INSTRUCTION MANUAL (2nd Edition)bulkseas managementAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for Pain Management After C-SectionDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan for Pain Management After C-SectionJezzy VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet: Right To KnowDocumento6 páginasHazardous Substance Fact Sheet: Right To KnowBadtzAinda não há avaliações
- Ricin: Prepared By:marwa Najm Supervised By: DR ShorshDocumento15 páginasRicin: Prepared By:marwa Najm Supervised By: DR ShorshShakila HamidAinda não há avaliações
- Perbedaan Tekanan Darah, Laju Jantung Dan Rate Pressure Product (RPP) Pada Pemberian Lidokain 1,5 MG/KGBB Intravena Sebelum Intubasi Dibandingkan Pemasangan Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA)Documento11 páginasPerbedaan Tekanan Darah, Laju Jantung Dan Rate Pressure Product (RPP) Pada Pemberian Lidokain 1,5 MG/KGBB Intravena Sebelum Intubasi Dibandingkan Pemasangan Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA)steven saputraAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 8 Lymphatic and Heart SystemDocumento5 páginasActivity 8 Lymphatic and Heart SystemDanielle MerlinAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Documento15 páginasCardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Mylene Jane Husain BartolomeAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System Gizmo - 5 Mark TestDocumento3 páginasCirculatory System Gizmo - 5 Mark TestDhruv VmAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan VentilatorDocumento25 páginasLesson Plan VentilatorLoma Waghmare (Jadhav)Ainda não há avaliações
- Initial Management of The Critically Ill Adult With An Unknown OverdoseDocumento32 páginasInitial Management of The Critically Ill Adult With An Unknown Overdosemayteveronica1000Ainda não há avaliações
- QuestionsDocumento4 páginasQuestionsKeerthi Chowdary AmaraneniAinda não há avaliações
- Physiologic Monitoring of The Surgical PatientDocumento56 páginasPhysiologic Monitoring of The Surgical PatientSeid Adem100% (2)
- DR Ediyono SP P Sub Dep Paru RSAL DR Ramelan: Farmasi UBY S2 April 2016Documento132 páginasDR Ediyono SP P Sub Dep Paru RSAL DR Ramelan: Farmasi UBY S2 April 2016Sukmawati Eka Bima SahputriAinda não há avaliações
- Starch, Wheat Powder MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocumento5 páginasStarch, Wheat Powder MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationAna Cicupy EmangfitriAinda não há avaliações
- ACOMA Acc. & Parts Catalog 20100706Documento32 páginasACOMA Acc. & Parts Catalog 20100706Benedictus hutomo manto100% (1)
- 190-Article Text - Full Paper-1150-1-10-20210113Documento8 páginas190-Article Text - Full Paper-1150-1-10-20210113maria tokanAinda não há avaliações
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Product Name: RFB Line - RFB-EC RFB-SE RFB-SA1 RFB-SADocumento4 páginasMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Product Name: RFB Line - RFB-EC RFB-SE RFB-SA1 RFB-SAAlfonso GarcíaAinda não há avaliações
- Register PasienDocumento4.526 páginasRegister PasienSri nur HidayatiAinda não há avaliações
- COVID-19 Screening ChecklistDocumento2 páginasCOVID-19 Screening ChecklistKantor DesakerasAinda não há avaliações
- Emphysema BrochureDocumento2 páginasEmphysema Brochureapi-242394302Ainda não há avaliações