Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
Enviado por
ParthPatelDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
Enviado por
ParthPatelDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Packet Tracer - Sub netting Scenario 1
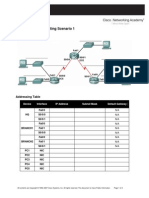
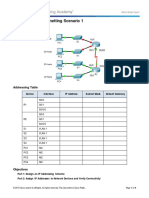
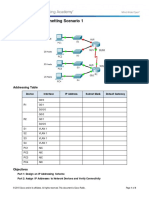
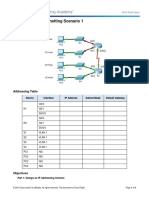
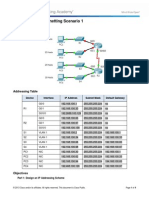
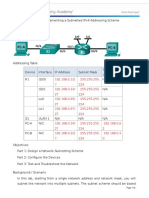
Topology
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
Subnet
Mask
IP Address
Default
Gateway
G0/0
192.168.100.1
255.255.255.224
N/A
G0/1
192.168.100.33
255.255.255.224
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.100.129
255.255.255.252
N/A
G0/0
192.168.100.65
255.255.255.224
N/A
G0/1
192.168.100.97
255.255.255.224
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.100.158
255.255.255.252
N/A
S1
VLAN 1
192.168.100.2
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.1
S2
VLAN 1
192.168.100.34
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.33
S3
VLAN 1
192.168.100.66
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.65
S4
VLAN 1
192.168.100.98
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.97
PC1
NIC
192.168.100.30
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.1
PC2
NIC
192.168.100.62
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.33
PC3
NIC
192.168.100.94
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.65
PC4
NIC
192.168.100.126
255.255.255.224
192.168.100.97
R1
R2
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 5
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
Objectives
Part 1: Design an IP Addressing Scheme
Part 2: Assign IP Addresses to Network Devices and Verify Connectivity
Scenario
In this activity, you are given the network address of 192.168.100.0/24 to
subnet and provide the IP addressing for the network shown in the topology.
Each LAN in the network requires enough space for, at least, 25 addresses for
end devices, the switch and the router. The connection between R1 to R2 will
require an IP address for each end of the link.
Part 1: Design an IP Addressing Scheme
Step 1:_Subnet the 192.168.100.0/24 network into the appropriate number
of subnets.
a. Based on the topology, how many subnets are needed? 5
b. How many bits must be borrowed to support the number of subnets in the
topology table? ______________________________________________________________
3
c. How many subnets does this create? 8
d. How many usable hosts does this create per subnet? 30
Note: If your answer is less than the 25 hosts required, then you borrowed
too many bits.
e. Calculate the binary value for the first five subnets. The first subnet is
already shown.
Net 0: 192. 168. 100. 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Net 1: 192. 168. 100. 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0
Net 2: 192. 168. 100. 0
Net 3: 192. 168. 100. 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
Net 4: 192. 168. 100. 1
0 0
f. Calculate the binary and decimal value of the new subnet mask.
11111111.11111111.11111111. 11100000
255. 255. 255. 224
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 5
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
g. Fill in the Subnet Table, listing the decimal value of all available subnets,
the first and last usable host address, and the broadcast address. Repeat
until all addresses are listed.
Note: You may not need to use all rows.
Subnet Table
Subnet
Numbe
r
Subnet
Address
First
Usable
Host
Address
Last
Usable
Host
Address
Broadcast
Address
192.168.100.0
192.168.100.1
192.168.100.30
192.168.100.31
192.168.100.32
192.168.100.33
192.168.100.62
192.168.100.63
192.168.100.64
192.168.100.65
192.168.100.94
192.168.100.95
192.168.100.96
192.168.100.97
192.168.100126
192.168.100.127192
192.168.100.128
192.168.100.129
192.168.100.158
192.168.100.159
192.168.100.160
192.168.100.161
192.168.100.190
192.168.100.191
192.168.100.192
192.168.100.193
192.168.100.222
192.168.100.223
192.168.100.224
192.168.100.225
192.168.100.254
192.168.100.255
8
9
10
Step 2:___________Assign the subnets to the network shown in the topology.
a. Assign Subnet 0 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface of
R1:
192.168.100.0/27
b. Assign Subnet 1 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/1 interface of
R1:
192.168.100.32/27
c. Assign Subnet 2 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface of
R2:
192.16.100.64/27
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 5
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
d. Assign Subnet 3 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/1 interface of
R2:
192.168.100.96/27
e. Assign Subnet 4 to the WAN link between R1 to R2: 192.168.100.128/27
Step 3:_____________________________________Document the addressing scheme.
Fill in the Subnet Table using the following guidelines:
a. Assign the first usable IP addresses to R1 for the two LAN links and the WAN
link.
b. Assign the first usable IP addresses to R2 for the LANs links. Assign the last
usable IP address for the WAN link.
c. Assign the second usable IP addresses to the switches.
d. Assign the last usable IP addresses to the hosts.
Part 2: Assign IP Addresses to Network Devices and Verify Connectivity
Most of the IP addressing is already configured on this network. Implement the
following steps to complete the addressing configuration.
Step 1:
Configure IP addressing on R1 LAN interfaces.
Step 2:
Configure IP addressing on S3, including the default gateway.
Step 3:
Configure IP addressing on PC4, including the default gateway.
Step 4:
Verify connectivity.
You can only verify connectivity from R1, S3, and PC4. However, you should be
able to ping every IP address listed in the Addressing Table.
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 4 of 5
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Question
Location
Possibl
e Points
Step 1a
Step 1b
Step 1c
Step 1d
Step 1e
Step 1f
Step 1g
10
Assign Subnets
Step 2
10
Document
Addressing
Step 3
40
Activity Section
Part 1: Design an IP
Addressing Scheme
Complete Subnet
Table
Part 1 Total
70
Packet Tracer Score
30
Total Score
2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Earned
Points
100
Page 5 of 5
Você também pode gostar
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Documento5 páginas8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Alex VolkovAinda não há avaliações
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN Instructions IGDocumento5 páginas6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN Instructions IGopiAinda não há avaliações
- 2.4.3.4 Packet TracerDocumento11 páginas2.4.3.4 Packet TracercoleparksAinda não há avaliações
- 7.1.4.9 Lab - Identifying IPv4 AddressesDocumento3 páginas7.1.4.9 Lab - Identifying IPv4 AddressesEduardo Haro38% (16)
- 19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMDocumento8 páginas19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMjohannachicaAinda não há avaliações
- 9.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing Scheme InstructionsDocumento3 páginas9.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing Scheme InstructionsAhmadHijazi100% (2)
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme Instruct IGDocumento8 páginas9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme Instruct IGKe Syukuran KuAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Lab B: Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and ClientDocumento24 páginasChapter 8 Lab B: Configuring A Remote Access VPN Server and ClientberlodonAinda não há avaliações
- 4.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes InstructionsDocumento3 páginas4.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes InstructionsDaniel OsorioAinda não há avaliações
- Lab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 3.5.2Documento4 páginasLab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 3.5.2Rico Agung FirmansyahAinda não há avaliações
- IPv4 Address Subnetting Part 2Documento2 páginasIPv4 Address Subnetting Part 2mueller_gbAinda não há avaliações
- SUBNET MASK VALUESDocumento6 páginasSUBNET MASK VALUESSrimannarayanaJamiliAinda não há avaliações
- Packet Tracer Sample PDFDocumento89 páginasPacket Tracer Sample PDFYidnekachewAinda não há avaliações
- Addressing Table: ObjectivesDocumento5 páginasAddressing Table: ObjectivesStasicc SAinda não há avaliações
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocumento5 páginas6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANSergio MonteAinda não há avaliações
- 4 2 4 4Documento5 páginas4 2 4 4john67% (3)
- CCNA 3 (v5.0) OSPF Practice Skills Assessment Exam Answer: Network DiagramDocumento22 páginasCCNA 3 (v5.0) OSPF Practice Skills Assessment Exam Answer: Network DiagramMark BrownAinda não há avaliações
- WAN Subnetting VLSMDocumento3 páginasWAN Subnetting VLSMMuz QazAinda não há avaliações
- E2 Lab 3 5 4Documento3 páginasE2 Lab 3 5 4Ninja NuggetAinda não há avaliações
- 11.4.3.6 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Connectivity IssuesDocumento13 páginas11.4.3.6 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Connectivity IssuesMiriam Arista0% (2)
- 9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFDocumento8 páginas9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFEl Amrani MoutiaAinda não há avaliações
- 3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationDocumento17 páginas3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationLarry Abisaí0% (2)
- Lab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationDocumento4 páginasLab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationJosue Isahu Sanchez MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Net LA-03EN SubnettingDocumento20 páginasNet LA-03EN SubnettinggAinda não há avaliações
- Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing DesignDocumento6 páginasBasic VLSM Calculation and Addressing DesignnujugtrAinda não há avaliações
- Subnetting Exercise SolutionsDocumento7 páginasSubnetting Exercise SolutionsMalikMohsin0% (1)
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructDocumento4 páginas9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructGanti nama100% (1)
- 9.3.1.2 Packet Tracer Simulation - Exploration of TCP and UDP CommunicationDocumento6 páginas9.3.1.2 Packet Tracer Simulation - Exploration of TCP and UDP CommunicationParthPatel0% (1)
- 6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router SettingsDocumento4 páginas6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router SettingsMichelle Ancajas100% (9)
- 8.2.1.4 PT - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing SchemeDocumento8 páginas8.2.1.4 PT - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Schemeyazmin caballero0% (1)
- CCNA 2 RSE Practice Skills Assessment v5.2– PT 2015Documento11 páginasCCNA 2 RSE Practice Skills Assessment v5.2– PT 2015Hermo MedranoAinda não há avaliações
- Subnetting Made EasyDocumento4 páginasSubnetting Made Easyfuhrer232842Ainda não há avaliações
- A Few Things To Keep in Mind While Completing This ActivityDocumento5 páginasA Few Things To Keep in Mind While Completing This ActivityDiego BenitesAinda não há avaliações
- 6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router SettingsDocumento4 páginas6.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router SettingsSergio Monte100% (3)
- 5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess NetworkDocumento6 páginas5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Networkرافد البركيAinda não há avaliações
- Lab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology DiagramDocumento6 páginasLab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology Diagramchanda_banda272Ainda não há avaliações
- 3 Router Igrp Configuration LabDocumento5 páginas3 Router Igrp Configuration LabSiddhant SingalAinda não há avaliações
- Ccna 3 Ex - OspfDocumento25 páginasCcna 3 Ex - OspfJosueChalenSarezAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA Routing and SwitchingDocumento9 páginasCCNA Routing and Switchingjohan12354Ainda não há avaliações
- Cisco IOS Modes TutorialDocumento11 páginasCisco IOS Modes Tutorialheruye mulugetaAinda não há avaliações
- En ERouting IPTM v4Documento55 páginasEn ERouting IPTM v4GµårÐïåñAinda não há avaliações
- Chaper 5 - SubnettingDocumento62 páginasChaper 5 - SubnettingCha DechavezAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 5.6.2: Advanced RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramDocumento7 páginasLab 5.6.2: Advanced RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramPaintMeAnEpicAinda não há avaliações
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsNo EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- 298413192-8-1-4-7 - Sin ResolverDocumento5 páginas298413192-8-1-4-7 - Sin ResolverClaudia Glorieux AlarcónAinda não há avaliações
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1JPDocumento5 páginas9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1JPAnonymous 9XGVHQcQRd100% (3)
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Documento4 páginas8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Duscosi100% (1)
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 PDFDocumento4 páginas8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 PDFSyammirul RashidAinda não há avaliações
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsDocumento4 páginas9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsJonny MonteroAinda não há avaliações
- 11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-ScenarioDocumento5 páginas11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-Scenariostudy timeAinda não há avaliações
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2Documento4 páginasAppendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2ParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 - ILMDocumento5 páginas8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 - ILMHanif AwalludinAinda não há avaliações
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions IGDocumento4 páginas9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions IGsalin zambranoAinda não há avaliações
- B3 - 322070 - Sai Kamble - Assig - 2Documento5 páginasB3 - 322070 - Sai Kamble - Assig - 2sai.22220063Ainda não há avaliações
- 9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsDocumento5 páginas9.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2 InstructionsAriel Fernando Cerquera GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsDocumento4 páginas9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsRadu Florin TriponAinda não há avaliações
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Documento4 páginas8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Rubén Darío Saa MontañoAinda não há avaliações
- ICT60215 - Task 1Documento17 páginasICT60215 - Task 1MitchAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 3.5.2 Subnetting Scenario 1Documento5 páginasLab 3.5.2 Subnetting Scenario 1Edgar Alejandro Ramirez100% (2)
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsDocumento4 páginas9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 InstructionsRizky Hoki VoLtager67% (3)
- Lab 7 - Viewing Wireless and Wired NIC InformationDocumento11 páginasLab 7 - Viewing Wireless and Wired NIC InformationParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 5 - Configuring A Switch Managment AddressDocumento10 páginasLab 5 - Configuring A Switch Managment AddressParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Configuring An Integrated RouterDocumento3 páginasAppendix Packet Tracer - Configuring An Integrated RouterParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- 11.2.5.7 Packet Tracer - Backing Up Configuration FilesDocumento2 páginas11.2.5.7 Packet Tracer - Backing Up Configuration FilesParthPatel33% (3)
- 11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHDocumento6 páginas11.2.4.6 Lab - Accessing Network Devices With SSHParthPatel0% (3)
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2Documento4 páginasAppendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2ParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- 11.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting ChallengeDocumento3 páginas11.4.1.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting ChallengeParthPatel0% (1)
- 11.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Test Connectivity With TracerouteDocumento3 páginas11.3.2.2 Packet Tracer - Test Connectivity With TracerouteParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- 11.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Using Show CommandsDocumento2 páginas11.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Using Show CommandsParthPatel0% (1)
- 11.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeDocumento4 páginas11.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeParthPatel0% (1)
- 11.2.4.7 Lab - Examining Telnet and SSH in WiresharkDocumento9 páginas11.2.4.7 Lab - Examining Telnet and SSH in WiresharkParthPatel100% (2)
- 11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesDocumento8 páginas11.2.4.8 Lab - Securing Network DevicesParthPatel60% (5)
- 10.2.2.7 Packet Tracer - DNS and DHCPDocumento4 páginas10.2.2.7 Packet Tracer - DNS and DHCPParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- 11.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Secure Passwords and SSHDocumento2 páginas11.2.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Secure Passwords and SSHParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- 10.3.1.4 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Implement ServicesDocumento4 páginas10.3.1.4 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Implement ServicesParthPatel0% (1)
- 8.1.4.6 Lab - Calculating IPv4 SubnetsDocumento7 páginas8.1.4.6 Lab - Calculating IPv4 SubnetscgruAinda não há avaliações
- 10.4.1.2 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Tutorial InstructionsDocumento3 páginas10.4.1.2 Packet Tracer Multiuser - Tutorial InstructionsKamijou SekaiAinda não há avaliações
- 3.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Explore A Network InstructionsDocumento5 páginas3.3.3.3 Packet Tracer - Explore A Network InstructionsWendhz ÜüAinda não há avaliações
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructDocumento4 páginas9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructGanti nama100% (1)
- Configure and Use FTP ServersDocumento4 páginasConfigure and Use FTP ServersParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- 10.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Web and EmailDocumento5 páginas10.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Web and EmailParthPatelAinda não há avaliações
- 10.2.2.9 Lab - Observing DNS ResolutionDocumento5 páginas10.2.2.9 Lab - Observing DNS ResolutionasdfjklAinda não há avaliações
- 9.3.1.2 Packet Tracer Simulation - Exploration of TCP and UDP CommunicationDocumento6 páginas9.3.1.2 Packet Tracer Simulation - Exploration of TCP and UDP CommunicationParthPatel0% (1)
- 8.1.4.8 Lab - Designing and Implementing A Subnetted IPv4 Addressing SchemeDocumento12 páginas8.1.4.8 Lab - Designing and Implementing A Subnetted IPv4 Addressing SchemeParthPatel90% (31)
- 8.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeDocumento2 páginas8.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeParthPatel0% (1)
- 7.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeDocumento2 páginas7.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration ChallengeParthPatel100% (1)
- 8.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing SchemeDocumento3 páginas8.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing SchemeParthPatel0% (1)
- 7.3.2.9 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 AddressingDocumento5 páginas7.3.2.9 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 AddressingParthPatel0% (3)
- 7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetDocumento8 páginas7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetParthPatel0% (5)
- Survival Part 5Documento36 páginasSurvival Part 5bmartindoyle6396Ainda não há avaliações
- UMRN authorization formDocumento1 páginaUMRN authorization formPraneeth SrivanthAinda não há avaliações
- Please Note That Cypress Is An Infineon Technologies CompanyDocumento18 páginasPlease Note That Cypress Is An Infineon Technologies Companyyoucef88Ainda não há avaliações
- Manasi Rakhecha: Work Experience SkillsDocumento1 páginaManasi Rakhecha: Work Experience SkillsShareena Fernandes0% (1)
- Guardian Unlimited - Weekend - Jon Ronson Meets Hacker Gary McKinnon PDFDocumento7 páginasGuardian Unlimited - Weekend - Jon Ronson Meets Hacker Gary McKinnon PDFJOHN TSOUREKIAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems Btcse-Oe43: By: Naved Alam Assistant Professor (ECE) SEST, Jamia HamdardDocumento42 páginasEmbedded Systems Btcse-Oe43: By: Naved Alam Assistant Professor (ECE) SEST, Jamia Hamdardanon_947471502Ainda não há avaliações
- Indonesia Top 10 E-Commerce Sites by Monthly Traffic 2021 StatistaDocumento1 páginaIndonesia Top 10 E-Commerce Sites by Monthly Traffic 2021 StatistaRino Adi NugrohoAinda não há avaliações
- Brief history and overview of the ARM architectureDocumento28 páginasBrief history and overview of the ARM architecturepositive vibesAinda não há avaliações
- Borri UPS & Critical Power CatalogueDocumento72 páginasBorri UPS & Critical Power CatalogueNguyễn Anh DanhAinda não há avaliações
- PVTsim Hands-On Webinar Handout - Introduction To EoS ModelingDocumento22 páginasPVTsim Hands-On Webinar Handout - Introduction To EoS ModelingsabrineAinda não há avaliações
- Re 1999 11Documento100 páginasRe 1999 11Enéas BaroneAinda não há avaliações
- Three-Dimensional Static and Dynamic Analysis of Structures: Edward L. WilsonDocumento20 páginasThree-Dimensional Static and Dynamic Analysis of Structures: Edward L. WilsonManuel FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Selecting data from parts tableDocumento4 páginasSelecting data from parts tablePie PimentelAinda não há avaliações
- Sigma linear motors direct drive technology overviewDocumento26 páginasSigma linear motors direct drive technology overviewMario StoyanovAinda não há avaliações
- Protection System Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocumento27 páginasProtection System Fundamentals and ApplicationsHEMANT RAMJIAinda não há avaliações
- PornDocumento15 páginasPornPeter Hermann50% (2)
- AC Corrosion Booklet On Cathodically Protected Pipelines Ed 2001Documento2 páginasAC Corrosion Booklet On Cathodically Protected Pipelines Ed 2001Nguyen Ninh BinhAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To Ai Chapter 1 & 2 (Rev)Documento15 páginasIntro To Ai Chapter 1 & 2 (Rev)Sebastian CincoAinda não há avaliações
- DC Motor DrivesDocumento11 páginasDC Motor DrivesVikram NikhilAinda não há avaliações
- Feederless-SFP-DC Cables-Flexi Multiradio Base Station Installation Site Requirements PDFDocumento15 páginasFeederless-SFP-DC Cables-Flexi Multiradio Base Station Installation Site Requirements PDFFlorin StanAinda não há avaliações
- Efficient Algorithm For Big Data ApplicationDocumento4 páginasEfficient Algorithm For Big Data ApplicationInternational Journal of Advanced and Innovative ResearchAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 Ethernet and VLAN: Lab 1-1 Ethernet Interface and Link Configuration Learning ObjectivesDocumento15 páginasModule 1 Ethernet and VLAN: Lab 1-1 Ethernet Interface and Link Configuration Learning ObjectivesChaima BelhediAinda não há avaliações
- CCIE EI v1.1 Blue PrintDocumento7 páginasCCIE EI v1.1 Blue PrintZeinAinda não há avaliações
- Hack Facebook Easy - Hack Facebook Live (RKPF) : Updated: 02-10-2021 (Onlineusers:8490)Documento7 páginasHack Facebook Easy - Hack Facebook Live (RKPF) : Updated: 02-10-2021 (Onlineusers:8490)Prince AJAinda não há avaliações
- Tm1 API GuideDocumento453 páginasTm1 API GuideMoataz DeiabAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 3Documento3 páginasExperiment 3AAAAALLENNAinda não há avaliações
- Records Management Program Deliverables: Session 1 - October 11, 2017Documento9 páginasRecords Management Program Deliverables: Session 1 - October 11, 2017Patricia Lorayne YapAinda não há avaliações
- Business Proposal: Goods DeliveryDocumento20 páginasBusiness Proposal: Goods Deliverysam100% (1)
- Hidraulico 246C JAYDocumento30 páginasHidraulico 246C JAYFranklin Labbe100% (3)
- Gis DatabasesDocumento27 páginasGis Databasessenwelo gulubaneAinda não há avaliações