Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Drying Agent
Enviado por
Apurba Sarker Apu0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
813 visualizações8 páginasDrying Agent
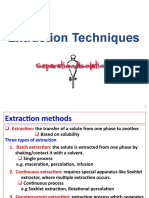
A drying agent is usually an anhydrous inorganic salt which reacts with the water present to form a hydrate. The process of synthesizing and isolating an organic compound often results in an organic compound or solution contaminated with traces of water. For instance, in aqueous extractions some water will be transferred into the organic phase because of the partial miscibility of the organic phase and water. Also, many reactions themselves are performed in an aqueous solution. This
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDrying Agent
A drying agent is usually an anhydrous inorganic salt which reacts with the water present to form a hydrate. The process of synthesizing and isolating an organic compound often results in an organic compound or solution contaminated with traces of water. For instance, in aqueous extractions some water will be transferred into the organic phase because of the partial miscibility of the organic phase and water. Also, many reactions themselves are performed in an aqueous solution. This
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
813 visualizações8 páginasDrying Agent
Enviado por
Apurba Sarker ApuDrying Agent
A drying agent is usually an anhydrous inorganic salt which reacts with the water present to form a hydrate. The process of synthesizing and isolating an organic compound often results in an organic compound or solution contaminated with traces of water. For instance, in aqueous extractions some water will be transferred into the organic phase because of the partial miscibility of the organic phase and water. Also, many reactions themselves are performed in an aqueous solution. This
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PPT, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 8
Drying Agent
A drying agent is usually an anhydrous inorganic salt which
reacts with the water present to form a hydrate.
The process of synthesizing and isolating an organic
compound often results in an organic compound or solution
contaminated with traces of water. For instance, in aqueous
extractions some water will be transferred into the organic
phase because of the partial miscibility of the organic phase
and water.
Also, many reactions themselves are performed in an
aqueous solution. This water must be removed before the
required compound can be properly characterized.
There are various ways of removing water and other
impurities from a solution. If water is one of the products, it
also has a detrimental effect on the yield and/or reaction
rate. Drying agents are distinguished by their capacity (the
amount of water they can absorb), the rate at which they
absorb the water, and their intensity (or completeness),
which is the amount of water left behind in the solvent at
equilibrium. Two most common drying agents are MgSO4
and Na2SO4.
MgSO4
It absorbs water from the organic compound. It is an acidic
compound and if the compound is basic then it will react
with the basic compound present in the solvent. MgSO4
should be used on case of acidic compound. It has larger
surface area because it is a powdered material. So after
absorption it forms clump. As it has larger surface area so it
can absorb water rapidly.
Na2So4
It is a natural drying agent. It has granule like
appearance so surface area of Na2So4 is not as
larger as MgSO4 and rate of absorption of water
is slower. It is only effective below about 30 °C,
but it can used with a variety of materials since it
is chemically fairly inert. Sodium sulfate is
added to the solution until the crystals no longer
clump together .
Procedure of using drying agent:
1) Add a small amount of the solid drying agent
directly to the organic solution. Swirl the
solution.
2) Observe the drying agent; if it is all clumped
together and when it is free-flowing.
There is no set “rule” as to how much drying agent needs
to be added. The amount required depends on the
amount of water in the solvent solution which you are
drying, and this amount varies from experiment to
experiment. Use as much as it takes to dry the solution.
In most cases, drying is as complete as it will get in 20
minutes. When drying is complete, you need to remove
the dried organic solution from the drying agent.
Você também pode gostar
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 11 Softy and Novelties - Definition, Composition, Legal Standards and Method of ManufactureDocumento15 páginasUnit 11 Softy and Novelties - Definition, Composition, Legal Standards and Method of ManufactureRonak RawatAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory I BSK1402 Lab Report: Name Fathul Aiman Bin Fahmi Matrix No. Sa18094 Section 02 DateDocumento8 páginasOrganic Chemistry Laboratory I BSK1402 Lab Report: Name Fathul Aiman Bin Fahmi Matrix No. Sa18094 Section 02 DateCucu AlbertAinda não há avaliações
- Biocatalysts and Enzyme TechnologyDocumento9 páginasBiocatalysts and Enzyme TechnologyMichelle Santillán0% (1)
- Manufacturing Sweetened Condensed MilkDocumento6 páginasManufacturing Sweetened Condensed Milksree anugraphics100% (1)
- Determination of Isoelectric Point (pIDocumento24 páginasDetermination of Isoelectric Point (pISangeeta RayAinda não há avaliações
- CH 12 Gravimetric Methods of AnalysisDocumento20 páginasCH 12 Gravimetric Methods of AnalysissathishAinda não há avaliações
- Disperse and Colloidal Systems: Jana NovotnáDocumento24 páginasDisperse and Colloidal Systems: Jana NovotnáVaishali PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Ammonium Sulfate PrecipitaionDocumento2 páginasAmmonium Sulfate Precipitaionanu100% (1)
- Syrups - PPTX 1Documento30 páginasSyrups - PPTX 1Samiksha SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid OralsDocumento55 páginasLiquid OralsShraddha RAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanisms of Moisture Transport Within SolidsDocumento7 páginasMechanisms of Moisture Transport Within SolidsDeeDeeJAinda não há avaliações
- Cipac MT 187Documento4 páginasCipac MT 187Chemist İnançAinda não há avaliações
- AMPHOTERIC L Tech DataDocumento3 páginasAMPHOTERIC L Tech DatadedeteAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory I BSK1402 Lab ReportDocumento10 páginasOrganic Chemistry Laboratory I BSK1402 Lab ReportCucu AlbertAinda não há avaliações
- FOOD FREEZING TECHNIQUESDocumento61 páginasFOOD FREEZING TECHNIQUESKumkum CrAinda não há avaliações
- BiosurfactantDocumento1 páginaBiosurfactantGregorius Budianto100% (1)
- A Thesis About BiosurfactantDocumento25 páginasA Thesis About BiosurfactantSandeep Kumar SaiAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of mixing time and SSL on gluten polymerizationDocumento7 páginasImpact of mixing time and SSL on gluten polymerizationDiego PinaresAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3.Waste-Water-TreatmentDocumento6 páginasLecture 3.Waste-Water-TreatmentDivya DiyaAinda não há avaliações
- HILIC Theory and Method DevelopmentDocumento48 páginasHILIC Theory and Method DevelopmentDeepak shahAinda não há avaliações
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)Documento45 páginasHigh Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)b_suribabu20Ainda não há avaliações
- HPLC - 4Documento24 páginasHPLC - 4Melisa Soledad Barco Jara100% (1)
- Capsicum Oil ExtractionDocumento17 páginasCapsicum Oil ExtractionSidra IbrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Apparatus ListDocumento7 páginasChemistry Apparatus ListHannaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 AeromicrobiologyDocumento8 páginasChapter 5 Aeromicrobiologyverbi fernendiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 Molecular Diffusion in Biological Solutions & GelsDocumento14 páginasChapter 5 Molecular Diffusion in Biological Solutions & Gelsrushdi100% (2)
- DryingDocumento51 páginasDryingShubham BhandariAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1-Introduction To Transition Metals ChemistryDocumento52 páginasLecture 1-Introduction To Transition Metals ChemistryFELIX ORATIAinda não há avaliações
- Water ActivityDocumento19 páginasWater ActivitySiri NalAinda não há avaliações
- Sulphur Cycle: Mihir Babaria - 4 Rahul Doshi - 59Documento4 páginasSulphur Cycle: Mihir Babaria - 4 Rahul Doshi - 59Mihir BabariaAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohol Determintion: General Method/DescriptionDocumento3 páginasAlcohol Determintion: General Method/DescriptionJannat ZahraAinda não há avaliações
- Centrifugation: Downstream Processing AssignmentDocumento10 páginasCentrifugation: Downstream Processing AssignmentPhani DeepthiAinda não há avaliações
- Surface Adsorption and Its ApplicationsDocumento19 páginasSurface Adsorption and Its Applicationsmudassir_hasan_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Chap-1-2 ExtractionDocumento73 páginasChap-1-2 Extractionlishan asefaAinda não há avaliações
- (TOTL-WI-13) Determination of Chloride in FertilizerDocumento7 páginas(TOTL-WI-13) Determination of Chloride in FertilizerakloioAinda não há avaliações
- Crystallizers and Their ControlDocumento34 páginasCrystallizers and Their ControlVinitaVartakAinda não há avaliações
- Fssai Ghee AdulterationDocumento2 páginasFssai Ghee AdulterationHemanth KumarAinda não há avaliações
- A. Heme Pigments: Natural Food Pigments Part 1Documento20 páginasA. Heme Pigments: Natural Food Pigments Part 1Balakumaran MAinda não há avaliações
- Sterilization of Fermenter-1Documento11 páginasSterilization of Fermenter-1Shalini M100% (1)
- 7Documento19 páginas7Shibu KumardAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 3Documento3 páginasExperiment 3R100% (1)
- Ultra FiltrationDocumento10 páginasUltra FiltrationSaanchi AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Skalar Methods: Analysis: Ortho Phosphate Range: 5 200 G P/liter Sample: Sea Water SANDocumento6 páginasSkalar Methods: Analysis: Ortho Phosphate Range: 5 200 G P/liter Sample: Sea Water SANBruno PereiraAinda não há avaliações
- Reactions of Synthetic ImportanceDocumento28 páginasReactions of Synthetic ImportanceRx Nadeem ChhipaAinda não há avaliações
- 921 Water DeterminationDocumento4 páginas921 Water DeterminationEspañola EloiseAinda não há avaliações
- Hazards from Untreated WastesDocumento6 páginasHazards from Untreated WastesAnindya GuhaAinda não há avaliações
- General Introduction: Chapter Four ExtractionDocumento19 páginasGeneral Introduction: Chapter Four ExtractionMujahid HaddadAinda não há avaliações
- Absorption of Drug From Non-Per Oral RoutesDocumento32 páginasAbsorption of Drug From Non-Per Oral Routesumamaheshwari33Ainda não há avaliações
- PengemulsiDocumento47 páginasPengemulsitika0638Ainda não há avaliações
- SMP Skim Milk Powder StandardsDocumento2 páginasSMP Skim Milk Powder StandardsShubham DubeyAinda não há avaliações
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography CHM260: Nor Akmalazura JaniDocumento62 páginasHigh Performance Liquid Chromatography CHM260: Nor Akmalazura JaniNurhayati HasanahAinda não há avaliações
- Method 8.7 - Refined Sugar: Reducing Sugars by The Knight and Allen MethodDocumento3 páginasMethod 8.7 - Refined Sugar: Reducing Sugars by The Knight and Allen Methodmari100% (1)
- Latest Technology in Cereals ProductionDocumento5 páginasLatest Technology in Cereals ProductionNadherah MohamadAinda não há avaliações
- ICBPT3SepProcIntro PDFDocumento37 páginasICBPT3SepProcIntro PDFSo Cho WingAinda não há avaliações
- Effervescent PharmaceuticalsDocumento37 páginasEffervescent Pharmaceuticalsatikah febrianiAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanism of Precipitate Formation NewDocumento12 páginasMechanism of Precipitate Formation NewAnonymous atBeojaAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid-Liquid ExtractionDocumento5 páginasLiquid-Liquid ExtractionFahad ShakeelAinda não há avaliações
- Ex 1 Post LabDocumento4 páginasEx 1 Post LabGicilKayeBarbacLovatoAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions PPT112Documento31 páginasSolutions PPT112sultanAinda não há avaliações
- Analgesic, Neuropharmacological, Anti-Diarrheal, and Cytotoxic Activities of The Extract of Solanum Sisymbriifolium (Lam.) LeavesDocumento11 páginasAnalgesic, Neuropharmacological, Anti-Diarrheal, and Cytotoxic Activities of The Extract of Solanum Sisymbriifolium (Lam.) LeavesApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Aquametry: East West UniversityDocumento17 páginasAquametry: East West UniversityApurba Sarker Apu100% (4)
- Phytochemical Analysis and Bioactivities of Aphanamixis Polystachya (Wall.) R. Parker Leaves From BangladeshDocumento7 páginasPhytochemical Analysis and Bioactivities of Aphanamixis Polystachya (Wall.) R. Parker Leaves From BangladeshApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Pharmacological Activities of Methanol Extract of Jatropha Gossypifolia FruitsDocumento5 páginasStudy of Pharmacological Activities of Methanol Extract of Jatropha Gossypifolia FruitsApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Non - Aqueous Acid - Base TitrationDocumento17 páginasNon - Aqueous Acid - Base TitrationApurba Sarker Apu100% (4)
- Phytochemical Analysis and Bioactivities of Argemone Mexicana Linn. LeavesDocumento8 páginasPhytochemical Analysis and Bioactivities of Argemone Mexicana Linn. LeavesApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Phytochemical Screening and in Vitro Evaluation of Pharmacological Activities of Aphanamixis Polystachya (Wall) Parker Fruit ExtractsDocumento6 páginasPhytochemical Screening and in Vitro Evaluation of Pharmacological Activities of Aphanamixis Polystachya (Wall) Parker Fruit ExtractsApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Analgesic, Neuropharmacological and Anti-Diarrheal Potential of Jatropha Gossypifolia (Linn.) Leaves in MiceDocumento6 páginasEvaluation of Analgesic, Neuropharmacological and Anti-Diarrheal Potential of Jatropha Gossypifolia (Linn.) Leaves in MiceApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment of Cytotoxic Activity of Two Medicinal Plants Using Brine Shrimp (Artemia Salina) As An Experimental ToolDocumento6 páginasAssessment of Cytotoxic Activity of Two Medicinal Plants Using Brine Shrimp (Artemia Salina) As An Experimental ToolApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemical Investigation and Biological Evaluation of The The Methanolic Extract of The Leaves of Nyctanthes Arbortristis in VitroDocumento8 páginasBiochemical Investigation and Biological Evaluation of The The Methanolic Extract of The Leaves of Nyctanthes Arbortristis in VitroApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Drying AgentDocumento13 páginasDrying AgentApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Fluorescence Spectroscopy: East West UniversityDocumento9 páginasFluorescence Spectroscopy: East West UniversityApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Analgesic, Neuropharmacological and Anti-Diarrheal Activities of Ethanol Extract of Solanum Sisymbriifolium FruitsDocumento6 páginasStudy of Analgesic, Neuropharmacological and Anti-Diarrheal Activities of Ethanol Extract of Solanum Sisymbriifolium FruitsApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To StereochemistryDocumento33 páginasIntroduction To StereochemistryApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Uropathogens Isolated From Pediatric Patients in A Selected Hospital of BangladeshDocumento3 páginasAntibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Uropathogens Isolated From Pediatric Patients in A Selected Hospital of BangladeshApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- HPLCDocumento145 páginasHPLCApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- Ca Channel BlockerDocumento22 páginasCa Channel BlockerApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid - Liquid ExtractionDocumento19 páginasLiquid - Liquid ExtractionApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Oral AntidiabeticsDocumento55 páginasOral AntidiabeticsApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Beta BlockersDocumento25 páginasBeta BlockersApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Antitubercular DrugsDocumento22 páginasAntitubercular DrugsApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Dose Calculation: 1) Preparation of 1% V/V Tween 80 in Saline: (For 150 ML)Documento3 páginasDose Calculation: 1) Preparation of 1% V/V Tween 80 in Saline: (For 150 ML)Apurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- ARBDocumento27 páginasARBApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetes MellitusDocumento29 páginasDiabetes MellitusApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Anti-Microbial TherapyDocumento34 páginasPrinciples of Anti-Microbial TherapyApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- ACE InhibitorDocumento19 páginasACE InhibitorApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Proton Pump Inhibitor Mechanism of ActionDocumento24 páginasProton Pump Inhibitor Mechanism of ActionApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Receptor BlockersDocumento11 páginasH2 Receptor BlockersApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Peptic Ulcers: PHRM 304Documento24 páginasPeptic Ulcers: PHRM 304Apurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Uropathogens Isolated From Pediatric Patients in A Selected Hospital of BangladeshDocumento3 páginasAntibiotic Susceptibility Patterns of Uropathogens Isolated From Pediatric Patients in A Selected Hospital of BangladeshApurba Sarker ApuAinda não há avaliações
- Science Quarter 4 Module 2Documento3 páginasScience Quarter 4 Module 2Christian AlbosAinda não há avaliações
- Synergistic Catalysis by Lewis Acid and Base Sites On Zro For Meerwein Ponndorf Verley ReductionDocumento7 páginasSynergistic Catalysis by Lewis Acid and Base Sites On Zro For Meerwein Ponndorf Verley ReductionRiza SaidAinda não há avaliações
- 8.10 CHNOPS Lab Organism 7Documento4 páginas8.10 CHNOPS Lab Organism 7Er FaenAinda não há avaliações
- GlicoliseDocumento13 páginasGlicoliseAna JuliaAinda não há avaliações
- 13X44 10130DSC13X44 Gori 44+ TDS (En) #3105Documento3 páginas13X44 10130DSC13X44 Gori 44+ TDS (En) #3105Ajith SomaratneAinda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Techniques Note-Ct105 (2) (Autosaved)Documento85 páginasLaboratory Techniques Note-Ct105 (2) (Autosaved)BORUTO ANIMEZONEAinda não há avaliações
- Antimalarial DrugsDocumento36 páginasAntimalarial DrugsKasim UmarAinda não há avaliações
- (23919531 - Open Agriculture) Cultivation of Agaricus Bisporus (Button Mushroom) and Its Usages in The Biosynthesis of NanoparticlesDocumento7 páginas(23919531 - Open Agriculture) Cultivation of Agaricus Bisporus (Button Mushroom) and Its Usages in The Biosynthesis of NanoparticlesAKAinda não há avaliações
- Automated and Accelerated Synthesis of Indole Derivatives On A Nano-Scale - Green ChemistryDocumento8 páginasAutomated and Accelerated Synthesis of Indole Derivatives On A Nano-Scale - Green Chemistrymarshall mathersAinda não há avaliações
- Stilbenes Preparation and AnalysisDocumento42 páginasStilbenes Preparation and AnalysisMiernha AyhoeeAinda não há avaliações
- ECO Brij L6L Liquid Laundry Detergent For Modern StainsDocumento1 páginaECO Brij L6L Liquid Laundry Detergent For Modern StainsrezaAinda não há avaliações
- A Sung CatalogDocumento44 páginasA Sung CatalogawasdaAinda não há avaliações
- CustomersDocumento572 páginasCustomersrajeev_snehaAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Data Sheet: Regalrez™ 1094 Hydrocarbon ResinDocumento2 páginasTechnical Data Sheet: Regalrez™ 1094 Hydrocarbon ResinPaul TsaiAinda não há avaliações
- Formulation Guide SilkgelDocumento2 páginasFormulation Guide SilkgelCatarinaAinda não há avaliações
- Carbon and Hydrogen Isotope Systematics of Bacterial Formation and Oxidation of Methane PDFDocumento24 páginasCarbon and Hydrogen Isotope Systematics of Bacterial Formation and Oxidation of Methane PDFxocitlaAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 1 Source and Characteristics of Industrial Waste WatersDocumento48 páginasCHAPTER 1 Source and Characteristics of Industrial Waste WatersJorge Rivera100% (3)
- Growth and Yield of Okra 2nd DraftDocumento17 páginasGrowth and Yield of Okra 2nd DraftSaheden SalilawanAinda não há avaliações
- Green Diesel Production From Upgrading of Cashew Nut Shell Liquid PDFDocumento11 páginasGreen Diesel Production From Upgrading of Cashew Nut Shell Liquid PDFDaniela J. TitusAinda não há avaliações
- 06 DNA Replication Damage and RepairDocumento14 páginas06 DNA Replication Damage and Repairفقوش عبودAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical Methodology For Emulsifiers Used Fatty Foods: A Review 1Documento2 páginasAnalytical Methodology For Emulsifiers Used Fatty Foods: A Review 1Monica chavez escamAinda não há avaliações
- Aldol & Similar Name Reaction - FinalDocumento32 páginasAldol & Similar Name Reaction - Finaldash guptaAinda não há avaliações
- Lec Notes LipidsDocumento13 páginasLec Notes LipidsJonah Micah MangacoAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Important Questions 2023-24Documento37 páginasCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Important Questions 2023-24Subramanian VasanthiAinda não há avaliações
- CARO - BE145L - A21 - Experiment 4 Final ReportDocumento8 páginasCARO - BE145L - A21 - Experiment 4 Final ReportRex KorrAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 6B CORROSIONDocumento19 páginasUnit 6B CORROSIONMeghana SAinda não há avaliações
- Process Aids Booklet ENG Print A4 AB VickersDocumento8 páginasProcess Aids Booklet ENG Print A4 AB VickersFabioAinda não há avaliações
- XXXVI/2. Paper and Paperboard For Baking Purposes: As of 01.04.2022Documento9 páginasXXXVI/2. Paper and Paperboard For Baking Purposes: As of 01.04.2022刘佳奇Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 - The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDocumento10 páginasLecture 2 - The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeKaye EvangelistaAinda não há avaliações
- Iso 1388 2 AfricanDocumento9 páginasIso 1388 2 AfricanJhonnathan VillacisAinda não há avaliações