Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
q4 Math Eqa Parents
Enviado por
api-296262817Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
q4 Math Eqa Parents
Enviado por
api-296262817Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
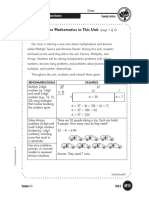
Math EQA
Dear Parents,
Here are the standards that we have covered in second grade this year. Our EQA will be a cumulative
approach to each of the standards covered this year.
4th 9 weeks
Arrays/Multiplication
Students will be able to partition a rectangle into rows and columns to create an array representing
repeated addition
Students will be able to identify the total amount in an array by determining the repeated addition
sentences used to describe the array by rows or by columns
Students will also be able to recognize and determine a number as even or odd by determining equal or
unequal pairs
Geometry/Fractions
Students should be able to identify common attributes (sides, angles, vertices) of the following plain
shapes: triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons
Students should be able to identify attributes of a cube (how many edges, vertices and faces)
Students should be able to recognize and create the following fractions halves, thirds, and fourths
Add and Subtract within 1000 (MGSE2.NBT.5)
Addition strategies (base ten blocks, decomposing, or number line)
Subtraction strategies (base ten blocks or number line)
Same usage and types of strategies as double digit, but students must be able to carry and borrow from
the hundreds place as well.
**See quarter 2 examples for strategies**
3rd 9 weeks
Time
Tell and write time to the nearest 5 minutes using AM and PM (MGSE2.MD.7)
students should be able to read a digital clock
students should be able to draw the hour and minute hands onto a clock to represent a certain time
students should be able to identify activities that would take place in the AM versus the PM
Example: John is eating breakfast at the time on the clock. What time is he eating breakfast. Do not
forget to label AM or PM.
Measurement
Select appropriate tools for measuring items (MGSE2.MD.1)
students should be able to use and estimate with these tools: rulers, yard sticks, meter sticks,
and measuring tape
Example: Which tool would you use to measure a basketball?
Measure the length of an object twice using two different measurements (MGSE2.MD.2)
Students should be able to measure an object using inches and centimeters, then relate the differences in
measurements by explaining how inches and centimeters are different.
Example: Explain why a crayon is 8 cm and only 3 inches.
Make reasonable estimates for measurement. (MGSE2.MD.3)
Students should be able to use inches, centimeters, feet, yards, and meters to estimate appropriate
lengths of items.
Example: What would be a reasonable estimate for the length of a pencil? 7 inches, 7 feet or 7 yards
Solve word problems involving adding, comparing or subtracting measurements. (MGSE2.MD.4)
Measure to determine how much longer one item is than another.
Add two measurements together.
Example addition: Betsy has a tower that is 23 feet tall. She has another tower that is 18 feet tall. How
tall would they be if she stacked the towers together?
Example subtraction: Taras doll is 13 inches tall. Her sisters doll is 18 inches tall. How much taller is
Taras doll?
Measure to create a data list and then plot the measurements on a line plot. (MGSE2.MD.9)
Money
Solve word problems involving coins and dollar bills. (MGSE2.MD.8)
Students should identify and know the value of pennies, nickels, dimes, quarters, and one dollar bills in
order to solve word problems involving money.
Example: Jenny has 3 quarter, 2 nickels and 5 pennies. How much money does Jenny have?
2nd 9 weeks
One- and two-step addition and subtraction word problems (MGSE2.OA.1)
Addition example: Mary brought in 32 box tops, and Sam brought in 41 box tops. How many box
tops do they have altogether?
Subtraction example: Susan made 24 cookies for her class. After she passed them out, she had
7 left. How many cookies did her class eat?
Multi-step: Jeremy was raking leaves. He found 7 red leaves and 5 brown leaves. The wind came
and blew 3 away. How many leaves does Jeremy have now?
Addition and Subtraction fluency strategies (MGSE2.OA.2)
Counting on, doubles, near doubles, make 10
Example: 8 + 2 + 5 Students should be able to use strategies to solve problems similar to this.
Add and subtract within 100 (MGSE2.NBT.5)
Addition: Solve using base 10, number line, or decomposing
Example: 33 + 21
Base 10:
Number Line:
33
43 53
Decomposing: 33 + 21
54
30 + 3
20 + 1
50 + 4 = 54
Subtraction: Solve using base 10 or number line
Example: 33 - 21
Base 10:
Number
Line
12
23
33
13
Interpret information on a graph (MGSE2.MD.10)
Students should be able to draw, read, and interpret bar and picture graphs.
1st 9 weeks
Place value with hundreds, tens, and ones (MGSE2.NBT.1)
Example: 524 is 5 hundreds, 2 tens, and 4 ones.
Read, write, and represent numbers up to 1000 in a variety of ways (MGSE2.NBT.3)
Standard form: 324
Expanded form: 300 + 20 + 4
Word form: three hundred twenty-four
Picture:
Skip count by 5, 10, and 100s (MGSE2.NBT.2)
Compare two and three digit numbers (MGSE2.NBT.4)
Students should use the symbols <, >, and = to compare numbers
Example : 825
800 + 50 + 2
Você também pode gostar
- 2014-15 Planning Template 2nd Grade MathDocumento10 páginas2014-15 Planning Template 2nd Grade Mathapi-249700554Ainda não há avaliações
- Second Grade Mathematics Unit 3 StandardsDocumento3 páginasSecond Grade Mathematics Unit 3 Standardsapi-325691485Ainda não há avaliações
- ACT Math Section and SAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionNo EverandACT Math Section and SAT Math Level 2 Subject Test Practice Problems 2013 EditionNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (3)
- M and D SituationsDocumento2 páginasM and D Situationsapi-260164071Ainda não há avaliações
- Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Parent Tip SheetDocumento2 páginasEureka Math Grade 2 Module 7 Parent Tip SheetL WadeAinda não há avaliações
- MathDocumento15 páginasMathapi-355584334Ainda não há avaliações
- Problemposing 131102211404 Phpapp01 PDFDocumento55 páginasProblemposing 131102211404 Phpapp01 PDFMutiara Dwi MeilindaAinda não há avaliações
- Year Level: 1/2 Topic: Maths Focus: Subtraction Unit OverviewDocumento10 páginasYear Level: 1/2 Topic: Maths Focus: Subtraction Unit Overviewapi-279201959Ainda não há avaliações
- Day 3Documento5 páginasDay 3Bethani ScottAinda não há avaliações
- Second Grade Mathematics Unit 5 StandardsDocumento2 páginasSecond Grade Mathematics Unit 5 Standardsapi-325691485Ainda não há avaliações
- Prac Lesson Plan Primary MathematicsDocumento9 páginasPrac Lesson Plan Primary Mathematicsapi-293527475Ainda não há avaliações
- 2010-2011 Early Elementary Mathematical Literacy Assessment (EEMLA) Common ErrorsDocumento2 páginas2010-2011 Early Elementary Mathematical Literacy Assessment (EEMLA) Common ErrorsKrishnendu RarhiAinda não há avaliações
- Exponent Evaluation Worksheet Is Attached BelowDocumento3 páginasExponent Evaluation Worksheet Is Attached Belowapi-311860591Ainda não há avaliações
- Eureka Mathtips For Parentsgrade 3 Module 3Documento2 páginasEureka Mathtips For Parentsgrade 3 Module 3api-261399250Ainda não há avaliações
- Maths TopicDocumento7 páginasMaths Topicjaheimcarl16Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 - Family LetterDocumento2 páginasUnit 2 - Family Letterapi-233210734Ainda não há avaliações
- Body of DiscreteDocumento185 páginasBody of DiscreteyacobAinda não há avaliações
- Problem PosingDocumento9 páginasProblem PosingRuth Baguio MirandaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Grade 8Documento15 páginasLesson Plan Grade 8api-459734860100% (1)
- Measurement of Two-Dimensional Figures Elise Wedel Grade: 7 Geometry 2 WeeksDocumento37 páginasMeasurement of Two-Dimensional Figures Elise Wedel Grade: 7 Geometry 2 WeeksJohnnyboy SalemAinda não há avaliações
- Year 5 t1 Unit 6Documento10 páginasYear 5 t1 Unit 6api-267136654Ainda não há avaliações
- LP Maths Doubling Halving Games Lesson 8Documento3 páginasLP Maths Doubling Halving Games Lesson 8api-156164130Ainda não há avaliações
- Geometry Observation Lesson For Area and PerimeterDocumento20 páginasGeometry Observation Lesson For Area and Perimeterapi-234842570Ainda não há avaliações
- Maths Lesson Plan - Grade 7 Chp4 ExponentsDocumento8 páginasMaths Lesson Plan - Grade 7 Chp4 Exponentssumit_majumdarAinda não há avaliações
- Unit Lesson Plan: Standards That Bridge The Entire UnitDocumento7 páginasUnit Lesson Plan: Standards That Bridge The Entire Unitapi-584007256Ainda não há avaliações
- Tedu 522 Activity DiaryDocumento8 páginasTedu 522 Activity Diaryapi-283147275Ainda não há avaliações
- Design Topic: Fractions - Subject(s) Math - Grade(s) - 4 - Designer(s) Kimberly Witham Understanding by DesignDocumento10 páginasDesign Topic: Fractions - Subject(s) Math - Grade(s) - 4 - Designer(s) Kimberly Witham Understanding by Designapi-300085736Ainda não há avaliações
- Raise The Bar On Problem SolvingDocumento10 páginasRaise The Bar On Problem Solvingapi-21940065Ainda não há avaliações
- Multiplication and Order of Operations: Goal Common Core State StandardDocumento3 páginasMultiplication and Order of Operations: Goal Common Core State StandardDavid TicoAinda não há avaliações
- Using Models To Build and Understanding of FunctionsDocumento9 páginasUsing Models To Build and Understanding of FunctionsTrabajos NbjAinda não há avaliações
- Mip 1 3Documento9 páginasMip 1 3BenAbudaAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For Grade 7 StudentsDocumento7 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For Grade 7 StudentsRomel John Ibasco Jamito100% (1)
- Maths Program Proforma Yr 6 T2Documento57 páginasMaths Program Proforma Yr 6 T2S TANCREDAinda não há avaliações
- Math LP Feb 23-27, 2015Documento9 páginasMath LP Feb 23-27, 2015Tasia Starling ScruggsAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiated Lessons 8th GradeDocumento4 páginasDifferentiated Lessons 8th Gradeapi-245618331Ainda não há avaliações
- Part-I Combinatorics: Elementary Counting Principles ObjectivesDocumento166 páginasPart-I Combinatorics: Elementary Counting Principles ObjectivesIvan MisicAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Program t3 w1-2Documento4 páginasMaths Program t3 w1-2api-250827437Ainda não há avaliações
- Math 05 11 13 Numberline AddingDocumento3 páginasMath 05 11 13 Numberline Addingapi-248032125Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson PlanDocumento7 páginasLesson Planapi-723369065Ainda não há avaliações
- Hannah Mellick Math 257 - 001 Instructor: Teresa Isom April 15th, 2020Documento6 páginasHannah Mellick Math 257 - 001 Instructor: Teresa Isom April 15th, 2020api-510694913Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Presentation Scoot GameDocumento4 páginasLesson Presentation Scoot Gameapi-273349792Ainda não há avaliações
- Carrillo Lesson1Documento7 páginasCarrillo Lesson1api-276580201Ainda não há avaliações
- Kincaid Ed 124 Final Project Development Instruction AssessmentDocumento11 páginasKincaid Ed 124 Final Project Development Instruction Assessmentapi-508325103Ainda não há avaliações
- 5 F A8 M Samenumeratorfracsw-Symbols WrefDocumento2 páginas5 F A8 M Samenumeratorfracsw-Symbols Wrefapi-291492450Ainda não há avaliações
- Array Lesson Plan-2Documento3 páginasArray Lesson Plan-2api-659399074Ainda não há avaliações
- UnitfouraDocumento2 páginasUnitfouraapi-132305143Ainda não há avaliações
- LessonsDocumento4 páginasLessonsapi-231033473Ainda não há avaliações
- Place Value UbD UnitDocumento10 páginasPlace Value UbD Unitkathryn moodyAinda não há avaliações
- Indirect Lesson PlanDocumento3 páginasIndirect Lesson Planapi-295821640Ainda não há avaliações
- 3rd Grade Unit 8 Parent Letter 13-14Documento3 páginas3rd Grade Unit 8 Parent Letter 13-14api-259997065Ainda não há avaliações
- Mtss Math Unit PlanDocumento2 páginasMtss Math Unit Planapi-273303177Ainda não há avaliações
- Subtraction Unit PlanDocumento4 páginasSubtraction Unit Planapi-291546390Ainda não há avaliações
- Poll Everywhere Lesson PlanDocumento3 páginasPoll Everywhere Lesson Planapi-2529031310% (1)
- Multiple Towers Division Stories Parent LetterDocumento2 páginasMultiple Towers Division Stories Parent Letterapi-297079632Ainda não há avaliações
- Bridges 3rd Grade Unit 2Documento2 páginasBridges 3rd Grade Unit 2api-289263859Ainda não há avaliações
- Vels and Ac Mathematics Lesson Plan Start and Jump NumbersDocumento7 páginasVels and Ac Mathematics Lesson Plan Start and Jump Numbersapi-221544422Ainda não há avaliações
- Q1 DLP Math G10 WEEK 1Documento5 páginasQ1 DLP Math G10 WEEK 1Baby DmAinda não há avaliações
- Ell Lesson Plan 1Documento5 páginasEll Lesson Plan 1api-266453331Ainda não há avaliações
- LayoutDocumento27 páginasLayoutAnonymous iZbVJqVAinda não há avaliações
- 2003 KS3 Maths - Paper 1 - Level 4-6Documento28 páginas2003 KS3 Maths - Paper 1 - Level 4-6Wong Kah Kei JoyceAinda não há avaliações
- 12 GRE Quant Practice QuestionsDocumento14 páginas12 GRE Quant Practice QuestionsSOMYA BANSALAinda não há avaliações
- Per g26 Pub 32704 Touchstone AssessmentQPHTMLMode1 32704O236 32704O236S10D1795 17060852160988057 JC1601372310008 32704O236S10D1795E1.html#Documento37 páginasPer g26 Pub 32704 Touchstone AssessmentQPHTMLMode1 32704O236 32704O236S10D1795 17060852160988057 JC1601372310008 32704O236S10D1795E1.html#Sandip pawarAinda não há avaliações
- Text-Cum-Workbook Arun T. Mavalankar H. C. Pradhan: Homi Bhabha Curriculum For Primary MathematicsDocumento198 páginasText-Cum-Workbook Arun T. Mavalankar H. C. Pradhan: Homi Bhabha Curriculum For Primary MathematicsShelly SinglaAinda não há avaliações
- Creative Thinking in Mathematics With Tangrams and The Geometer's SketchpadDocumento9 páginasCreative Thinking in Mathematics With Tangrams and The Geometer's Sketchpadupendar reddy MalluAinda não há avaliações
- DLL Theorems On RectangleDocumento5 páginasDLL Theorems On RectanglePatrick Guerra100% (1)
- National Fire Alarm and Signaling CodeDocumento2 páginasNational Fire Alarm and Signaling Codeabdulkidwai2009Ainda não há avaliações
- Plan Composition SchemeDocumento2 páginasPlan Composition SchemeJohn Lexter ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- 868289Documento4 páginas868289Andrei346Ainda não há avaliações
- Yearly PlanDocumento36 páginasYearly Planapi-542955727Ainda não há avaliações
- Plane and Solid Geometry-With AnswersDocumento7 páginasPlane and Solid Geometry-With Answersjovit100% (7)
- UKMT - JMC - Junior Mathematical Challenge 2013 - ExtendedDocumento17 páginasUKMT - JMC - Junior Mathematical Challenge 2013 - Extendedthatday826Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 6 Learner's PacketDocumento32 páginasGrade 6 Learner's PacketMark Bruce Adonis CometaAinda não há avaliações
- Design Against Fluctuating Loads of Helical SpringsDocumento29 páginasDesign Against Fluctuating Loads of Helical SpringsVikranth Deepak100% (1)
- Math9 Q3 Mod7 TrapezoidsAndKite V3Documento29 páginasMath9 Q3 Mod7 TrapezoidsAndKite V3alexablisssAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 6 Maths Practice WorksheetsDocumento2 páginasCBSE Class 6 Maths Practice WorksheetsANJALI SURYAWANSHIAinda não há avaliações
- Term 2 Assignment 1 Quadrilaterals - AnswersDocumento5 páginasTerm 2 Assignment 1 Quadrilaterals - Answersmridulika015Ainda não há avaliações
- Math9 Q3 Module6Documento17 páginasMath9 Q3 Module6Erl jhumo EdrosaAinda não há avaliações
- Jan 2020 CSEC Maths P2 SolutionsDocumento29 páginasJan 2020 CSEC Maths P2 SolutionscgxxfxrAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Maths Test: Class: VIIIDocumento7 páginasAdvanced Maths Test: Class: VIIIKamal100% (1)
- Qutada KhaledDocumento21 páginasQutada KhaledIsam Al HassanAinda não há avaliações
- AreaDocumento15 páginasAreanavyaAinda não há avaliações
- 8 Maths WorksheetsDocumento42 páginas8 Maths WorksheetsTarak Bhardwaj0% (1)
- Geometry HandbookDocumento82 páginasGeometry HandbookAshok Reddy100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths Chapter 11 Perimeter and AreaDocumento39 páginasNCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths Chapter 11 Perimeter and AreaashaAinda não há avaliações
- Ge6152 Engineering Graphics Reg2013 QBDocumento16 páginasGe6152 Engineering Graphics Reg2013 QBKarthik GanesanAinda não há avaliações
- Warm - Up: Definition: A Rectangle Is A Parallelogram With One Right AngleDocumento25 páginasWarm - Up: Definition: A Rectangle Is A Parallelogram With One Right AngleJack LinksAinda não há avaliações
- 1St Quarter Summative Test in English Iv (Objectives Based On Melc) Table of Specification Level of Behavior NO. OF Items % of Item Item PlacementDocumento11 páginas1St Quarter Summative Test in English Iv (Objectives Based On Melc) Table of Specification Level of Behavior NO. OF Items % of Item Item PlacementJAMAICA ATUTUBOAinda não há avaliações
- Engr. Lucas - Sketchup Manual PDFDocumento36 páginasEngr. Lucas - Sketchup Manual PDFAdrian Rhomel BandongAinda não há avaliações
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.No EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorNo EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Poker: A Beginners Guide To No Limit Texas Holdem and Understand Poker Strategies in Order to Win the Games of PokerNo EverandPoker: A Beginners Guide To No Limit Texas Holdem and Understand Poker Strategies in Order to Win the Games of PokerNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (49)
- Alchemy Elementals: A Tool for Planetary Healing: An Immersive Audio Experience for Spiritual AwakeningNo EverandAlchemy Elementals: A Tool for Planetary Healing: An Immersive Audio Experience for Spiritual AwakeningNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsNo EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- Basic Bridge: Learn to Play the World's Greatest Card Game in 15 Easy LessonsNo EverandBasic Bridge: Learn to Play the World's Greatest Card Game in 15 Easy LessonsAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeNo EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormNo EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Ainda não há avaliações
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNo EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingNo EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (21)
- Molly's Game: The True Story of the 26-Year-Old Woman Behind the Most Exclusive, High-Stakes Underground Poker Game in the WorldNo EverandMolly's Game: The True Story of the 26-Year-Old Woman Behind the Most Exclusive, High-Stakes Underground Poker Game in the WorldNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (129)
- Poker: How to Play Texas Hold'em Poker: A Beginner's Guide to Learn How to Play Poker, the Rules, Hands, Table, & ChipsNo EverandPoker: How to Play Texas Hold'em Poker: A Beginner's Guide to Learn How to Play Poker, the Rules, Hands, Table, & ChipsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldNo EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (80)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeNo EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeNo EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (8)
- Phil Gordon's Little Green Book: Lessons and Teachings in No Limit Texas Hold'emNo EverandPhil Gordon's Little Green Book: Lessons and Teachings in No Limit Texas Hold'emNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (64)
- The Book of Card Games: The Complete Rules to the Classics, Family Favorites, and Forgotten GamesNo EverandThe Book of Card Games: The Complete Rules to the Classics, Family Favorites, and Forgotten GamesAinda não há avaliações