Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Astrology Is The Study of The Movements and Relative Positions of Celestial Objects As A Means
Enviado por
Ishwarya SrikanthTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Astrology Is The Study of The Movements and Relative Positions of Celestial Objects As A Means
Enviado por
Ishwarya SrikanthDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
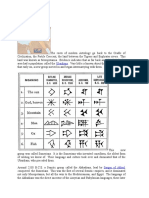
Astrology is the study of the movements and relative positions of celestial objects as a means
for divining information about human affairs and terrestrial events. Astrology has been dated to at
least the 2nd millennium BCE, and has its roots incalendrical systems used to predict seasonal
shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Many cultures have
attached importance to astronomical events, and some such as the Indians, Chinese,
and Maya developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial
observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its
roots to 19th-17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from which it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the
Arab world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is
often
associated
with
systems
ofhoroscopes that
purport
to
explain
aspects
of
person's personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial
objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.
Throughout most of its history astrology was considered a scholarly tradition and was common in
academic circles, often in close relation with astronomy, alchemy, meteorology, and medicine. It
was present in political circles, and is mentioned in various works of literature, from Dante
Alighieri and Geoffrey Chaucer to William Shakespeare, Lope de Vega and Caldern de la
Barca.
With the onset of the scientific revolution astrology was called into question; it has been
challenged successfully both ontheoretical and experimental grounds, and has been shown to
have no scientific validity or explanatory power. Astrology thus lost its academic and theoretical
standing, and common belief in astrology has largely declined. Astrology is now recognized to
be pseudoscience
Você também pode gostar
- Astrology Astrologia: EtymologyDocumento2 páginasAstrology Astrologia: EtymologyammuAinda não há avaliações
- Astr 2Documento1 páginaAstr 2rahulAinda não há avaliações
- Divination: Astrology Consists of Several Pseudoscientific Systems ofDocumento1 páginaDivination: Astrology Consists of Several Pseudoscientific Systems ofAnil Kumar BAinda não há avaliações
- Astrology History Part 1Documento4 páginasAstrology History Part 1kate trishaAinda não há avaliações
- AstrologyDocumento54 páginasAstrologyRamendra Singh Bhadauria (Astrobhadauria)100% (6)
- Astronomy - Its Historical Relationship With AstronomyDocumento6 páginasAstronomy - Its Historical Relationship With AstronomyLakshyaAinda não há avaliações
- As 1Documento1 páginaAs 1ammuAinda não há avaliações
- Astrology From WikipediaDocumento373 páginasAstrology From WikipediadimulatorAinda não há avaliações
- Astrology Aspects For Beginners: Learn About Astrology Basics, Horoscopes, Zodiac Signs and Astrological CompatibilityNo EverandAstrology Aspects For Beginners: Learn About Astrology Basics, Horoscopes, Zodiac Signs and Astrological CompatibilityNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (4)
- Brief History of Western AstrologyDocumento7 páginasBrief History of Western Astrologymurx2Ainda não há avaliações
- Start Reading AstrologyDocumento362 páginasStart Reading AstrologyAnonymous 2HXuAe50% (2)
- Astrology Is The Study of The Movements and RelatiDocumento10 páginasAstrology Is The Study of The Movements and RelatimoonthinkerAinda não há avaliações
- Astronomy Vs AstrologyDocumento4 páginasAstronomy Vs Astrologyserena lhaineAinda não há avaliações
- AstronumeratorDocumento18 páginasAstronumeratorjanarthanan1981Ainda não há avaliações
- A History of AstrologyDocumento1 páginaA History of AstrologyioanamaiAinda não há avaliações
- Constellations, Fixed Stars and The Zodiac in Islamic AstronomyDocumento11 páginasConstellations, Fixed Stars and The Zodiac in Islamic AstronomyMuhammad Azhar SaleemAinda não há avaliações
- The History of AstrologyDocumento36 páginasThe History of AstrologyDharani Dharendra DasAinda não há avaliações
- Astrology 101: From Sun Signs to Moon Signs, Your Guide to AstrologyNo EverandAstrology 101: From Sun Signs to Moon Signs, Your Guide to AstrologyNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (12)
- Astrology: Principles and Practice, Theological Viewpoints, Scientific Analysis and Cultural Impact - Shubhangi MaheshwariDocumento80 páginasAstrology: Principles and Practice, Theological Viewpoints, Scientific Analysis and Cultural Impact - Shubhangi Maheshwari蔡舒Ainda não há avaliações
- Astrology: 1 EtymologyDocumento21 páginasAstrology: 1 Etymologyj.miguel593515100% (1)
- Astrology & Astronomy in Iran and Ancient MesopotamiaDocumento11 páginasAstrology & Astronomy in Iran and Ancient MesopotamiaAna Paula Rodrigues100% (1)
- Astronomy Definition and HistoryDocumento16 páginasAstronomy Definition and HistoryMark RecareAinda não há avaliações
- Evolving Paper FinalDocumento11 páginasEvolving Paper FinalanaAinda não há avaliações
- A Brief Astrology History PDFDocumento48 páginasA Brief Astrology History PDFalex50% (2)
- Astrology (DHI Pingree)Documento7 páginasAstrology (DHI Pingree)Anonymous HxLd544Ainda não há avaliações
- Blinded by Starlight: The Pineal Gland and Western AstronomiaNo EverandBlinded by Starlight: The Pineal Gland and Western AstronomiaAinda não há avaliações
- Skies of Destiny: Analyzing the Influence of Planetary Interpretations in Medieval Europe and Islamic Golden Age: AI-Generated BooksNo EverandSkies of Destiny: Analyzing the Influence of Planetary Interpretations in Medieval Europe and Islamic Golden Age: AI-Generated BooksAinda não há avaliações
- A Brief History of AstrologyDocumento48 páginasA Brief History of Astrologycatchdgreen100% (1)
- Astronomy in Ancient IndiaDocumento22 páginasAstronomy in Ancient IndiaRahul KanthAinda não há avaliações
- AstrologyDocumento23 páginasAstrologytemp111tempAinda não há avaliações
- AstrologyDocumento17 páginasAstrologyAniPolnaAinda não há avaliações
- Diffrences Between Astronomy and AstrologyDocumento9 páginasDiffrences Between Astronomy and AstrologyNegrila RaresAinda não há avaliações
- To What Extent Does Greek Astrology ReprDocumento13 páginasTo What Extent Does Greek Astrology ReprNenad PetrövicAinda não há avaliações
- The+Lunario +Surfacing+the+Ilokano's+Belief+in+Astrology+as+a+Vehicle+to+Good+Life PDFDocumento18 páginasThe+Lunario +Surfacing+the+Ilokano's+Belief+in+Astrology+as+a+Vehicle+to+Good+Life PDFHenry Languisan100% (3)
- Paper Comm CapstoneDocumento12 páginasPaper Comm Capstoneapi-377794603Ainda não há avaliações
- Search Britannicaclick Here To Search Browse Login: AstrologyDocumento7 páginasSearch Britannicaclick Here To Search Browse Login: AstrologyrahulAinda não há avaliações
- History of AstronomyDocumento23 páginasHistory of Astronomygerardo_romero_41Ainda não há avaliações
- Astrology - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocumento13 páginasAstrology - Britannica Online EncyclopediaRohit SahuAinda não há avaliações
- Astrology - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento19 páginasAstrology - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNikhil ZopeAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4: Astronomy and AstrologyDocumento13 páginasUnit 4: Astronomy and AstrologyPraveen MaligiAinda não há avaliações
- The Followers of The Stars On The Early Sources An PDFDocumento31 páginasThe Followers of The Stars On The Early Sources An PDFAroonwan KongmebholAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Upload - AstroDocumento3 páginas1 Upload - AstroCiara AnneAinda não há avaliações
- Astrology BasicsDocumento31 páginasAstrology BasicsGetto VocabAinda não há avaliações
- Astrology The Science of Signs in The HDocumento28 páginasAstrology The Science of Signs in The HOana ToaderAinda não há avaliações
- Astrology: Aligning Your Personality with the Cosmos and Zodiac SignsNo EverandAstrology: Aligning Your Personality with the Cosmos and Zodiac SignsAinda não há avaliações
- Original 25Documento1 páginaOriginal 25APKAinda não há avaliações
- Astrology - Intro To Encyc - Nicholas CampionDocumento3 páginasAstrology - Intro To Encyc - Nicholas CampionajakukAinda não há avaliações
- Astro 3Documento2 páginasAstro 3rahulAinda não há avaliações
- Tic Time Lords - Demetra GeorgeDocumento5 páginasTic Time Lords - Demetra Georgekether.thipharet560167% (6)
- Science Copy Lesson 1Documento3 páginasScience Copy Lesson 1Mhie RelatorAinda não há avaliações
- Transmission Western AstrologyDocumento10 páginasTransmission Western AstrologyceudekarnakAinda não há avaliações
- Development of Science in AsiaDocumento8 páginasDevelopment of Science in AsiaEdison Canlas100% (1)
- Department of Business Administration Lucknow UniversityDocumento22 páginasDepartment of Business Administration Lucknow Universityabhinav pandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Melakartha Raga ChartDocumento1 páginaMelakartha Raga ChartIshwarya SrikanthAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Steps in Reliability AnalysisDocumento1 páginaBasic Steps in Reliability AnalysisIshwarya SrikanthAinda não há avaliações
- Swagatham KrishnaDocumento1 páginaSwagatham KrishnaIshwarya Srikanth100% (2)
- Materials Science: Fatigue AnalysisDocumento3 páginasMaterials Science: Fatigue AnalysisIshwarya SrikanthAinda não há avaliações
- Vibration Fatigue Is ADocumento2 páginasVibration Fatigue Is AIshwarya SrikanthAinda não há avaliações
- Materials Science: Fatigue LifeDocumento3 páginasMaterials Science: Fatigue LifeIshwarya SrikanthAinda não há avaliações
- Fatigue AnalysisDocumento6 páginasFatigue AnalysisIshwarya SrikanthAinda não há avaliações
- Materials Science: Fatigue LifeDocumento3 páginasMaterials Science: Fatigue LifeIshwarya SrikanthAinda não há avaliações
- Fatigue AnalysisDocumento4 páginasFatigue AnalysisIshwarya SrikanthAinda não há avaliações