Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
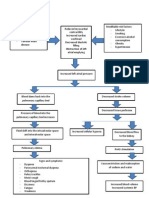
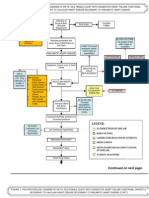
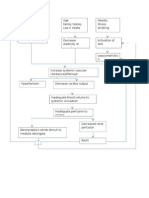
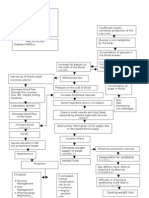
Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram
Enviado por
JacinthaVanathayahDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram
Enviado por
JacinthaVanathayahDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
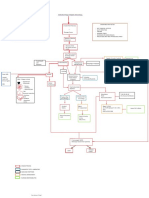
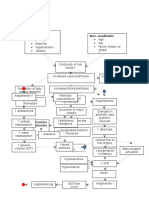
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: (Book -based)
Modifiable Factors:
Non-modifiable Factors:
Increase in age- 55 years old and
above
Gender- female
Sedentary lifestyle
Decreased elasticity of blood vessels and formation of plaques
on blood vessels
Narrowing of the blood vessels
Necrosis and scarring of the vascular endothelium
Impediment of blood flow to the body
Increased workload of the heart
Dilation of ventricles
Increased in preload
Increased stretching of myocardial muscle
Excessive stretching of myocardial muscle
Ineffective cardiac muscle contraction and increase O2 demand of
cardiac muscle cells
Decreased contraction of cardiac muscle
Decreased cardiac output and systemic perfusion
www.NursesLabs.com
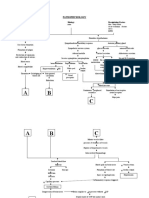
Activation of neurohormonal pathways in order to increase circulating
blood vessel
Continued neurohormonal stimulation
Cardiac remodelling
Decreased blood filling
Increased stroke volume and decreased cardiac output
Increased wall tension
Inadequate perfusion
PALLOR
Decreased
blood flow to
the kidneys
Kidneys
produce
hormones
Salt and water
retention
EDEMA
Decreased
perfusion in the
coronary
arteries
Deprivation of
cardiac muscle
cells of nutrients
needed for
survival
Increase
pulmonary
pressure
Separation of
mitral valve
leaflets
FATIGUE &
WEAKNESS
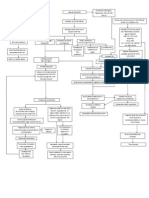
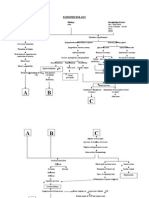
Increase
pulmonary
pressure
Impaired left
ventricular
relaxation
Normal Balance
between oxygen
supply and demand
is disrupted
Increase diastolic
pressure exceeding
hydrostatic &
osmotic pressure in
pulmonary
capillaries
ISCHEMIA
Increased
capillary
pressure in the
Conversion of
aerobic
metabolism to
anaerobic
Causes reduced
contractility
Decreases
the hearts
ability to
Fluid shifts from the
circulating blood
into the interstitium,
bronchioles, bronchi
& alveoli
Decreased
adenosine
phosphate
Increased lactic
acid production
Decreased lung
expansion
Pulmonary
Congestion
www.NursesLabs.com
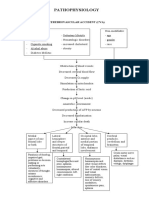
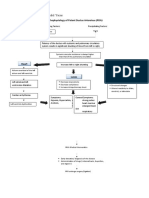
BRADYCARDIA
Irritation of
myocardial cells
CHEST PAIN
POSITIVE
TROPONIN T
DYSPNEA
Fluid trapped in
pulmonary
trees
BILATERAL
CRACKLES
www.NursesLabs.com
Você também pode gostar
- Pathophysiology HypertensionDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of CHFDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of CHFImae Mayo60% (5)
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocumento2 páginasAngina Pectoris Pathophysiologydana88% (8)
- Dka Patho DiagramDocumento1 páginaDka Patho DiagramGrae TaclobAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- ACS PathophysiologyDocumento2 páginasACS PathophysiologyFerliza OblenaAinda não há avaliações
- 3 PathophysiologyDocumento4 páginas3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiAinda não há avaliações
- A Case Study On Ischemic Stroke: J.H. Cerilles State CollegeDocumento21 páginasA Case Study On Ischemic Stroke: J.H. Cerilles State CollegeNicole Aranding100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDocumento6 páginasPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaAinda não há avaliações
- PathophysiologyDocumento4 páginasPathophysiologyAngelou Joefred Congreso100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of DMDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- ARF PathophysiologyDocumento2 páginasARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaPathophysiologynitlihpAinda não há avaliações
- Nstemi PathoDocumento2 páginasNstemi PathoSheana TmplAinda não há avaliações
- The Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureDocumento4 páginasThe Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureMar Ble50% (2)
- Pathophysiology ASCVDDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology ASCVDAlvheen JoaquinAinda não há avaliações
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocumento3 páginasAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsAinda não há avaliações
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog50% (4)
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocumento2 páginasSubarachnoid HemorrhageJethro Bacayo Zamora100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVADocumento1 páginaPathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (10)
- Concept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn NograDocumento3 páginasConcept Map of Subarachnoid Hemmorhage by Rhealyn NograRhealyn NograAinda não há avaliações
- Stroke PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasStroke PathophysiologyMaureen EricaAinda não há avaliações
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocumento1 páginaHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology CVADocumento2 páginasPathophysiology CVASewyel Garburi100% (6)
- Final CVADocumento76 páginasFinal CVAGabriel Apalisok100% (1)
- CKD PathoDocumento5 páginasCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology ESRDDocumento9 páginasPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocumento3 páginasChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramJake CaballoAinda não há avaliações
- Schematic Pathophysiology CVADocumento10 páginasSchematic Pathophysiology CVAheiyu100% (5)
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento2 páginasPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentJohn Michael FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Patho MIDocumento2 páginasPatho MIbanyenye25100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CHFDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
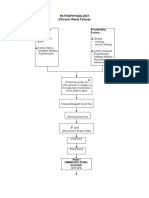
- Pathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)Documento3 páginasPathophysiology (Chronic Renal Failure)marshmalou86% (7)
- Ovarian Cancer, The NEw PathophyDocumento3 páginasOvarian Cancer, The NEw PathophylieselannjacobAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology of AtherosclerosisAzrul Hakim100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart Failurea_samiane64% (11)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- CVA PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasCVA Pathophysiologyshmily_0810Ainda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Documento2 páginasPathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Rodel Yacas100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocumento4 páginasPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyAinda não há avaliações
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocumento2 páginasPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Pathophysiology LeptospirosisDocumento1 páginaPathophysiology Leptospirosisjeoffrey_castro100% (3)
- Copd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Documento3 páginasCopd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Israel Soria EsperoAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocumento3 páginasPathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionronvhadzAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular SystemDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular SystemMon GabrielAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid and Hemo Dynamic Imbalances W 2Documento49 páginasFluid and Hemo Dynamic Imbalances W 2erwilli5Ainda não há avaliações
- D.5. Oxygenation and PerfusionDocumento98 páginasD.5. Oxygenation and PerfusionTricia Denise EstabilloAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac ArrhythmiaDocumento3 páginasCardiac Arrhythmiajae_lee_73Ainda não há avaliações
- KC PathoDocumento7 páginasKC PathoLomie GumayagayAinda não há avaliações
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocumento3 páginasSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoAinda não há avaliações
- Circulation: Ms. Jonalyn P. SantosDocumento18 páginasCirculation: Ms. Jonalyn P. SantosHoward John M. RamiterreAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsErrol B. TiozonAinda não há avaliações
- Risk Factor: Non Modifiable ModifiableDocumento3 páginasRisk Factor: Non Modifiable ModifiableRic VelascoAinda não há avaliações