Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Newton S Laws and Friction
Enviado por
api-275290316Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Newton S Laws and Friction
Enviado por
api-275290316Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Newton's Laws and Friction
Name:
1.
2.
Date:
A car accelerates uniformly from rest to a speed
of 10 meters per second in 2 seconds. The
acceleration of the car is
A.
0.2 m/sec2
B.
C.
10 m/sec2
D. 20 m/sec2
3.
5 m/sec2
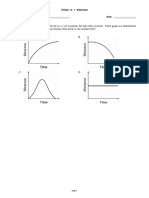
Which graph best represents the motion of an
object that was initially at rest and is accelerating
uniformly?
A.
B.
C.
D.
The diagram here shows a 1-kilogram stone being
dropped from a bridge 100 meters above a gorge.
4.
The graph shown represents the relationship
between velocity and time for a 2.0-kilogram cart
that is initially at rest and starts moving northward.
Which graph of distance traveled versus time
represents the motion of the freely falling stone?
A.
C.
B.
What is the acceleration of the cart shown at
t = 8 seconds?
D.
page 1
A.
0 m/s2
B.
C.
20 m/s2
D.
10 m/s2
20 m/s2
5.
Which graph best represents the motion of a freely
falling body near the Earth's surface?
A.
B.
C.
D.
7.
The diagram pictured shows speed as a function
of time for four cars, A, B, C, and D, in
straight-line motion. Which car experienced the
greatest average acceleration during this 6.0-second
interval?
A.
8.
6.
A locomotive starts from rest and accelerates at
0.12 meter per second2 to a speed of 2.4 meters
per second in 20 seconds. This motion could best
be described as
A.
constant acceleration and constant velocity
B.
increasing acceleration and constant velocity
C.
constant acceleration and increasing velocity
car A
B.
car B
C.
car C
D. car D
A car is traveling at a constant speed of 14 meters
per second along a straight highway. A tree and
a speed limit sign are beside the highway. As
it passes the tree, the car starts to accelerate.
The car is accelerated uniformly at 2.0 meters
per second2 until it reaches the speed limit sign,
5.0 seconds later.
When the car reaches the sign, the car's speed is
D. increasing acceleration and increasing velocity
page 2
A.
less than the speed limit
B.
greater than the speed limit
C.
equal to the speed limit
Newton's Laws and Friction
9.
Which two graphs best represent the motion of an
object falling freely from rest near Earth's surface?
11.
A.
B.
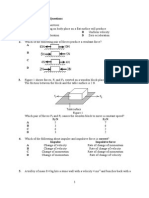
The diagram shows a student applying a 10-newton
force to slide a piece of wood at constant speed
across a horizontal surface. After the wood is cut
in half, one piece is placed on top of the other, as
shown.
What is the magnitude of the force, F, required to
slide the stacked wood at constant speed across
the surface?
A.
40 N
B.
20 N
C.
10 N
D. 5.0 N
C.
D.
12.
A 6-newton force and an 8-newton force act
concurrently on a box located on a frictionless
horizontal surface. Which top-view diagram shows
the forces producing the smallest magnitude of
accleration of the box?
A.
B.
10.
A person kicks a 4.0-kilogram door with a
48-newton force causing the door to accelerate at
12 meters per second2 . What is the magnitude of
the force exerted by the door on the person?
A.
48 N
B.
24 N
C.
12 N
C.
D. 4.0 N
D.
page 3
Newton's Laws and Friction
13.
A di erent force is applied to each of four
1-kilogram blocks to slide them across a uniform
steel surface at constant speed as shown below.
In which diagram is the coe cient of friction
between the block and steel smallest?
15.
Calculate the magnitude of the frictional force
acting on the box. [Show all work, including the
equation and substitution with units.]
16.
A car's performance is tested on various horizontal
road surfaces. The brakes are applied, causing the
rubber tires of the car to slide along the road
without rolling. The tires encounter the greatest
force of friction to stop the car on
A.
B.
C.
D.
14.
A.
dry concrete
B.
dry asphalt
C.
wet concrete
D. wet asphalt
Base your answer(s) to the following question(s)
on the information and diagram below.
A horizontal force of 8.0 newtons is used
to pull a 20.-newton wooden box moving
toward the right along a horizontal, wood
surface, as shown.
17.
Starting at point P on the diagram below, use a
metric ruler and a scale of 1.0 cm = 4.0 N to draw
a vector representing the normal force acting on
the box. Label the vector FN .
If a 65-kilogram astronaut exerts a force with a
magnitude of 50. newtons on a satellite that she
is repairing, the magnitude of the force that the
satellite exerts on her is
A.
0N
B.
50. N less than her weight
C.
50. N more than her weight
D. 50. N
page 4
Newton's Laws and Friction
18.
The data table below lists the mass and speed of
four di erent objects.
19.
Data Table
Object Mass (kg)
A
4.0
8.0
Speed (m/s)
6.0
6.0
5.0
3.0
16.0
What additional force, when applied to the object,
will establish equilibrium?
1.5
Which object has the greatest inertia?
A.
B.
Two forces act concurrently on an object on a
horizontal, frictionless surface, as shown in the
diagram below.
C.
D. D
A.
16 N toward the right
B.
16 N toward the left
C.
4 N toward the right
D. 4 N toward the left
page 5
Newton's Laws and Friction
20.
A 100.0-kilogram boy and a 50.0-kilogram girl, each holding a spring scale, pull against each other as shown in
the diagram below.
The graph below shows the relationship between the magnitude of the force that the boy applies on his spring scale
and time.
Which graph best represents the relationship between the magnitude of the force that the girl applies on her spring
scale and time?
A.
B.
C.
D.
page 6
Newton's Laws and Friction
Problem-Attic format version 4.4.268
c 20112016 EducAide Software
_
Licensed for use by Chris Munzert
Terms of Use at www.problem-attic.com
Newton's Laws and Friction
06/06/2016
1.
Answer:
2.
Answer:
3.
Answer:
16.
Answer:
4.
Answer:
17.
Answer:
5.
Answer:
18.
Answer:
6.
Answer:
19.
Answer:
7.
Answer:
20.
Answer:
8.
Answer:
9.
Answer:
10.
Answer:
11.
Answer:
12.
Answer:
13.
Answer:
14.
Answer:
[graph] vector 5.0 cm ( 0.2 cm)
long, directed upward. Example:
15.
Answer:
Você também pode gostar
- CSP Exam Equation Fully Explained DEMODocumento33 páginasCSP Exam Equation Fully Explained DEMOFff63% (8)
- As Newtons Laws and Momentum QuestionsDocumento61 páginasAs Newtons Laws and Momentum Questionshasan_shahryar2008Ainda não há avaliações
- Heating and CoolingDocumento45 páginasHeating and CoolingGillianne AndradeAinda não há avaliações
- RPT Chem Form 4 2020 (DLP)Documento25 páginasRPT Chem Form 4 2020 (DLP)WONG KEE PING MoeAinda não há avaliações
- 1d Forces Concepts Practice TestDocumento9 páginas1d Forces Concepts Practice TestNütella VallejosAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 Physics QuestionDocumento24 páginasGrade 9 Physics QuestionTsegaye D LemmaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics TestDocumento5 páginasPhysics TestAnonymous FH0ak9INfUAinda não há avaliações
- (Momentum, Works and Power) Quiz2023Documento14 páginas(Momentum, Works and Power) Quiz2023Haigou WaaaahAinda não há avaliações
- MODUL 1 FizikDocumento14 páginasMODUL 1 FizikMohd HafizuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Form 4 Modul WAJADocumento14 páginasPhysics Form 4 Modul WAJARamanath RamAinda não há avaliações
- Modul 1 f4f5Documento13 páginasModul 1 f4f5Tamil ArasuAinda não há avaliações
- Modul 1Documento13 páginasModul 1Ms PaulinaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Y10 Term 2 Exam Paper1Documento14 páginasPhysics Y10 Term 2 Exam Paper1Ezra Loganathan MuniandiAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Choice Review - DynamicsDocumento10 páginasMultiple Choice Review - DynamicsPremkumar NaikarAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Documento15 páginasPaper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Junaidah Mohamad RamliAinda não há avaliações
- Test 2 (August) Physics Form 4Documento5 páginasTest 2 (August) Physics Form 4Macita KaoruAinda não há avaliações
- T-Forces and Motion AssessmentDocumento12 páginasT-Forces and Motion AssessmentGan Hock KiamAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Energy And Momentum Practice TestDocumento11 páginasChapter 2 Energy And Momentum Practice TestMohamad SotoudehAinda não há avaliações
- AP Physics 1 - Test 05 - Force and Motion Score:: A B C D EDocumento6 páginasAP Physics 1 - Test 05 - Force and Motion Score:: A B C D ESTAinda não há avaliações
- PretestDocumento6 páginasPretestEdna Mae CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Newtons First and Second Laws Quiz1Documento4 páginasNewtons First and Second Laws Quiz1Aldous ChouAinda não há avaliações
- 10.dynamics FrictionDocumento5 páginas10.dynamics FrictionBryan Cedric NarneAinda não há avaliações
- Form 4 Physics Final Exam ReviewDocumento21 páginasForm 4 Physics Final Exam ReviewMohd AzlanAinda não há avaliações
- PhysDocumento10 páginasPhysahmedAinda não há avaliações
- PSI AP Physics I Dynamics Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocumento10 páginasPSI AP Physics I Dynamics Multiple-Choice QuestionsKarla PereraAinda não há avaliações
- Momentum 1Documento3 páginasMomentum 1api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011Documento19 páginasPeperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011Jill Peary RajuAinda não há avaliações
- Practica IiDocumento9 páginasPractica IiEduardo FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- AP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewDocumento6 páginasAP Physics Semester One MC Exam ReviewJordana BrenesAinda não há avaliações
- (UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestDocumento14 páginas(UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestMon Belle AmourAinda não há avaliações
- HL Paper1Documento21 páginasHL Paper1Proleteriat Dictatorship of Koperia0% (1)
- This Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options. Choose The Best Option For Each Question Then Blacken The Correct Space On The Answer Sheet. Answer All QuestionsDocumento8 páginasThis Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options. Choose The Best Option For Each Question Then Blacken The Correct Space On The Answer Sheet. Answer All Questionsjoe zulkefliAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Paper PDFDocumento18 páginasPhysics Paper PDFRana IrfanAinda não há avaliações
- Forces and Laws of Motion ExplainedDocumento3 páginasForces and Laws of Motion Explained박상현Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit test physics friction forces Newton's lawsDocumento8 páginasUnit test physics friction forces Newton's lawsDa babyAinda não há avaliações
- AP Phys 1 Quiz MomentumDocumento10 páginasAP Phys 1 Quiz MomentumWenyang LiAinda não há avaliações
- Motion in 1 DimensionDocumento11 páginasMotion in 1 Dimensionapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- 2.2 Forces ReviewDocumento17 páginas2.2 Forces ReviewAmrit sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- KUE Phys 2033 Home TestDocumento3 páginasKUE Phys 2033 Home TestHailemariam WeldegebralAinda não há avaliações
- Work Power and EnergyDocumento8 páginasWork Power and Energyapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- SECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DDocumento17 páginasSECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DNurlailie Md JamilAinda não há avaliações
- Regents Physics Holiday Homework Study GuideDocumento9 páginasRegents Physics Holiday Homework Study GuideAashna ShahAinda não há avaliações
- End of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CDocumento4 páginasEnd of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CChristina ZhangAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocumento14 páginasRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Grade 11 Unit 4 WorksheetDocumento14 páginasPhysics Grade 11 Unit 4 Worksheetsample nameAinda não há avaliações
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4Th Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento37 páginasPhysics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4Th Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFwadeperlid9d98k88% (8)
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocumento17 páginasRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBaoduy NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- CH 4-5 AP Problems All-1Documento21 páginasCH 4-5 AP Problems All-1Christian ChiuAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: KinematicsDocumento38 páginasMultiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: Kinematics张书Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics 2007 EUEEDocumento8 páginasPhysics 2007 EUEElikinaw demisieAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics Problems Solved Step-by-StepDocumento4 páginasMechanics Problems Solved Step-by-StepGokul NathAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz No. 1-Unit 1, 2, 3 - KINEMATICS, STATICS, DYNAMICS & ENERGY (SET A) - For StudentsDocumento6 páginasQuiz No. 1-Unit 1, 2, 3 - KINEMATICS, STATICS, DYNAMICS & ENERGY (SET A) - For StudentsChristian Nathaniel Ramon Palma100% (1)
- Phy Test Paper 2023 FinalDocumento21 páginasPhy Test Paper 2023 Finalshallom udehAinda não há avaliações
- General Physics (Phys 1011) : Worksheet 3Documento3 páginasGeneral Physics (Phys 1011) : Worksheet 3MeklitAinda não há avaliações
- Fizik KiDocumento9 páginasFizik KiKiTTyAinda não há avaliações
- Forces and NL Practice TestDocumento8 páginasForces and NL Practice TestCASIÑO SHANE VAST ANDREIAinda não há avaliações
- Physics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsDocumento9 páginasPhysics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsNathaly SosaAinda não há avaliações
- MCAS Forces and Equilibrium PracticeDocumento11 páginasMCAS Forces and Equilibrium PracticeSyd MalaxosAinda não há avaliações
- College Physics 4th Edition by Giambattista ISBN Test BankDocumento34 páginasCollege Physics 4th Edition by Giambattista ISBN Test Bankwilma100% (18)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- TextbookpreviewDocumento1 páginaTextbookpreviewapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Work Power and EnergyDocumento8 páginasWork Power and Energyapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Biotech Stock Game 1Documento6 páginasBiotech Stock Game 1api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Upstream Culture Part IIDocumento32 páginasUpstream Culture Part IIapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Momentum 1Documento3 páginasMomentum 1api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Upstream Culture Part I 1Documento18 páginasUpstream Culture Part I 1api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Practical Exam Study Guide Biotech 1 2016Documento1 páginaPractical Exam Study Guide Biotech 1 2016api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Newton S Laws and FrictionDocumento7 páginasNewton S Laws and Frictionapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Motion in 1 DimensionDocumento11 páginasMotion in 1 Dimensionapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Stock Game AlternativeDocumento1 páginaStock Game Alternativeapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Transformation Quick GuideDocumento2 páginasTransformation Quick Guideapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol c2987Documento1 página5 Minute Transformation Protocol c2987api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Rainforest GuideDocumento71 páginasRainforest Guideapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Research To Devel To ProdDocumento31 páginasResearch To Devel To Prodapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- b75 Lab 3, Rules SheetDocumento13 páginasb75 Lab 3, Rules SheetDuane HallAinda não há avaliações
- Molarity Worksheet 1Documento1 páginaMolarity Worksheet 1api-275290316100% (1)
- Metrology Lab 1310 3Documento8 páginasMetrology Lab 1310 3api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Common Solutions Lab-1Documento1 páginaCommon Solutions Lab-1api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Lsdocumentation 4Documento26 páginasLsdocumentation 4api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- 1310 Quiz 1 Study GuideDocumento1 página1310 Quiz 1 Study Guideapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Standard Operating Procedure Template - Single PageDocumento2 páginasStandard Operating Procedure Template - Single Pageapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Metric System PPT 1Documento20 páginasMetric System PPT 1api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Balsop 1 To 3Documento3 páginasBalsop 1 To 3api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Laboratory Math 4Documento30 páginasLaboratory Math 4api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Balsop 1 To 3Documento3 páginasBalsop 1 To 3api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Using The Scientific Method in BiotechDocumento2 páginasUsing The Scientific Method in Biotechapi-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Hazardcommunication 1Documento11 páginasHazardcommunication 1api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- Bacterial Growth 2016 Biotech 1Documento19 páginasBacterial Growth 2016 Biotech 1api-275290316Ainda não há avaliações
- IsolationDocumento20 páginasIsolationJolene MoniQue Lim SimpaoAinda não há avaliações
- Structure and Bonding IPADDocumento4 páginasStructure and Bonding IPADLarissa RubarajAinda não há avaliações
- Performance of emulsion explosives containing glass micro-balloonsDocumento7 páginasPerformance of emulsion explosives containing glass micro-balloonsOscar PamosAinda não há avaliações
- Heat exchanger specification sheetDocumento2 páginasHeat exchanger specification sheetDycka Anugerah PuryantoroAinda não há avaliações
- AkzoNobel SC CatalogDocumento41 páginasAkzoNobel SC CatalogVB JazminAinda não há avaliações
- 12.elastic ConstantsDocumento18 páginas12.elastic ConstantsaderancAinda não há avaliações
- AC Circuit Problems and SolutionsDocumento4 páginasAC Circuit Problems and SolutionsGarlapati Srinivasa RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Separation of HCl-H2SO4 by MDDocumento7 páginasSeparation of HCl-H2SO4 by MDKuldeep BhattAinda não há avaliações
- 2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual WTDocumento6 páginas2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual WTAndy DellingerAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of A JetDocumento14 páginasImpact of A JetKamarul Yusri100% (4)
- Exercise EC4Documento23 páginasExercise EC4babel_stanAinda não há avaliações
- Sa (CM)Documento5 páginasSa (CM)Sagar SwarupAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 10-Magnetism (2016)Documento74 páginasPhysics 10-Magnetism (2016)kimchen edenelleAinda não há avaliações
- To Estimate The Charge Induced On Each of The Two Identical Stryo Foam (Or Pith) Balls Suspended in A Vertical Plane by Making Use of Coulomb'S LawDocumento8 páginasTo Estimate The Charge Induced On Each of The Two Identical Stryo Foam (Or Pith) Balls Suspended in A Vertical Plane by Making Use of Coulomb'S LawAryan BudhathokiAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Code No. 1/2 Set: 3 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 General InstructionsDocumento5 páginasChemistry Code No. 1/2 Set: 3 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 General InstructionsShalini KumariAinda não há avaliações
- Curvature Radiation From A Quantum-Electrodynamics Point of ViewDocumento22 páginasCurvature Radiation From A Quantum-Electrodynamics Point of ViewMohammed NourAinda não há avaliações
- Precalculus Unit 6 Vectors NotesDocumento30 páginasPrecalculus Unit 6 Vectors Notesapi-287816312100% (1)
- Commercial Softener Specifications and Flow RatesDocumento1 páginaCommercial Softener Specifications and Flow Ratesrhusseinpos4765Ainda não há avaliações
- ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY PPT SampleDocumento10 páginasATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY PPT SamplegungankerkettaAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 21 Levee With Toe DrainDocumento24 páginasTutorial 21 Levee With Toe DrainMarcos MaAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Analysis of DomesDocumento10 páginasStructural Analysis of DomesThotho Kennedy100% (2)
- Torsion PDFDocumento8 páginasTorsion PDFrobertorcovAinda não há avaliações
- Applyingasuitablerouteforpreparation Fe 3 O4 Nanoparticlesby AmmoniaandinvestigationoftheirphysicalanddifferentmagneticpropertiesDocumento9 páginasApplyingasuitablerouteforpreparation Fe 3 O4 Nanoparticlesby AmmoniaandinvestigationoftheirphysicalanddifferentmagneticpropertiesGurudas VisputeAinda não há avaliações
- 2008 HKCEE Physics P2 SolDocumento24 páginas2008 HKCEE Physics P2 SolAlex KongAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Project On Properties of ElasticityDocumento25 páginasPhysics Project On Properties of ElasticityCsa Raj50% (2)
- Nuclear Reactor InstrumentationDocumento12 páginasNuclear Reactor InstrumentationRachit KanchanAinda não há avaliações
- Linear MotionDocumento29 páginasLinear MotionElyna RedzuanAinda não há avaliações
- Projectile MotionDocumento15 páginasProjectile MotionAndi Rafika Dwi Rachma100% (1)