Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Huawei Anti-DDoS Solution Brochure
Enviado por
jjfloressDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Huawei Anti-DDoS Solution Brochure
Enviado por
jjfloressDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
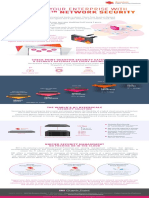
Anti-DDoS Solution
Highlights
ZTW attacks
Efficient and speedy: 200Gbit/s defense performance and
response within seconds
Application-layer
attacks
Malformed
packet attacks
Heavy traffic
attacks
Protected service system
Leaser self-service
system
Overview
With the IT and Internet evolution, the Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
attack has already broken away from original hacker behaviors. Instead, it
forms an integral dark industry chain with overwhelming damages.
At present, a single DDoS attack consumes more than 100 Gbit/s
bandwidth, ten times of that in 2007. DDoS attacks have increased by 20
times and over 30,000,000 zombie hosts flood the network. Moreover,
attack tools become intelligent and attack behaviors become hidden and
emulational. Especially, those attacks upon DC applications are rampant,
disabling the current defense measures of customers.
Huawei anti-DDoS solution incorporates extensive experience in network
security and full understanding of customer demands. Designed for
carriers, enterprises, data centers, and ICP service providers (including
Web portals, game service providers, online videos, DNS service providers,
and CDN services), the solution enhances the defense capability
against application-layer attacks and the attacks in IPv6-IPv4 composite
networking. This fully ensures network security and service continuity.
High-performance multi-core CPU, providing anti-DDoS products
covering 2G to 200G performance.
Self-learning of the service model and per-packet detect technology.
Once a traffic or packet anomaly is found, the defense policy is
automatically triggered. The defense latency is within two seconds.
Precise and comprehensive: "V-ISA" reputation technical
system, Can defend against hundreds of attacks
"V-ISA" reputation technical system, Can defend against hundreds of
DDoS attacks, with the industry-leading defense types.
Defense against over 200 zombies, Trojan horses, and worms,
protecting users from hackers.
IPv4/IPv6, as the first to support IPv6 attack defense.
Terminal identification technology, precisely identifying illegitimate
clients and ensuring zero false positive.
Malformed packet filtering
Feature-based filtering
Defense against forged IP address attacks
Behavior detection based on the real IP address
Session-based defense
Behavior analysis
Traffic shaping
Value-added operation: protection for thousands of leasers
and diverse self-services
AntiDDoS1000 series
AntiDDoS8000 series
Self-configuration of defense policies and generation of independent
security reports, providing invisibility into defense effects as a kind of
policy router.
Self-extraction of attack fingerprints, implementing emergency defense
and effectively defending against zero-day attacks as a kind of application
router.
Anti-DDoS Solution
Specifications
AntiDDoS1000 Series
AntiDDoS8000 Series
Model
AntiDDoS1520
AntiDDoS1550
AntiDDoS1500-D
AntiDDoS8030
AntiDDoS8080
AntiDDoS8160
Flood defense performance
3 Mpps
3 Mpps
3 Mpps
30 Mpps (15
Mpps per SPU)
75 Mpps (15
Mpps per SPU)
150 Mpps (15
Mpps per SPU)
Detecting/Cleaning
performance
2 Gbit/s
5 Gbit/s
5 Gbit/s
(detecting)
40 Gbit/s (20
Gbit/s per SPU
100 Gbit/s (20
Gbit/s per SPU)
200 Gbit/s (20
Gbit/s per SPU)
Defense start latency
2 seconds
2 seconds
2 seconds
2 seconds
2 seconds
2 seconds
Fixed interface
4 GE (RJ45)+4 GE (combo)
Expansion slot
2 FIC
16
2 FIC
None
2 FIC
Expansion interface card
2 10 GE (SFP+)
2 10 GE (SFP+)+8 GE (RJ45)
8 1 GE (SFP)
8 1 GE (RJ45)
1 10 GE (XFP)
2 10 GE (XFP)
1 10 G POS (XFP)
12 1 GE (SFP)
20 1 GE (SFP)
Bypass card
4 1 GE (RJ45)
Dual-link LC/UPC multi-mode optical interface
Dual-link LC/UPC single-mode optical interface
None
Dimensions (H W D)
43.6 442
560
43.6 442
560
43.6 442
560
175 442 650
(DC)
220 442 650
(AC)
620 442 650
(DC)
709 442 650
(AC)
1420 442
650 (DC)
1598 442
650 (AC)
Maximum power
consumption
150 W
150 W
150 W
1330 W (DC)
1368 W (AC)
3038 W (DC)
3231 W (AC)
5824 W (DC)
6195 W (AC)
IPv4 defense types
Anomaly filtering
Blacklist, HTTP field-based filtering, TCP/UDP/Other protocol load feature-based filtering
Protocol vulnerability
defense
Defense against IP spoofing, LAND, Fraggle, Smurf, WinNuke, Ping of Death, Tear Drop, IP Option, IP fragment control
packet, TCP label validity check, large ICMP control packet, ICMP redirect control packet, and ICMP unreachable
control packet attacks
Transport-layer attack
defense
Defense against SYN flood, ACK flood, SYN-ACK flood, FIN/RST flood, TCP fragment flood, UDP flood, UDP fragment
flood, and ICMP flood attacks
Scanning and sniffing
attack defense
Defense against port scanning, address scanning, Tracert control packet, IP Option, IP timestamp, and IP routing record
attacks
DNS attack defense
Defense against forged source DNS query flood attacks, real source DNS query flood attacks, DNS reply flood attacks,
DNS cache poisoning attacks, DNS protocol vulnerability attacks, and fast flux botnet
Web attack defense
Defense against HTTP get/post flood attacks, CC attacks, HTTP slow header/post attacks, HTTPS flood attacks, SSL DoS/
DDoS attacks, TCP connection attacks, Sockstress attacks, TCP retransmission attacks, and TCP null connection attacks
VoIP attack defense
Defense against SIP flood attacks
Zombie/Trojan horse/
Worm attack defense
Defense against over 200 zombies, Trojan horses, and worms, such as LOIC, HOIC, Slowloris, Pyloris, HttpDosTool,
Slowhttptest, and Thc-ssl-dos
IPv6 defense types
IPv4 defense types
Defense against ICMP fragment attacks, blacklist, HTTP field-based filtering, TCP/UDP/Other prorocol load featurebased filtering, SYN flood attacks, ACK flood attacks, SYN-ACK flood attacks, FIN/RST flood attacks, TCP fragment flood
attacks, UDP flood attacks, UDP fragment flood attacks, ICMP flood attacks, Forged source DNS query flood attacks,
real source DNS query flood attacks, DNS reply flood attacks, DNS cache poisoning attacks, DNS protocol vulnerability
attacks, fast flux botnet, HTTP get/post flood attacks, CC attacks, HTTP slow header/post flood attacks, HTTPS flood
attacks, SSL DoS/DDoS attacks, TCP connection attacks, Sockstress attacks, TCP retransmission attacks, TCP null
connection attacks, and SIP flood attacks
IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack attack
defense
Supported
enterprise.huawei.com
Você também pode gostar
- CheckPoint NG VPN 1/Firewall 1: Advanced Configuration and TroubleshootingNo EverandCheckPoint NG VPN 1/Firewall 1: Advanced Configuration and TroubleshootingAinda não há avaliações
- Huawei Anti-DDoS Solution Mainslide - ISPDocumento24 páginasHuawei Anti-DDoS Solution Mainslide - ISPFeleke AfeworkAinda não há avaliações
- Radware DefensePro SpectDocumento6 páginasRadware DefensePro SpectCes LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Radware Spec & PriceDocumento133 páginasRadware Spec & Pricefaizal azizAinda não há avaliações
- ADC. Application Deiivery Controller. Petrl@Documento102 páginasADC. Application Deiivery Controller. Petrl@Ivan Boris Quisbert100% (1)
- DDoS Protection PDFDocumento56 páginasDDoS Protection PDFming liAinda não há avaliações
- Cloud Application and Network Security 10-12-2022Documento1.693 páginasCloud Application and Network Security 10-12-2022Sandi ACAinda não há avaliações
- Grid Stream Solution OverviewDocumento11 páginasGrid Stream Solution OverviewMed Amine TAHIRIAinda não há avaliações
- Radware ERT Premium Customer Guide-WelcomeDocumento9 páginasRadware ERT Premium Customer Guide-Welcometest202121Ainda não há avaliações
- 08-Huawei Cyber Security Guide For PartnersDocumento30 páginas08-Huawei Cyber Security Guide For Partnerskoprael zuky100% (1)
- AlteonOS 32-0-0 CLI Application GuideDocumento977 páginasAlteonOS 32-0-0 CLI Application GuideVitaly KroivetsAinda não há avaliações
- Radware Certainty Support GuideDocumento56 páginasRadware Certainty Support Guidebalamurali_aAinda não há avaliações
- F5 5G WP BuildingBetter5GSecurity Final 120720Documento14 páginasF5 5G WP BuildingBetter5GSecurity Final 120720Jussein TorresAinda não há avaliações
- 300-101 DefensePro-Level-1 Training Outline V5-Feb 21 2018 PDFDocumento4 páginas300-101 DefensePro-Level-1 Training Outline V5-Feb 21 2018 PDFAlberto HuamaniAinda não há avaliações
- CWNA QuestionsDocumento17 páginasCWNA Questions沈云email=jarod416@gmail.comAinda não há avaliações
- Radware-4008 Data SheetDocumento1 páginaRadware-4008 Data SheetkhandeshaAinda não há avaliações
- Radware Alteon Tech SpecsDocumento2 páginasRadware Alteon Tech Specstest202121Ainda não há avaliações
- Radware DefensePro Tech Specs 2018 USDocumento3 páginasRadware DefensePro Tech Specs 2018 USAyush BaloniAinda não há avaliações
- Arbor-Advanced DDoS Trends and ProtectionDocumento43 páginasArbor-Advanced DDoS Trends and ProtectionmejamesonAinda não há avaliações
- Bastion Quickstart enDocumento29 páginasBastion Quickstart enHalil DemirAinda não há avaliações
- 5G Sannew012019Documento58 páginas5G Sannew012019VijayNishaAinda não há avaliações
- Bitrate MinDocumento12 páginasBitrate MinDan-ko S Valen-tinoAinda não há avaliações
- Network Congestion ManagementDocumento15 páginasNetwork Congestion Managementcarlos_lopez_gordoAinda não há avaliações
- Cloud WAF CDN Technical in DepthDocumento46 páginasCloud WAF CDN Technical in DepthtuanltAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Network Taps: The First Step To VisibilityDocumento16 páginasUnderstanding Network Taps: The First Step To VisibilityCCIE Detect100% (1)
- Firewall Analyzer Administrator GuideDocumento608 páginasFirewall Analyzer Administrator GuideJota SantosAinda não há avaliações
- CheckPoint Firewall BladesDocumento2 páginasCheckPoint Firewall BladesMehnaz PriyankaAinda não há avaliações
- GigamonDocumento52 páginasGigamonsathiaseelans5356Ainda não há avaliações
- S05M01 - Version 6 OverviewDocumento26 páginasS05M01 - Version 6 Overviewkhalid saidiAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Analysis of The EIGRP Routing Protocol: Mr. Syed IslamDocumento382 páginasCritical Analysis of The EIGRP Routing Protocol: Mr. Syed IslamAadan CaddeAinda não há avaliações
- Feasibility Study ExampleDocumento3 páginasFeasibility Study Examplewmarcia20050% (2)
- Ebook SDWAN When The Internet Becomes The Network 2Documento14 páginasEbook SDWAN When The Internet Becomes The Network 2Razvan FilipAinda não há avaliações
- Radware LP - Alteon5224 ProductPresentationDocumento26 páginasRadware LP - Alteon5224 ProductPresentationanas1988MAAinda não há avaliações
- Switch v7 Ch08Documento65 páginasSwitch v7 Ch08TheltonAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco Endpoint Overview-MatrixDocumento18 páginasCisco Endpoint Overview-Matriximran_aftech@yahoo.comAinda não há avaliações
- EVE COMM COOK BOOK LatestDocumento167 páginasEVE COMM COOK BOOK LatestarthuriphoneAinda não há avaliações
- Horizontal StackingDocumento8 páginasHorizontal StackingSimon SparksAinda não há avaliações
- Radius Manager GuideDocumento73 páginasRadius Manager GuideAlex KobeissyAinda não há avaliações
- Buyer's Guide For Complete Privileged Access Management (PAM)Documento37 páginasBuyer's Guide For Complete Privileged Access Management (PAM)vphuc1984Ainda não há avaliações
- Ruckus Wireless 802 11u Hotspot 2 - 0 (v1)Documento12 páginasRuckus Wireless 802 11u Hotspot 2 - 0 (v1)javierdb2012Ainda não há avaliações
- IES 1248 71 - v3 50 - UsesGruideDocumento295 páginasIES 1248 71 - v3 50 - UsesGruideNguyễn HảiAinda não há avaliações
- 8000 Intelligent Network Manager SR6.1 Software Installation ManualDocumento205 páginas8000 Intelligent Network Manager SR6.1 Software Installation Manualtho anhAinda não há avaliações
- GNS3 - Creating The Simplest TopologyDocumento18 páginasGNS3 - Creating The Simplest Topologyclu5t3rAinda não há avaliações
- Configuration Guidefor BIG-IP Global Traffic ManagerDocumento350 páginasConfiguration Guidefor BIG-IP Global Traffic ManagerjavirodzAinda não há avaliações
- CISCO Firepower NXGFWDocumento24 páginasCISCO Firepower NXGFWkishorsriramAinda não há avaliações
- CAMBIUM EPMPCnPIlotCnMaestro Seminar ShortOct2015-3Documento93 páginasCAMBIUM EPMPCnPIlotCnMaestro Seminar ShortOct2015-3sellabiAinda não há avaliações
- How To Connect Lora RAK811 To The Things NetworkDocumento17 páginasHow To Connect Lora RAK811 To The Things NetworkAravind VinasAinda não há avaliações
- Faculty Class Alert Using GSMDocumento80 páginasFaculty Class Alert Using GSMpraveen_kodgirwarAinda não há avaliações
- Sandvine SPBDocumento6 páginasSandvine SPBКирилл Симонов100% (1)
- Firewalls For Network SecDocumento48 páginasFirewalls For Network Sectarnedo1Ainda não há avaliações
- DS - HP ProLiant DL360p Gen8 ServerDocumento4 páginasDS - HP ProLiant DL360p Gen8 Serverprae90Ainda não há avaliações
- Radware Installation and Maintenance Guide-Feb-2011Documento115 páginasRadware Installation and Maintenance Guide-Feb-2011Sook SabuyAinda não há avaliações
- The Hershey Company - 216706-9.4 - Zscaler 2022 - Renewal - 2-23-2022 - Change OrderDocumento2 páginasThe Hershey Company - 216706-9.4 - Zscaler 2022 - Renewal - 2-23-2022 - Change OrderCamila SatoAinda não há avaliações
- Vsphere 4.1 Cheat SheetDocumento2 páginasVsphere 4.1 Cheat SheetstrcdplyAinda não há avaliações
- BT Managed Cloud Security (Zscaler) Service AnnexDocumento12 páginasBT Managed Cloud Security (Zscaler) Service AnnexPrasad KshirsagarAinda não há avaliações
- Lenel Systems International Inc.: Hardware Products CatalogDocumento68 páginasLenel Systems International Inc.: Hardware Products CatalogFranklin AlvaradoAinda não há avaliações
- slx-20 1 1-L2guideDocumento291 páginasslx-20 1 1-L2guidePrinceRaiAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco IronPortDocumento59 páginasCisco IronPortMuralyAinda não há avaliações
- Check Point - Automated Web Application and Api ProtectionDocumento4 páginasCheck Point - Automated Web Application and Api ProtectionjjfloressAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum Network Security InfographicDocumento1 páginaQuantum Network Security InfographicjjfloressAinda não há avaliações
- 8021 XDocumento40 páginas8021 XjjfloressAinda não há avaliações
- Module 12 Lab AppendixDocumento13 páginasModule 12 Lab AppendixjjfloressAinda não há avaliações
- Bcse308l Computer-Networks TH 11.0 67 Bcse308lDocumento3 páginasBcse308l Computer-Networks TH 11.0 67 Bcse308lDeepanshi RoyAinda não há avaliações
- C Socket Programming Tutorial Writing Client Server Programs in C Using Sockets Corporate Microcomputing DepartmentDocumento31 páginasC Socket Programming Tutorial Writing Client Server Programs in C Using Sockets Corporate Microcomputing Departmentaditya_kumar_meAinda não há avaliações
- Managed Gigabit Switches: Product HighlightsDocumento11 páginasManaged Gigabit Switches: Product HighlightsChuks ValentineAinda não há avaliações
- 46xxsettingsNEW (00000003)Documento199 páginas46xxsettingsNEW (00000003)Maina MathengeAinda não há avaliações
- H3C VSR1000&VSR2000 H3C-CMW710-E0322-X64 版本说明书Documento38 páginasH3C VSR1000&VSR2000 H3C-CMW710-E0322-X64 版本说明书firstwang0123Ainda não há avaliações
- 21.7.5 Packet Tracer - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using The CLI - ITExamAnswersDocumento5 páginas21.7.5 Packet Tracer - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using The CLI - ITExamAnswersdounia bensalahAinda não há avaliações
- Neutrinoe224 FDD Enb Data Sheet-Baibs - Qafaqata - 2.16.X-02Documento5 páginasNeutrinoe224 FDD Enb Data Sheet-Baibs - Qafaqata - 2.16.X-02ChinbatAinda não há avaliações
- ODR002031 Configure OSPF On NE Series Routers (V8) ISSUE 1Documento94 páginasODR002031 Configure OSPF On NE Series Routers (V8) ISSUE 1Randy DookheranAinda não há avaliações
- Konfigurasi Vyatta Dalam LANDocumento4 páginasKonfigurasi Vyatta Dalam LANryo100% (4)
- CCNA Notes Guide Updated ImpDocumento480 páginasCCNA Notes Guide Updated ImpArslan Kamran JuttAinda não há avaliações
- HN8255Ws Datasheet: Product DetailsDocumento4 páginasHN8255Ws Datasheet: Product Details박철민Ainda não há avaliações
- CCNA4-Lab 2: DHCP: Scenario For DHCP ConfigurationDocumento2 páginasCCNA4-Lab 2: DHCP: Scenario For DHCP ConfigurationNhựt LưuAinda não há avaliações
- ServicesDocumento11 páginasServicesSAPDHRUVAinda não há avaliações
- EXEMYS - RS232 To TCPDocumento2 páginasEXEMYS - RS232 To TCPJorge_Andril_5370Ainda não há avaliações
- Flame Alert: Some Readers Are Throwing Fits Because I Dared To Compare DOS To Bash. I Can Compare CMD - Exe To Bash If I Want To. Nanny Nanny Nah NahDocumento10 páginasFlame Alert: Some Readers Are Throwing Fits Because I Dared To Compare DOS To Bash. I Can Compare CMD - Exe To Bash If I Want To. Nanny Nanny Nah Nahgetmak99Ainda não há avaliações
- TCP VS UdpDocumento5 páginasTCP VS UdpLavanya_123Ainda não há avaliações
- C79000-G8976-1466 ROS v5.5 RSG909R ConfigurationManualDocumento432 páginasC79000-G8976-1466 ROS v5.5 RSG909R ConfigurationManualSever SudakovAinda não há avaliações
- Remove All The Ads From Internet On The RouterDocumento1 páginaRemove All The Ads From Internet On The RouterChakil JaifarAinda não há avaliações
- LogDocumento478 páginasLogMaria Isabel AlesnaAinda não há avaliações
- Not As Good As Nmap Handy IfDocumento1 páginaNot As Good As Nmap Handy Ifopenid_9V8YnhpLAinda não há avaliações
- PMP 450x System Release Notes 16.1Documento30 páginasPMP 450x System Release Notes 16.1Yesid Barreto ClavijoAinda não há avaliações
- Data Sheet 150m Wireless N Adsl2 Routerdt 850w PDFDocumento4 páginasData Sheet 150m Wireless N Adsl2 Routerdt 850w PDFvinod7668Ainda não há avaliações
- FortiADC Deployment Guide. High-Performance SSL Inspection With FortiADC and FortiGateDocumento50 páginasFortiADC Deployment Guide. High-Performance SSL Inspection With FortiADC and FortiGateHoang ThinhAinda não há avaliações
- B44 CCNA Bangla TutorialDocumento40 páginasB44 CCNA Bangla TutorialDipta Dasgupta20% (5)
- Diameter Signaling Control (DSC) - AlepoDocumento2 páginasDiameter Signaling Control (DSC) - AlepojrashevAinda não há avaliações
- 400 101 PDFDocumento986 páginas400 101 PDFJoel Maxmillan RugarabamuAinda não há avaliações
- ZXA10 C220: Command Manual (Volume I)Documento222 páginasZXA10 C220: Command Manual (Volume I)Damian RattalinoAinda não há avaliações
- The Mac Address: by Ahmed El HefnyDocumento10 páginasThe Mac Address: by Ahmed El HefnyHoussemAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter4 - Network AssuranceDocumento17 páginasChapter4 - Network AssuranceBeza GetachewAinda não há avaliações
- Ip AddressingDocumento36 páginasIp Addressingrahul jainAinda não há avaliações