Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Balanced Suspension Skeletal Traction
Enviado por
fegerileneDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Balanced Suspension Skeletal Traction
Enviado por
fegerileneDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NURSING CARE MANAGEMENT 102
ORTHOPEDIC NURSING
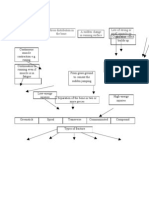
BALANCED SUSPENSION SKELETAL TRACTION
Balanced suspension traction is used to stabilize fractures of the femur and requires an invasive procedure in which
pins, screws or wires are surgically installed.
Weights used in skeletal traction generally range from 25-40lbs (11-18kg)
Purpose:
To maintain the anatomical position of the fractured bone.
Materials needed:
1. Thomas splint – placement of the thigh 7. Rest splint
2. Pearson attachment – placement of the leg 8. 3 ropes:
3. Steinman’s holder a. Thigh rope – the shortest
4. Steinman’s pin b. Suspension rope – the longest
5. Traction weight c. Traction rope
a. 10% of the body weight 9. Slings and pins
b. Inside of the suspension rope 10. Foot board
6. Suspension weight
a. 50% of the traction weight
Thomas Splint
Pearson Attachment
Rest Splint Steinman Holder
Steinman Pin
Steps in the application of traction: 1. Verify doctor’s order
2. Inform patient about the need and purpose of the b. Check the principles of sling application and
procedure make the necessary adjustment and also
3. Preparation: check the correct alignment.
a. Identify the different types of orthopedic bed
b. assemble the needed equipments 7. Apply suspension traction
Thomas Splint a. One end of the thigh rope to be attached to
Pearson attachment the lateral aspect of the ischial ring with a
c. Know the affected extremity slip knot.
d. Where to stand – look for the last pulley and b. Attach suspension rope on the mid part of the
stand on the side thigh rope, to the 1st pulley
c. Insert the suspension weight
4. Mount the Thomas and Pearson on the rest splint. d. Hang it on the 1st pulley
5 Principles in the application of slings e. Then pass it on the 2nd pulley under the rest
Not too tight not too close splint and clobe it with hitch knot on the
1 inch distance between the slings to Thomas splint
promote aeration or ventilation f. And another clobe hitch knot on the Pearson,
Popliteal and heel portion should be from and finally close it with a knot to secure it.
sling
Smooth and right side should come in 8. Remove the rest splint
contact with the patient’s skin 9. Apply foot support
10. Check the principle of traction emphasizing the 5
(2) longer and wider slings for thigh
Principles of traction and discuss the nursing
portion and (3) for the leg area
care.
How to apply sling?
Swing the patient to and from side to side to check the
Start from the medial side to the lateral side
efficiency of traction
Secure both ends together 1. Patient should be on a dorsal recumbent position.
Fan fold nicely on the lateral aspect and 2. Line of pull should be in line with the deformity
secure with pin or clip positioning of a diamond bar positioning of a
Observe the principle of not too tight and pulley.
not too loose and avoiding hitting the a. 1st pulley should be in line with the thigh
patient’s extremity with the pin b. 2nd pulley should be in line with the knee or
The thigh rope should be attached on the screw
medial aspect to the lateral aspect. c. 3rd pulley should be in line with the (1st) and
(2nd) pulley.
5. Insertion of the apparatus under the affected
extremity 3. Should always be continuous; emphasize the
Three Manpower needed importance of manual traction.
a. To insert the whole apparatus under the 4. Avoid friction
affected extremity 5. Provide counter traction – patient’s body weight
b. Manual traction to be released after the will serve as counter traction.
completion of traction weight in the 3rd pulley
c. To lift the affected extremity Removal of Traction
Simultaneously at the count of three 1. Apply rest splint.
Instruction to the patient: 2. Hang suspension weight on the 1st pulley.
o Hold on the trapeze 3. Remove the knot on the Pearson attachment and
o Flexed the unaffected leg at the count Thomas splint. – to completely remove
of 3 suspension weight.
The three manpower must do their work 4. Apply manual traction on the Steinman pin
simultaneously holder.
5. Remove the traction weight on the 3rd pulley;
6. Application of traction weight secure the traction rope on the rest splint another
a. Rope attached to the Steinman pin holder to on the Thomas and Pearson attachment.
run along the 3rd pulley and attached the
prescribed weight.
Suspension Rope
Traction Rope
Steinman Holder
Thigh rope
Steinman Pin
Thomas Splint
Rest Splint
Pearson Attachment
1st Pulley
2nd Pulley
1st Pulley
Suspension
Rope
Traction Rope
Suspension Weight Trapeze
Vertical Bar Horizontal Bar
Diagonal Bar
Vertical Bar
Traction Weight
The Thomas Splint (half ring) is applied in various ways: with the ring fitted posteriorly against the ischium or
anteriorly in the groin. The thigh rest in the canvas or bandage strip sling with the popliteal space left free. The
leather ring should not be wrapped or padded. If kept smooth, dry and polished, the leather of the ring is being
designed to rest against the skin and resist moisture.
The Pearson Attachment is attached by clamps to the Thomas Splint at the knee level. A canvas or bandage-strip
sling supports the lower leg and provides the desired degree of knee flexion. A footplate is attached to the distal
end of the Pearson Attachment to support the foot in a neutral position. The heel should be left free.
The traction should be in line with the long axis of the femoral shaft and is maintained by the rope, pulley and
weights attached to the skeletal tractor, which is fitted onto the wire or pin. Counter traction and balanced
suspension are provided by the ropes, pulleys and weights attached to the Pearson attachment. When all is
operational the thigh and Thomas splint will be suspended at about 45 degree angle with the bed and the lower
leg and Pearson attachment will be suspended horizontally to the mattress.
The patient may sit up, turn toward the traction side and raise his hips above the bed by means of the trapeze and
still maintain the line of traction.
Você também pode gostar
- Balance Skeletal TractionDocumento7 páginasBalance Skeletal TractionNina Ann LiwanagAinda não há avaliações
- Balanced Suspension Skeletal TractionDocumento4 páginasBalanced Suspension Skeletal TractionPrince Rener Velasco Pera100% (1)
- Balance Skeletal Traction. BST ProcedureDocumento4 páginasBalance Skeletal Traction. BST Procedurehannjazz80% (10)
- 2.balance Skeletal TractionDocumento18 páginas2.balance Skeletal TractionKatrina Ponce75% (4)
- Balance Skeletal TractionDocumento4 páginasBalance Skeletal TractionIris BalinoAinda não há avaliações
- Traction, Etc...... IDocumento12 páginasTraction, Etc...... IJolo Q. Bilaos67% (3)
- Ortho GadgetsDocumento18 páginasOrtho Gadgetsmckulit_joey100% (3)
- Khaye:: Traction: Is The Act of Pulling or Drawing Which Is Associated With Counter TractionDocumento4 páginasKhaye:: Traction: Is The Act of Pulling or Drawing Which Is Associated With Counter TractionChloe MorningstarAinda não há avaliações
- Balance Skeletal TractionDocumento5 páginasBalance Skeletal TractionRachel Ann JimenezAinda não há avaliações
- BST RetdemDocumento6 páginasBST Retdemandrea villanuevaAinda não há avaliações
- Care of Patients in TractionDocumento105 páginasCare of Patients in TractionFelipe Quidayan67% (3)
- Casts. Braces. TractionDocumento3 páginasCasts. Braces. TractionClancy Anne Garcia Naval100% (1)
- Orthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic CenterDocumento7 páginasOrthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic Centerhannjazz100% (5)
- Skeletal TractionDocumento7 páginasSkeletal TractionAnnalyn Austria100% (2)
- Braces Ortho..Documento16 páginasBraces Ortho..karendelarosa062770% (1)
- Splints and Casts Indications and MethodsDocumento9 páginasSplints and Casts Indications and MethodsJay GaneshAinda não há avaliações
- Cast and BracesDocumento58 páginasCast and BracesNikki M. Arapol100% (1)
- Case of OsteosarcomaDocumento25 páginasCase of Osteosarcomadocs2009100% (3)
- Pathophysiology Bone Fracture (Tibia)Documento1 páginaPathophysiology Bone Fracture (Tibia)Brainan Aquino0% (2)
- Pott's DiseaseDocumento30 páginasPott's DiseaseLucila Lugo100% (1)
- Traction PicturesDocumento3 páginasTraction Picturessophia yemaneAinda não há avaliações
- Cast, Brace, Traction CompilationDocumento13 páginasCast, Brace, Traction CompilationMar Ordanza100% (1)
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyDocumento3 páginasPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanAinda não há avaliações
- List of Casts and MoldsDocumento4 páginasList of Casts and MoldsCharisse CamantigueAinda não há avaliações
- Cast and TractionsDocumento6 páginasCast and Tractionsmiss RN100% (12)
- Cast and TractionsDocumento3 páginasCast and TractionsMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioAinda não há avaliações
- Perioperative of ORIFDocumento27 páginasPerioperative of ORIFSometwo C. Hangal91% (11)
- Ortho BracesDocumento6 páginasOrtho BracesSanny RamosAinda não há avaliações
- POC Review NotesDocumento9 páginasPOC Review NotesMagdaraog Gabrielle A.Ainda não há avaliações
- Fracture !!!!!!Documento31 páginasFracture !!!!!!Maryjoy MertallaAinda não há avaliações
- Osteosarcoma CaseDocumento28 páginasOsteosarcoma CaseChristine Karen Ang SuarezAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Background, Demographic Data, Dordon's Functional Health, Drug Study SAint Louis UniversityDocumento21 páginasNCP Background, Demographic Data, Dordon's Functional Health, Drug Study SAint Louis Universitypa3kmedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Orthopedic NursingDocumento9 páginasOrthopedic Nursingsilimaanghang100% (3)
- Orthopedic Nursing Orthopedic Gadget-A Piece of Special Device Designed To Correct Deformoities or To PreserveDocumento5 páginasOrthopedic Nursing Orthopedic Gadget-A Piece of Special Device Designed To Correct Deformoities or To PreserveSophia Kaye AguinaldoAinda não há avaliações
- Basic or InstrumentsDocumento21 páginasBasic or InstrumentsMabes100% (1)
- Orthopedic HardwareDocumento27 páginasOrthopedic HardwareJasmin Jacob100% (3)
- NCP BkaDocumento4 páginasNCP BkaKeeshia CesnerosAinda não há avaliações
- OsteosarcomaDocumento9 páginasOsteosarcomaFamela LauzonAinda não há avaliações
- NCP: FracturesDocumento21 páginasNCP: FracturesJavie100% (1)
- Balance Skeletal TractionDocumento3 páginasBalance Skeletal TractionLourdes PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- Orthopedic HardwareDocumento36 páginasOrthopedic HardwareMarivic Diano100% (1)
- GOSO&POADocumento1 páginaGOSO&POALaly Rose CanubasAinda não há avaliações
- Adm Traction PDFDocumento10 páginasAdm Traction PDFbitha p bAinda não há avaliações
- NCP PottsDocumento3 páginasNCP PottsFenie Jane Quinlat LapastoraAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocumento8 páginasAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Galeazzi Fracture and Monteggia FractureDocumento31 páginasGaleazzi Fracture and Monteggia FracturenihthaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Management of A Patient With Femoral Neck FractureDocumento12 páginasNursing Management of A Patient With Femoral Neck Fracturedanni L100% (6)
- NCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitDocumento2 páginasNCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitArt Christian Ramos0% (1)
- Orthopedic Nursing: TractionDocumento2 páginasOrthopedic Nursing: TractionGhee EvangelistaAinda não há avaliações
- Return Demo FormatDocumento4 páginasReturn Demo Formatfamy15Ainda não há avaliações
- Balance Skeletal TractionDocumento5 páginasBalance Skeletal Tractionbimbong120% (1)
- BST ChecklistDocumento3 páginasBST ChecklistAlthea TuguinayAinda não há avaliações
- Orthopedic Nursing LectureDocumento34 páginasOrthopedic Nursing Lecturesjardio100% (2)
- Balance Skeletal Traction ApplicationDocumento6 páginasBalance Skeletal Traction ApplicationAia JavierAinda não há avaliações
- The Balanced Skeletal TractionDocumento1 páginaThe Balanced Skeletal TractionGemarie Adarlo CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- BST ChecklistDocumento3 páginasBST ChecklistBailey100% (1)
- Orthopedic NursingDocumento2 páginasOrthopedic NursingMichelle TamorAinda não há avaliações
- BST ChecklistDocumento3 páginasBST ChecklistJovan C. SayabocAinda não há avaliações
- Taping Reference Sheet-3815621Documento3 páginasTaping Reference Sheet-3815621api-383568582Ainda não há avaliações
- Ortho LecDocumento7 páginasOrtho LecKemmy GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Detergents (Anionic Surfactants, MBAS)Documento1 páginaDetergents (Anionic Surfactants, MBAS)Anggun SaputriAinda não há avaliações
- HW7 A SolutionsDocumento6 páginasHW7 A Solutionsmmsingh91100% (1)
- What Is Host Program? How To Create Host Program? and What Is .Prog File?Documento5 páginasWhat Is Host Program? How To Create Host Program? and What Is .Prog File?redroAinda não há avaliações
- An Experimental and Statistical Study of Olfactory PreferencesDocumento7 páginasAn Experimental and Statistical Study of Olfactory Preferencesjungseong parkAinda não há avaliações
- Btech Ec 7 Sem Digital Image Processing Nec032 2019Documento1 páginaBtech Ec 7 Sem Digital Image Processing Nec032 2019Deepak SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Package Changepoint': R Topics DocumentedDocumento28 páginasPackage Changepoint': R Topics Documentedivan estevesAinda não há avaliações
- Struktur Baja 1Documento33 páginasStruktur Baja 1Agung S NurcahyanaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Digital ForensicsDocumento5 páginasChapter 3 Digital ForensicsAbhinav GadekarAinda não há avaliações
- User AgentDocumento2 páginasUser AgenthuongAinda não há avaliações
- Fuels and Combustion (Unit-Viii) 1. (A) Explain How Fuels Are Classified With Suitable ExamplesDocumento15 páginasFuels and Combustion (Unit-Viii) 1. (A) Explain How Fuels Are Classified With Suitable ExamplesengineeringchemistryAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines On Water ProofingDocumento88 páginasGuidelines On Water ProofingViệt Đặng XuânAinda não há avaliações
- When Bad Things Happen To Good MissilesDocumento9 páginasWhen Bad Things Happen To Good Missilesmykingboody2156Ainda não há avaliações
- Ec1102n - Mimi Nur Nabila Binti Alias - 2019293128 - Final ExamDocumento17 páginasEc1102n - Mimi Nur Nabila Binti Alias - 2019293128 - Final ExammimiAinda não há avaliações
- BaseballDocumento37 páginasBaseballBeeWinAinda não há avaliações
- OneTen-Frontend Web Development FundamentalsDocumento5 páginasOneTen-Frontend Web Development FundamentalsOkpetah Chioma christabelAinda não há avaliações
- RRU5909 Technical SpecificationsDocumento7 páginasRRU5909 Technical SpecificationsDmitry059100% (1)
- Notation Composer 3 Users GuideDocumento690 páginasNotation Composer 3 Users GuideSvedot MakedonecAinda não há avaliações
- Brochure - Digilogic Systems PVT Ltd.Documento28 páginasBrochure - Digilogic Systems PVT Ltd.ManojGRamakrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Inductiveand Deductive Reasoning in Geometry October 27 2022Documento9 páginasInductiveand Deductive Reasoning in Geometry October 27 2022Seif DelawarAinda não há avaliações
- Switchgear and Protection May 2022Documento1 páginaSwitchgear and Protection May 2022Sanapala RAJENDRA PRASADAinda não há avaliações
- Project, Program and Portfolio SelectionDocumento40 páginasProject, Program and Portfolio Selectionsaif ur rehman shahid hussain (aviator)Ainda não há avaliações
- Dke672 ch2Documento44 páginasDke672 ch2Siraj MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- 5 - WQU - 622 CTSP - M5 - CompiledContentDocumento34 páginas5 - WQU - 622 CTSP - M5 - CompiledContentJoe NgAinda não há avaliações
- Kalman FilterDocumento14 páginasKalman FilterNeetaa MunjalAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook Remote Server ManagementDocumento10 páginasEbook Remote Server ManagementPiruletoAinda não há avaliações
- 2003 - Serriano - Form Follows SoftwareDocumento21 páginas2003 - Serriano - Form Follows SoftwareMina Hazal TasciAinda não há avaliações
- Open-Air Theatre in The Centre of The City: Acoustic Design and Noise Environment ControlDocumento3 páginasOpen-Air Theatre in The Centre of The City: Acoustic Design and Noise Environment ControlArchitectural Visualizations ArchitecturelandsAinda não há avaliações
- Day 2 - S3 S4 - Introduction To Jbase Database1Documento48 páginasDay 2 - S3 S4 - Introduction To Jbase Database1alasad parvezAinda não há avaliações
- Petroleum Formation Evaluation Questions AnswersDocumento2 páginasPetroleum Formation Evaluation Questions AnswersdeusdedithaugustokiaAinda não há avaliações
- BBBBBDocumento11 páginasBBBBBAlfredo ErguetaAinda não há avaliações