Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Molecular Genetics. Shoeb
Enviado por
Mohammad ShoebDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Molecular Genetics. Shoeb
Enviado por
Mohammad ShoebDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MOLECULAR GENETICS You Are Here*
molecular basis of inheritance
Genes ---> Enzymes ---> Metabolism (phenotype)
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology*
DNA -transcription--> RNA -translation--> Protein
Concept Activity -17.1 Overview of Protein Synthesis - INFORMATION
What is a GENE = ? a basic unit of heredity in a living organism
DNA is the genetic material...
- a segment of DNA that specifies a morphological trait
- a discrete piece of deoxyribonucleic acid
- linear polymer of repeating nucleotide monomers
nucleotides* --> A adenine, C cytosine
T thymidine, G guanine
yield --> a polynucleotide*
[ but what about, retroviruses, as HIV & TMV, which contain RNA ]
Technology with a Twist - Understanding Genetics
INFORMATION PROCESSING & the CENTRAL DOGMA
- the letters of the genetic alphabet... are the nucleotides A, T, G, & C of DNA
- the unit of information is CODON = genetic 'word'
a triplet sequence of nucleotides 'CAT' in a polynucleotide
3 nucleotides = 1 codon (word) = 1 amino acid in a polypeptide
- the definition of (codon) word = amino acid
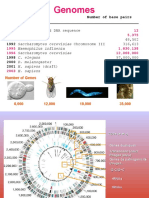
- Size of Human Genome: ≈ 3,000,000,000 base pairs or 1.5b in single strand of DNA genes
≈ 500,000,000 possible codons (words or amino acids)
- average page your textbook = approx 850 words
thus, human genome is equal to 588,000 pages or 470 copies of bio text book
reading at 3 bases/sec it would take you about 47.6 years @ 8h/d - 7d/w
WOW... extreme nanotechnology
µ Mice & humans (indeed, most or all mammals including dogs, cats, rabbits, monkeys, & apes)
have roughly the same number of nucleotides in their genomes -- about 3 billion bp.
It is estimated that 99.9% of the 3billion n's of human genome is same person to person.
What makes us Human*? champ & human DNA differ by only 15 million bases
Você também pode gostar
- Transfer of Genetic InformationDocumento13 páginasTransfer of Genetic InformationStevanus JonathanAinda não há avaliações
- Bir Bahadur Thapa Guided by Dr. Giri Pd. Joshi: 3 Semester CDB, TU-KirtipurDocumento78 páginasBir Bahadur Thapa Guided by Dr. Giri Pd. Joshi: 3 Semester CDB, TU-KirtipurvivekAinda não há avaliações
- Struktur DNA RNA Dan SinProt 2023bDocumento59 páginasStruktur DNA RNA Dan SinProt 2023bReri GarnetaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Basis of HeredityDocumento21 páginasChemical Basis of HeredityEmelinda CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Protein Synthesis 2023Documento24 páginasProtein Synthesis 2023Arlene SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Dna, Genes and GenomesDocumento4 páginasDna, Genes and GenomesRobert Martin PuertaAinda não há avaliações
- DNA, RNA, Protein-Gene ExpressionDocumento18 páginasDNA, RNA, Protein-Gene ExpressionFahim AbidAinda não há avaliações
- FTR Notes - Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocumento153 páginasFTR Notes - Molecular Basis of InheritanceAriba AzizAinda não há avaliações
- CYTOGENDocumento7 páginasCYTOGENRio CamoniasAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Week - Genome Organization and DNA ReplicationDocumento76 páginas2nd Week - Genome Organization and DNA ReplicationyazicigaamzeAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Methods in Molecular Biology: Manipulations With DnaDocumento17 páginasBasic Methods in Molecular Biology: Manipulations With DnaAniruddha RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Mol BiomarkerDocumento81 páginasMol Biomarkerمحمد علیAinda não há avaliações
- Central DogmaDocumento28 páginasCentral DogmaBryant Villarin BaldivicioAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetDocumento10 páginasLesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetEnriquez, Hannah Roniella R.Ainda não há avaliações
- 003 Mitochondrial DNA 2BDocumento21 páginas003 Mitochondrial DNA 2BObansa JohnAinda não há avaliações
- Genetics NotesDocumento7 páginasGenetics NotesTiffany BheaAinda não há avaliações
- R DNA TechnologyDocumento17 páginasR DNA TechnologyDRMEHUL DAVEAinda não há avaliações
- 12LectF Transcription 2017Documento44 páginas12LectF Transcription 2017Nofa RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Human Molecular GeneticsDocumento46 páginasHuman Molecular GeneticsMuhammad Ahsanul KahfiAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Biology-Lecture 1 5 QuestionsDocumento20 páginasMolecular Biology-Lecture 1 5 QuestionsLara ShayaAinda não há avaliações
- Materi GenetikDocumento3 páginasMateri GenetikAKMELIA NAJWAAinda não há avaliações
- La Souris, La Mouche Et L'Homme A. Human Genome Project: B. DNA Computers/DNA Nanorobots: C. PhylogenomicsDocumento12 páginasLa Souris, La Mouche Et L'Homme A. Human Genome Project: B. DNA Computers/DNA Nanorobots: C. PhylogenomicsFadhili DungaAinda não há avaliações
- Genome Organization: Mardalisa, B.SC., M.SiDocumento25 páginasGenome Organization: Mardalisa, B.SC., M.SiArbella VeronickaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Genetics: BIO100 Sumaiya Afrin SohaDocumento30 páginasIntroduction To Genetics: BIO100 Sumaiya Afrin SohaNafees Hasan Chowdhury100% (1)
- I. Basics of Molecular Biology:: DNA, RNA, Protein, Transcription, Translation, GenomeDocumento56 páginasI. Basics of Molecular Biology:: DNA, RNA, Protein, Transcription, Translation, GenomeSorin LazarAinda não há avaliações
- DNA StructureDocumento50 páginasDNA StructureAngelo LucindoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Molecular BiologyDocumento82 páginasIntroduction To Molecular Biologyfarzaana100% (2)
- The Flow of Genetic Information: DNA RNA ProteinDocumento134 páginasThe Flow of Genetic Information: DNA RNA ProteinkaleijaAinda não há avaliações
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocumento5 páginasHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- Lecture - 30oct13Documento41 páginasLecture - 30oct13Dagon BrownAinda não há avaliações
- Genomes: Number of Base PairsDocumento38 páginasGenomes: Number of Base PairsshooberAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 6 PDFDocumento15 páginasLecture 6 PDFNazir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Bio IntroDocumento28 páginasBio IntroCarera PatriciaAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleic AcidsDocumento37 páginasNucleic AcidsValine Cysteine MethionineAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleic Acids: Biology Study GuideDocumento2 páginasNucleic Acids: Biology Study GuideLaura MeowAinda não há avaliações
- Handouts - DNA and RNADocumento1 páginaHandouts - DNA and RNARufa NarioAinda não há avaliações
- CMMB-Fund Mol BioDocumento45 páginasCMMB-Fund Mol BioMahmud RakibAinda não há avaliações
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFDocumento55 páginasNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFAleine Leilanie Oro0% (1)
- Chapter-6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocumento10 páginasChapter-6 Molecular Basis of InheritancebpmbhamoraAinda não há avaliações
- Fine Structure of A GeneDocumento58 páginasFine Structure of A GeneMarie Serena McConnellAinda não há avaliações
- Extranuclear Inheritance. 2. Lineage Markers: Y Chromosome and MtdnaDocumento31 páginasExtranuclear Inheritance. 2. Lineage Markers: Y Chromosome and Mtdnarafiya IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Molecular BiologyDocumento39 páginasPrinciples of Molecular BiologyNando NanginAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular BiologyDocumento52 páginasMolecular Biologychandu SahaAinda não há avaliações
- Week 10 Nucleic Acid ChemistryDocumento2 páginasWeek 10 Nucleic Acid ChemistryRochelle NabaunagAinda não há avaliações
- Week 5 - GeneticsDocumento23 páginasWeek 5 - GeneticsJuan Pablo Valencia LondoñoAinda não há avaliações
- TP 2 PCR 21 - 22Documento50 páginasTP 2 PCR 21 - 22Vera MenezesAinda não há avaliações
- Genetic Engineering: o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocumento24 páginasGenetic Engineering: o o o o o o o o o o o o o oMasthankhan PatanAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance: WWW - Cbse123.co - CCDocumento33 páginasMolecular Basis of Inheritance: WWW - Cbse123.co - CCRayanAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2Documento7 páginasLesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2almafebe caselAinda não há avaliações
- Bacaan SlideDocumento11 páginasBacaan SlidemuhnameiskristinAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT IV-Genome OrganizationDocumento119 páginasUNIT IV-Genome OrganizationLakshya GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Functions of The Genetic MaterialDocumento31 páginasFunctions of The Genetic MaterialZara HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Recombinant DNA II: Making, Screening and Analyzing cDNA Clones Genomic DNA ClonesDocumento23 páginasRecombinant DNA II: Making, Screening and Analyzing cDNA Clones Genomic DNA Clonessri murniati naibahoAinda não há avaliações
- Biomed 08Documento14 páginasBiomed 08api-3706483Ainda não há avaliações
- C Value ParadoxDocumento4 páginasC Value ParadoxEr Purushottam PalAinda não há avaliações
- CYTOGENDocumento8 páginasCYTOGENRio CamoniasAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 24Documento13 páginasChapter 24Venus LandichoAinda não há avaliações
- Genetics: Unit III - Living Things and Its Environment - Heredity: Inheritance & VariationDocumento4 páginasGenetics: Unit III - Living Things and Its Environment - Heredity: Inheritance & VariationKirito TobioAinda não há avaliações
- L7S12. Central Dogma and Genetic Engineering - FDocumento35 páginasL7S12. Central Dogma and Genetic Engineering - FSichayra GamotiaAinda não há avaliações