Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Modal Verbs
Enviado por
ingles78Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Modal Verbs
Enviado por
ingles78Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
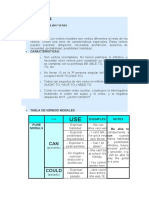
MODAL VERBS
DEFINICIÓN: Son verbos diferentes. Tienen una serie de características
especiales. Estos verbos pueden expresar: obligación, necesidad, prohibición,
ausencia de necesidad, probabilidad, posibilidad, habilidad…
CARACTERÍSTICAS:
o Son verbos incompletos. No tienen participio ni infinitivo, y necesitan
otros verbos para completar su conjugación: CAN se completa con la
perífrasis BE ABLE TO, MUST con HAVE TO, etc.
o No llevan -S en la 3ª persona singular del presente simple, excepto
HAVE TO (HAS TO)
o Todos van seguidos de otro verbo en infinitivo sin TO, excepto OUGHT
TO, HAVE TO y NEED TO.
o Como no necesitan verbo auxiliar, construyen la interrogativa
invirtiendo el orden del sujeto y el verbo , y la negativa añadiendo
NOT. ¡¡OJO!! CANNOT
MODAL
USE EXAMPLES NOTES
VERBS
- We can drive
- Expresar habilidad
very well
- I can't talk, I've - Be able to (ser capaz de
- Expresar posibilidad
got a very sore algo…) complementa a can
o imposibilidad
throat cuando indica habilidad y
CAN
posibilidad:
(presente) - Expresar o pedir - Can I sit down,
permiso please? e.g. Robots will be able to
control our lives in fifty
- She can't be at
years.
school. It's
- En negativa holiday.
expresar deducción y
prohibición. - You cannot smoke
here.
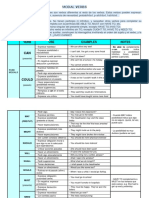
COULD
- Expresar habilidad en - Jane could drive
(pasado) pasado. before she was 18.
- Pedir algo - Could you pass
educadamente. the salt, please?
- Expresar posibilidad - It was so hot I
o imposibilidad en el couldn't walk in
pasado. the sand.
- Hacer
- This passport
especulaciones
could be his.
(posibilidad remota)
- We could play
- Hacer sugerencias.
bingo today.
- They said they
- Remplaza a can en el could do it
estilo indirecto themselves.
- You could have
- Expresar una
bought some more
crítica.
food.
- May I leave the
- Pedir algo.
classroom?
- You may go to
- Expresar permiso.
the toilet.
MAY - Cuando MAY indica
- The headmaster posibilidad indica que algo
- Expresar posibilidad
(PRE/FUT) may visit the class no es seguro. (quizá, tal
(presente o futura)
today. vez, puede que)
- That may be the
- Hacer thief that was
especulaciones. arrested by the
police.
- Expresar posibilidad - They might invite
(más dudosa) us to the party.
- La posibilidad es muy
MIGHT
- They might have dudosa (pudiera ser que)
- Hacer
broken the
especulaciones
window…
Es más frecuente que
SHOULD - You should do OUGHT TO
- Dar y pedir consejos
more physical
(debería)
exercise
- Expresar obligación - You should be
moral o que algo no es more tolerant
lo adecuado que
esperabamos
- Criticar acciones - She should have
pasadas been quiet
- You ought to do
- Dar consejos more physical
OUGHT exercise Normas establecidas
TO
- Expresar obligación - You ought to be
moral more tolerant
- Expresar obligación - You must go to - HAVE TO *complementa
(autoridad fuerte) school a MUST en los tiempos que
este carece, e.g. She had
MUST
- En negativa: - You mustn't to get up early yesterday.
expresar prohibición smoke in hospitals
(presente)
- They must be
- Expresar deducción happy. They've
(afirmativa) won the lottery
- Need we go
- Expresar necesidad
now?
- The trees need
- Con sentido pasivo
pruning.
NEED
- En negativa: - You needn't get
ausencia de obligación up early at
= don't have to weekends (no hace
(contra la norma) falata que)
- Expresar obligación (+ - You have to be 18
suave) to drive a car
HAVE HAD TO
(GOT) TO* - You don't have to
- En negativa:
wear a uniform in
ausencia de obligación
this school
MODALESPERFECTOS:
Se refieren al pasado: expresan conclusiones, suposiciones y conjeturas que
hacemos sobre hechos pasados y se forman con un modal + have + participio. (3º
columna de verbos irregulares o –ed en verbos regulares)
MUST + HAVE + PARTICIPIO: conclusiones lógicas en el pasado, e.g. Sheila was
absent yesterday. She must have been ill.
CAN+ HAVE + PARTICIPIO: hecho pasado que parece imposible. E.g. She can
have passed her exams- She didn’t study at all.
COULD + HAVE + PARTICIPIO : indica que hubo posibilidad de hacer algo en el
pasado pero realmente no se hizo, e.g. He could have helped us, but he came too
late.
MAY / MIGHT + HAVE + PARTICIPIO: expresan una suposición sobre el
pasado, e.g. Call her again. She may / might not have heard you the first time.
SHOULD / OUGHT TO + HAVE + PARTICIPIO: Para lamentar que no se siguió
un consejo en el pasado, e.g. She looks worse. She should / ought to have seen a
doctor last week. Para lamentar que no se haya cumplido lo que esperábamos, e.g.
They should have been home by now. En negativa, demuestran nuestra opinión
crítica sobre algo que no debería haber ocurrido, e.g. I'm very angry with her. She
shouldn't have been so rude.
Você também pode gostar
- Modal VerbsDocumento6 páginasModal Verbsingles78Ainda não há avaliações
- Modal VerbsDocumento12 páginasModal VerbsRaquel Marcos-alberca Calonge100% (1)
- MODAL VERBS GUIDEDocumento11 páginasMODAL VERBS GUIDEluis100% (1)
- Modal Auxiliary VerbsDocumento2 páginasModal Auxiliary VerbsVíctor DaríoAinda não há avaliações
- English GrammarDocumento10 páginasEnglish GrammarMaria Cebrian Perruca100% (1)
- Apuntes de Ingles 130831154737 Phpapp01Documento103 páginasApuntes de Ingles 130831154737 Phpapp01Linda JaberAinda não há avaliações
- Resumen de Los Tiempos Verbales Del InglésDocumento5 páginasResumen de Los Tiempos Verbales Del InglésErick Pereda100% (1)
- Algunos Phrasal Verbs ImprescindiblesDocumento57 páginasAlgunos Phrasal Verbs Imprescindiblesommapc100% (3)
- Apuntes InglesDocumento18 páginasApuntes InglesMiguel MiguelAinda não há avaliações
- Los Phrasal VerbsDocumento23 páginasLos Phrasal Verbszpc1977100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocumento33 páginasReported Speechcandelade123100% (2)
- Conectores en InglésDocumento6 páginasConectores en InglésIsai Garcia FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Present Simple & Present ContinuousDocumento5 páginasPresent Simple & Present ContinuoussilviaAinda não há avaliações
- INGLES ApuntesDocumento48 páginasINGLES ApuntesSelu Sánchez100% (1)
- Comparative and Superlative RulesDocumento1 páginaComparative and Superlative RulesMaríaAinda não há avaliações
- 04 Inglés Gramática 02Documento30 páginas04 Inglés Gramática 02jose luis de las muelas75% (4)
- Phrasal Verbs Separable and Inseparable ListDocumento5 páginasPhrasal Verbs Separable and Inseparable ListEli Roldan100% (2)
- Lista Phrasal Verbs B1 dominar inglésDocumento9 páginasLista Phrasal Verbs B1 dominar inglésMartha MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Ingles Verbos IrregularesDocumento2 páginasIngles Verbos IrregularesDEXTER03041950% (10)
- The Definite Article A and AN in EnglishDocumento169 páginasThe Definite Article A and AN in EnglishMaria Eliana Montaño100% (1)
- Summary TensesDocumento7 páginasSummary TensesLiliana MimizaAinda não há avaliações
- Ingles Nivel BasicoDocumento38 páginasIngles Nivel Basicosusti_i100% (1)
- Lista de Adjetivos en InglésDocumento2 páginasLista de Adjetivos en InglésAlejandrarmb71% (34)
- Lista de Verbos en Inglés ConjugadosDocumento11 páginasLista de Verbos en Inglés ConjugadosRicardo Morales Hernandez100% (2)
- Apuntes Inglés B2Documento29 páginasApuntes Inglés B2Enrique Dorta88% (8)
- Present Perfect SimpleDocumento2 páginasPresent Perfect Simplekittycow60% (5)
- Pasado Simple Verbo To Be May-2013-Lae-2Documento22 páginasPasado Simple Verbo To Be May-2013-Lae-2Filogonio Salgado Romano100% (1)
- English VocabularyDocumento117 páginasEnglish Vocabularyelisa245887100% (8)
- Verbos, AdverbiosDocumento6 páginasVerbos, AdverbiosMarco CataldiAinda não há avaliações
- List of Irregular English Verbs Ordered by Spanish MeaningDocumento4 páginasList of Irregular English Verbs Ordered by Spanish MeaningEli SanAinda não há avaliações
- Adverbios en Inglés: Lista y EjemplosDocumento24 páginasAdverbios en Inglés: Lista y EjemplosMauricio Ligueño100% (1)
- Comparative and SuperlativesDocumento3 páginasComparative and SuperlativesEnglishin FonquetaAinda não há avaliações
- (Writing) EssayDocumento12 páginas(Writing) EssayMoises Moises Moises100% (1)
- Introducción a conceptos clave de la ética como la libertad, responsabilidad y debates filosóficosDocumento3 páginasIntroducción a conceptos clave de la ética como la libertad, responsabilidad y debates filosóficosCarlos Garcia DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Sintaxis 22-23. Repaso de Teoría y PrácticaDocumento18 páginasSintaxis 22-23. Repaso de Teoría y Prácticapro180% (1)
- Manual Nivel b1Documento166 páginasManual Nivel b1virferriz78% (9)
- Material de Clase4. English IDocumento14 páginasMaterial de Clase4. English IHovanTaTarian0% (2)
- Tiempos Verbales (Inglés)Documento7 páginasTiempos Verbales (Inglés)MiZuKiRuHm100% (2)
- Apuntes Ingles Eoi LaredoDocumento120 páginasApuntes Ingles Eoi Laredopj100100% (1)
- Curso de Ingles Nivel MedioDocumento24 páginasCurso de Ingles Nivel MedioWILBERTH88% (8)
- Phrasal VerbsDocumento11 páginasPhrasal Verbsmjesusra80% (5)
- Phrasal Verbs Present Perfect ContinuousDocumento6 páginasPhrasal Verbs Present Perfect Continuoussebastian benavidesAinda não há avaliações
- Modal+verbs TheoryDocumento4 páginasModal+verbs TheoryTania Sarmiento CornesAinda não há avaliações
- Verbos ModalesDocumento3 páginasVerbos ModalesAugusto ChocobarAinda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs ChartDocumento5 páginasModal Verbs Chartscatach100% (1)
- Verbos Nivel Inicial (1) + EjemplosDocumento10 páginasVerbos Nivel Inicial (1) + EjemplosStefania FerreAinda não há avaliações
- GRAMMAR Modal VerbsDocumento7 páginasGRAMMAR Modal VerbsPablo OlaizAinda não há avaliações
- MODAL VERBSDocumento3 páginasMODAL VERBSANYOLY Y SUAREZ MEDINAAinda não há avaliações
- ModalesDocumento2 páginasModalesMontse López LópezAinda não há avaliações
- Verbos modales en inglésDocumento21 páginasVerbos modales en inglésVanessa CarriónAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar Modal VerbsDocumento10 páginasGrammar Modal VerbsNoemí Martínez DelgadoAinda não há avaliações
- El VerboDocumento24 páginasEl Verboandielo mejia sotaAinda não há avaliações
- El Subjuntivo Gran Repaso V2Documento47 páginasEl Subjuntivo Gran Repaso V2Napoleon Pique100% (1)
- Documento Sin TítuloDocumento2 páginasDocumento Sin TítuloJUST PAU SARALEGUI MARTINSAinda não há avaliações
- El PresenteDocumento8 páginasEl PresentemyselfAinda não há avaliações
- Cuadro de Las Funciones Sintácticas OracionalesDocumento1 páginaCuadro de Las Funciones Sintácticas OracionalesMiguel Calleja de la PuenteAinda não há avaliações
- Inglés Mod III Ud 5 RDocumento19 páginasInglés Mod III Ud 5 RRojas JulianaAinda não há avaliações
- EL Verbo. Primer AñoDocumento8 páginasEL Verbo. Primer AñoMaria Cecilia FaríasAinda não há avaliações
- Ilovepdf MergedDocumento2 páginasIlovepdf Mergedeloy1992pmAinda não há avaliações
- Reconocimiento Unidad 1 PsicologíaDocumento3 páginasReconocimiento Unidad 1 PsicologíaYEZIDAinda não há avaliações
- El Derecho A Expresarme en Mi Lengua MaternaDocumento11 páginasEl Derecho A Expresarme en Mi Lengua MaternaRuben DarioAinda não há avaliações
- Guia LyLDocumento7 páginasGuia LyLJuan Sebastian Celi OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- Preparación para lluvias intensasDocumento6 páginasPreparación para lluvias intensasDelia catalina Leon menizAinda não há avaliações
- Conjunto 2 de Números Enteros ZDocumento44 páginasConjunto 2 de Números Enteros ZXimena UgaldeAinda não há avaliações
- Producción Final de La Materia Propedéutico de EspañolDocumento31 páginasProducción Final de La Materia Propedéutico de EspañolCarlos Grabiel Olmos GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Briones (2002) Epistemología de Las Ciencias SocialesDocumento233 páginasBriones (2002) Epistemología de Las Ciencias SocialesSebastian Andres Espinoza AncavilAinda não há avaliações
- Practica Calificada de Informática e InternetDocumento3 páginasPractica Calificada de Informática e InternetjhonAinda não há avaliações
- Horario Estudios Ingleses US 3º AnualDocumento4 páginasHorario Estudios Ingleses US 3º AnualMariangeles Laguna BenítezAinda não há avaliações
- Fichas Expresión Escrita PDFDocumento48 páginasFichas Expresión Escrita PDFCarmen NietoAinda não há avaliações
- Autores Mayas GuatemaltecosDocumento4 páginasAutores Mayas GuatemaltecosMeridasInternt72% (18)
- POO y KATAS EjerciciosDocumento18 páginasPOO y KATAS EjerciciosEverson Vidal Mamani HuaytaAinda não há avaliações
- Origen Del Apellido Searle en ChileDocumento98 páginasOrigen Del Apellido Searle en Chilejaime0% (1)
- Tareas y Destrezas Comunicativas: PrimariaDocumento42 páginasTareas y Destrezas Comunicativas: PrimariaEMANUEL NICULAIAinda não há avaliações
- Ada 2 Modificadores Del Sujeto y Predicado.Documento10 páginasAda 2 Modificadores Del Sujeto y Predicado.RODRIGO JAZIEL TORAYA PEREZAinda não há avaliações
- Ensayo Cultura Linguistica Unidad 3Documento5 páginasEnsayo Cultura Linguistica Unidad 3yennypaola123100% (1)
- La Antropología en Su Lugar-Gloria Artís-Coord PDFDocumento134 páginasLa Antropología en Su Lugar-Gloria Artís-Coord PDFMiguel Kike CHipanaAinda não há avaliações
- Material de Figuras Literarias - Maria Auxiliadora - 5toDocumento5 páginasMaterial de Figuras Literarias - Maria Auxiliadora - 5toYelka OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- Ralph JohnsonDocumento5 páginasRalph JohnsonAnfell7Ainda não há avaliações
- La PronunciacionDocumento3 páginasLa PronunciacionMaria Leal GomezAinda não há avaliações
- SoñarDocumento5 páginasSoñarAnahi EspinozaAinda não há avaliações
- Cuestionario - Categorías de La LenguaDocumento3 páginasCuestionario - Categorías de La LenguaLuis Camacho FrancabandieraAinda não há avaliações
- Competencia Comunicativa ANTECEDENTESDocumento20 páginasCompetencia Comunicativa ANTECEDENTESIlluminans Tu CorazonAinda não há avaliações
- Taller de Lectura y Redacción, GuíaDocumento10 páginasTaller de Lectura y Redacción, GuíaManuel Beltran Nogues50% (4)
- Lenguaje Oral y EscritoDocumento7 páginasLenguaje Oral y EscritoJosmary Yanez ChirinosAinda não há avaliações
- Atrapasueño LiterarioDocumento2 páginasAtrapasueño LiterarioHermana Fabiola Misionera Catequista100% (1)
- Planteamiento Del Problema Skates ErnestoDocumento4 páginasPlanteamiento Del Problema Skates ErnestoErnesto Veisa SAinda não há avaliações
- EjerciciosDocumento2 páginasEjerciciosSilvio92% (12)
- 1991 09 057Documento100 páginas1991 09 057Roberto KlesAinda não há avaliações
- ATENCIÓN CON LAS MAYÚSCULASDocumento8 páginasATENCIÓN CON LAS MAYÚSCULASpaulaAinda não há avaliações