Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Nursing Review Notes 2
Enviado por
api-3822508100%(5)100% acharam este documento útil (5 votos)
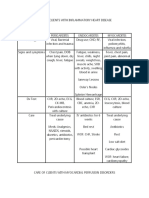
4K visualizações4 páginasNursing Bullets www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com. Protein 6-8g / dL 101-200 1. Intermittent claudication Cramp-like pain that occurs with exercise and is relieved by rest 2. Cardiac tamponade tachycardia distant or muffled heart sounds 3. Thrombophlebitis or deep vein thrombosis (DVT) redness and / or warmth of the affected leg tenderness at the
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoNursing Bullets www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com. Protein 6-8g / dL 101-200 1. Intermittent claudication Cramp-like pain that occurs with exercise and is relieved by rest 2. Cardiac tamponade tachycardia distant or muffled heart sounds 3. Thrombophlebitis or deep vein thrombosis (DVT) redness and / or warmth of the affected leg tenderness at the
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
100%(5)100% acharam este documento útil (5 votos)
4K visualizações4 páginasNursing Review Notes 2
Enviado por
api-3822508Nursing Bullets www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com. Protein 6-8g / dL 101-200 1. Intermittent claudication Cramp-like pain that occurs with exercise and is relieved by rest 2. Cardiac tamponade tachycardia distant or muffled heart sounds 3. Thrombophlebitis or deep vein thrombosis (DVT) redness and / or warmth of the affected leg tenderness at the
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 4
Nursing Bullets www.nurseacademy.blogspot.
com
101-200 10. Signs of depression after Myocardial
Infarction
withdrawal
1. Intermittent claudication crying
Cramp-like pain that occurs with apathy
exercise and is relieved by rest
11. Aortic Abdominal Aneurysm
2. Cardiac tamponade assessment
tachycardia subjective feeling of the “heart
distant or muffled heart sounds beating” in the abdomen
jugular vein distention pulsatile abdominal mass
falling blood pressure systolic bruit over the mass
accompanied by pulsus paradoxus
12. Elective cardioversion
3. Thrombophlebitis or deep vein Remove oxygen temporarily
thrombosis (DVT)
redness and/or warmth of the 13. P-R interval
affected leg 0.12-0.20 seconds
tenderness at the sit
possible dilated veins (if 14. QRS
superficial) 0.4-0.10
low grade fever
edema distal to the obstruction 15. First-degree heart block
possible positive Homans' sign in Prolonged P-R interval (>0.20)
the affected extremity
16. Atrial fibrillation
4. Classical sign of cardiogenic shock erratic or no identifiable P waves
altered sensorium (confusion)
tachycardia 17. Multiple Gated Acquisition Scan
(MUGA)
hypotension
IV line
tachypnea
oliguria 18. Soft Tissue Injury
cold, clammy, cyanotic skin Rest
Ice
5. Unstable angina Compression
increase in frequency, duration, Elevation
and severity over time
19. Before electroconvulsive therapy
6. Stable angina Succinylcholine (Anectine)-muscle
Paroxysmal chest discomfort relaxant
triggered by predictable physical
or emotional factors 20. Beta-blockers
Decrease workload of the heart
7. Angina decubitus
Chest discomfort that increases 21. NSAIDS
when reclining 1 hour before or 2 hours after
meals
8. Nocturnal angina
Chest discomfort associated with 22. Normal value: Protein
sleep 6-8g/dL
9. Early stage of acute myocardial
infarction
ST segment elevation
The Nurse’s Academy www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com
Nursing Bullets www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com
23. Side effects: fluoxetine (Prozac) 37. Cardiac arrest in pedia
Dry mouth Prolonged hypoxemia
Diarrhea 38. Panic disorder attack
Weight loss Sense of impending doom
Reduced libido
39. Cogentin
24. Xanax (alprazolam) Contraindicated to glaucoma and
Short-term relief prostatic hypertrophy
25. Newborn’s normal weight loss (first 40. Thrombophlebitis
few days) Elevate leg (2 pillows)
5-110% of birth weight
41. Fluorosis
26. Assessing heart rate via radial pulse Chalky white to yellowish staining
>2 years old
42. Vwentricular fibrillation
27. Side effects: Aminophylline Assess pulse
Restlessness
Palpitations 43. Portal hypertension
Potential complication of
28. Seizures in children hemorrhage
Infection
Fatigue 44. Cleft lip repair (2 months)
Nor eating well Elbow restraint
High fluid intake
Fluid retention 45. Post segmental lung resection
Assess
29. Side effects: Isoniazid (INH) Suction secretion
Peripheral neuropathy
46. Congestive heart failure
30. Perforated peptic ulcer High-fowler’s position
Nausea and vomiting
Abdominal distention 47. Herpes simplex
Contact precautions
31. Acute pancreatitis
Respiratory infection 48. Suctioning tracheostomy
Pain on epigastric area radiating to Instill saline to remove mucus
the back plug
32. Separation anxiety 49. Homeopathic medicine
6-30 months Boost immune response
33. chlorpromazine (Thorazine) 50. Injury prevention for pre-schoolers
avoid direct sunlight Set good example
34. AIDS 51. Child who can use car seat
CD4 lymphocyte <200 (normal Weight: 40 lbs/18 kg
value: 600-1000)
52. Ovulation period
35. Stranger anxiety Cycle in days minus 14 days
Begins: 6-8months
Peaks: 9 months
36. Female growth spurt
2 years earlier than male 53. Findings in hypoxemia
Restlessness
Irritability
The Nurse’s Academy www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com
Nursing Bullets www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com
Agityations Long-term use of steroids
Dyspnea Smoking
Disorientation
Confusion 67. Stoma with high risk for skin
Delirium breakdown
Hallucination Ileostomy
Loss of consciousness
68. Removing flatus from 1 piece
54. Newborn in incubator drainable ostomy
Monitor temperature Provide privacy
Open the button of the pouch
55. Initial treatment for Ewing’s sarcoma Release flatus
Chemotherapy and radiation Close the button of the pouch
56. Isoniazid 69. HSV-1
Liver function test Immunosuppression
Causes heaptocellular injury and
hepatitis 70. Tonsillectomy
Report persistent cough
57. Russel’s traction
Neurovascular circulation check 71. Pneumococcal pneumonia
Bronchial breath sound in outer
58. Priority for child with sickle cell lung field
disease
Avoid overheating during physical 72. Developmental right hip dysplasia
activity Characteristic limp
59. General guide to serving size in 73. Multiple Sclerosis client
children Avoid activities leading to
1 tablespoon of solid food per dehydration
year
74. CAD patient
60. Anti-psychotic medications’ side Avoid very heavy meals
effects
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome 75. Rhabdomyosarcoma
(hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, Muscles
malignant hypertension)
76. KUB radiographic test
61. Readiness for toilet training No preparation necessary
Complete myelination of spinal
cord 77. Central venous pressure (CVP)
Right heart function
62. Birth weight
Double: 6months 78. Swan-ganz catheter
Triple: 1 year Left heart function
Quadruple: 18 months
79. Levothyroxine (synthroid)
63. Cystic fibrosis (2 years old) Take in the morning
Continue normal activities
80. Venous stasis ulcer healing
64. Burn patient Proper nutrition
High protein, high carbohydrate
81. Child with diabetes mellitus
65. Not affected by hemodialysis Bed wetting
Low hemoglobin (anemia)
82. Chiropractic treatment
66. Delayed wound healing Spinal cord manipulation
The Nurse’s Academy www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com
Nursing Bullets www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com
83. Best indicator of good wound healing 98. Eye contact for native American
Reddened tissue Rude, impolite, aggressive
84. Congestive heart failure with 99. School aged children
pulmonary edema Obesity is the common disorder
Decreased cardiac output
100. Major depression
85. Volume overload Sad
S3 heart sound Hopeless
Psychomotor retardation/agitation
86. 5th disease (erythema infectiosum) Chronic generalized local pain
Not contagious, does not need Appetite/sleep disturbances
isolation GI complaints
Impaired libido
87. Risk for depression
Steroids
88. Lithium effect
2 weeks
89. Lead poisoning
Nuerologic signs and symptoms
Neuropathy
Footdrop
Anemia
90. Late pregnancy fetal growth
retardation
Pregnancy induced hypertension
91. Anemia in sickle cell disease
Increase red cell destruction,
decrease production
92. Diet for cystic fibrosis
High protein and calorie,
unrestricted fat
93. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (5
years old)
5:1
94. Fetal alcohol syndrome
Cranial facial abnormalities
95. Most accurate to determine
tuberculosis
Sputum culture
96. Sudden infant disease syndrome
before 6 months old
97. Newborn of mother addicted to
heroin
Jitteriness 24-48 hours
Irritability
Poor feeding
The Nurse’s Academy www.nurseacademy.blogspot.com
Você também pode gostar
- Syncope CasesNo EverandSyncope CasesRoberto García-CiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Infusion Reaction, Anaphylaxis and Hypersensitivity ManagementDocumento10 páginasInfusion Reaction, Anaphylaxis and Hypersensitivity ManagementDiah Rahayu SetiawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Vertigo Vertigo: Pembimbing: Dr. Nella, Sp. SDocumento40 páginasVertigo Vertigo: Pembimbing: Dr. Nella, Sp. SAbdil AbdelAinda não há avaliações
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocumento21 páginasSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsKetan patilAinda não há avaliações
- Neuromuscular Blocking DrugsDocumento4 páginasNeuromuscular Blocking DrugsNix14Ainda não há avaliações
- OxytocinDocumento2 páginasOxytocinshefawAinda não há avaliações
- WEEK 10 & 11 Midterm 316Documento9 páginasWEEK 10 & 11 Midterm 316Baylon AngelicaAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Emergencies FlashcardsDocumento109 páginasMedical Emergencies Flashcardsmkct111Ainda não há avaliações
- Buzz Words MRCPDocumento74 páginasBuzz Words MRCPKyrillos G FahmyAinda não há avaliações
- Oral RevalidaDocumento14 páginasOral RevalidaAyaBasilioAinda não há avaliações
- Cerebral Aneurysm-Parkinsons DiseaseDocumento3 páginasCerebral Aneurysm-Parkinsons Diseaseanime listAinda não há avaliações
- CCRN Cert Review Neuro 2Documento15 páginasCCRN Cert Review Neuro 2Giovanni MictilAinda não há avaliações
- 1538 Exam 5 IntracranialDocumento31 páginas1538 Exam 5 IntracranialJade EdanoAinda não há avaliações
- Hemolytic Transfusion ReactionDocumento3 páginasHemolytic Transfusion ReactionAinin SofiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Medicine SYMPTOMS ENGLISH IN MEDICINE 2019Documento1 páginaMedicine SYMPTOMS ENGLISH IN MEDICINE 2019JaimeAinda não há avaliações
- ROS, PE, PathoDocumento8 páginasROS, PE, PathoMichelle Vera GabunAinda não há avaliações
- NCLEX Tips for SuccessDocumento8 páginasNCLEX Tips for SuccessManuel Láncara100% (1)
- Postoperative Surgical Complications 2015Documento26 páginasPostoperative Surgical Complications 2015AlaaGaballaAinda não há avaliações
- Textbook of Critical CareDocumento1.733 páginasTextbook of Critical CareAdina Neagoe100% (1)
- Care of Clients With Angina PectorisDocumento8 páginasCare of Clients With Angina PectorisaryshamyleeAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Handbook (Sick Calls Book 2009)Documento287 páginasMedical Handbook (Sick Calls Book 2009)Luc Mouws100% (1)
- Ii - Pedia-Rn DisordersDocumento15 páginasIi - Pedia-Rn DisordersAnnie Rose Dorothy MamingAinda não há avaliações
- Seizure Disorder Types: Partial - Local Onset May or May Not Impair Consciousness SimpleDocumento4 páginasSeizure Disorder Types: Partial - Local Onset May or May Not Impair Consciousness Simpleampogison08Ainda não há avaliações
- Abdominal Pain Causes and DiagnosisDocumento22 páginasAbdominal Pain Causes and DiagnosisAaronBradyAinda não há avaliações
- Managing Eclampsia: Emergency Teaching ProgramDocumento38 páginasManaging Eclampsia: Emergency Teaching ProgramMemento MagicAinda não há avaliações
- Notes On Paediatrics (Aindrani Akka)Documento220 páginasNotes On Paediatrics (Aindrani Akka)Lasantha RathnayakeAinda não há avaliações
- Journal Reading Acute Spinal Cord InjuryDocumento14 páginasJournal Reading Acute Spinal Cord InjuryamandaAinda não há avaliações
- Spinal Epidural Anaesthesia 2Documento29 páginasSpinal Epidural Anaesthesia 2ilham novesar0% (1)
- Mari Zita Spa OnDocumento57 páginasMari Zita Spa OnMarty BrownAinda não há avaliações
- DRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraDocumento15 páginasDRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraCharm Abyss la MorenaAinda não há avaliações
- Caisson's Disease and Nitrogen Bubbles in JointsDocumento630 páginasCaisson's Disease and Nitrogen Bubbles in JointsAnurag Behera100% (1)
- Malaysian Radiography Standard GuidelinesDocumento178 páginasMalaysian Radiography Standard GuidelinesIrwan Iskandar JusohAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study JSGSDocumento8 páginasDrug Study JSGSJohannes SantosAinda não há avaliações
- IIA - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocumento14 páginasIIA - Altered Tissue PerfusionDharylle CariñoAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Jufri Latief (Compartment Syndromes)Documento11 páginasDr. Jufri Latief (Compartment Syndromes)shintaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Module 5Documento3 páginasDrug Study Module 5Krisyll Meah Torred RamalAinda não há avaliações
- Australian College of Rural and Remote Medicine - Rural Emergency Skills Training (REST) (2012, Australian College of Rural and Remote Medicine)Documento258 páginasAustralian College of Rural and Remote Medicine - Rural Emergency Skills Training (REST) (2012, Australian College of Rural and Remote Medicine)Ehsan Elahi100% (1)
- Tetanus: DR - Vemuri ChaitanyaDocumento49 páginasTetanus: DR - Vemuri ChaitanyaalifAinda não há avaliações
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study ClinidineDocumento6 páginasCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study ClinidinehahahahaaaaaaaAinda não há avaliações
- Neonatal Seizures: Lamiaa Mohsen, M.D Cairo UniversityDocumento36 páginasNeonatal Seizures: Lamiaa Mohsen, M.D Cairo UniversityAdliah ZahiraAinda não há avaliações
- Aconitum Napelus-A Comprehensive Study: Dr. Kulwant SinghDocumento7 páginasAconitum Napelus-A Comprehensive Study: Dr. Kulwant Singhantonio andresAinda não há avaliações
- Peros: General AssessmentDocumento4 páginasPeros: General AssessmentKaycee TolingAinda não há avaliações
- Ragama Medicine Case BookDocumento391 páginasRagama Medicine Case BookSanjaya WijesekaraAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Case Study BurnDocumento27 páginasSample Case Study BurnRj Cordero75% (4)
- Nclex Random Fact To StudyDocumento431 páginasNclex Random Fact To StudyNeko Neko100% (1)
- Drugs 1Documento5 páginasDrugs 1Charme Jean RaygonAinda não há avaliações
- Safe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingDocumento16 páginasSafe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingJo ckerAinda não há avaliações
- Compilation of Ms NotesDocumento49 páginasCompilation of Ms Noteschoyaks100% (1)
- Case Study UrtiDocumento9 páginasCase Study UrtiRonica GonzagaAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiac Disease NotesDocumento4 páginasCardiac Disease NotesKyla Mae JumaritoAinda não há avaliações
- Medurg MidtermDocumento4 páginasMedurg Midtermmark OrpillaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study: Pharmacokinetics Absorption SiteDocumento3 páginasDrug Study: Pharmacokinetics Absorption SiteCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaAinda não há avaliações
- Kejang Demam Pada AnakDocumento18 páginasKejang Demam Pada AnakDianaAinda não há avaliações
- Atherosclerosis Angina Pectoris Myocardial InfarctionDocumento2 páginasAtherosclerosis Angina Pectoris Myocardial InfarctionKaren Mae AlcantaraAinda não há avaliações
- Increased Intracranial Pressure and Seizure Feb 14Documento2 páginasIncreased Intracranial Pressure and Seizure Feb 14anime listAinda não há avaliações
- NCM 116: Neurologic Dysfunctions: Joyce Bernadette P. Andot - Anna Delle Nicole P. Aranding, BSN-IIIDocumento46 páginasNCM 116: Neurologic Dysfunctions: Joyce Bernadette P. Andot - Anna Delle Nicole P. Aranding, BSN-IIIMercy Anne EcatAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical InstrumentsDocumento15 páginasSurgical Instrumentsapi-3840195Ainda não há avaliações
- ReviewDocumento12 páginasReviewapi-3700537Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Process of A Client With CholelithiasisDocumento21 páginasNursing Process of A Client With Cholelithiasisapi-3822508100% (6)
- Nursing MGT of Clients With BurnsDocumento145 páginasNursing MGT of Clients With Burnsapi-3822508100% (7)
- Psychiatric Nursing 1Documento11 páginasPsychiatric Nursing 1api-3731845100% (1)
- MS AddsDocumento4 páginasMS Addsapi-3731294Ainda não há avaliações
- OB Nursing ProcessDocumento26 páginasOB Nursing Processapi-38225080% (1)
- Bullets in Medical Surgical NursingDocumento11 páginasBullets in Medical Surgical NursingzequerradmAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Surgical Exam Part 1Documento16 páginasMedical Surgical Exam Part 1api-382250888% (42)
- NCP: Cholecystitis With CholelithiasisDocumento9 páginasNCP: Cholecystitis With CholelithiasisJavie100% (7)
- Care of The Patient With Neuro DisordersDocumento70 páginasCare of The Patient With Neuro Disordersapi-382250850% (4)
- Bullets in Medical Surgical NursingDocumento8 páginasBullets in Medical Surgical Nursingapi-3731294100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan (MI)Documento2 páginasNursing Care Plan (MI)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoAinda não há avaliações
- Sarv Suraksha Policy Wording PDFDocumento11 páginasSarv Suraksha Policy Wording PDFKARTHIKEYAN MAinda não há avaliações
- Hypertension Case PresentationDocumento32 páginasHypertension Case PresentationAnnaMaeGacutanMarantanAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Coronary Artery DiseaseLorraineAnneSantiagoCandelario91% (22)
- Mapeh 7-With TosDocumento5 páginasMapeh 7-With TosLorraine Calvez Donio100% (1)
- Heart Failure Dissertation IdeasDocumento7 páginasHeart Failure Dissertation IdeasWriteMyBiologyPaperSingapore100% (1)
- Pathology B - Midterm Ratio: Prelim TopicsDocumento69 páginasPathology B - Midterm Ratio: Prelim TopicsHuey Manalang JavierAinda não há avaliações
- 2018-Rad, Bidi, Khaligh - 2018 - Causes of Late Referral To The Emergency Department in Patients With Myocardial Infarction in IranDocumento9 páginas2018-Rad, Bidi, Khaligh - 2018 - Causes of Late Referral To The Emergency Department in Patients With Myocardial Infarction in Irancipto susiloAinda não há avaliações
- Dex AmgDocumento3 páginasDex AmgHenri Coandă Școala PostlicealăAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 DiabetesDocumento36 páginasCardiovascular Disease and Type 2 DiabetesDeviDwiPuspitasariAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 15Documento27 páginasChapter 15Jessica nonyeAinda não há avaliações
- AK Tripathi - Essentials of Medicine For Dental Students, 2nd EditionDocumento310 páginasAK Tripathi - Essentials of Medicine For Dental Students, 2nd EditionCassie Von Peenq79% (14)
- Biochemical Markers in Cardiovascular Disease: An OverviewDocumento52 páginasBiochemical Markers in Cardiovascular Disease: An Overviewkarin amalia sabrina100% (1)
- Stemi PathwayDocumento12 páginasStemi PathwaysyifaAinda não há avaliações
- Isosorbide NitratesDocumento3 páginasIsosorbide Nitratesapi-3797941Ainda não há avaliações
- CASE STUDY Unstable Angina - 3Documento25 páginasCASE STUDY Unstable Angina - 3Renee RoSeAinda não há avaliações
- Hypertension: Management and TreatmentDocumento9 páginasHypertension: Management and TreatmentSheila May Teope SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Banana Peel Defense Paper 1Documento39 páginasBanana Peel Defense Paper 1John Michael Bravante DiezAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 1Documento57 páginasMedical Surgical Nursing Practice Test Part 1Tina Van Winks100% (2)
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocumento27 páginasAcute Coronary SyndromeHassan MuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- Best Cardiologist in Hyderabad Dr. SanjeevDocumento6 páginasBest Cardiologist in Hyderabad Dr. SanjeevBest CardiologistinHyderabadAinda não há avaliações
- Care of Adults 25 Cardiovascular ManagementDocumento39 páginasCare of Adults 25 Cardiovascular ManagementGaras AnnaBerniceAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Medicine Essentials For Clerkship Students 2Documento369 páginasInternal Medicine Essentials For Clerkship Students 2Sudhir Tyagi100% (30)
- 12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocumento7 páginas12 Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemJAN CAMILLE LENONAinda não há avaliações
- About Getz PharmaDocumento57 páginasAbout Getz PharmaSuleman Iqbal BhattiAinda não há avaliações
- PBH 101: Preventing Heart DiseaseDocumento12 páginasPBH 101: Preventing Heart Diseaseish ishokAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Epidemiology - The Essentials (PDFDrive)Documento349 páginasClinical Epidemiology - The Essentials (PDFDrive)Mirna WidasriAinda não há avaliações
- 2.best Insight Cardio Metabolic TeamDocumento61 páginas2.best Insight Cardio Metabolic TeamSaQlain BalochAinda não há avaliações
- Sudhakar Thesis - 7858997398264548256Documento9 páginasSudhakar Thesis - 7858997398264548256mounika chigurupatiAinda não há avaliações
- Preoperative AssessmentDocumento81 páginasPreoperative AssessmentJavier LopezAinda não há avaliações
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (13)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNo EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (402)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeAinda não há avaliações
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (78)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementNo EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (40)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNo EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- Chakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.No EverandChakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesNo EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (34)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (41)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNo EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (327)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNo EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Seeing What Others Don't: The Remarkable Ways We Gain InsightsNo EverandSeeing What Others Don't: The Remarkable Ways We Gain InsightsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (288)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingNo EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsAinda não há avaliações
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNo EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (33)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassNo EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (23)